The Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Hydroxyl Substituted Chalcone Analogs with in Vitro Anti-Free Radicals Pharmacological Activity and in Vivo Anti-Oxidation Activity in a Free Radical-Injury Alzheimer’s Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction

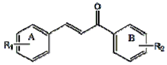 | ||||||
| No. | R1 | R2 | Melting point (°C) | Physical properties/ Molecular formula | 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) | MS( m/z ) |
| C1 | 2-OH | H | 76–78 | Yellow crystal/ | 6.89 (1H, d, J = 16, =CH) | 223.0[M−H]+ |
| C15H12O2 | 7.29 (1H, d, J = 16, =HC) | |||||
| 6.89 ~ 8.10 (m, 9H, ArH) | ||||||
| 10.31 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C2 | H | 2'-OH | 88–90 | Yellow crystal/ | 7.02 (1H, d,d, J = 16, =CH) | 223.0[M−H]+ |
| C15H12O2 | 7.42 (1H, d,d, J = 16, =CH) | |||||
| 7.02 ~ 8.28 (m, 9H, ArH) | ||||||
| 12.47(s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C3 | 4-OH | H | 83–85 | Yellow crystal/ | 7.75 (1H, d,d, J = 15.6, =CH) | 223.0[M−H]+ |
| C15H12O2 | 8.14 (1H, d,d, J = 15.6, HC=) | |||||
| 6.86 ~ 7.75 (m, 9H, ArH) | ||||||
| 10.15 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C4 | 4-OH | 2'-OH | 193–195 | Transparent crystal/ | 7.43 (d, J = 15.2, 1H, CH= ) | 239.0[M−H]+ |
| C15H12O3 | 7.81 (d, J = 15.2, 1H, CH= ) | |||||
| 6.79 ~ 7.80 (m, 8H, ArH) | ||||||
| 9.58 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| 11.64 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C5 | 4-OH, | 2'-OH | 158–160 | Transparent crystal/ | 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3) | 269.1[M−H]+ |
| 3-OCH3 | C15H11NO5 | 7.75 (d, J = 16, 1H, CH= ) | ||||
| 8.15 (d, J = 16, 1H, CH= ) | ||||||
| 6.78 ~ 7.77 (m, 7H, ArH) | ||||||
| 9.14 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C6 | 4-OH, | 2'-OH | 144–146 | Yellow crystal/ | 7.56 (d, J = 16.4, 1H, CH= ) | 284.0[M−H]+ |
| 3-NO3 | C15H11NO5 | 7.97 (d, J = 16.4, 1H, CH= ) | ||||
| 7.02 ~ 8.10 (m, 7H, ArH) | ||||||
| 11.18 (s, 1H, OH) | ||||||
| C7 | 4-OH, | 2'-OH | 172–174 | Red crystal/ | 3.88 (s, 6H, OCH3) | 298.9[M−H]+ |
| 3,5-2OCH3 | C17H16O5 | 7.62 (d, J = 16, 1H, CH=) | ||||
| 8.02 (d, J = 16, 1H, CH=) | ||||||
| 7.02 ~ 8.35 (m, 6H, ArH) | ||||||
| 9.20 (s, 1H, OH), 12.91 (s, 1H, OH) |
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of C1–7
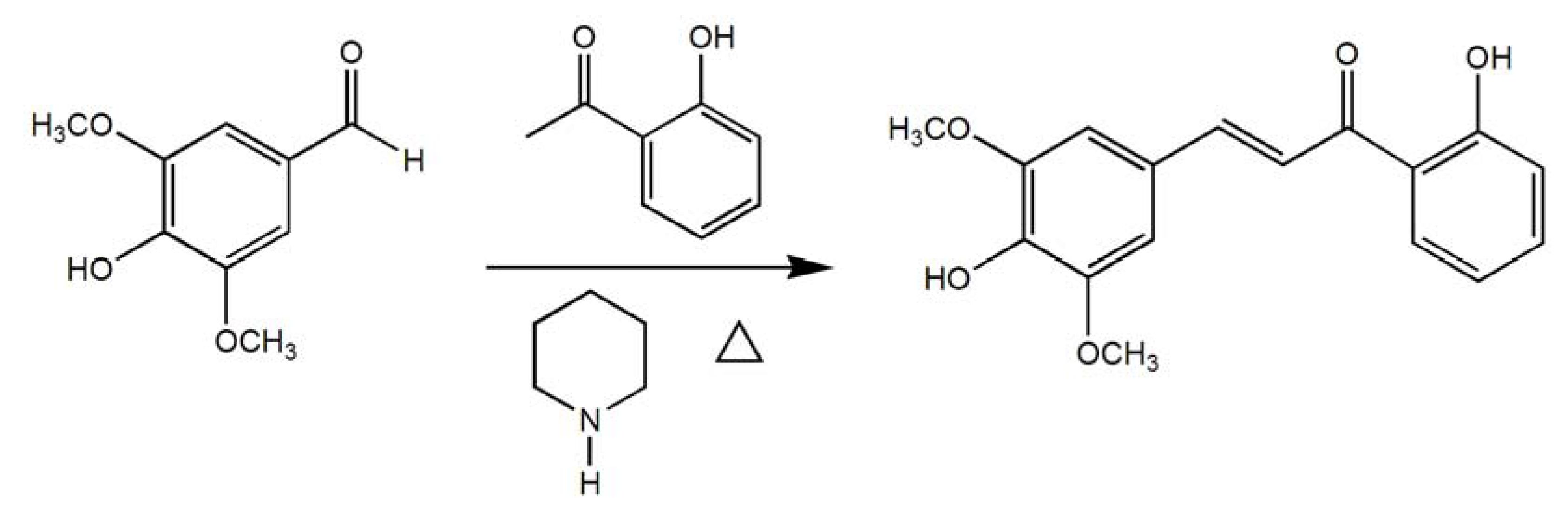
2.2. Activity of C1–7 in Scavenging DPPH and OH Free Radicals
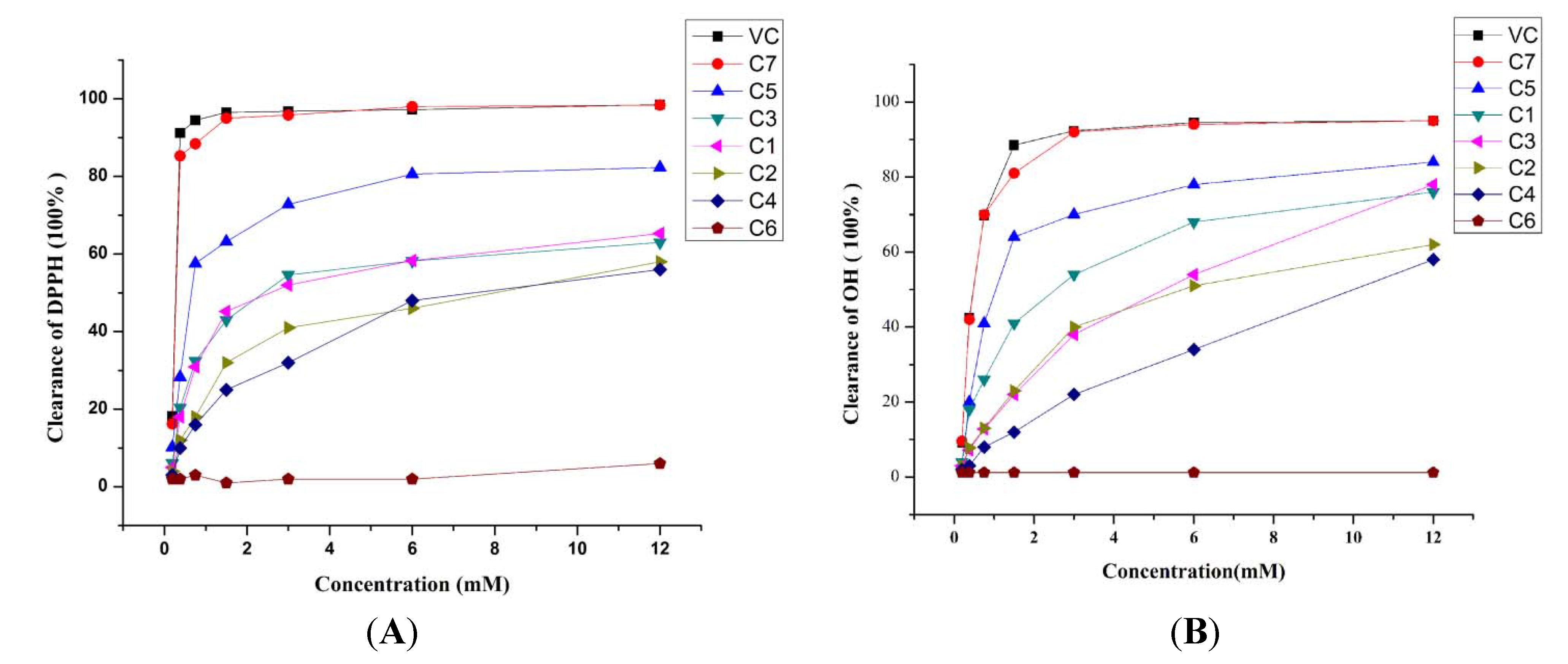
| Compound | OH· clearance IC50 (mM) | DPPH· clearance IC50 (mM) |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.655 | 0.836 |
| C2 | 2.741 | 1.688 |
| C3 | 10.040 | 0.769 |
| C4 | 5.726 | 3.65 |
| C5 | 0.750 | 0.521 |
| C6 | ----- | ----- |
| C7 | 0.441 | 0.255 |
| Vit C | 0.442 | 0.241 |
2.3. Impact of C7 on SOD, MDA and GSH-PX Levels in Scopolamine-Induced AD Model

3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Chemistry
3.3. Pharmacology
3.3.1. Tests of Activity of C1–7 in Scavenging DPPH-free Radicals
3.3.2. Tests of Activity of C1–7 in Scavenging OH Free Radicals
3.3.3. Tests of C7 on SOD, MDA and GSH-PX Levels on Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Models
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Samples Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Harman, D. Ageing: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. (Eds.) Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997.
- Devasagayam, T.P.; Tilak, J.C.; Boloor, K.K.; Sane, K.S.; Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Lele, R.D. Free radicals and antioxidants in human health: Current status and future prospects. JAPI 2004, 52, 794–804. [Google Scholar]
- Praticò, D. Evidence of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease brain and antioxidant therapy. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1147, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnen, J.A.; Larson, E.B.; Gray, S.L.; Wilson, A.; Kohama, S.G.; Crane, P.K.; Breitner, J.C.S.; Montine, T.J. Free radical damage to cerebral cortex in Alzheimer’s disease, microvascular brain injury, and smoking. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, J.M. Oxidative stress leading to loss of critical proteases in Alzheimer’s disease: An alternative view of the etiology of AD. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2000, 924, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E.; Ince, P.G..; Haynes, L.J.; Theaker, R.C.; Baxter, G.L.; Forster, G.; Lace, G.L.; Shaw, P.J.; Matthews, F.E.; Savva, G.M.; et al. Population variation in oxidative stress and astrocyte DNA damage in relation to Alzheimer-type pathology in the ageing brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2010, 36, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hamel, E.; Nicolakakis, N.; Aboulkassim, T.; Ongali, B.; Tong, X.K. Oxidative stress and cerebrovascular dysfunction in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mecocci, P.; Mangialasche, F.; Polidori, M.C. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: A selective status report. Neurosci. Res. Commun. 2004, 35, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrup, K. Reimagining Alzheimer’s disease—An age-based hypothesis. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16755–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, J.T.; Puttfarcken, P. Oxidative stress, glutamate and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 1993, 262, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Sies, H. (Ed.) Antioxidants in Disease, Mechanisms and Therapy; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996.
- Kontush, A.; Schekatolina, S. Vitamin E in neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2004, 1031, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Lenegre, A.; Avril, I.; Doumont, G. Antagonism by exifone, A new cognitive enhancing agent of the amnesias induced by four benzodiazepines in mice. Psychopharmacology 1988, 95, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, D.K.; Devasagayam, T.P. Antioxidant and prooxidant nature of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives ferulic and caffeic acid. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3369–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.M.; Guo, H.X. The effect of substituted groups in benzen ring on the condensation reaction of acetophenones with benzaldehydes. Chin. J. Synth. Chem. 1999, 7, 422–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ognyan, P.; Yordanka, I.; Mariana, G. SOCl2/EtOH: Catalytic system for synthesis of chalcones. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 315–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, M.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Chakraborty, R. Antioxidant activity of natural plant sources in dairy dessert (Sandesh) under thermal treatment. LWT-Food. Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 816–825. [Google Scholar]
- Poorichaya, S.; Chada, P.; Somjai, N.; Supeenun, U.; Noppawan, P.M. Comparative Antioxidant Activities of Curcumin and Its Demethoxy and Hydrogenated Derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhur, A.; Craig, D.; Hart, D.J.; Mcllroy, S.P.; Passmore, A.P. Behavioural and psychological syndromes in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psych. 2004, 19, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Snyderab, P.J.; Bednarb, M.M.; Cromera, J.R.; Maruffcd, P. Reversal of scopolamine-induced deficits with a single dose of donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Alzheimers Dement. 2005, 1, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.S.; Teng, W.Y.; Zhang, C.D. Protective effect of cyclophilin A against Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (25–35)-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2009, 122, 716–724. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, G.P.; Cairns, N.J.; Müller, W.E. Piracetam reverses hippocampal membrane alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 1999, 106, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waegemans, T.; Wilsher, C.R.; Danniau, A.; Ferris, S.H.; Kurz, A.; Winblad, B. Clinical Efficacy of Piracetam in Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2002, 13, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Markesbery, W.R.; Carney, J.M. Oxidative alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.A.; Ehmann, W.D.; Butler, S.M.; Markesbery, W.R. Elevated thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and antioxidant enzyme activity in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1995, 45, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Özkök, E.; Cengiz, S.; Agachan, B.; Yilmaz, H.; Öztürk, O. Changes in oxidative stress in Wistar albino rats during senescence. Adv. Mol. Med. 2007, 3, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Molyneux, P. The use of the stable free radical DPPH for estimating antioxidant activity. Songklanakarin. J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Goupy, P.; Dufour, C.; Loonis, M.; Dangles, O. Quantitative Kinetic Analysis of Hydrogen Transfer Reactions from Dietary Polyphenols to the DPPH Radical. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 615–622. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Xu, D.; Lei, R.; Li, N.; Li, K. Free-Radical Scavenging Capacity Using the Fenton Reaction with Rhodamine B as the Spectrophotometric Indicator. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 730–735. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J. The Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Hydroxyl Substituted Chalcone Analogs with in Vitro Anti-Free Radicals Pharmacological Activity and in Vivo Anti-Oxidation Activity in a Free Radical-Injury Alzheimer’s Model. Molecules 2013, 18, 1693-1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021693
Pan Y, Chen Y, Li Q, Yu X, Wang J, Zheng J. The Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Hydroxyl Substituted Chalcone Analogs with in Vitro Anti-Free Radicals Pharmacological Activity and in Vivo Anti-Oxidation Activity in a Free Radical-Injury Alzheimer’s Model. Molecules. 2013; 18(2):1693-1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021693
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Ying, Yicun Chen, Qingnan Li, Xiaoyu Yu, Jinzhi Wang, and Jinhong Zheng. 2013. "The Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Hydroxyl Substituted Chalcone Analogs with in Vitro Anti-Free Radicals Pharmacological Activity and in Vivo Anti-Oxidation Activity in a Free Radical-Injury Alzheimer’s Model" Molecules 18, no. 2: 1693-1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021693
APA StylePan, Y., Chen, Y., Li, Q., Yu, X., Wang, J., & Zheng, J. (2013). The Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Hydroxyl Substituted Chalcone Analogs with in Vitro Anti-Free Radicals Pharmacological Activity and in Vivo Anti-Oxidation Activity in a Free Radical-Injury Alzheimer’s Model. Molecules, 18(2), 1693-1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18021693




