Melaleuca alternifolia Concentrate Inhibits in Vitro Entry of Influenza Virus into Host Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
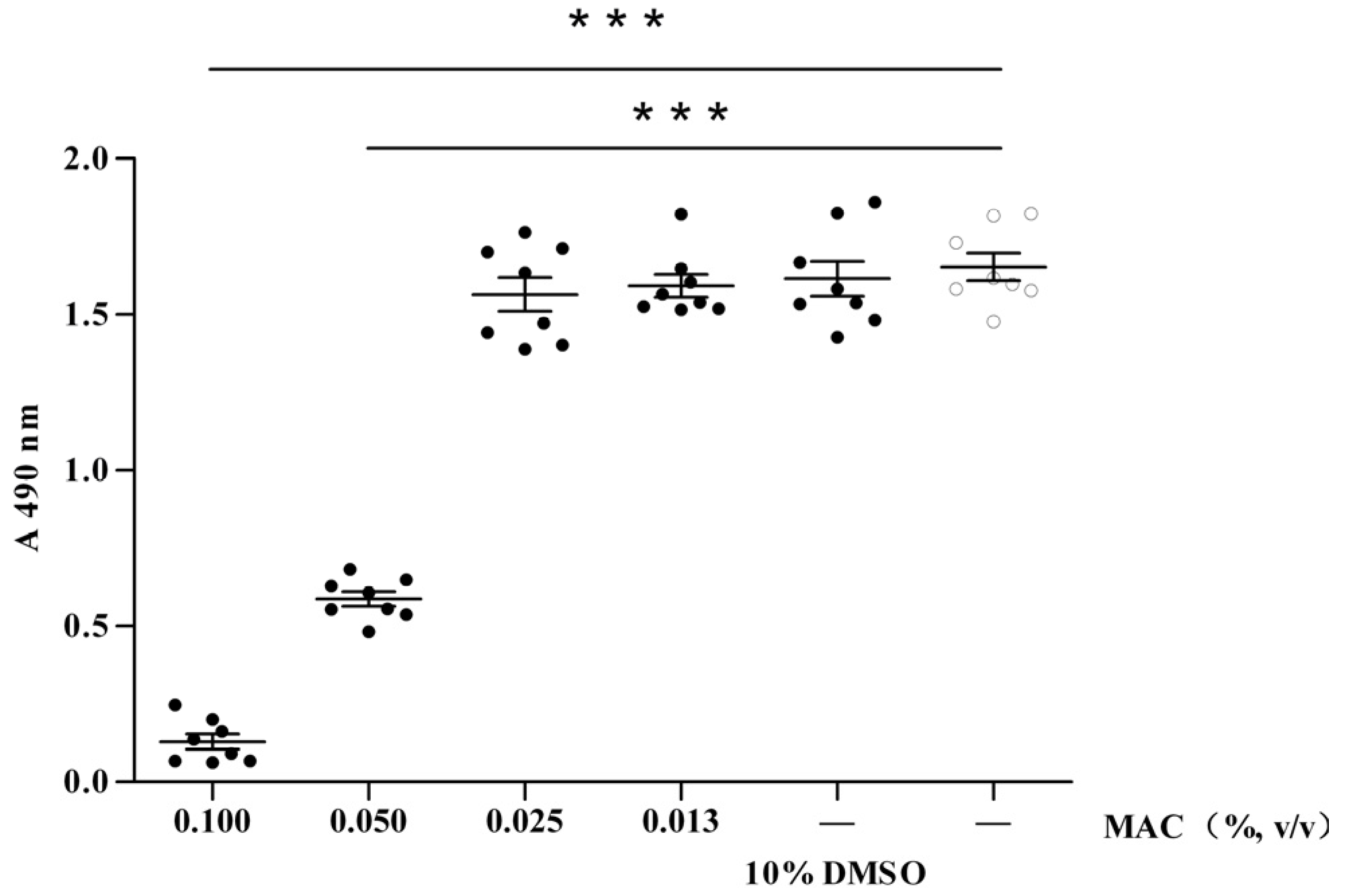
2.1. Cytotoxic Test of MAC
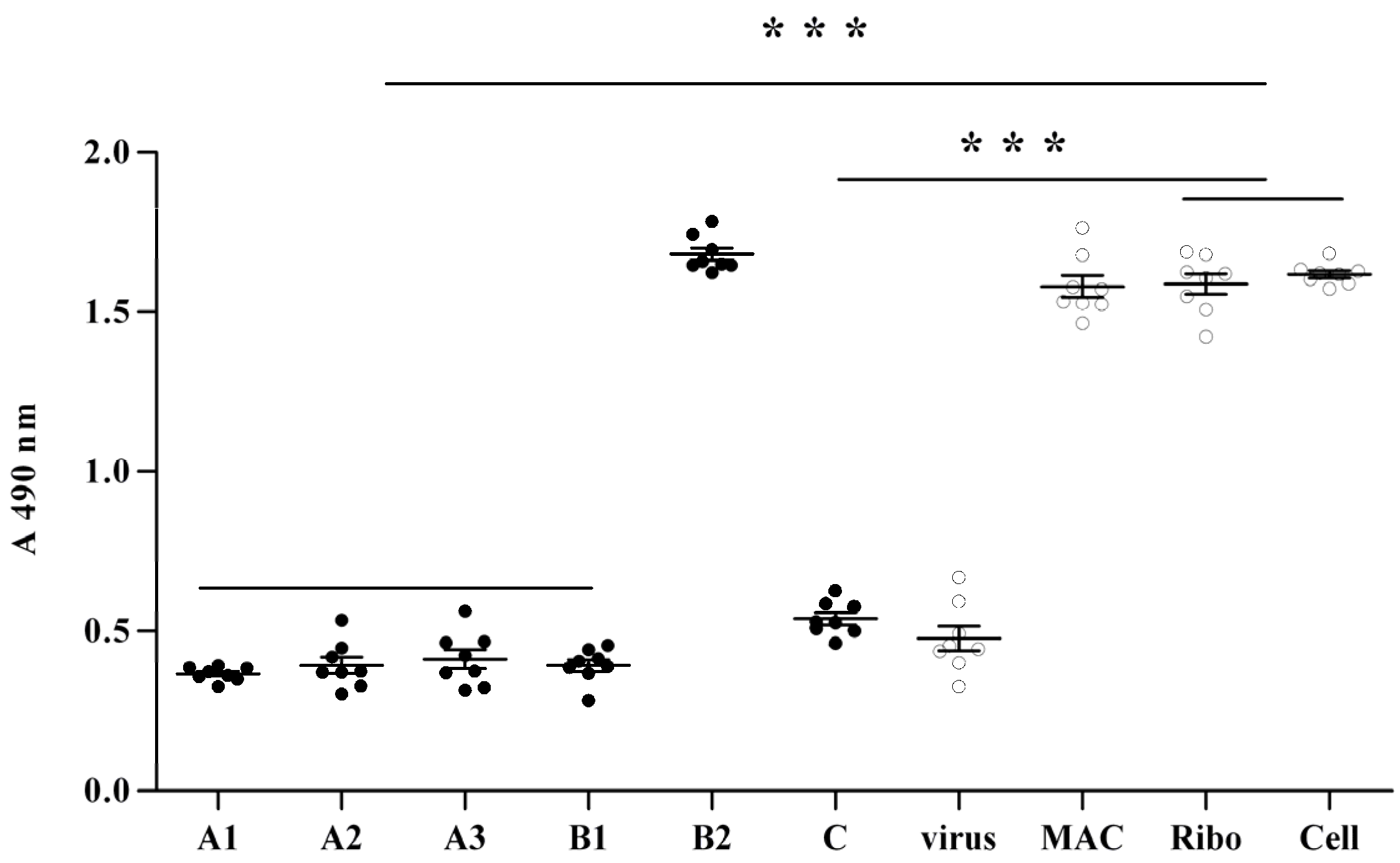
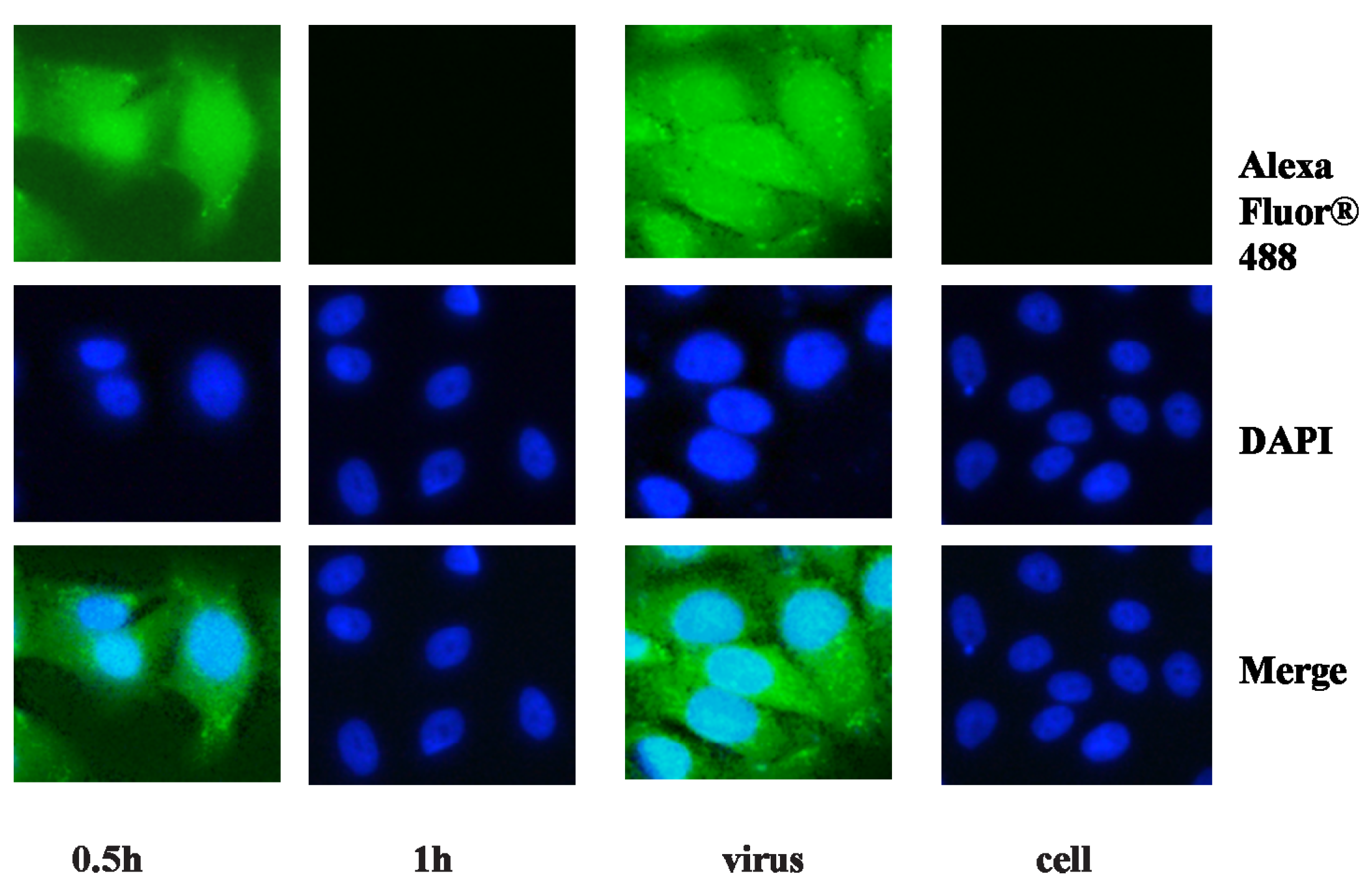
2.2. Anti-Viral Effect Assay of MAC in Vitro
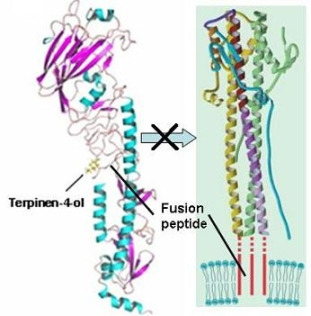
2.3. Molecular Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies
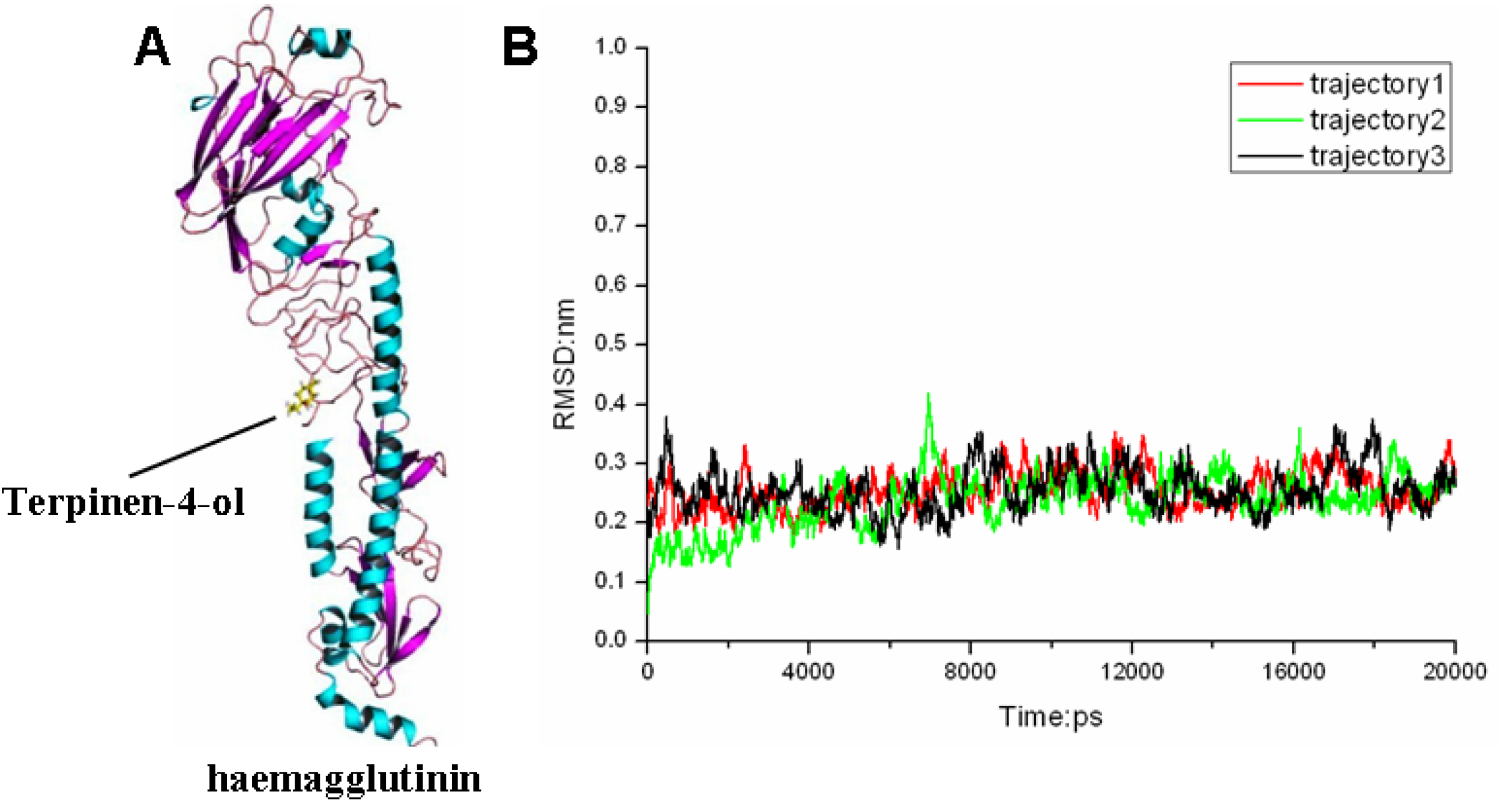
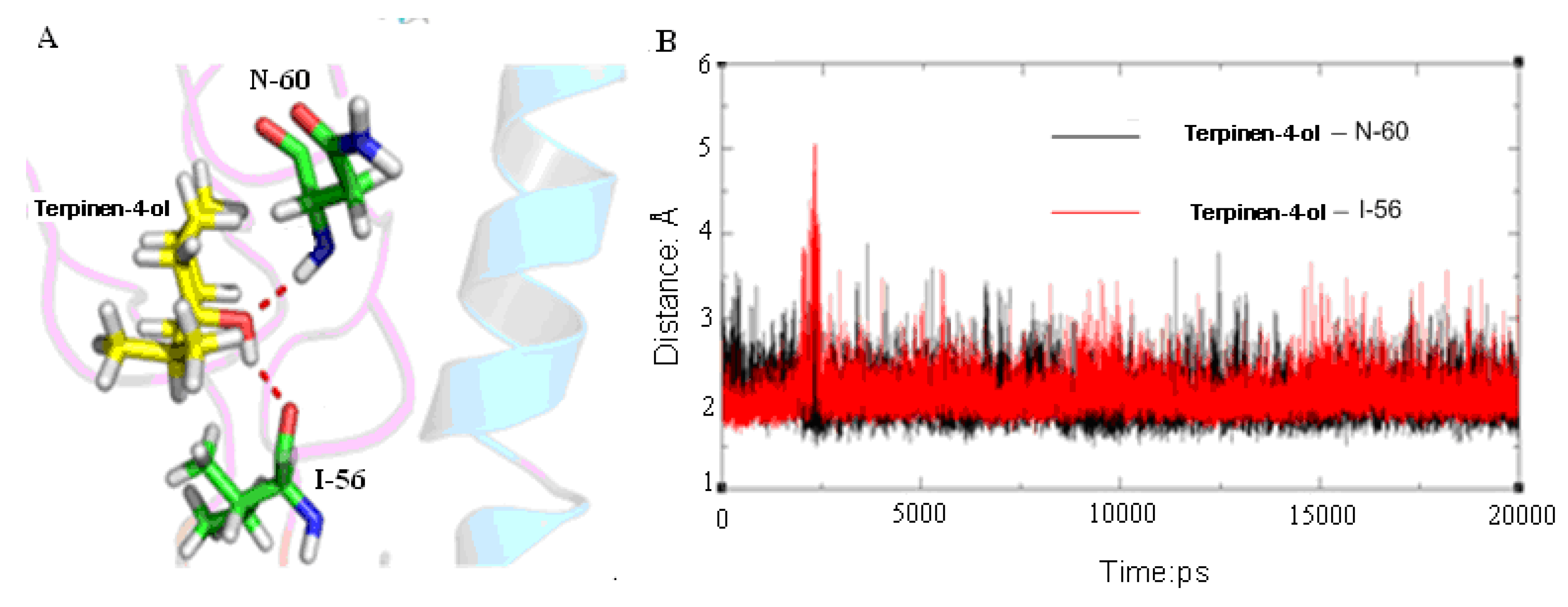
| Contribution | Trajectory1 | Trajectory2 | Trajectory3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | std | mean | std | mean | std | |||
| Eelec | −9.7112 | 2.3507 | −9.4458 | 1.7139 | −7.8287 | 3.4801 | ||
| EvdW | −27.6956 | 2.0215 | −27.3646 | 1.9431 | −28.3145 | 2.0685 | ||
| Gnonpolar | −3.7310 | 0.0814 | −3.7539 | 0.1006 | −3.7499 | 0.1036 | ||
| GGB | 15.3067 | 1.9963 | 13.5294 | 1.2774 | 14.7480 | 1.7067 | ||
| −TΔS | 14.2991 | 5.4078 | 13.9034 | 4.9706 | 14.5704 | 5.1095 | ||
| ΔGGB | −25.8310 | 1.9734 | −27.0349 | 2.0078 | −25.1450 | 2.6133 | ||
| ΔGGB(binding) | −11.5319 | −13.1215 | −10.5746 | |||||
3. Experimental
3.1. Bio-Safety
3.2. Cells and Virus
3.3. Melaleuca Alternifolia Concentrate (MAC)
3.4. Virus Titrations
3.5. MTT Assay to Determine the Cellular Viability of MDCK Cells
3.6. Bioimaging in 96 Well Plates
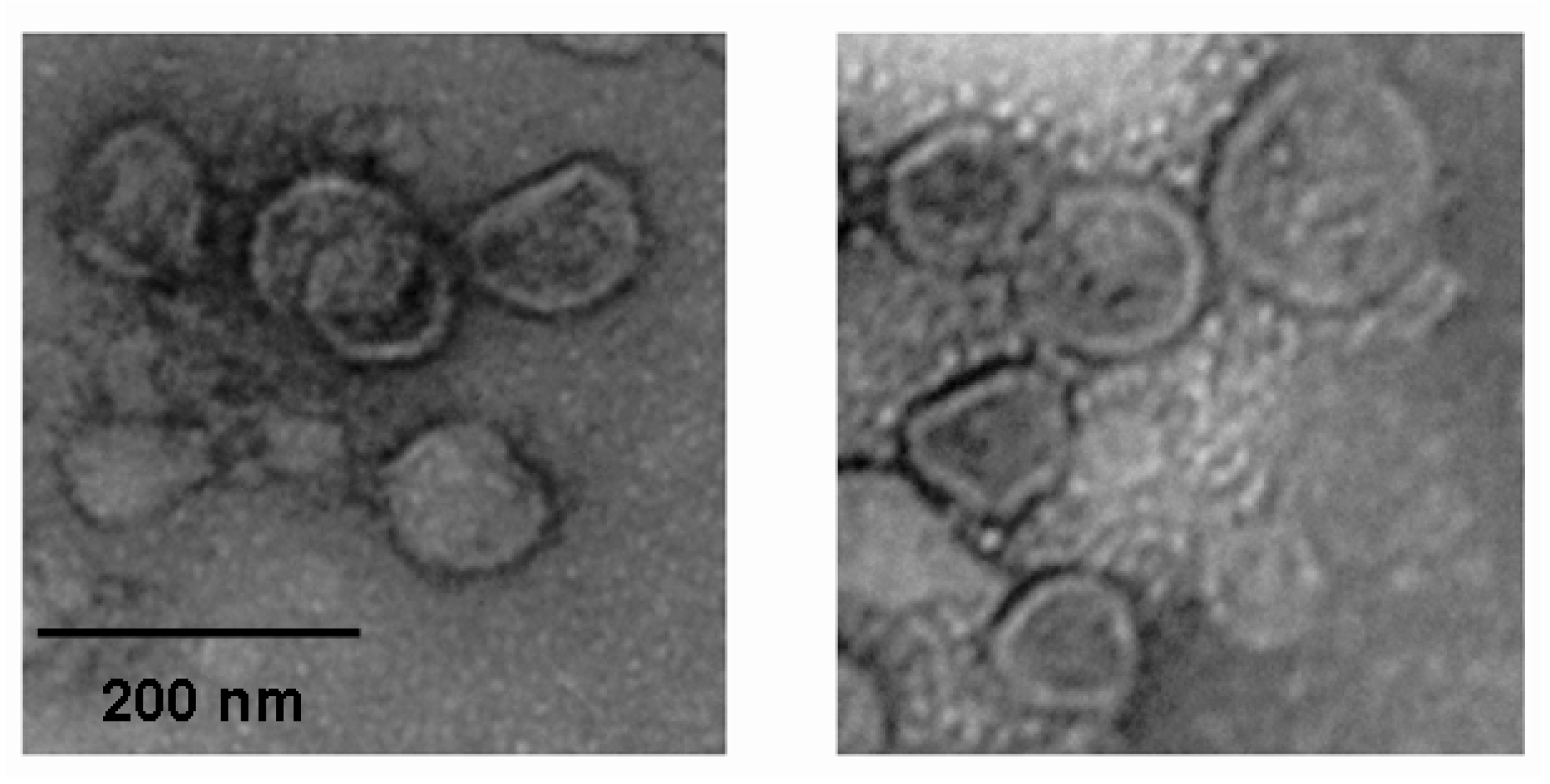
3.7. Electron Microscopy Observation of the Influenza Virus Morphology
3.8. Statistical Analysis
3.9. Molecular Docking
3.10. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.11. Binding Free Energy Calculation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Influenza (Seasonal). Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/index.html/ (accessed on 23 August 2012).
- Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M. Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 1648–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Bahlky, H. Avian influenza: The tip of the iceberg. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2009, 3, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Scalera, N.M.; Mossad, S.B. The first pandemic of the 21st century: A review of the 2009 pandemic variant influenza A (H1N1) virus. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelle, P.Y.; Bernillon, P.; Desenclos, J.C. A preliminary estimation of the reproduction ratio for new influenza A (H1N1) from the outbreak in Mexico, 2009. Euro Surveill. 2009, 14, 19205. [Google Scholar]
- Girarda, M.P.; Tamb, J.S.; Assossouc, O.M.; Kienyb, M.P. The 2009 A (H1N1) influenza virus pandemic: A review. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeki, T. Antiviral treatment for patients hospitalized with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1). N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujike, M.; Shimabukuro, K.; Mochizuki, K.; Obuchi, M.; Kageyama, T.; Shirakura, M.; Kishida, N.; Yamashita, K.; Horikawa, H.; Kato, Y.; et al. Oseltamivir-resistant influenza viruses A (H1N1) during 2007–2009 influenza seasons, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M.; Abed, Y.; Papenburg, J.; Bouhy, X.; Hamelin, M.E.; Boivin, G. Emergence of oseltamivir-resistant pandemic H1N1 virus during prophylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2296–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.T.; Hsu, C.C.; Lee, P.I.; Chuang, J.H. Mass psychogenic illness in nationwide in-school vaccination for pandemic influenza A(H1N1) 2009, Taiwan, November 2009–January 2010. Euro Surveill. 2010, 15, 19575. [Google Scholar]
- Seale, H.; Heywood, A.E.; McLaws, M.L.; Ward, K.F.; Lowbridge, C.P.; Van, D.; MacIntyre, C.R. Why do I need it? I am not at risk! Public perceptions towards the pandemic (H1N1) 2009 vaccine. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachiotis, G.; Mouchtouri, V.A.; Kremastinou, J.; Gourgoulianis, K.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Low acceptance of vaccination against the 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) among healthcare workers in Greece. Euro Surveill. 2010, 15, 19486. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Intent to receive influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent and seasonal influenza vaccines—Two counties, north carolina, August 2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 1401–1405.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Preliminary results: Surveillance for guillain-barre syndrome after receipt of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine—United States, 2009–2010. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2010, 59, 657–661.
- Wiley, D.C.; Skehel, J.J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 365–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Receptor binding and membrane fusion in virus entry: The influenza hemagglutinin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 531–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.K.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. Protein intrinsic disorder toolbox for comparative analysis of viral proteins. BMC Genomics. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowitz, S.G.; Choppin, P.W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology 1975, 68, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamblin, S.J.; Haire, L.F.; Russell, R.J.; Stevens, D.J.; Xiao, B.; Ha, Y.; Vasisht, N.; Steinhauer, D.A.; Daniels, R.S.; Elliot, A.; et al. The structure and receptor binding properties of the 1918 influenza hemagglutinin. Science 2004, 303, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Corper, A.L.; Basler, C.F.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Palese, P.; Wilson, I.A. Structure of the uncleaved human H1 hemagglutinin from the extinct 1918 influenza virus. Science 2004, 303, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Vavricka, C.; Yan, J.H.; Gao, G.F. In silico characterization of the functional and structural modules of the hemagglutinin protein from the swine-origin influenza virus A (H1N1)-2009. Sci. ChinaLife Sci. 2010, 53, 633–642. [Google Scholar]
- Lafourcade, C.; Sobo, K.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Garin, J.; van der Goot, F.G. Regulation of the V-ATPase along the endocytic pathway occurs through reversible subunit association and membrane localization. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehel, J.J.; Bayley, P.M.; Brown, E.B.; Martin, S.R.; Waterfield, M.D.; White, J.M.; Wilson, I.A.; Wiley, D.C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmann, T. Membrane fusion mechanisms: the influenza hemagglutinin paradigm and its implications for intracellular fusion. Traffic 2000, 1, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Helenius, A. Transport of incoming influenza virus nucleocapsids into the nucleus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 232–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Kuntz, I.D.; White, J.M. Structure-based identification of an inducer of the low-pH conformational change in the influenza virus hemagglutinin: irreversible inhibition of infectivity. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8808–8820. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto, J.; Kakui, M.; Iwasaki, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Sugimoto, H.; Hattori, N. Identification of a novel HA conformational change inhibitor of human influenza virus. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, F.S.; Compans, R.W.; Cho, Y.K.; Kang, S.M. Ginseng and salviae herbs play a role as immune activators and modulate immune responses during influenza virus infection. Vaccine 2007, 25, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.W.; Han, C.; Song, X.; Green, L.A.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Cen, C.; Yang, B.; Chen, G.; He, J.J. Inhibition of HIV-1 entry by extracts derived from traditional Chinese medicinal herbal plants. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford, J.S.; Lambkin, R.; Guralnik, M.; Rosenbloom, R.A.; Petteruti, M.P.; Digian, K.; Lefante, C. Preclinical in vitro activity of QR-435 against influenza A virus as a virucide and in paper masks for prevention of viral transmission. Am. J. Ther. 2007, 14, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, S.R.; Chu, T.Y.; Reddy, G.R.; Tseng, S.N.; Chen, H.L.; Tang, W.F.; Wu, M.S.; Yeh, J.Y.; Chao, Y.S.; Hsu, J.T.; et al. Pyrazole compound BPR1P0034 with potent and selective anti-influenza virus activity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.A. Bush sense: Australian Essential Oils & Aromatic Compounds; Griffin Press: Adelaide, Australia, 2000; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, P.H.; Brand, C.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V.; Prager, R.H.; Finlay-Jones, J.J. Terpinen-4-ol, the main component of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil), suppresses inflammatory mediator production by activated human monocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2000, 49, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Fusillier, C.; Jarde, T.; Laroye, H.; Damez, M.; Vasson, M.P.; Guillot, J. Potential anti-inflammatory effects of Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil on human peripheral blood leukocytes. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caelli, M.; Porteous, J.; Carson, C.F.; Heller, R.; Riley, T.V. Tea tree oil as an alternative topical decolonization agent for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 46, 236–237. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, C.J.; Carson, C.F.; Hammer, K.A.; Riley, T.V. Susceptibility of pseudomonads to Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and components. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, P.; Schon, K.; Reichling, J. Antiviral activity of Australian tea tree oil and eucalyptus oil against herpes simplex virus in cell culture. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Garozzo, A.; Timpanaro, R.; Bisignano, B.; Furneri, P.M.; Bisignano, G.; Castro, A. In vitro antiviral activity of Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garozzo, A.; Timpanaro, R.; Stivala, A.; Bisignano, G.; Castro, A. Activity of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil on Influenza virus A/PR/8: study on the mechanism of action. Antiviral Res. 2011, 89, 8983–8988. [Google Scholar]
- Mondello, F.; de Bernardis, F.; Girolamo, A.; Cassone, A.; Salvatore, G. In vivo activity of terpinen-4-ol, the main bioactive component of Melaleuca alternifolia Cheel (tea tree) oil against azole-susceptible and -resistant human pathogenic Candida species. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.A.; Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V. Antifungal activity of the components of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, V.; Morcia, C.; Faccioli, P.; Vale, G.; Tacconi, G.; Malnati, M. In vitro antifungal activity of the tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) essential oil and its major components against plant pathogens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 44, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, B.; Piccirilli, E.; Ceddia, T.; Pontieri, E.; Aureli, P.; Ferrini, A.M. Antimycotic activity of Melaleuca alternifolia essential oil and its major components. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, C.F.; Riley, T.V. Antimicrobial activity of the major components of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1995, 78, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhou, L.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, S.N.; Liu, Q.; Hu, S.L.; Li, T.R.; Chen, Y.B.; Jiang, J.X. The inhibitory effect of Zingiber corallinum Hance essential oil on drug-resistant bacteria and evaluation of its acute toxicity. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, BR139–BR146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kang, H.Y.; Gwak, K.S.; Lee, G.S.; Jeung, E.B.; Choi, I.G. Inhibitory effect of the essential oil from Chamaecyparis obtusa on the growth of food-borne pathogens. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.D.; Jung, E.K.; Kil, B.S.; Lee, K.Y. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oil from Artemisia feddei. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, R.J.; Kerry, P.S.; Stevens, D.J.; Steinhauer, D.A.; Martin, S.R.; Gamblin, S.J.; Skehel, J.J. Structure of influenza hemagglutinin in complex with an inhibitor of membrane fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17736–17741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullough, P.A.; Hughson, F.M.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature 1994, 371, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, F.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X.; Lu, Q.; Vavricka, C.J.; Liu, D. Crystal structure of the swine-origin A (H1N1)-2009 influenza A virus hemagglutinin (HA) reveals similar antigenicity to that of the 1918 pandemic virus. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.; Darden, T.; Cheatham, I.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.; Luo, R. Amber 11; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Lee, M.C.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Cieplak, P.; Luo, R.; Lee, T. A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.; Schlegel, H.; Scuseria, G.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.; Montgomery, J., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.; Burant, J.; et al. Gaussian 03, Revision E. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bayly, C.I.; Cieplak, P.; Cornell, W.; Kollman, P.A. A well-behaved electrostatic potential based method using charge restraints for deriving atomic charges: The RESP model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogolari, F.; Brigo, A.; Molinari, H. Protocol for MM/PBSA molecular dynamics simulations of proteins. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Ojha, R.P.; Maiti, S. Energetics of the human Tel-22 quadruplex-telomestatin interaction: A molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 6828–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, J.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cieplak, P.; Kollman, P.A.; David, A. Continuum solvent studies of the stability of DNA, RNA, and phosphoramidate-DNA helices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9401–9409. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, L.T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Massova, I.; Kollman, P.A. Molecular dynamics and free-energy calculations applied to affinity maturation in antibody 48G7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14330–14335. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds Melaleuca Alternifolia Concentrate are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Duan, S.; Chu, C.; Xu, J.; Zeng, G.; Lam, A.K.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Yin, Y.; Fang, D.; Reynolds, M.J.; et al. Melaleuca alternifolia Concentrate Inhibits in Vitro Entry of Influenza Virus into Host Cells. Molecules 2013, 18, 9550-9566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089550
Li X, Duan S, Chu C, Xu J, Zeng G, Lam AK-Y, Zhou J, Yin Y, Fang D, Reynolds MJ, et al. Melaleuca alternifolia Concentrate Inhibits in Vitro Entry of Influenza Virus into Host Cells. Molecules. 2013; 18(8):9550-9566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinghua, Songwei Duan, Cordia Chu, Jun Xu, Gucheng Zeng, Alfred King-Yin Lam, Junmei Zhou, Yue Yin, Danyun Fang, Maxwell John Reynolds, and et al. 2013. "Melaleuca alternifolia Concentrate Inhibits in Vitro Entry of Influenza Virus into Host Cells" Molecules 18, no. 8: 9550-9566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089550
APA StyleLi, X., Duan, S., Chu, C., Xu, J., Zeng, G., Lam, A. K.-Y., Zhou, J., Yin, Y., Fang, D., Reynolds, M. J., Gu, H., & Jiang, L. (2013). Melaleuca alternifolia Concentrate Inhibits in Vitro Entry of Influenza Virus into Host Cells. Molecules, 18(8), 9550-9566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18089550