Analytical Study for the Charge-Transfer Complexes of Rosuvastatin Calcium with π-Acceptors
Abstract
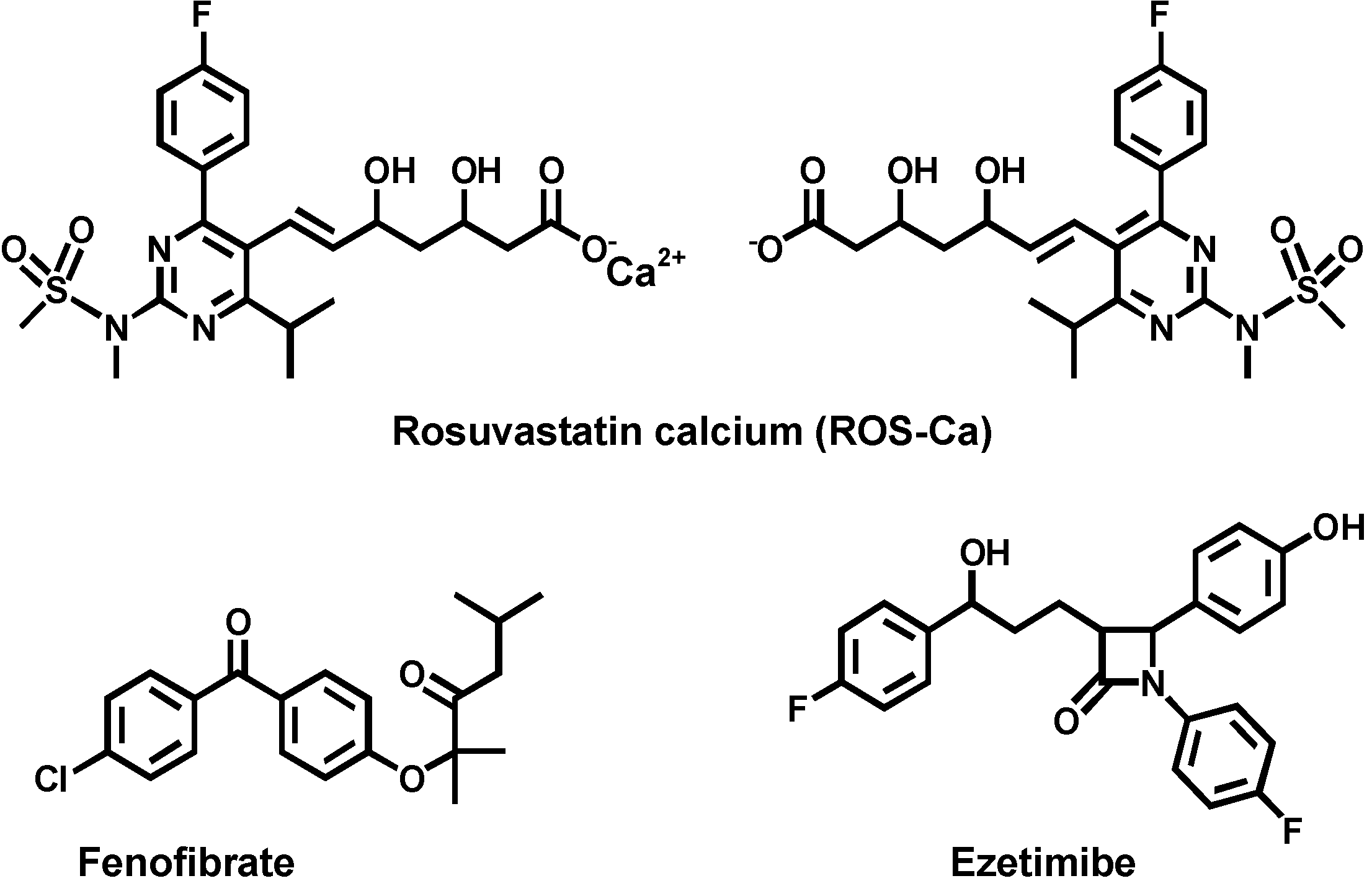
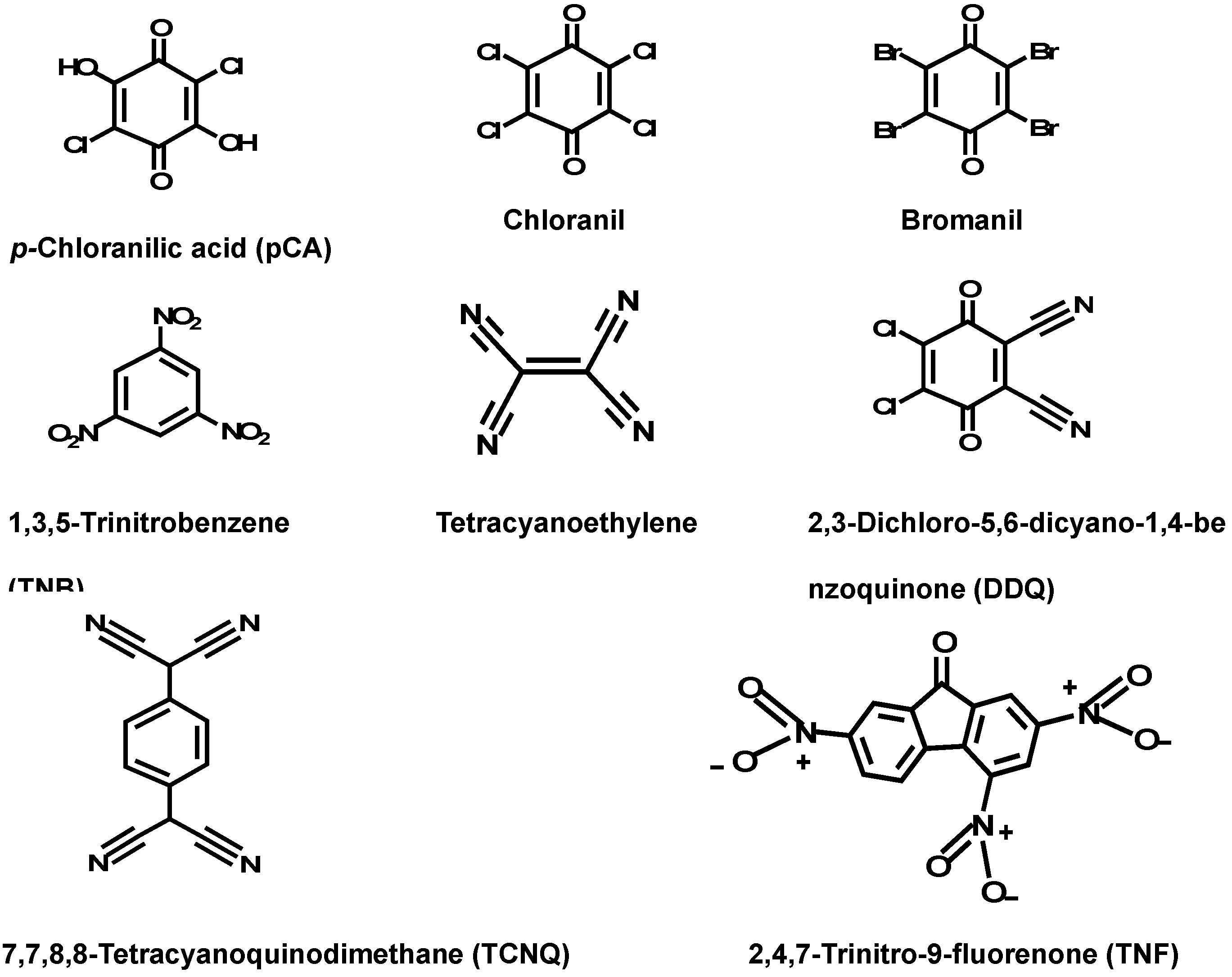
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Spectral Characteristics of the Reaction

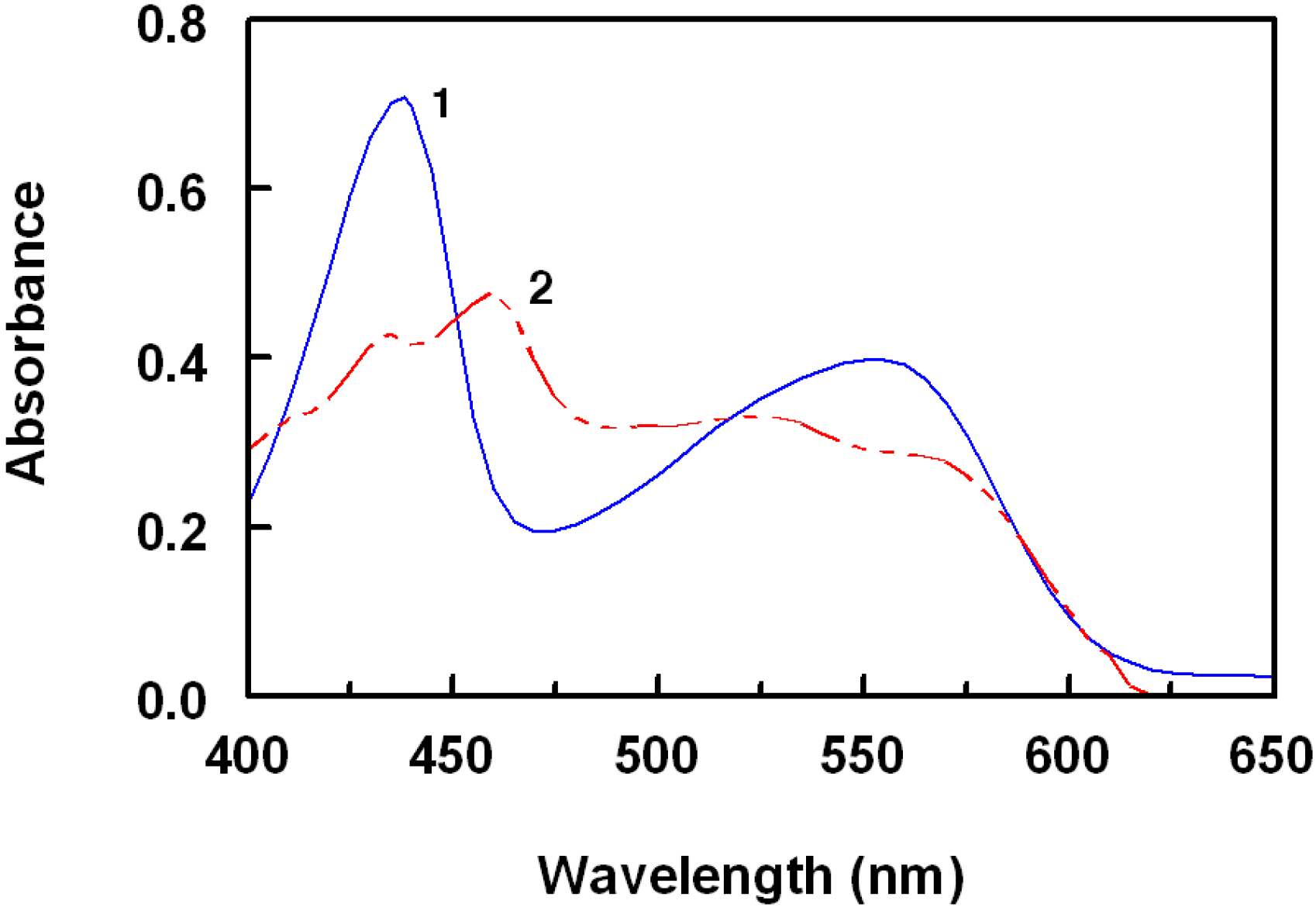
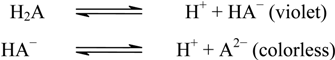

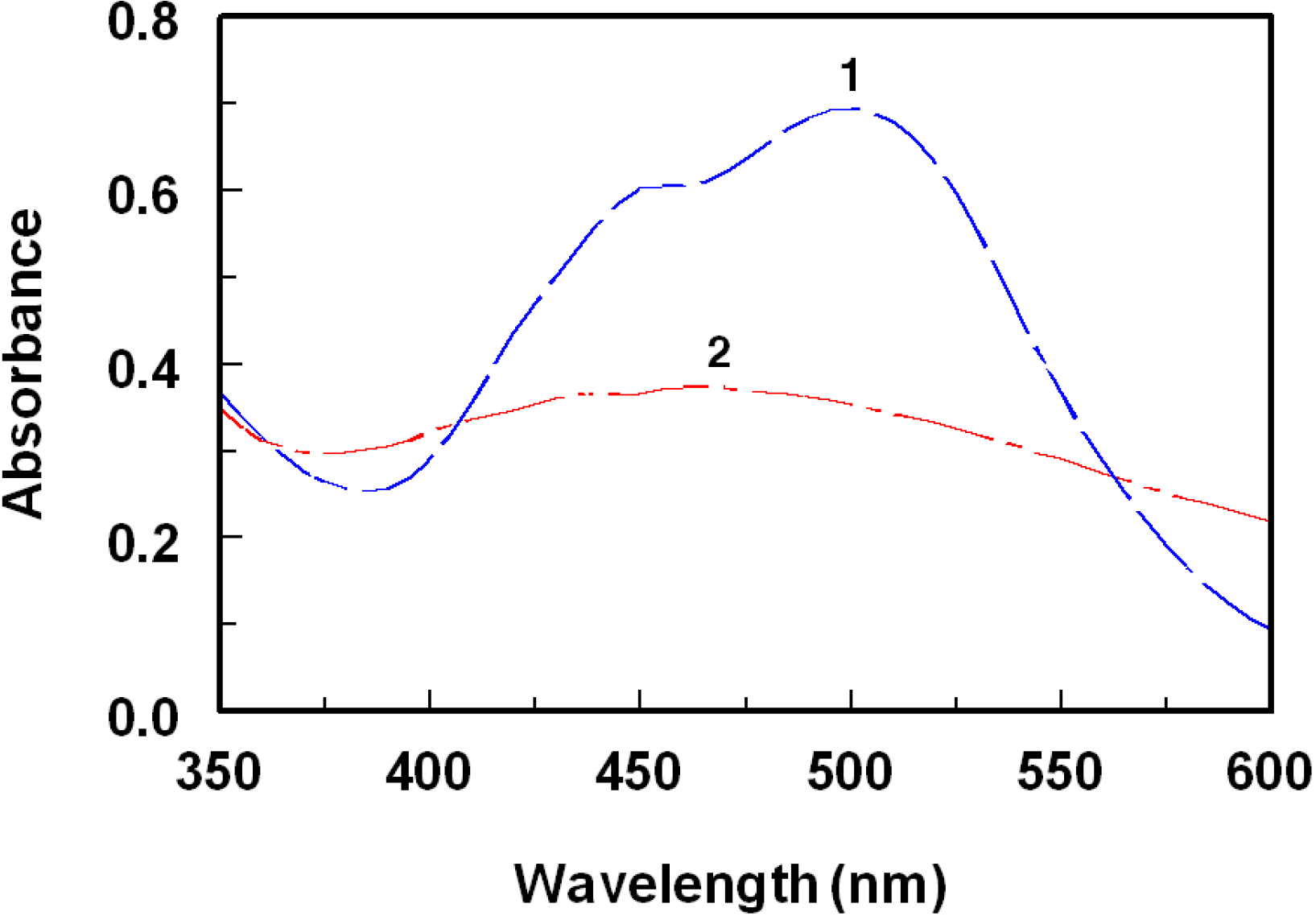
2.2. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
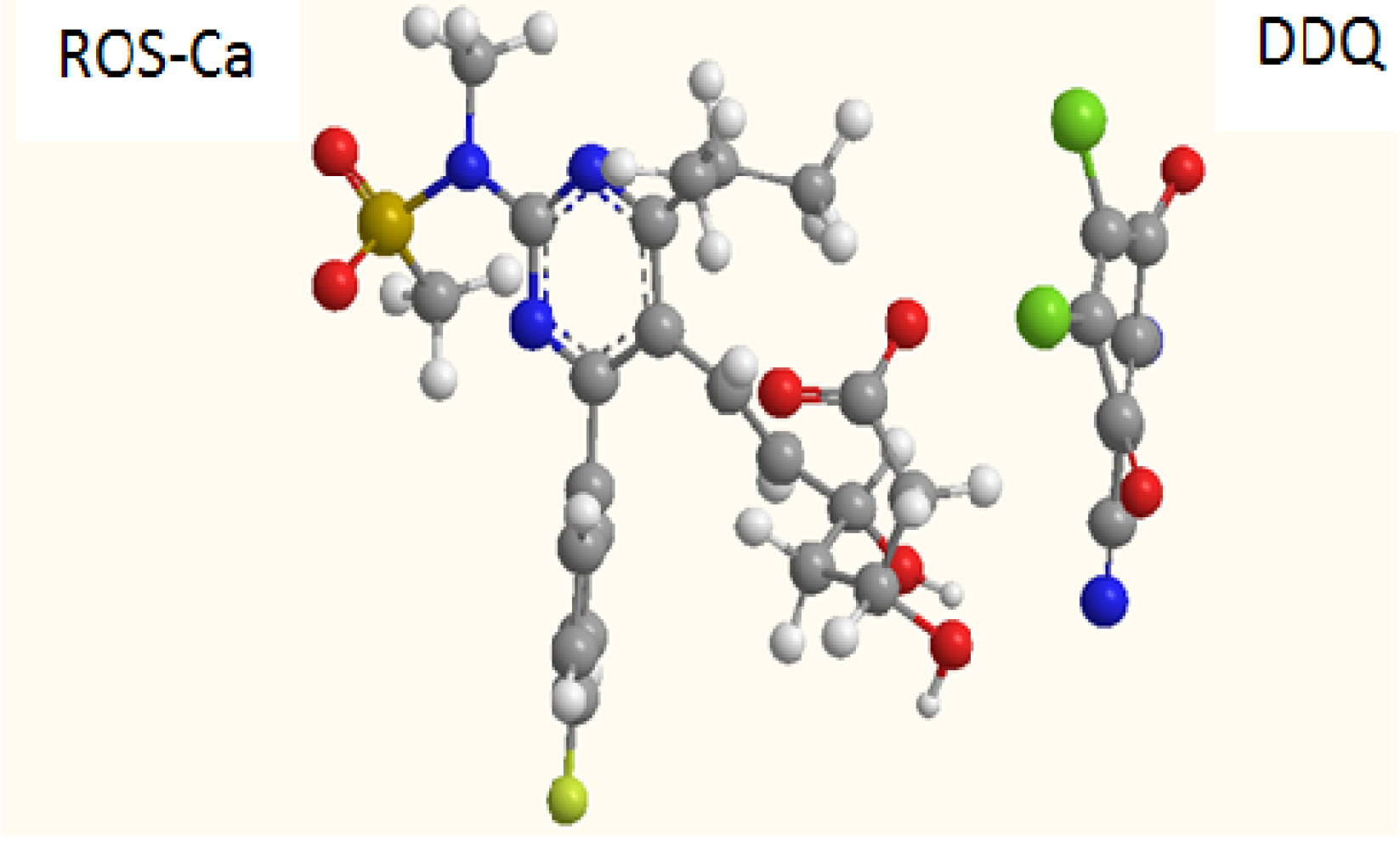
2.3. Molar Ratio of the Reaction, Molecular Modeling, and Proposing the Site of Interaction
| Acceptor a | Condition | Molar absorptivity (ε × 10−4) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent conc. (mg mL−1) | Solvent | Time (min) | λmax (nm) | ||
| pCA | 4 | Acetonitrile | At once b | 518 | 1.4 |
| DDQ (1.9) | 2 | Methanol | At once b | 460 | 3.0 |
| TCNE (2.2) | 2 | Acetonitrile | 15 | 412 | 1.8 |
| TNB (0.7) | 4 | Acetonitrile | 30 | 435 | 0.64 |
| TCNQ (1.7) | 1 | Acetonitrile | 15 | 840 | 4.0 |
| Bromanil (1.37) | 5 | Acetonitrile | 5 | 498 | 0.88 |
| Chloranil (1.37) | 5 | Acetonitrile | 5 | 460 | 2.2 |
| TNF (1.1) | 5 | Acetonitrile | 60 | 412 | 0.25 |
2.4. Development and Validation of the Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Calibration Curves, Linearity and Sensitivity
2.4.2. Precision
2.4.3. Specificity and Interference
| Acceptor | Range (μg mL−1) | Intercept | Slope | Correlation coefficient | LOD (μg mL−1) | LOQ (μg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCNQ | 5–50 | 0.0032 | 0.0388 | 0.9995 | 0.41 | 1.37 |
| TNB | 4–30 | 0.0171 | 0.0137 | 0.9992 | 1.52 | 5.07 |
| DDQ | 2–40 | 0.0146 | 0.0304 | 0.9990 | 1.14 | 3.80 |
| pCA | 10–150 | 0.0211 | 0.0061 | 0.9987 | 1.82 | 6.07 |
| TCNE | 5–60 | 0.0062 | 0.0183 | 0.9989 | 4.32 | 14.39 |
| Bromanil | 25–100 | 0.0074 | 0.0087 | 0.9993 | 5.11 | 17.02 |
| Chloranil | 40–200 | 0.0171 | 0.0021 | 0.9984 | 12.24 | 40.76 |
| Acceptor-based method | ROS-Ca (μg mL−1) | Within-assay, n = 6 | Between-assays, n = 6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (μg mL −1 ± SD) | RSD | Mean (μg mL −1 ± SD) | RSD | ||
| pCA | 50 | 48.78 ± 0.41 | 0.84 | 50.05 ± 0.84 | 1.68 |
| DDQ | 20 | 20.51 ± 0.25 | 1.22 | 19.56 ± 0.36 | 1.84 |
| TCNE | 40 | 40.57 ± 0.75 | 1.85 | 38.96 ± 0.75 | 1.93 |
| TNB | 20 | 20.73 ± 0.23 | 1.11 | 19.55 ± 0.35 | 1.79 |
| TCNQ | 40 | 38.78 ± 0.16 | 0.41 | 38.04 ± 0.29 | 0.76 |
| Bromanil | 80 | 81.57 ± 0.84 | 1.03 | 78.24 ± 0.81 | 1.04 |
| Chloranil | 200 | 198.78 ± 2.69 | 1.35 | 201.05 ± 2.08 | 1.03 |
2.4.4. Ruggedness and Robustness
2.5. Application of the Method to the Analysis of Tablets
| Method | Label claim (% ± SD) a | t-values b | F-values b |
|---|---|---|---|
| pCA | 99.58 ± 1.77 | 1.55 | 2.41 |
| DDQ | 100.21 ± 1.43 | 1.26 | 1.57 |
| TCNE | 99.54 ± 1.58 | 1.86 | 1.92 |
| TNB | 99.82 ± 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.47 |
| TCNQ | 100.09 ± 1.96 | 0.61 | 2.20 |
| Bromanil | 100.29 ± 1.32 | 1.72 | 1.34 |
| Chloranil | 100.46 ± 1.82 | 2.10 | 2.55 |
| Reported c | 99.95 ± 1.14 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Apparatus
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Preparation of Standard and Tablets Sample Solutions
3.3.1. Preparation of Stock Standard ROS-Ca Solution
3.3.2. Preparation of Tablets Sample Solution
3.4. General Analytical Procedure
3.5. Determination of Molar Ratio
3.6. Molecular Modeling for the CT Complex of ROS-Ca with DDQ
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng-Lai, A. Rosuvastatin: A new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Heart Dis. 2003, 5, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.W. Rosuvastatin in the management of hyperlipidemia. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 1368–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A.; Samad, A.; Tandon, M.; Saini, G.S.; Sharma, P.L.; Pillai, K.K. The effects of rosuvastatin on the serum cortisol, serum lipid, and serum mevalonic acid levels in the healthy Indian male population. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2010, 11, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, B.G.; Patel, N.M.; Shah, P.B. Determination of simvastatin, pravastatin sodium and rosuvastatin calcium in tablet dosage forms by HPTLC. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 69, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, H.O.; Ambasana, M.A.; Thakkar, R.S.; Saravaia, H.T.; Shah, A.K. A new improved RP-HPLC method for assay of rosuvastatin calcium in tablets. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, C.B.; Channabasavaraj, K.P.; Chudasama, J.D.; Mani, T.T. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for determination of rosuvastatin calcium in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Inter. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Suslu, I.; Çelebier, M.; Altınoz, S. Determination of rosuvastatin in pharmaceutical formulations by capillary zone electrophoresis. Chromatographia 2007, 66, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, I.A.; Sultan, M.A.; Al-Arfaj, H.A. Novel selective kinetic spectrophotometric method for determination of norfloxacin in its pharmaceutical formulations. Talanta. 2009, 78, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Abdine, H.H.; Amer, S.M.; Al-Rayes, L.I. Spectrophotometric study for the reaction between fluvoxamine and 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulphonate: Kinetic, mechanism and use for determination of fluvoxamine in its dosage forms. Spectrochim. Acta. A 2009, 72, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Hussein, S.A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Hassan, AI. Spectrophotometric determination of H(2)-receptor antagonists via their oxidation with cerium(IV). Spectrochim. Acta A 2008, 69, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Rasul, A.; Masood, Z. Spectrophotometry in Pharmaceutical Analysis; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gorog, S. Ultraviolet-visible Spectrophotometry in Pharmaceutical Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Refaat, I.H.; Askal, H.F.; Marzouq, M.A. Generic nonextractive spectrophotometric method for determination of 4-quinolone antibiotics by formation of ion-pair complexes with beta-naphthol. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Uyar, B.; Celebier, M.; Altinoz, S. Spectrophotometric determination of rosuvastatin calcium in tablets. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Sevda, R.R.; Ravetkar, A.S.; Shirote, P.J. UV Spectrophotometric estimation of rosuvastatin calcium and fenofibrate in bulk drug and dosage form using simultaneous equation method. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2011, 3, 629–635. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Mishra, P.; Shah, K. Simple UV spectrophotometric determination of rosuvastatin calcium in pure form and in pharmaceutical formulations. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Marothu, V.K.; Dannana, G.S. Extractive spectrophotometric methods for the determination of rosuvastatin calcium in pure form and in pharmaceutical formulations by using Safranin O and Methylene blue. E-J. Chem. 2007, 4, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, I.A. Development and validation of spectrophotometric methods for determination of fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Wani, T.A.; Khalil, N.Y.; Al-Shaikh, A.A.; Al-Morshadi, N. Development of a novel 96-microwell assay with high throughput for determination of olmesartan medoxomil in its tablets. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A.; Khalil, N.Y.; Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Darwish, I.A. Novel microwell-based spectrophotometric assay for determination of atorvastatin calcium in its pharmaceutical formulations. Chem. Cent. J. 2011, 5, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A. Kinetic spectrophotometric assays for determination of trimetazidine dihydrochloride. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 551, 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A. Analytical study for the charge transfer complexes of losartan potassium. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 549, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.A.; Refaat, I.H. Spectrophotometric analysis of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors based on formation of charge-transfer complexes with tetracyanoquinodimethane and chloranilic acid. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, I.; Abdel-Wadood, H.; Abdel-Latif, N. Validated spectrophotometric and fluorimetric methods for analysis of clozapine in tablets and urine. Ann. Chim. 2005, 95, 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Liu, X.J.; Zhao, F.L. Spectrophotometric determination of azithromycin by charge transfer reaction. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2006, 26, 913–916. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.; Rucker, G. Utility of pi-acceptors in alkaloid assay. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim.) 1977, 310, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melby, L.R. The Chemistry of the Cyano Group; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1970; pp. 656–659. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, A. Solvation effects on the electron-transfer reaction of TCNQ anion radical and 2,3-dichloro-5, 6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone. Bull. Soc. Jpn. 1975, 48, 2440. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, R. Organic Charge-Transfer Complexes; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; p. 470. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Longman group UK Ltd.: London, UK, 1989; pp. 1442–1444.
- The United States Pharmacopeia 24, The National Formulary 19; United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.: Rockville, ML, USA, 2008.
- Agouridis, A.P.; Tsimihodimos, V.; Filippatos, T.D.; Tselepis, A.D.; Elisaf, M.S. High doses of rosuvastatin are superior to low doses of rosuvastatin plus fenofibrate or n-3 fatty acids in mixed dyslipidemia. Lipids 2011, 46, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashiri, M.A.; Nohara, A.; Noguchi, T.; Tada, H.; Nakanishi, C.; Mori, M.; Konno, T.; Hayashi, K.; Fujino, N.; Inazu, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of coadministration of rosuvastatin, ezetimibe, and colestimide in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Job, P. Advanced Physicochemical Experiments, 2nd ed.; Oliner and Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1964; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzoman, N.Z.; Sultan, M.A.; Maher, H.M.; Alshehri, M.M.; Wani, T.A.; Darwish, I.A. Analytical Study for the Charge-Transfer Complexes of Rosuvastatin Calcium with π-Acceptors. Molecules 2013, 18, 7711-7725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077711
Alzoman NZ, Sultan MA, Maher HM, Alshehri MM, Wani TA, Darwish IA. Analytical Study for the Charge-Transfer Complexes of Rosuvastatin Calcium with π-Acceptors. Molecules. 2013; 18(7):7711-7725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077711
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzoman, Nourah Z., Maha A. Sultan, Hadir M. Maher, Mona M. Alshehri, Tanveer A. Wani, and Ibrahim A. Darwish. 2013. "Analytical Study for the Charge-Transfer Complexes of Rosuvastatin Calcium with π-Acceptors" Molecules 18, no. 7: 7711-7725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077711
APA StyleAlzoman, N. Z., Sultan, M. A., Maher, H. M., Alshehri, M. M., Wani, T. A., & Darwish, I. A. (2013). Analytical Study for the Charge-Transfer Complexes of Rosuvastatin Calcium with π-Acceptors. Molecules, 18(7), 7711-7725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077711





