Two-Stage Prediction of the Effects of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Luciferase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Single Toxicity
| No. | F | α | β | R2 | RMSE | f | EC50 | EC10 | NOEC | t | pi(M1) | pi(M2) | pi(M3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL1 | W | 12.02 | 5.015 | 0.998 | 0.0165 | 0.70 | 3.39[3.26–3.69] × 10−3 | 1.43[1.13–1.69] × 10−3 | 7.04 × 10−4 | 1.62 | 2.09 × 10−2 | 1.82 × 10−2 | 1.26 × 10−2 |
| IL2 | W | 6.321 | 6.893 | 0.961 | 0.0344 | 0.66 | 1.07[0.875–1.49] × 10−1 | 5.71[3.30–7.32] × 10−2 | 4.89 × 10−2 | 2.23 | 8.35 × 10−1 | 5.75 × 10−1 | 8.78 × 10−1 |
| IL3 | L | 2.090 | 1.654 | 0.956 | 0.0381 | 0.70 | 5.45[3.26–9.66] × 10−2 | 2.56[NA–7.30] × 10−3 | 3.11 × 10−3 | 2.64 | 3.74 × 10−2 | 2.93 × 10−1 | 5.58 × 10−2 |
| IL4 | W | 17.60 | 5.141 | 0.998 | 0.0202 | 0.70 | 3.21[3.00–3.45] × 10−4 | 1.38[1.02–1.65] × 10−4 | 6.55 × 10−5 | 2.46 | 2.02 × 10−3 | 1.72 × 10−3 | 1.18 × 10−3 |
| IL5 | L | 34.97 | 12.11 | 0.994 | 0.0357 | 0.57 | 1.29[1.20–1.53] × 10−3 | 8.50[5.30–9.19] × 10−4 | 3.65 × 10−4 | 1.21 | 1.24 × 10−2 | 6.93 × 10−3 | 6.55 × 10−3 |
| IL6 | W | 11.74 | 4.118 | 0.996 | 0.0268 | 0.57 | 1.15[1.03–1.31] × 10−3 | 4.01[2.54–5.43] × 10−4 | 8.61 × 10−5 | 1.35 | 5.87 × 10−3 | 6.18 × 10−3 | 1.55 × 10−3 |
| IL7 | W | 14.18 | 5.564 | 0.986 | 0.0530 | 0.70 | 2.43[2.02–2.92] × 10−3 | 1.11[NA–1.63] × 10−3 | 4.45 × 10−4 | 1.77 | 1.62 × 10−2 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 7.99 × 10−3 |
| IL8 | W | 13.58 | 5.246 | 0.994 | 0.0333 | 0.70 | 2.20[1.95–2.49] × 10−3 | 9.61[5.10–8.60] × 10−4 | 3.56 × 10−4 | 2.89 | 1.41 × 10−2 | 1.18 × 10−2 | 6.39 × 10−3 |
| IL9 | L | 7.850 | 3.774 | 0.995 | 0.0096 | 0.70 | 8.32[7.70–9.05] × 10−3 | 2.18[1.82–2.53] × 10−3 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 2.85 | 3.19 × 10−2 | 4.47 × 10−2 | 2.05 × 10−2 |
| IL10 | W | 7.272 | 2.692 | 0.995 | 0.0163 | 0.70 | 1.45[1.31–1.61] × 10−3 | 2.90[1.90–3.93] × 10−4 | 8.93 × 10−5 | 1.68 | 4.24 × 10−3 | 7.79 × 10−3 | 1.60 × 10−3 |
| IL11 | W | 8.810 | 3.848 | 0.999 | 0.0119 | 0.57 | 4.12[2.24–5.75] × 10−3 | 1.34[1.07–1.66] × 10−3 | 4.39 × 10−4 | 1.19 | 1.96 × 10−2 | 2.21 × 10−2 | 7.88 × 10−3 |
| M1 | W | 3.963 | 2.682 | 0.999 | 0.0083 | 0.66 | 2.43[2.30–2.57] × 10−2 | 4.82[3.95–5.70] × 10−3 | 1.88 × 10−3 | 2.38 | |||
| M2 | W | 5.112 | 3.251 | 0.981 | 0.0390 | 0.66 | 2.06[1.67–2.52] × 10−2 | 5.44[1.22–9.16] × 10−3 | 2.11 × 10−3 | 2.64 | |||
| M3 | W | 3.039 | 2.405 | 0.993 | 0.0181 | 0.66 | 3.83[3.37–4.38] × 10−2 | 6.31[3.65–9.17] × 10−3 | 1.93 × 10−3 | 2.53 |

2.2. Mixture Toxicity
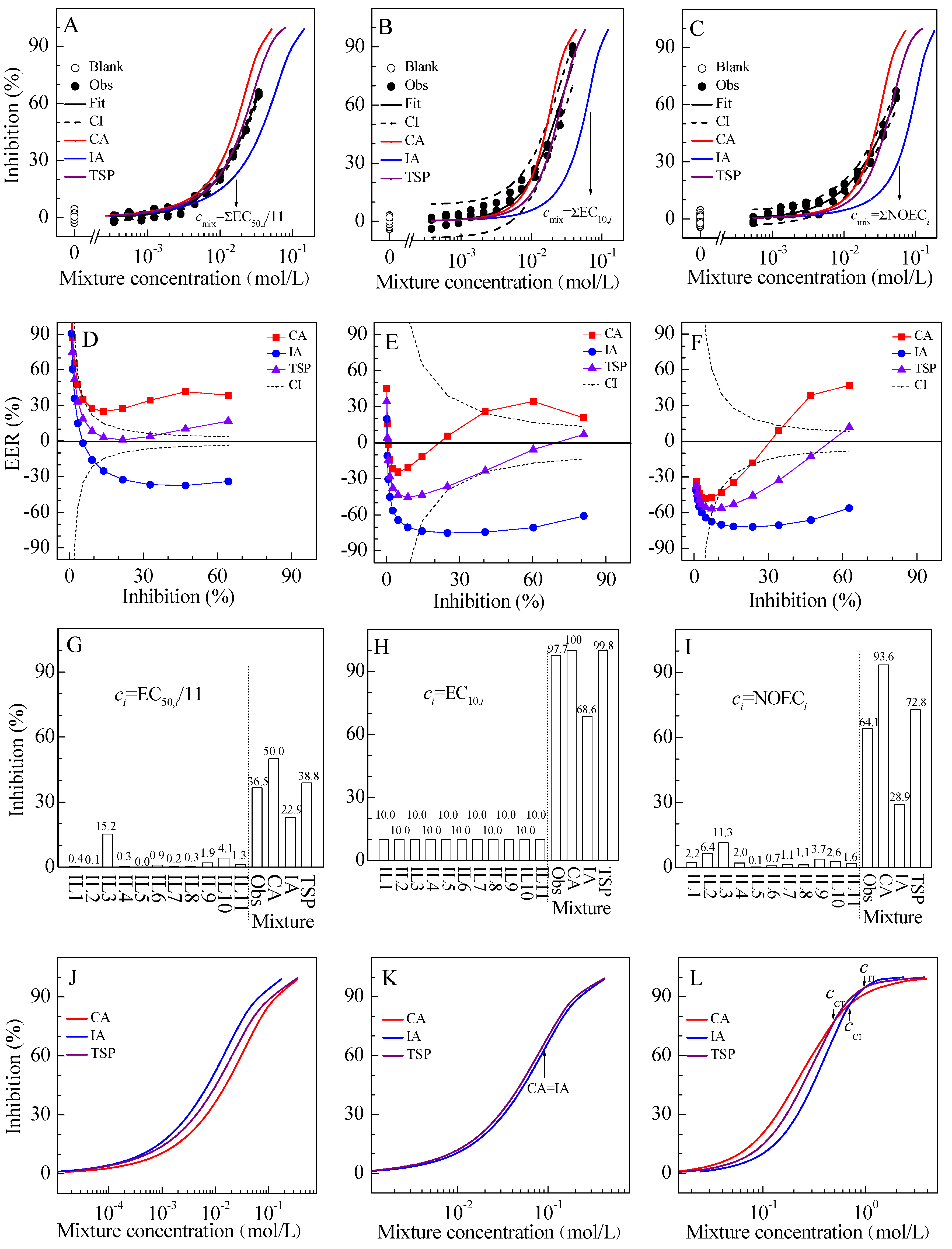
2.3. Location Relationship among CA, IA, and TSP Curves
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals

3.2. Luciferase Toxicity Test
3.3. Experimental Design and Toxicity Prediction of Mixtures



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suk, W.A.; Olden, K.; Yang, R.S.H. Chemical mixtures research: Significance and future perspectives. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 891–892. [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus, T.; Scholze, M.; Grimme, L.H. The single substance and mixture toxicity of quinolones to the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 49, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.; Altenburger, R.; Backhaus, T.; Blanck, H.; Boedeker, W.; Gramatica, P.; Hamer, V.; Scholze, M.; Vighi, M.; Grimme, L.H. Joint algal toxicity of 16 dissimilarly acting chemicals is predictable by the concept of independent action. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 63, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghans, M. Studies on Combination Effects of Environmentally Relevant Toxicants. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2004; pp. 78–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ra, J.S.; Lee, B.C.; Chang, N.I.; Kim, S.D. Estimating the combined toxicity by two-step prediction model on the complicated chemical mixtures from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.W.; Huang, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.Y.; Qiao, X.L.; Dong, Y.Y. Integrated fuzzy concentration addition-independent action (IFCA-IA) model outperforms two-stage prediction (TSP) for predicting mixture toxicity. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.W.; Yun, Y.S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.S.; Liu, H.L. Effect of ionic liquid on the toxicity of pesticide to Vibrio-qinghaiensis sp.-Q67. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Carvalho, P.J.; Gardas, R.L.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M.; Santos, L.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Mutual solubilities of water and hydrophobic ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13082–13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.R.; Wang, S.H.; Yun, M.X.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Sun, Z.J. The toxic effects of ionic liquids on the activities of acetylcholinesterase and cellulase in earthworms. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, J.; Molter, K.; Stock, F.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Poczobutt, J.; Hoffmann, J.; Ondruschka, B.; Filser, J.; Jastorff, B. Biological effects of imidazolium ionic liquids with varying chain lengths in acute Vibrio fischeri and WST-1 cell viability assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2004, 58, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.W.; Jeon, Y.C.; Pham, T.P.T.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.S. The ecotoxicity of ionic liquids and traditional organic solvents on microalga Selenastrum capricornutum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2008, 71, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Papaiconomou, N.; Lee, J.M.; Salminen, J.; Clark, D.S.; Prausnitz, J.M. In vitro cytotoxicities of ionic liquids: Effect of cation rings, functional groups, and anions. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzke, M.; Stolte, S.; Arning, U.; Uebers, U.; Filser, J. Imidazolium based ionic liquids in soils: Effects of the side chain length on wheat (Triticum aestivum) and cress (Lepidium sativum) as affected by different clays and organic matter. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, D.M.; Brown, L.M.; Lamberti, G.A. Acute toxic effects of ionic liquids on zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) survival and feeding. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretti, C.; Chiappe, C.; Baldetti, I.; Brunini, S.; Monni, G.; Intorre, L. Acute toxicity of ionic liquids for three freshwater organisms: Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Daphnia magna and Danio rerio. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2009, 72, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, H.; Hallett, J.P.; Villar-Garcia, I.J.; Hunt, P.A.; Welton, T. Mixtures of ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7780–7802. [Google Scholar]
- Matzke, M.; Stolte, S.; Boschen, A.; Filser, J. Mixture effects and predictability of combination effects of imidazolium based ionic liquids as well as imidazolium based ionic liquids and cadmium on terrestrial plants (Triticum aestivum) and limnic green algae (Scenedesmus vacuolatus). Green Chem. 2008, 10, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.S.; Dou, R.N.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, J. Evaluation on the toxicity of ionic liquid mixture with antagonism and synergism to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.S.; Yu, Z.Y.; Liu, H.L. Significant contributions of ionic liquids containing tetrafluoroborate and trifluoromethanesulfonate to antagonisms and synergisms in multi-component mixtures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionova, N.S.; Petushkov, V.N. Effect of different salts and detergents on luciferin-luciferase luminescence of the enchytraeid Fridericia heliota. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 83, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, H.; Ueda, I.; Eyring, H. Combined effects of dissociable and undissociable local anesthetics upon ATP-induced firefly bioluminescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 1868–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.L.; Liu, S.S.; Zhu, X.W.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, L.J. Predicting hormetic effects of ionic liquid mixtures on luciferase activity using the concentration addition model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.L.; Liu, S.S.; Su, B.X.; Qin, L.T. Predicting synergistic toxicity of heavy metals and ionic liquids on photobacterium Q67. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, S.; Arning, J.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Matzke, M.; Stock, F.; Thiele, K.; Uerdingen, M.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Anion effects on the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of ionic liquids: Eco(cyto)activity as complicated, but unavoidable parameter for task-specific optimization. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D. NECS, NOECS and the ECx. Australas. J. Ecotoxicol. 2008, 14, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Warne, M.S.J.; van Dam, R. NOEC and LOEC data should no longer be generated or used. Australas. J. Ecotoxicol. 2008, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Hoeven, N.; Noppert, F.; Leopold, A. How to measure no effect. Part I: Towards a new measure of chronic toxicity in ecotoxicology. Introduction and workshop results. Environmetrics 1997, 8, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.J.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Hahn, M.E.; Webster, T.F. Generalized concentration addition predicts joint effects of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists with partial agonists and competitive antagonists. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 666–672. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.S.; Liu, L.; Chen, F. Application of the concentration addition model in the assessment of chemical mixture toxicity (in Chinese). Acta Chim. Sin. 2013, 71, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Syberg, K.; Elleby, A.; Pedersen, H.; Cedergreen, N.; Forbes, V.E. Mixture toxicity of three toxicants with similar and dissimilar modes of action to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2008, 69, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Schaumann, G.E. Development of QSAR-based two-stage prediction model for estimating mixture toxicity. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2013, 24, 841–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Kortenkamp, A. Something from “nothing”—Eight weak estrogenic chemicals combined at concentrations below NOECs produce significant mixture effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Food Quality Protection Act of 1996. Public Law 104–170, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Könemann, H. Structure-activity relationships and additivity in fish toxicities of environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 1980, 4, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedeker, W.; Drescher, K.; Altenburger, R.; Faust, M.; Grimme, L. Combined effects of toxicants: The need and soundness of assessment approaches in ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 1993, 134, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Z. A Study on the Properties and Applications of Firefly Luciferase . (in Chinese). In Master Thesis; East China Normal University: Shanghai, China, 2007; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, S.S.; Song, X.Q.; Ge, H.L. Prediction for the mixture toxicity of six organophosphorus pesticides to the luminescent bacterium Q67. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2008, 71, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.L.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, F.; Luo, J.H.; Lv, D.Z.; Su, B.X. Microplate luminometry for toxicity bioassay of chemicals on luciferase (in Chinese). Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2013, 33, 2766–2770. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.W.; Liu, S.S.; Ge, H.L.; Liu, Y. Comparison between two confidence intervals of dose-response relationships (in Chinese). China Environ. Sci. 2009, 29, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett, C.W. New tables for multiple comparisons with a control. Biometrics 1964, 20, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Liu, S.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.Y. A new effect residual ratio (ERR) method for the validation of the concentration addition and independent action models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, H.-L.; Liu, S.-S.; Su, B.-X.; Zhu, X.-W. Two-Stage Prediction of the Effects of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Luciferase. Molecules 2014, 19, 6877-6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056877
Ge H-L, Liu S-S, Su B-X, Zhu X-W. Two-Stage Prediction of the Effects of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Luciferase. Molecules. 2014; 19(5):6877-6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056877
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Hui-Lin, Shu-Shen Liu, Bing-Xia Su, and Xiang-Wei Zhu. 2014. "Two-Stage Prediction of the Effects of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Luciferase" Molecules 19, no. 5: 6877-6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056877
APA StyleGe, H.-L., Liu, S.-S., Su, B.-X., & Zhu, X.-W. (2014). Two-Stage Prediction of the Effects of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquid Mixtures on Luciferase. Molecules, 19(5), 6877-6890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056877




