The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weight, Food and Water Intake, and Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)
2.2. Relaxation Response
| Body Weight (g) | Food Intake (g/Day) | Water Intake (mL/Day) | ΔSBP (mmHg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day-1 | Week 7 | Gain | Week 3 | Week 7 | |||
| WKY | 125.7 ± 2.2 | 347.5 ± 1.9 | 221.9 ± 3.5 | 18.4 ± 0.5 | 29.9 ± 0.8 | 3.6 ± 1.8 | 16.4 ± 4.7 |
| SHR-control | 136.1 ± 1.2 | 331.6 ± 7.7 | 195.5 ± 6.8 | 19.8 ± 0.4 | 33.2 ± 1.1 | 35.6 ± 0.7 # | 72.9 ± 2.4 ## |
| SHR-ELE | 136.7 ± 0.4 | 321.5 ± 3.8 | 184.8 ± 3.7 | 19.2 ± 0.8 | 35.6 ± 1.4 | 17.8 ± 2.5 **,## | 67.1 ± 2.3 *,## |
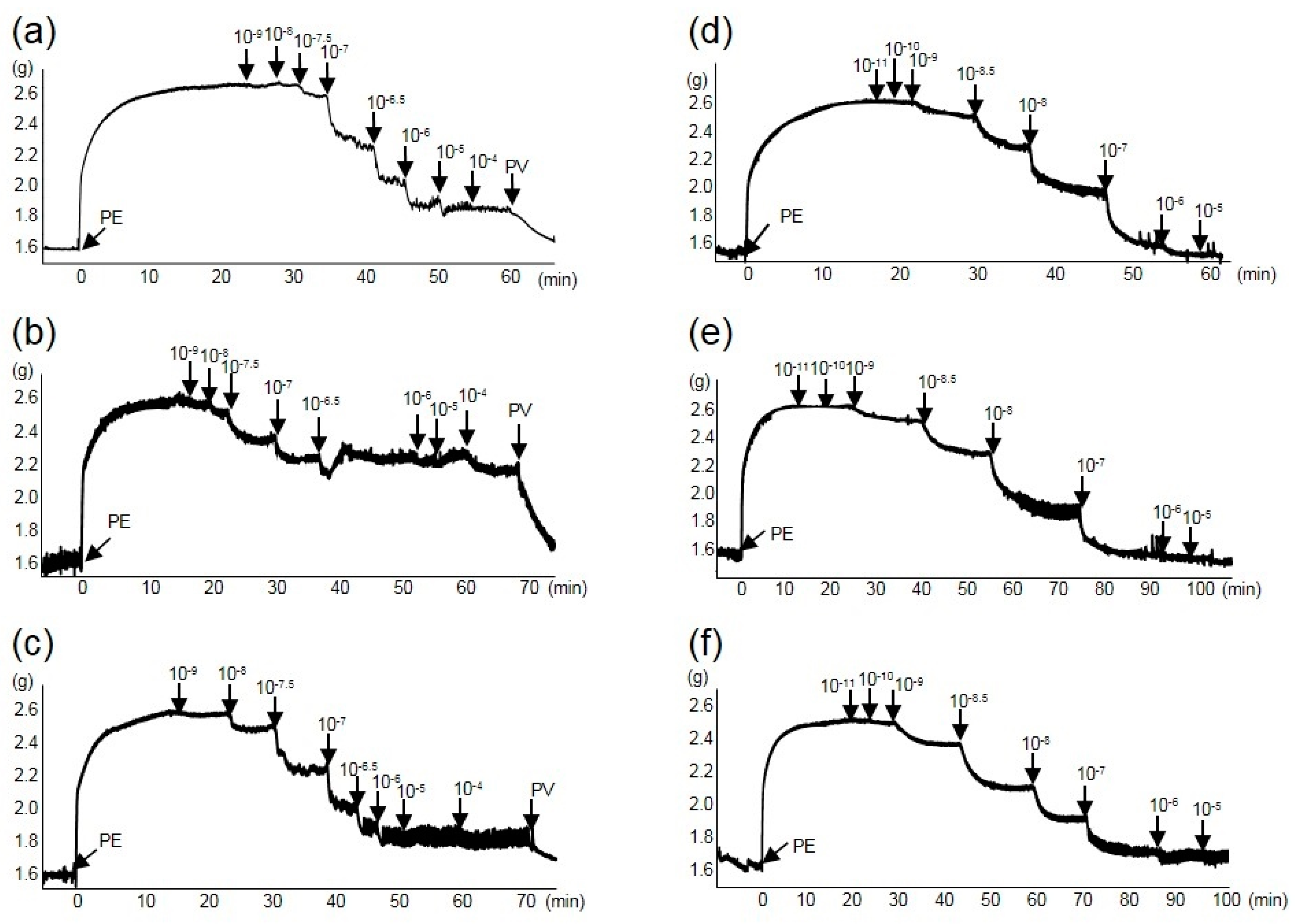

2.3. The Effect of ELE on Plasma NO

2.4. Measurement of Aortic Media Thickness
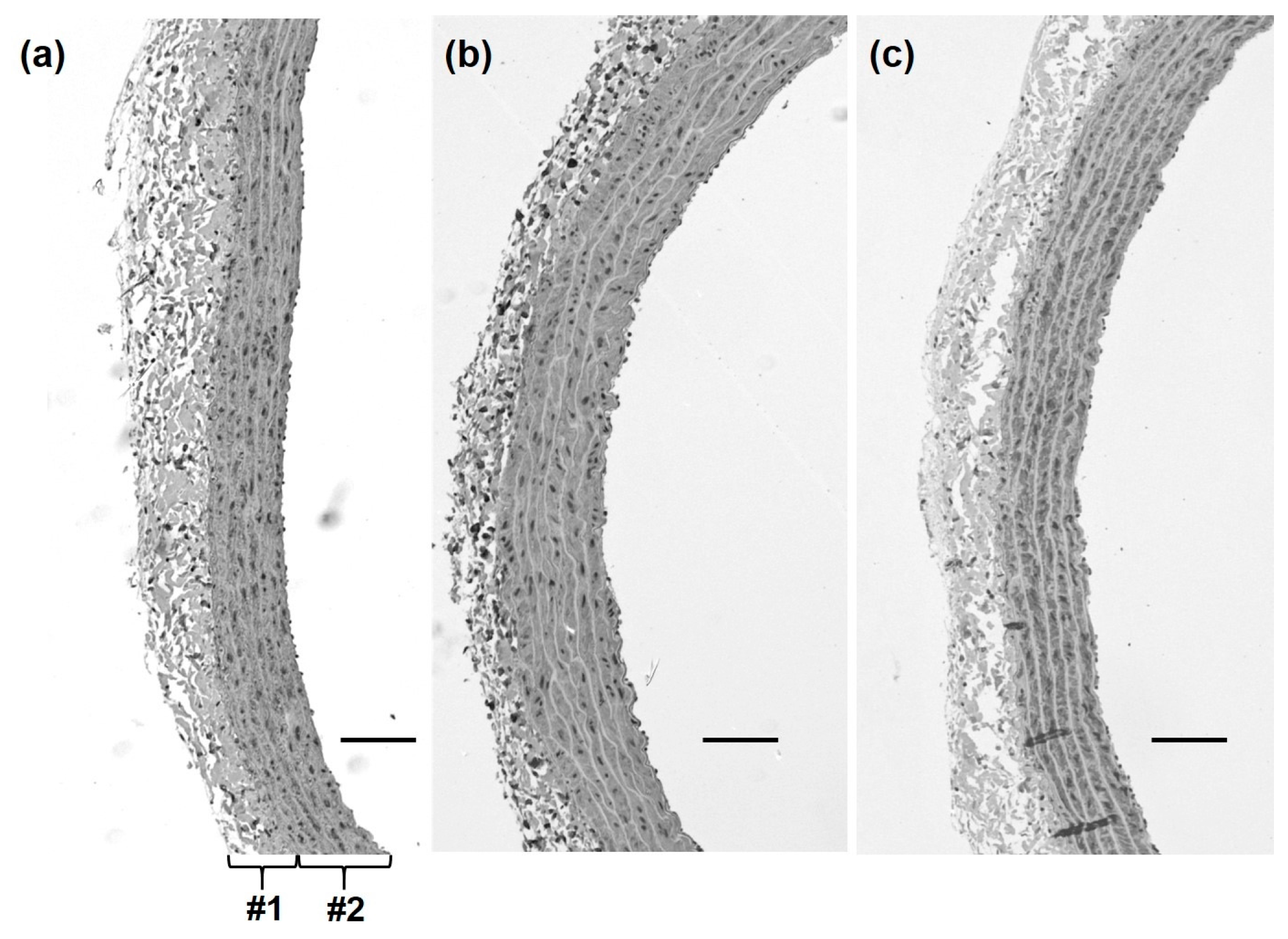
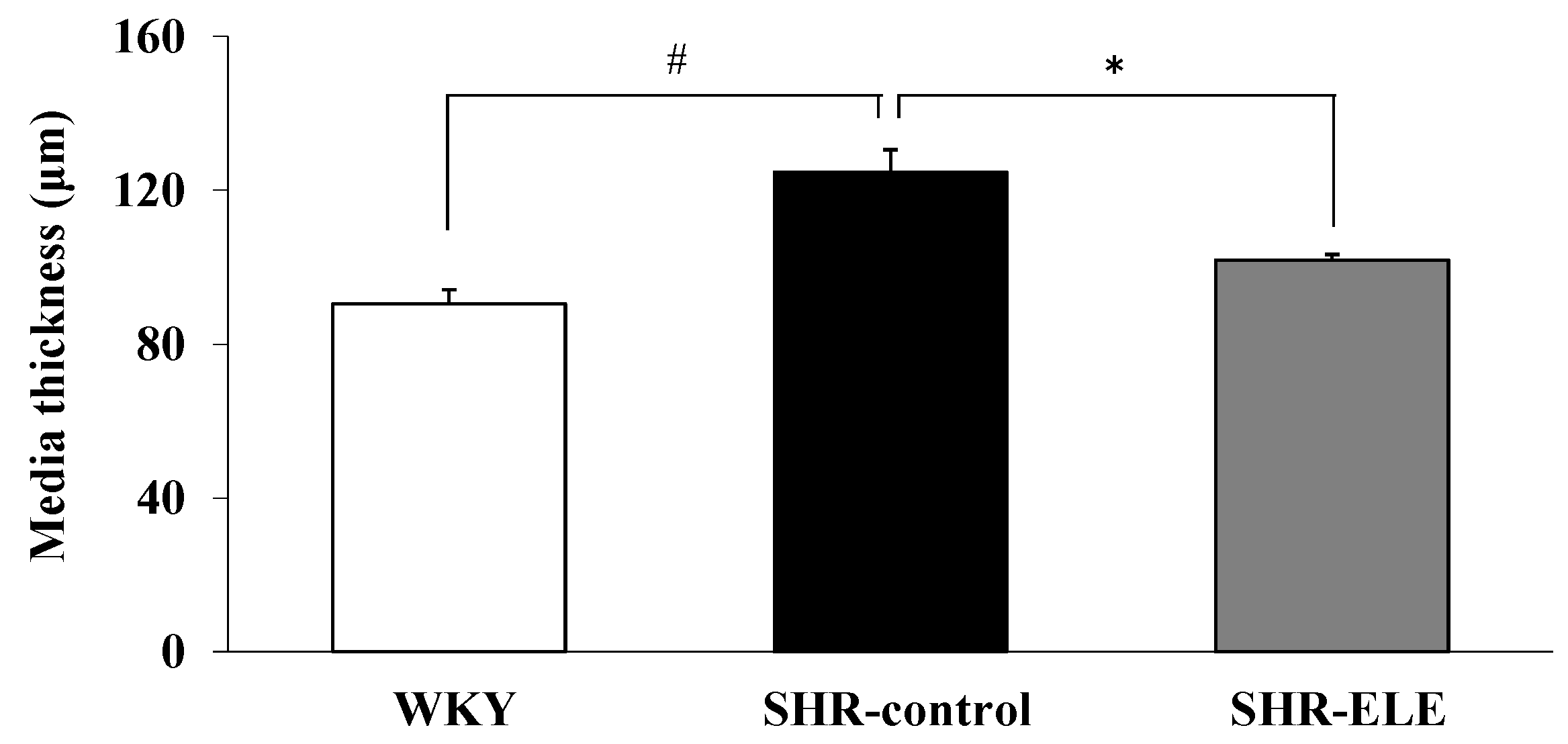
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Preparation of ELE
4.4. Long-Term Administration of ELE
4.5. Measurement of Endothelial Function Using Thoracic Aorta Rings
4.6. Quantification of NO in Rat Plasma
4.7. Immunohistochemical Analysis to Visualize Thoracic Aorta Smooth Muscle Cells
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. A Global Brief on Hypertension-Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis; WHO Reference Number: WHO/DCO/WHD/2013.2; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Evora, P.R.; Evora, P.M.; Celotto, A.C.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Joviliano, E.E. Cardiovascular therapeutics targets on the NO-sGC-cGMP signaling pathway: A critical overview. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Margaritis, M.; Shirodaria, C.; Antoniades, C. Translating the effects of statins: From redox regulation to suppression of vascular wall inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 108, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félétou, M.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Endothelial dysfunction: A multifaceted disorder (the Wiggers award lecture). Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sena, C.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Seiça, R. Endothelial dysfunction—A major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 2216–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Buga, G.M.; Wood, K.S.; Byrns, R.E.; Chaudhuri, G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9265–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Gryglewski, R.; Bunting, S.; Vane, J.R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature 1976, 263, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, A.; Burnett, J.C. Intact and altered endothelium in regulation of vasomotion. Circulation 1992, 86, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Schachinger, V.; Britten, M.B.; Zeiher, A.M. Prognostic impact of coronary vasodilator dysfunction on adverse long-term outcome of coronary heart disease. Circulation 2000, 101, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiangsu New Medical College. Chinese Materia Medica Dictionary; Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 1977; p. 1031. [Google Scholar]
- Guizhou Province Institute for Drug Control and Guizhou Province Chinese Medicine Research Laboratories. A hypertensive clinical study on Eucommia leaves. Chin. Med. Herbs Res. 1978, 8, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Namba, T.; Hattori, M.; Yie, J.N.; Ma, Y.H.; Nomura, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Koizumi, T.; Katayama, K.; Lu, W. Studies on Tu-Chung leaves (I) Pharmacological effects of the water extract in vivo. Wakan Iyaku Gakkaishi 1986, 3, 89–97. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Metori, K.; Ohashi, S.; Takahashi, S. Effects of du-zhong leaf extract on serum and hepatic lipids in rats fed a high-fat diet. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, G.C.; Hsieh, C.L. Reactive oxygen species scavenging activity of Du-zhong (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.) and its active compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3431–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, M.J.; Cho, S.Y.; Park, S.A.; Park, K.K.; Jung, U.J.; Park, H.M.; Choi, M.S. Hypoglycemic effect of Du-zhong (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.) leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 67, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Amitani, K.; Zamami, Y.; Takatori, S.; Hobara, N.; Kawamura, N.; Hirata, T.; Wada, A.; Kitamura, Y.; Kawasaki, H. Ameliorative effect of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaves extract (ELE) on insulin resistance and abnormal perivascular innervation in fructose-drinking rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Hirata, T.; Wada, A.; Kawamura, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fujimura, K.; Ueda, T.; Yurugi, Y.; Soya, H.; Nishibe, S. Chronic administration of Eucommia leaf stimulates metabolic function of rats across several organs. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Wada, A.; Ueda, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Miyashita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Tsukamoto, S.; Nohara, T. Anti-obesity compounds in green leaves of Eucommia ulmoides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Odagiri, N.; Imai, R.; Yoshii, T.; Tagashira, E.; Nakata, C.; Nakamura, T.; Asaumi, M.; Onizuka, S.; Yahara, M.; Nohara, T. Effect of Eucommia leaf (Eucommia ulmoides OLIVER Leaf; Du-Zhong yge) extract on blood pressure (I). Nat. Med. 1997, 51, 392–398. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, C.Y.; Chen, C.X.; Deyama, T.; Nishibe, S. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant effects of the aqueous extracts of the Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaf and bark: Implications on their antihypertensive action. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 40, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Uezono, K.; Nakazawa, Y. Antihypertensive mechanism of Food for Specified Health Use: “Eucommia leaf glycoside” and its clinical application. J. Health Sci. 2000, 22, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ueda, T.; Kajimoto, O.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Kajimoto, Y. Hypotensive effects of beverage containing “Eucommia leaf glycoside” on high normal blood pressure and mild hypertensive subjects. Int. Symp. Eucommia Ulmoides 2007, 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainani, G.S.; Maru, V.G. Role of endothelial cell dysfunction in essential hypertension. J. Assoc. Phys. India 2004, 52, 966–969. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.C.; Alves, M.J.; Rondon, M.U.; Barretto, A.C.; Middlekauff, H.R.; Negrao, C.E. Sympathetic activation restrains endothelium-mediated muscle vasodilatation in heart failure patients. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H593–H599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Yen, M.H.; Li, C.Y.; Ding, Y.A. Alterations of nitric oxide synthase expression with aging and hypertension in rats. Hypertension 1998, 31, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Yen, M.H. Higher level of plasma nitric oxide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokawa, H.; Morikawa, K. Hydrogen peroxide is an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in animals and humans. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2005, 39, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Hong, H.J.; Chou, T.C.; Ding, Y.A.; Yen, M.H. Evidence for inducible nitric oxide synthase in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 228, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adcock, I.M.; Brown, C.R.; Kwon, O.; Barnes, P.J. Oxidative stress induces NF kappa B DNA binding and inducible NOS mRNA in human epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 199, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalba, G.; Beaumont, F.J.; San, J.G.; Fortuño, A.; Fortuño, M.A.; Etayo, J.C.; Díez, J. Vascular NADH/NADPH oxidase is involved in enhanced superoxide production in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2000, 35, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.; Galisteo, M.; Vera, R.; Villar, I.C.; Zarzuelo, A.; Tamargo, J.; Pérez-Vizcaíno, F.; Duarte, J. Quercetin downregulates NADPH oxidase, increases eNOS activity and prevents endothelial dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y. Administration of telmisartan reduced systolic blood pressure and oxidative stress probably through the activation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway and NO release in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Napoli, C.; de Nigris, F.; Williams-Ignarro, S.; Pignalosa, O.; Sica, V.; Ignarro, L.J. Nitric oxide and atherosclerosis: An update. Nitric Oxide 2006, 15, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Catalán, V.; Fortuño, A.; Frühbeck, G. Leptin inhibits the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by angiotensin II through nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, Y. Studies on Functionality and Application of Eucommia Leaf to Preservation of Health. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, C.; Hattori, M. Simultaneous determination of ten bioactive constituents in Eucommia ulmoides leaves and Tochu tea products by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-MS). J. Tradit. Med. 2008, 25, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, T.; Ikeda, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Nishibe, S. The Chemistry and Bioactivity of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaves. Studies Nat. Prod. Chem. 2014, 41, 225–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Kawamura, N.; Tsuboi, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Hirata, T.; Ueda, T.; Tagawa, C.; Nakazawa, Y.; Onizuka, S.; Tagashira, E.; et al. Effect of the Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract on blood pressure. Int. Symp. Eucommia Ulmoides 2007, 1, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.M.; Park, J.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.M. Geniposidic acid protects against d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Krawczyk, M.; Zgola-Grzeskowiak, A. Determination of antioxidant activity, rutin, quercetin, phenolic acids and trace elements in tea infusions: Influence of citric acid addition on extraction of metals. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2015, 40, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Jokura, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujii, A.; Tokimitsu, I.; Saito, I. Chlorogenic acid attenuates hypertension and improves endothelial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Hirata, T.; Hosoo, S.; Nakajima, K.; Wada, A.; Yurugi, Y.; Soya, H.; Matsui, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ogata, M.; Nishibe, S. Asperuloside stimulates metabolic function in rats across several organs under high-fat diet conditions, acting like the major ingredient of Eucommia leaves with anti-obesity activity. J. Nutr. Sci. 2012, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Naramoto, K.; Koyama, M. Blood-pressure-lowering effect of fermented buckwheat sprouts in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosoo, S.; Koyama, M.; Kato, M.; Hirata, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Wada, A.; Wada, K.; Nishibe, S.; Nakamura, K. The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules 2015, 20, 21971-21981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219826
Hosoo S, Koyama M, Kato M, Hirata T, Yamaguchi Y, Yamasaki H, Wada A, Wada K, Nishibe S, Nakamura K. The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules. 2015; 20(12):21971-21981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219826
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosoo, Shingo, Masahiro Koyama, Mai Kato, Tetsuya Hirata, Yasuyo Yamaguchi, Hiroo Yamasaki, Atsunori Wada, Keiji Wada, Sansei Nishibe, and Kozo Nakamura. 2015. "The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats" Molecules 20, no. 12: 21971-21981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219826
APA StyleHosoo, S., Koyama, M., Kato, M., Hirata, T., Yamaguchi, Y., Yamasaki, H., Wada, A., Wada, K., Nishibe, S., & Nakamura, K. (2015). The Restorative Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Leaf Extract on Vascular Function in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules, 20(12), 21971-21981. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219826





