Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Escherichia coli Ultrastructure, Membrane Integrity and Molecular Composition as Assessed by FTIR Spectroscopy and Microscopic Imaging Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
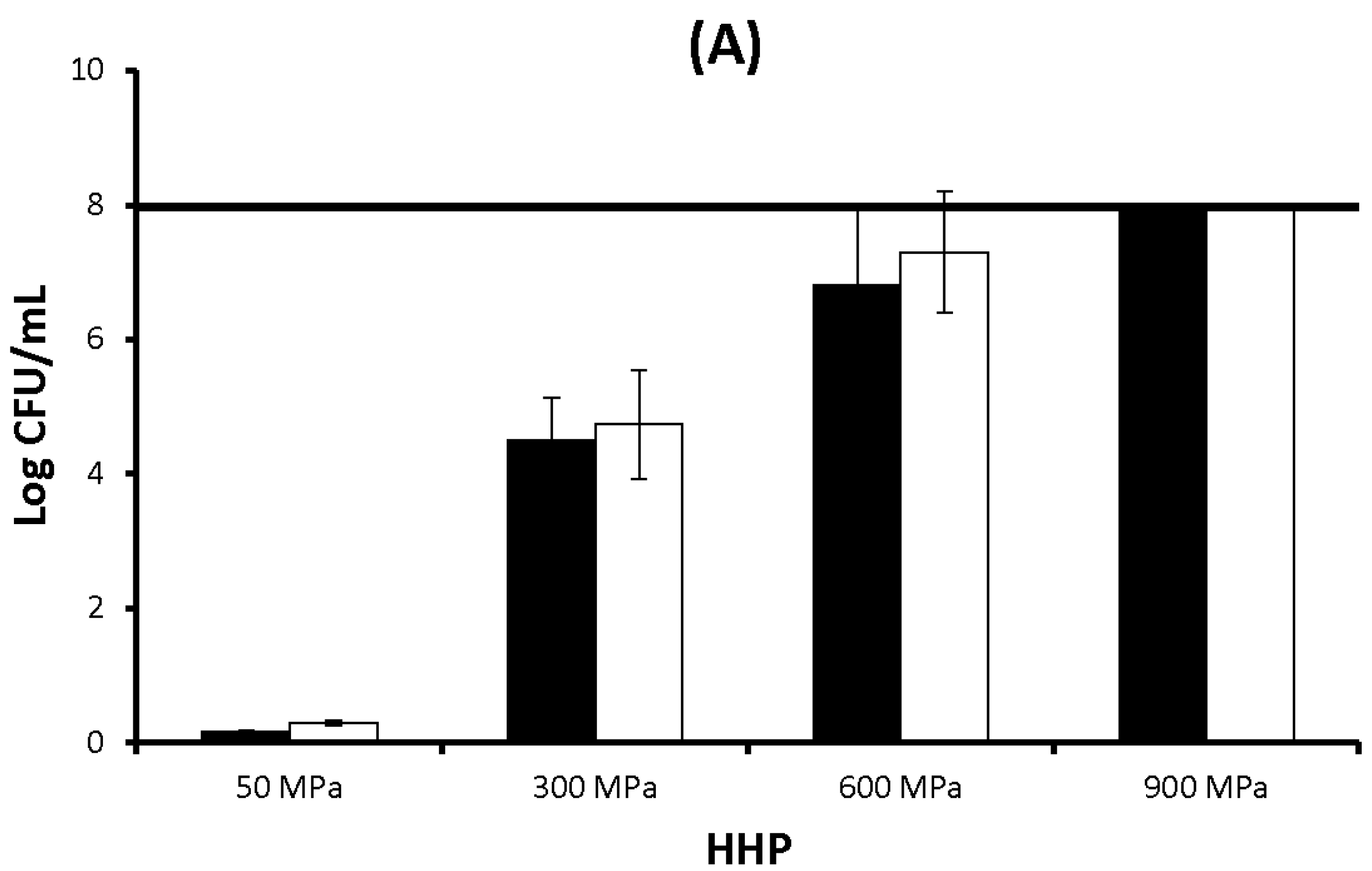
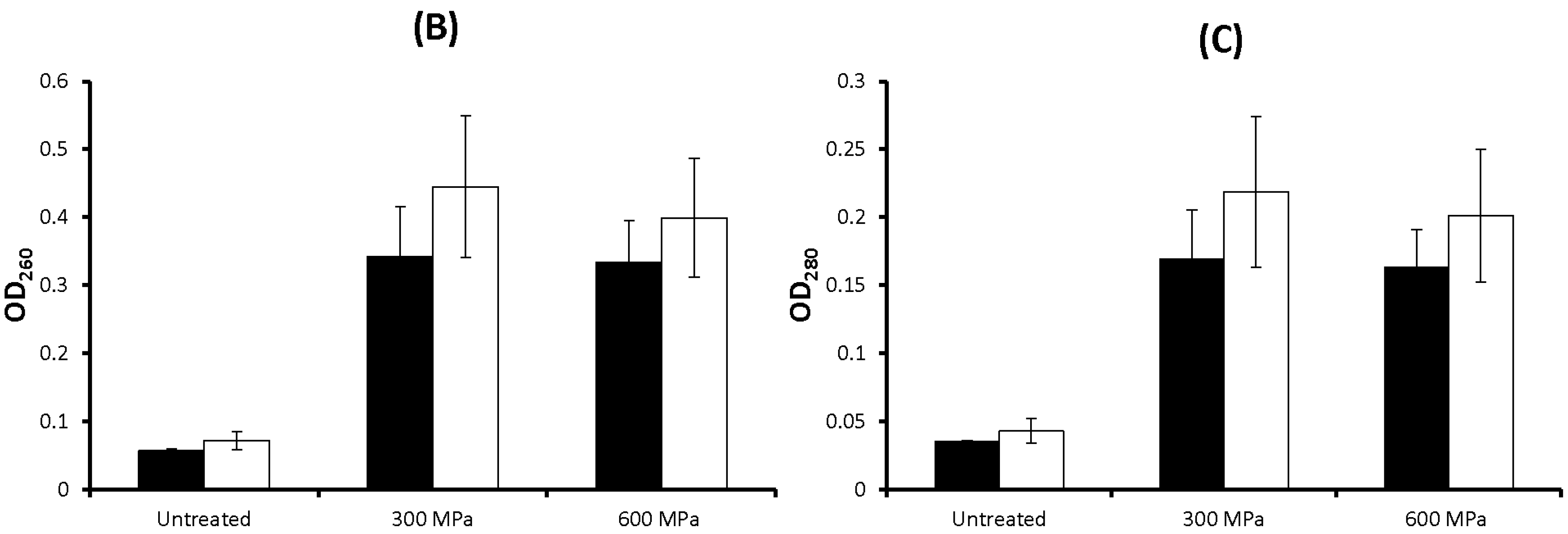
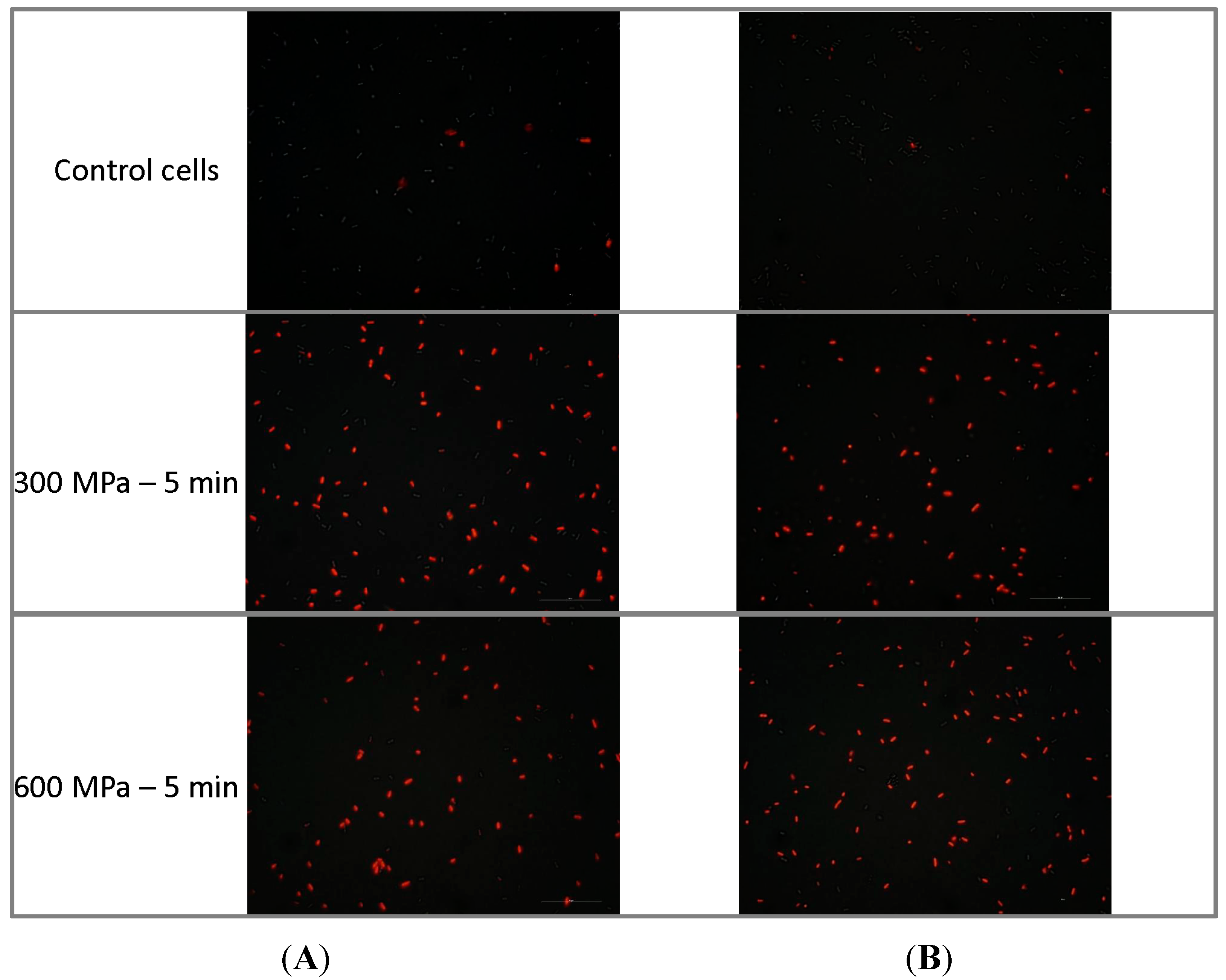


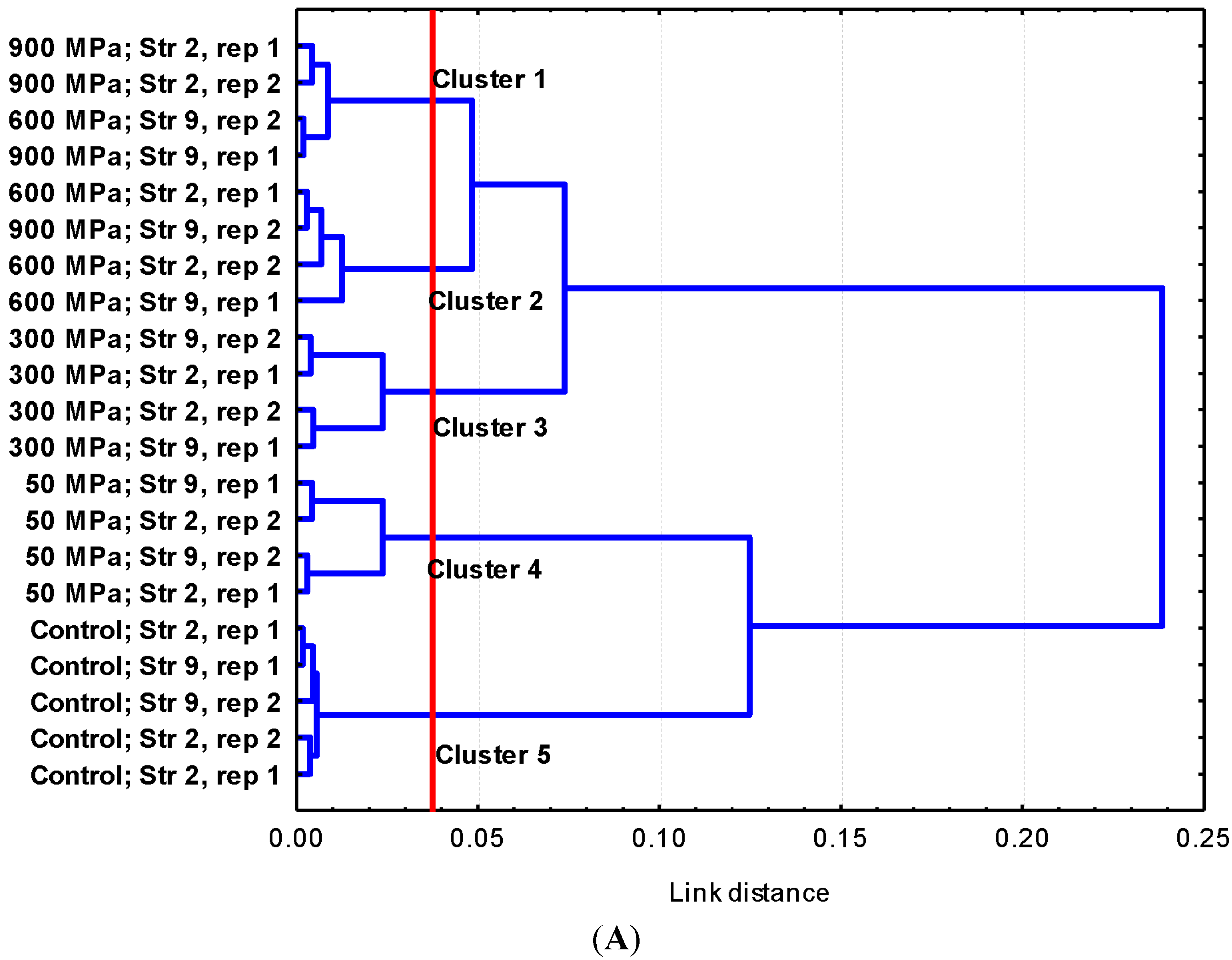
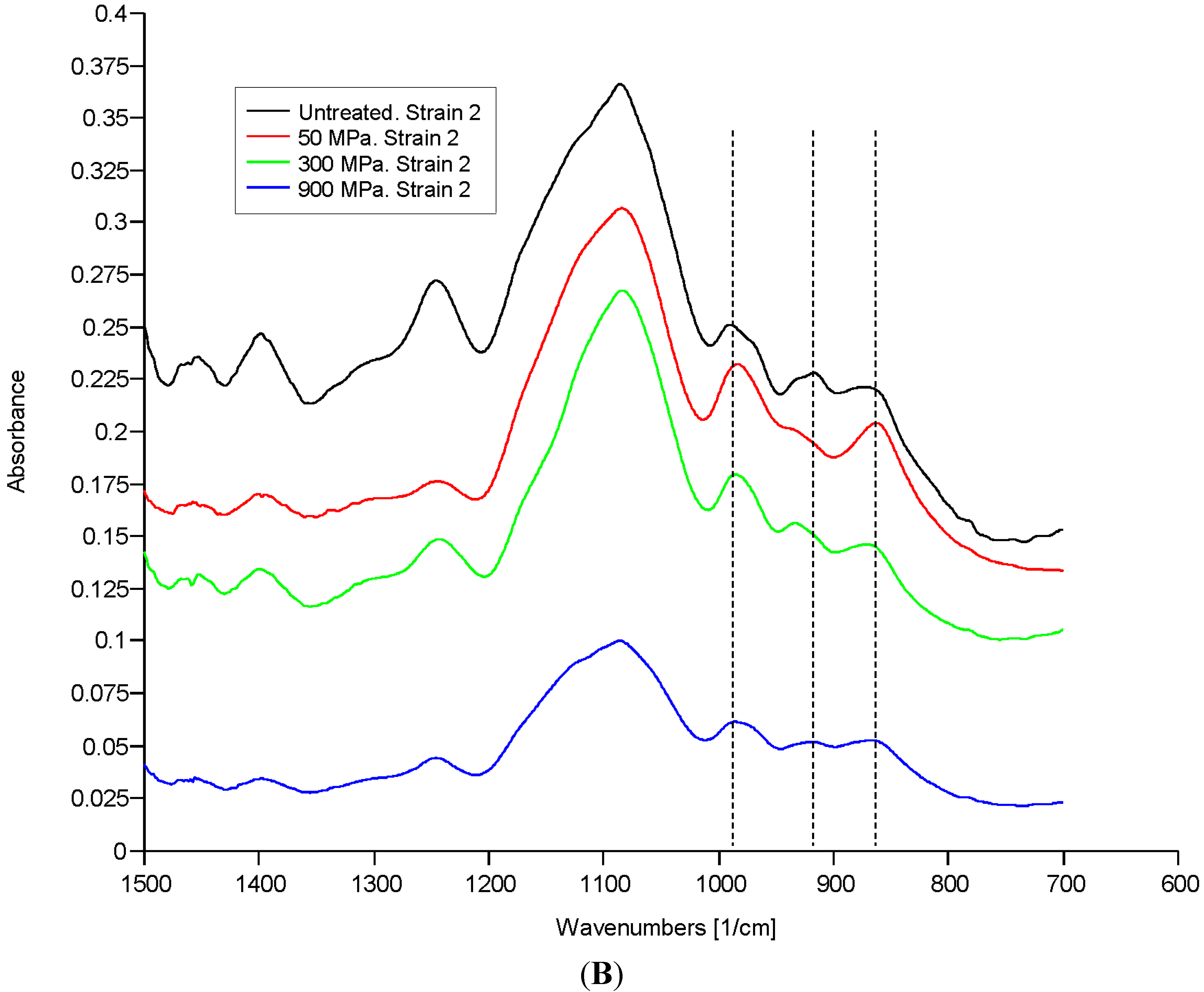
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
3.2. HHP Treatments
3.3. Membrane Integrity Tests
3.3.1. Assessment of Propidium Iodide (PI) Uptake
3.3.2. Measurement of Cellular Leakage
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analyses
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Considine, K.M.; Kelly, A.L.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Hill, C.; Sleator, R.D. High pressure processing—Effects on microbial food safety and food quality. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, K.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Hernández, M.; Raspor, P.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. High hydrostatic pressure as emergent technology for the elimination of foodborne viruses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendueles, E.; Omer, M.K.; Alvseike, O.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R.; Prieto, M. Microbiological food safety assessment of high hydrostatic pressure processing. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, M.K.; Alvseike, O.; Holck, A.; Axelsson, L.; Prieto, M.; Skjerve, E.; Heir, E. The application of High Pressure Processing to reduce pathogenic Escherichia coli in Norwegian dry-fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The European Union Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents and Food-borne Outbreaks in 2012. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar]
- Alpas, H.; Kalchayanand, N.; Bozoglu, F.; Sikes, A.; Dunne, C.P.; Ray, B. Variation in Resistance to Hydrostatic Pressure among Strains of Food-Borne Pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 4248–4251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benito, A.; Ventoura, G.; Casadei, M.; Robindon, T.; Mackey, B.M. Variation in resistance of natural isolates of Escherichia coli O157 to high hydrostatic pressure, mild heat and other stresses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robey, M.; Benito, A.; Hutson, R.H.; Pascual, C.; Park, S.F.; Mackey, B.M. Variation in resistance to high hydrostatic pressure and rpoS heterogeneity in natural isolates of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4901–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Alvseike, O.; Omer, M.K.; Heir, E.; Axelsson, L.; Holck, A.; Prieto, M. Heterogeneity in resistance to food-related stresses and biofilm formation ability among verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 161, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañas, P.; Pagán, R. Microbial inactivation by new technologies of food preservation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 1387–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagán, R.; Mackey, B. Relationship between membrane damage and cells death in pressure-treated Escherichia coli cells: differences between exponential- and stationary- phase cells and variation among strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2829–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. On-line fluorescence determination of pressure mediated outer membrane damage in Escherichia coli. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañas, P.; Mackey, B.M. Morphological and physiological changes induced by high hydrostatic pressure in exponential- and stationary- phase cells of Escherichia coli: Relationship with cells death. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, B.; Mañas, P.; Mackey, B.M. The relationship between membrane damage, release of protein and loss of viability in Escherichia coli exposed to high hydrostatic pressure. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 137, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smelt, J.P.P.M.; Rijke, A.G.F.; Hayhurst, A. Possible mechanism of high-pressure inactivation of microorganisms. High Press. Res. 1994, 12, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, P.C.; Glaasker, E.; Smelt, J.P.P.M. Effects of high pressure on inactivation kinetics and events related to proton efflux in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niven, G.W.; Miles, C.C.; Mackey, B.M. The effects of hydrostatic pressure on ribosome conformation in Escherichia coli: An in vivo study using differential scanning calorimetry. Microbiology 1999, 145, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, H.M.; Herberhold, H.; Fahsel, S.; Ganzle, M.G.; Winter, R.; Vogel, R.F. Effect of pressure-induced membrane phase transitions on inactivation of HorA, an ATP-dependent multidrug resistance transporter, in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, B.M.; Mañas, P. Inactivation of Escherichia coli by high pressure. In High Pressure Microbiology; Michiels, C., Aertsen, A., Bartlett, D., Yayanos, Y., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 53–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, B.M.; Forestiere, N.S.; Isaacs, N.S.; Stenning, R.; Brooker, B. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure on Salmonella Thompson and Listeria monocytogenes examined by electron microscopy. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 19, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Sohn, K.H.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, H.J. High hydrostatic pressure inactivation of Lactobacillus viridescens and its effects on ultrastructure of cells. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 36, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletunc, G.; Lee, J.; Alpas, H.; Bozoglu, F. Evaluation of structural changes induced by high hydrostatic pressure in Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Mouwen, D.J.M.; López, M.; Prieto, M. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterize molecular composition and stress response in foodborne pathogenic bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methnol. 2011, 84, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Prieto, M. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy in Food Microbiology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Prieto, M. Changes in ultrastructure and Fourier transform infrared spectrum of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium cells after exposure to stress conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7598–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Carvajal, A.; Arguello, H.; Martínez-Lobo, F.J.; Naharro, G.; Rubio, P. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of a commercial citrus fruit extract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Al-Alami, N.I.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Rasco, B.A. Using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) absorbance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to study the effect of chlorine-induced bacterial injury in water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8992–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; She, Z.; Qian, G.; Ren, Z. Effect of ultra-strong static magnetic field on bacteria: Application of Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy combined with cluster analysis and deconvolution. Bioelectromagnetics 2009, 30, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartz, L.; de Jong, B.; Hjertqvist, M.; Plym-Forshell, L.; Alsterlund, R.; Lofdahl, S.; Osterman, B.; Stahl, A.; Eriksson, E.; Hansson, H.; et al. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in southern Sweden associated with consumption of fermented sausage; aspects of sausage production that increase the risk of contamination. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouwen, D.J.M.; Weijtens, M.J.B.M.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Prieto, M. Discrimination of enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus PCR types of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, D. Infrared spectroscopy in microbiology. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 102–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the two E. coli strainsare available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prieto-Calvo, M.; Prieto, M.; López, M.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Escherichia coli Ultrastructure, Membrane Integrity and Molecular Composition as Assessed by FTIR Spectroscopy and Microscopic Imaging Techniques. Molecules 2014, 19, 21310-21323. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191221310
Prieto-Calvo M, Prieto M, López M, Alvarez-Ordóñez A. Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Escherichia coli Ultrastructure, Membrane Integrity and Molecular Composition as Assessed by FTIR Spectroscopy and Microscopic Imaging Techniques. Molecules. 2014; 19(12):21310-21323. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191221310
Chicago/Turabian StylePrieto-Calvo, María, Miguel Prieto, Mercedes López, and Avelino Alvarez-Ordóñez. 2014. "Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Escherichia coli Ultrastructure, Membrane Integrity and Molecular Composition as Assessed by FTIR Spectroscopy and Microscopic Imaging Techniques" Molecules 19, no. 12: 21310-21323. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191221310
APA StylePrieto-Calvo, M., Prieto, M., López, M., & Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. (2014). Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Escherichia coli Ultrastructure, Membrane Integrity and Molecular Composition as Assessed by FTIR Spectroscopy and Microscopic Imaging Techniques. Molecules, 19(12), 21310-21323. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191221310




