Photoaffinity Labeling of Plasma Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Plasma Proteins

2.1. Human Serum Albumin
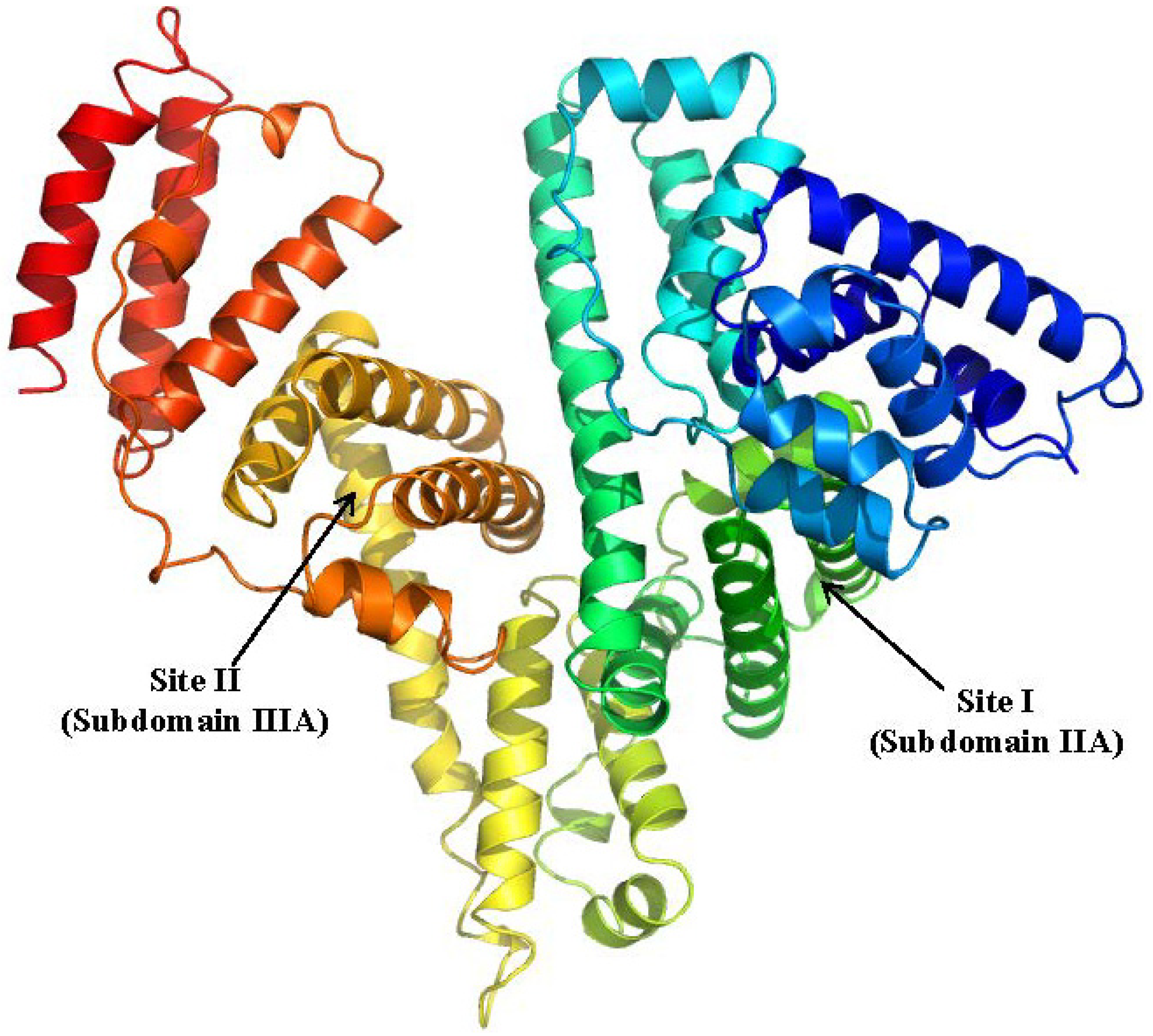
2.1.1. Ketoprofen
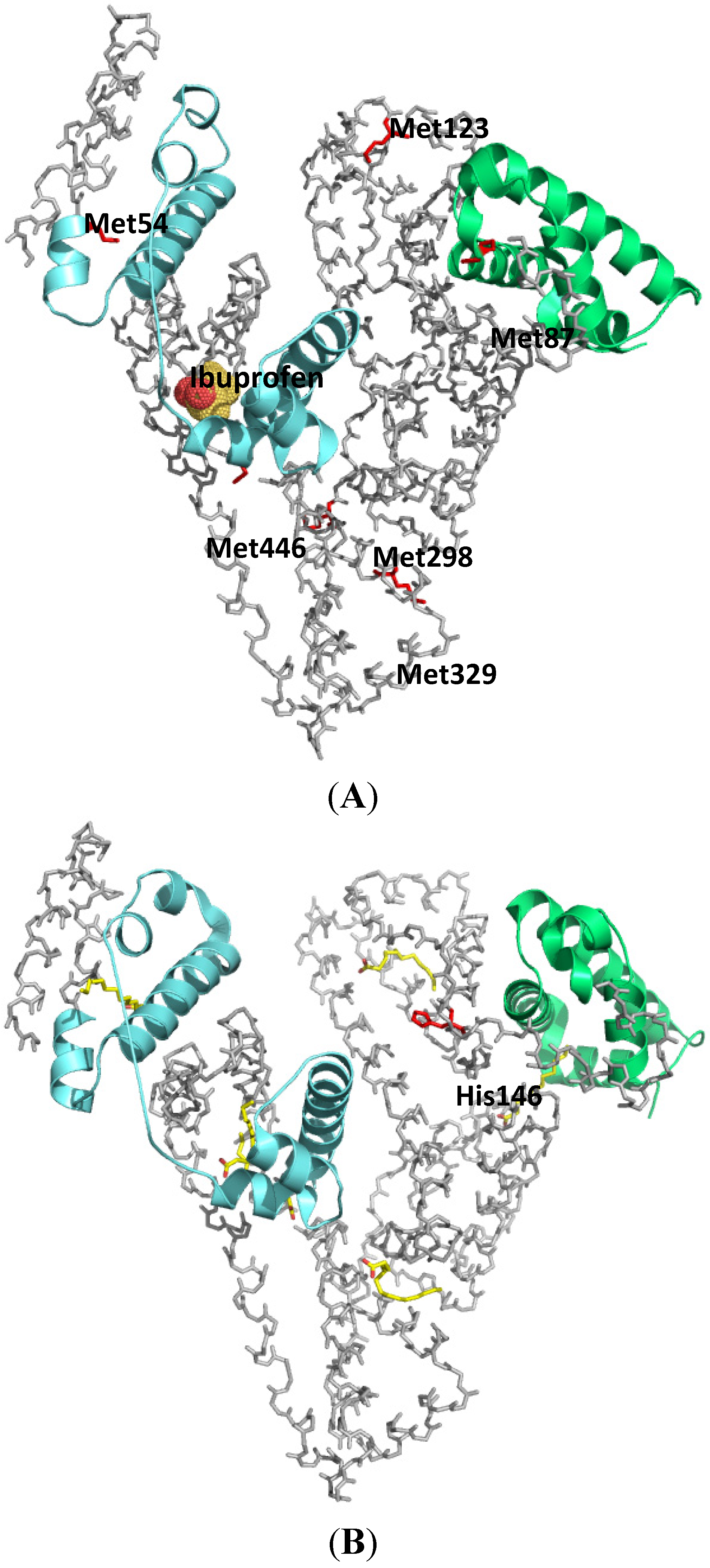
2.1.2. Flunitrazepam
2.1.3. Halothane
2.1.4. Leukotriene
2.2. α1-Acid Glycoprotein
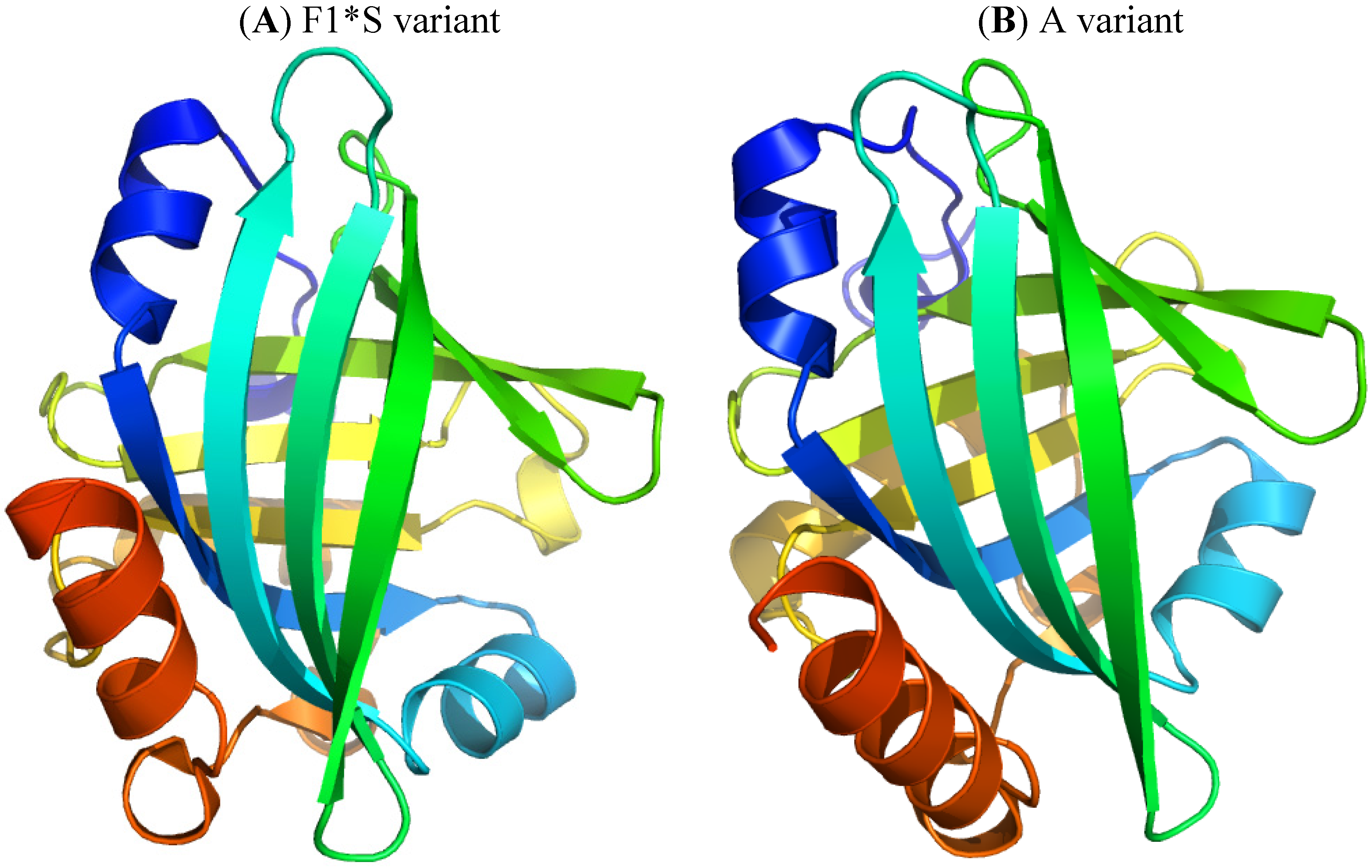
2.2.1. Flunitrazepam
2.2.2. 7-Hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01)
2.2.3. 3-(2-(3-Azido-4-iodophenylpropionamido)-ethoxy)thalidomide
2.3. Thyroxine-Binding Prealbumin (Transthyretin)
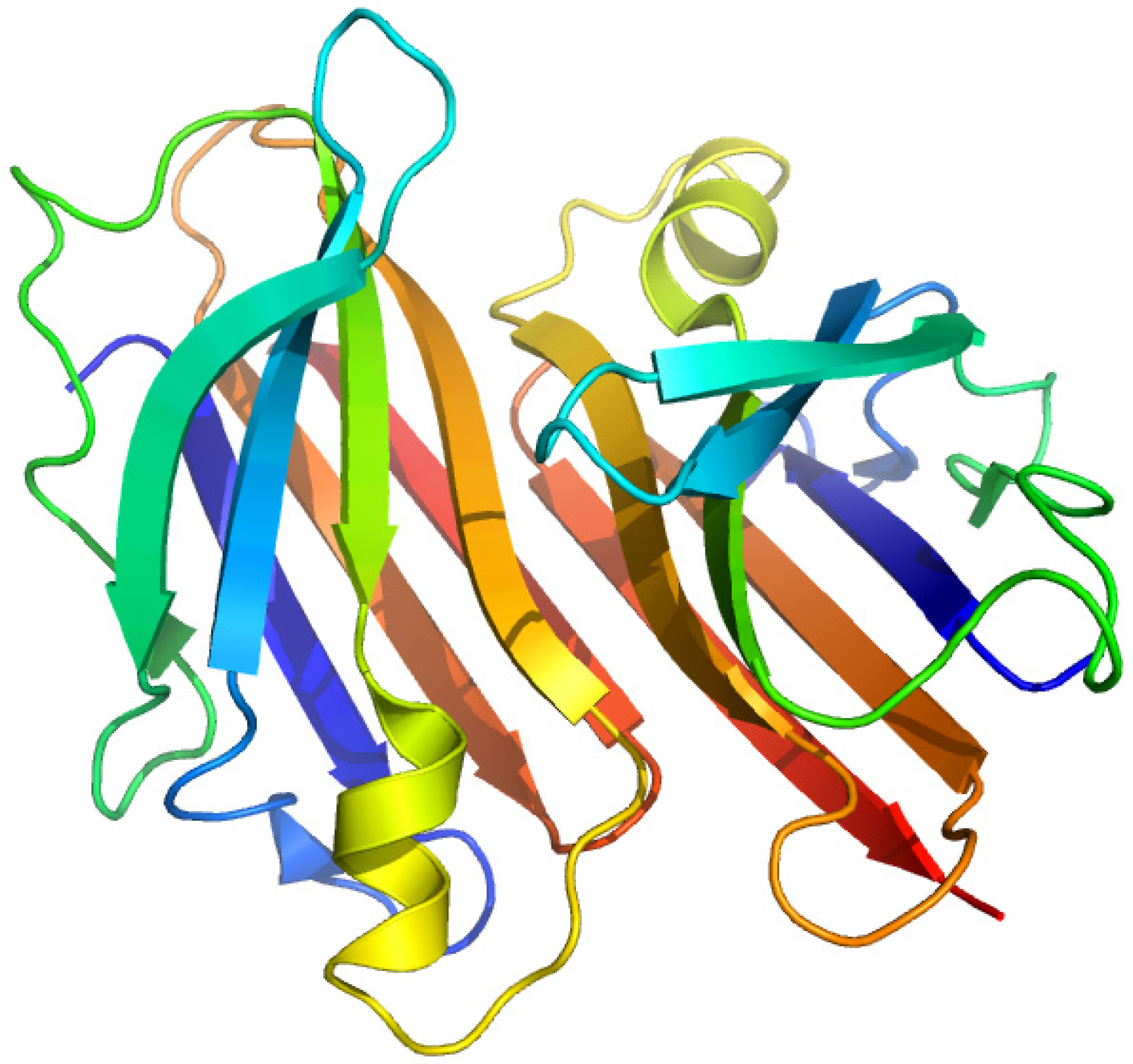
2.3.1. [3'5'-125I]-Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine
2.3.2. Thyroxine Derivatives
2.4. Plasma Retinol-Binding Protein
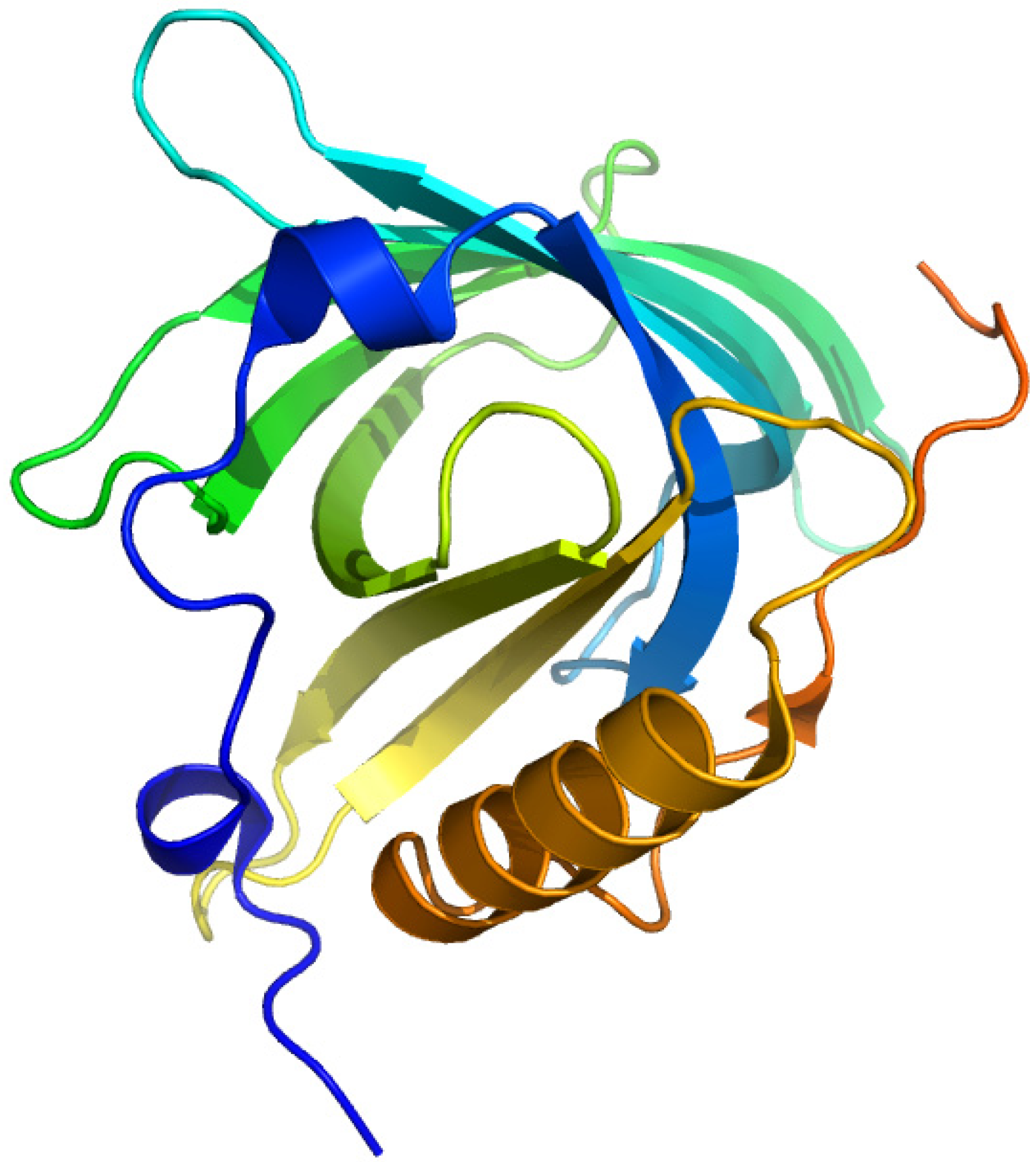

2.4.1. All-Trans-Retinoic Acid and Azidoretinoids
2.5. Vitamin D-Binding Protein (Gc-Globulin)
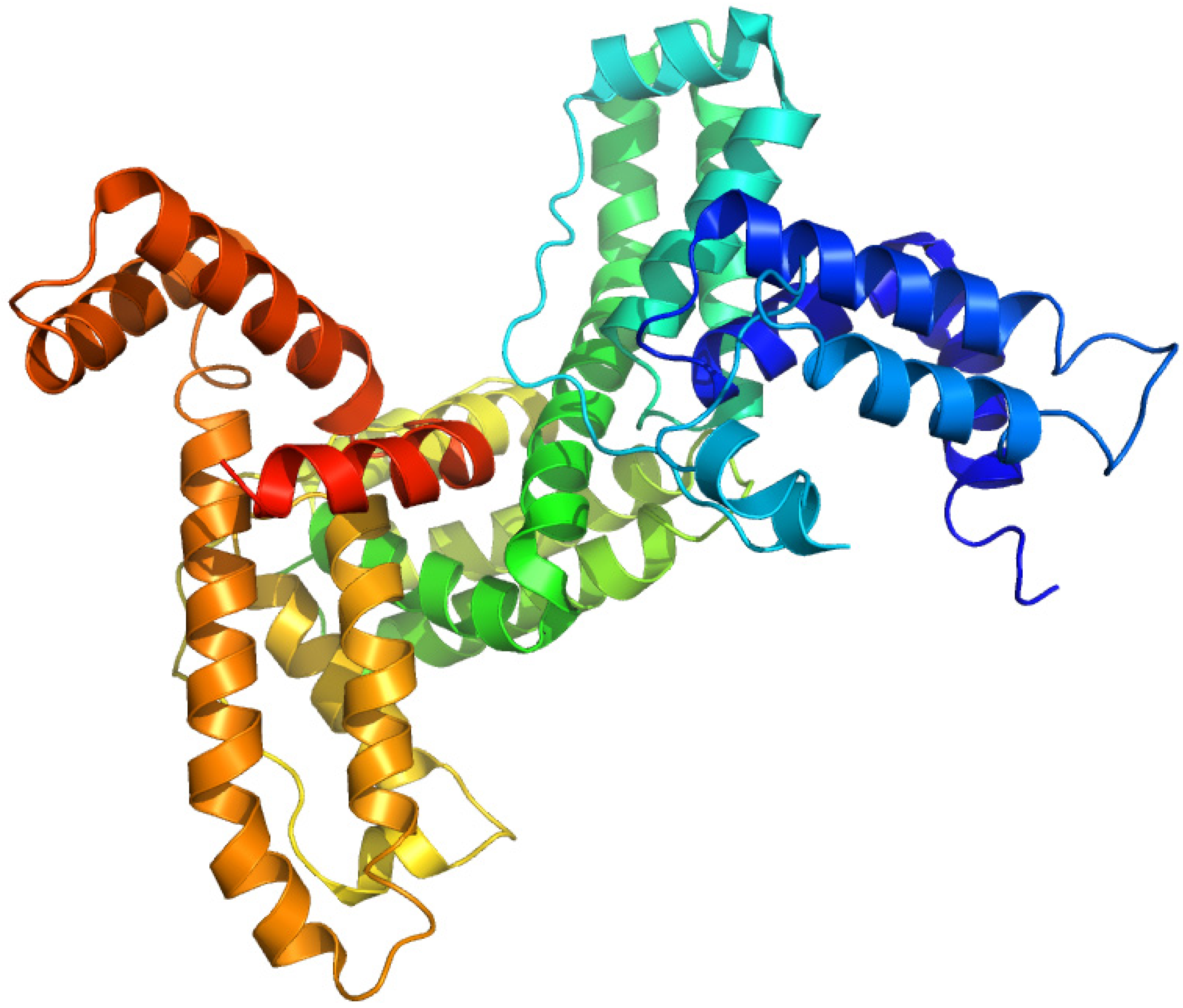
2.5.1. 1,25-Dihydroxy-[26,27-3H]vitamin D3
2.5.2. 3-Deoxy-3-azido-25-hydroxyvitamin D3
2.5.3. 25-Hydroxy(26,27-3H)vitamin D3 -3β-3'-[N-(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)amino]propyl Ether
2.6. α-Fetoprotein
2.6.1. 16-Diazo[3H]estrone and 4-azido[3H]estradiol
2.7. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin
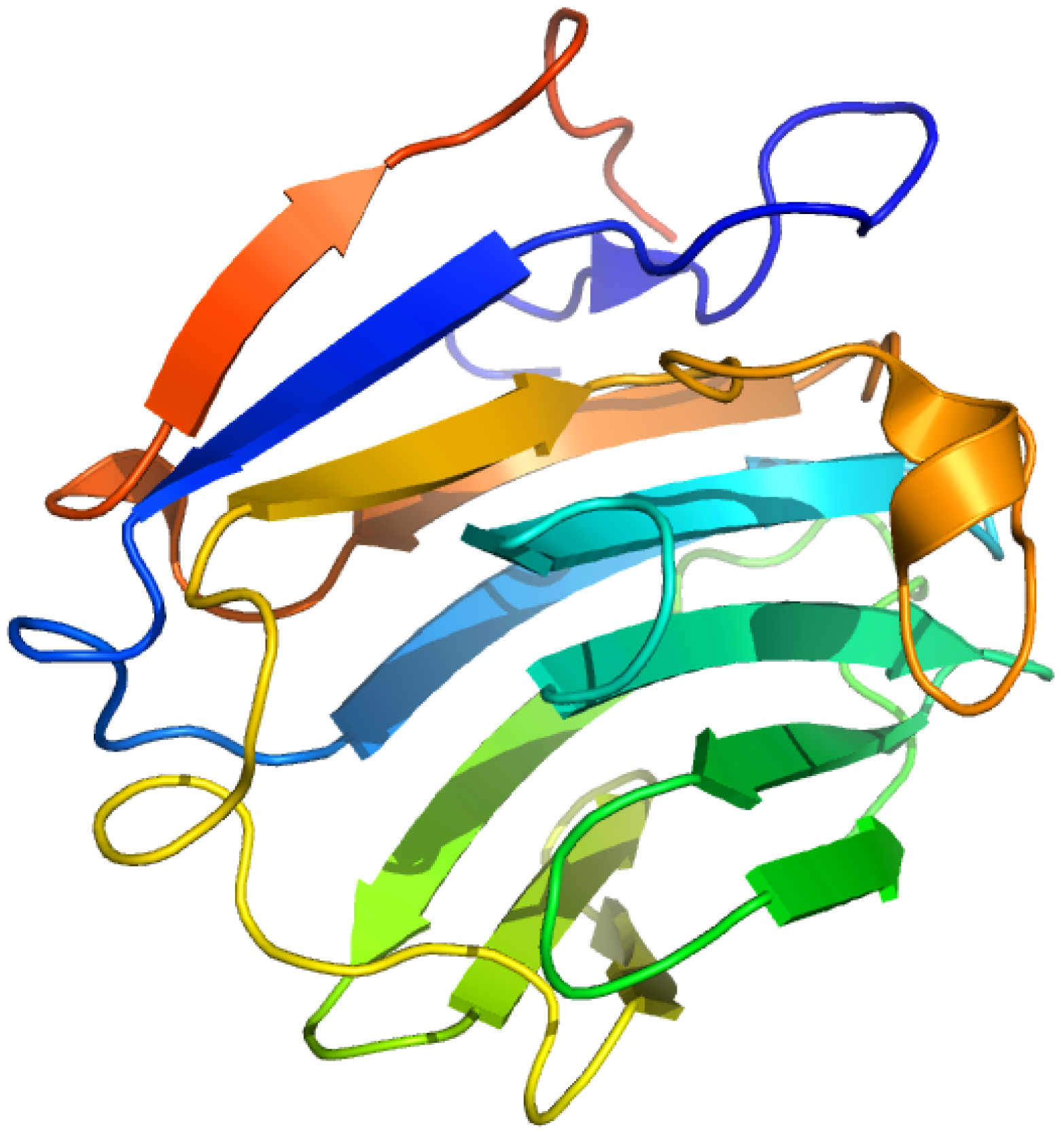
2.7.1. [3H]Δ6-Testosterone ([1,2-3H]17β-hydroxy-4,6-androstadien-3-one) and Δ6-[17-3H] Estradiol
2.8. Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin
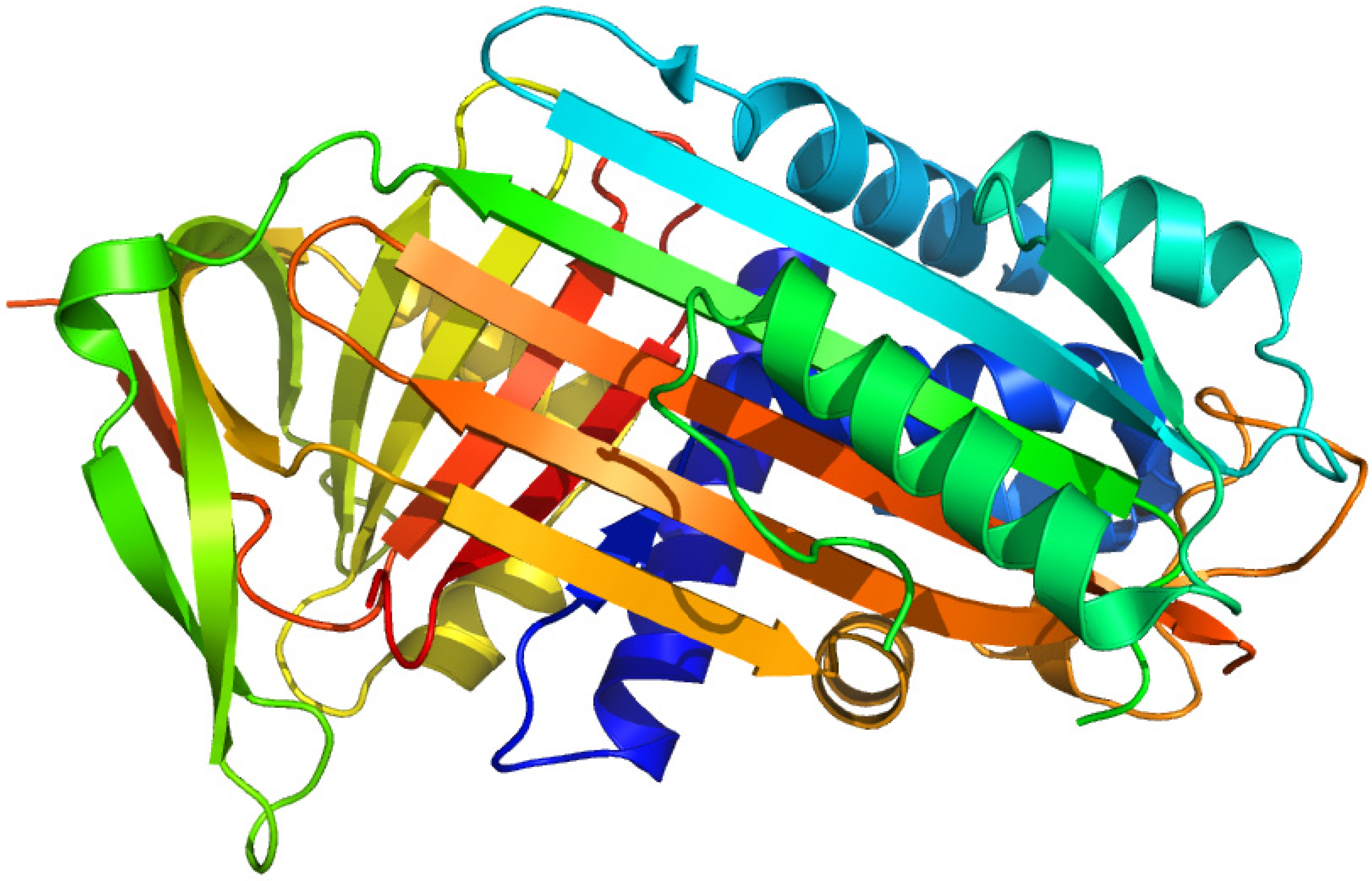
2.8.1. 21-Diazo-21-[6,7-3H]deoxycorticosterone and Unsubstituted Tritiated Δ6-derivatives of Cortisol, Corticosterone, Progesterone and Testosterone
3. Conclusions
| Natural ligand with photoreactive moiety | Chemical structure | Photoirradiation wavelengths (nm) and time | Target protein | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14C]Halotane |  | 254 (10 s) | Albumin | [23] |
| [3H8]Leukotriene E4 |  | 300 (4 min) | Albumin, glutathione transferases | [28] |
| [14C]Ketoprofen |  | 310 (30 min) | HSA | [11] |
| [3H]Flunitrazepam |  | 310 (30 min) | HSA, AGP, benzodiazepine receptor | [22,38] |
| [3H]7-Hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) |  | 310 (30 min) | AGP | [41] |
| [3H]Glibenclamide |  | 254 (3 min) | 140 kDa sulfonylurea receptor in the rat beta-cell membrane and albumin | [100] |
| [3H]Benzylpenicillin |  | 254 (2 min) | 127 kDa brush border membrane protein from rabbit small intestine and albumin | [101] |
| [3',5'-125I]Thyroxine ([125I]T4),
[3'-125I]Triiodothyronine |  | >300 (80 s) | Human thyroxine binding globulin and bovine serum albumin | [47] |
| All-trans-[11,12-3H]Retinoic acid |  | 365 (15 min) | Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein and albumin | [56] |
| [14C]Doxorubicin |  | >254 (5 min) | Junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum | [102] |
| [3H]Taxol |  | 254 (30 min) | Tubulin | [103] |
| [5-3H]Dolastatin 10 |  | 254nm (10 min) | Beta-tubulin | [104] |
| [3H]Colchicine |  | >305 (5 min) | Tubulin | [105] |
| [3H]Vinblastine |  | >310 (7 min) | Tubulin | [104] |
| [3H]Forskolin |  | 254 (30 s) | Erythrocyte D-glucose transporter | [106] |
| [3H]Cytochalasin B |  | 254 (30 s) | Human erythrocyte glucose transporter | [107] |
| [3H]Nitrendipine |  | 254 (20 s) | 32 kDa cardiac membrane protein | [108] |
| [3H]Bumetanide |  | Flash lights (2 min)
300–400 (10 min) | Na+-K+-Cl− cotransporter | [109,110] |
| [3H]Clonazepam |  | Shortwave UV (60 min) | Central type of benzodiazepine receptor | [111] |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hatanaka, Y.; Sadakane, Y. Photoaffinity labeling in drug discovery and developments: Chemical gateway for entering proteomic frontier. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, H.; Knowles, J.R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977, 46, 69–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, H. Photogenerated Reagents in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Elsevier Science, North Holland Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Schaller, J.; Gerber, S.; Kaempfer, U.; Lejon, S.; Trachsel, C. Human Blood Plasma Proteins: Structure and Function; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, West Sussex, UK/Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Structure and ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. Dan. Med. Bull. 1990, 37, 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dorman, G.; Prestwich, G.D. Benzophenone photophores in biochemistry. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5661–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1976, 12, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestwich, G.D.; Dorman, G.; Elliott, J.T.; Marecak, D.M.; Chaudhary, A. Benzophenone photoprobes for phosphoinositides, peptides and drugs. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 65, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, V.T.; Kuniyasu, A.; Nakayama, H.; Matsushita, Y.; Hirono, S.; Otagiri, M. Helix 6 of subdomain III A of human serum albumin is the region primarily photolabeled by ketoprofen, an arylpropionic acid NSAID containing a benzophenone moiety. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1434, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Chuang, V.T.; Ito, T.; Suenaga, A.; Watanabe, H.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Arginine 485 of human serum albumin interacts with the benzophenone moiety of ketoprofen in the binding pocket of subdomain III A and III B. Pharmazie 2012, 67, 414–418. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, V.T.; Otagiri, M. How do fatty acids cause allosteric binding of drugs to human serum albumin? Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.O.; Mensberg, K.L.; Kragh-Hansen, U. Effects of ionic strength and pH on the binding of medium-chain fatty acids to human serum albumin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 233, 395–405. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, K.; Maruyama, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Narazaki, R.; Fukuhara, A.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Interactive binding to the two principal ligand binding sites of humanserum albumin: Effect of the neutral-to-base transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1432, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Chuang, V.T.; Minomo, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Bhagavan, N.V.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Histidine146 of human serum albumin plays a prominent role at the interface of subdomains IA and IIA in allosteric ligand binding. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosa, T.; Maruyama, T.; Sakai, N.; Yonemura, N.; Yahara, S.; Otagiri, M. Species differences of serum albumins: III. Analysis of structural characteristics and ligand binding properties during N-B transitions. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ha, C.E.; Bhagavan, N.V. Site-directed mutagenesis study of the role of histidine residues in the neutral-to-basic transition of human serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1724, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliszan, R.; Noctor, T.A.; Wainer, I.W. Stereochemical aspects of benzodiazepine binding to human serum albumin. II. Quantitative relationships between structure and enantioselective retention in high performance liquid affinity chromatography. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 42, 512–517. [Google Scholar]
- Noctor, T.A.; Pham, C.D.; Kaliszan, R.; Wainer, I.W. Stereochemical aspects of benzodiazepine binding to human serum albumin. I. Enantioselective high performance liquid affinity chromatographic examination of chiral and achiral binding interactions between 1,4-benzodiazepines and human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 42, 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman-Gold, R. Photoaffinity labeling of benzodiazepine-receptors: Possible mechanism of reaction. Neurochem. Int. 1983, 5, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, V.T.; Otagiri, M. Flunitrazepam, a 7-nitro-1,4-benzodiazepine that is unable to bind to theindole-benzodiazepine site of human serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1546, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckenhoff, R.G.; Shuman, H. Halothane binding to soluble proteins determined by photoaffinity labeling. Anesthesiology 1993, 79, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckenhoff, R.G. Amino acid resolution of halothane binding sites in serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15521–15526. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A.A.; Curry, S.; Franks, N.P. Binding of the general anesthetics propofol and halothane to human serum albumin. High resolution crystal structures. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38731–38738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, F.A.; Morton, D.R.; Wynalda, M.A. Albumin stabilizes leukotriene A4. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 4680–4683. [Google Scholar]
- Zsila, F.; Bikadi, Z.; Lockwood, S.F. In vitro binding of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) to human serum albumin: Evidence from spectroscopic, molecular modeling, and competitive displacement studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3725–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, E.; Muller, M.; Huber, M.; Keppler, D.; Kurz, G. Direct photoaffinity labeling of leukotriene binding sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 186, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herve, F.; Duche, J.C.; d’Athis, P.; Marche, C.; Barre, J.; Tillement, J.P. Binding of disopyramide, Methadone, Dipyridamole, Chlorpromazine, Lignocaine and progesterone to the two main genetic variants of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: Evidence for drug-binding differences between the variants and for the presence of two separate drug-binding sites on alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Pharmacogenetics 1996, 6, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, J.W. Alpha 1 -acid glycoprotein and binding of basic drugs. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1983, 5, 635–648. [Google Scholar]
- Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T.; Imai, T.; Imamura, Y. Fluorescent investigations of binding of phenprocoumon to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otagiri, M.; Yamamichi, R.; Imai, T.; Imamura, Y.; Takadate, A. Study on the binding of dicumarol to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein using circular dichroism spectroscopy. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1988, 36, 4958–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otagiri, M.; Yamamichi, R.; Maruyama, T.; Imai, T.; Suenaga, A.; Imamura, Y.; Kimachi, K. Drug binding to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein studied by circular dichroism. Pharm. Res. 1989, 6, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P.; Eap, C.B. Contribution of the variants of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein to its binding of drugs. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1989, 300, 379–397. [Google Scholar]
- Herve, F.; Gomas, E.; Duche, J.C.; Tillement, J.P. Evidence for differences in the binding of drugs to the two main genetic variants of human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 36, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M.; Takadate, A. Characterization of drug binding sites on alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1990, 38, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, D.L.; Ravelli, R.B.; Mueller, U.; Skerra, A. The 1.8-A crystal structure of alpha1-acid glycoprotein (Orosomucoid) solved by UV RIP reveals the broad drug-binding activity of this human plasma lipocalin. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 384, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, V.T.; Hijioka, M.; Katsuki, M.; Nishi, K.; Hara, T.; Kaneko, K.; Ueno, M.; Kuniyasu, A.; Nakayama, H.; Otagiri, M. Characterization of benzodiazepine binding site on human alpha1-acid glycoprotein using flunitrazepam as a photolabeling agent. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1725, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W.; Moehler, H. [3H]clonazepam, like [3H]flunitrazepam, is a photoaffinity label for the central type of benzodiazepine receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1982, 81, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Chuang, V.T.; Nishi, K.; Suenaga, A.; Otagiri, M. Tryptophan residues play an important role in the extraordinarily high affinity binding interaction of UCN-01 to human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Chuang, V.T.; Nishi, K.; Kawahara, K.; Nakayama, H.; Yamaotsu, N.; Hirono, S.; Otagiri, M. Use of photoaffinity labeling and site-directed mutagenesis for identification of the key residue responsible for extraordinarily high affinity binding of UCN-01 in human alpha1-acid glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, B.E.; Jiang, H.; Liu, J.O. Binding of thalidomide to alpha1-acid glycoprotein may be involved in its inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 7552–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.L.; Lim, C.F.; Hall, J.G.; Barlow, J.W.; Craik, D.J.; Topliss, D.J.; Stockigt, J.R. Drug competition for thyroxine binding to transthyretin (prealbumin): Comparison with effects on thyroxine-binding globulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1989, 68, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapunpoj, P.; Leelawatwattana, L. Evolutionary changes to transthyretin: Structure-function relationships. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5330–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y. Transthyretin: It’s miracle function and pathogenesis. Rinsho Byori 2009, 57, 228–235. [Google Scholar]
- Klabunde, T.; Petrassi, H.M.; Oza, V.B.; Raman, P.; Kelly, J.W.; Sacchettini, J.C. Rational design of potent human transthyretin amyloid disease inhibitors. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozin, B.; Cahnmann, H.J.; Nikodem, V.M. Identification of thyroid hormone receptors in rat liver nuclei by photoaffinity labeling with l-thyroxine and triiodo-l-thyronine. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 5197–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Walt, B.; Nikodem, V.M.; Cahnmann, H.J. Use of un-derivatized thyroid hormones for photoaffinity labeling of binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3508–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahnmann, H.J.; Matsuura, T. Photochromism of 2,6-dinitrodiphenyl ethers enhanced in the presence of a host biomolecule*. Photochem. Photobiol. 1982, 35, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somack, R.; Nordeen, S.K.; Eberhardt, N.L. Photoaffinity labeling of human thyroxine-binding prealbumin with thyroxine and N-(ethyl-2-diazomalonyl)thyroxine. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 5651–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, D.S. Plasma retinol-binding protein. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1980, 348, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, N.; Slosberg, E.; Scarlata, S. Interactions of retinol with binding proteins: Studies with retinol-binding protein and with transthyretin. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 11118–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, N. Retinoid-binding proteins: Mediators of retinoid action. Biochem. J. 2000, 348 (Pt 3), 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.H.; Chrysina, E.D.; Irons, L.I.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Acharya, K.R.; Brew, K. Role of conserved residues in structure and stability: Tryptophans of human serum retinol-binding protein, a model for the lipocalin superfamily. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 2301–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor, H.M.; Newcomer, M.E. The structure of human retinol-binding protein (RBP) with its carrier protein transthyretin reveals an interaction with the carboxy terminus of RBP. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Ho, Y.C.; Rando, R.R. Photoaffinity labeling of retinoic acid-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Radominska-Pandya, A. Direct photoaffinity labeling of cellular retinoic acid-binding protein I (CRABP-I) with all-trans-retinoic acid: Identification of amino acids in the ligand binding site. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 12568–12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.A.; Dawson, M.I.; McCormick, A.M.; Napoli, J.L. Specific, covalent binding of an azidoretinoid to cellular retinoic acid-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 135, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamori, Y.; Sakaue, H.; Kasuga, M. RBP4, an unexpected adipokine. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 30–31, Discussion 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, P.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Wabitsch, M. RBP4: A controversial adipokine. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauchenzauner, M.; Laimer, M.; Wiedmann, M.; Tschoner, A.; Salzmann, K.; Sturm, W.; Sandhofer, A.; Walser, G.; Luef, G.; Ebenbichler, C.F. The novel insulin resistance parameters RBP4 and GLP-1 in patients treated with valproic acid: Just a sidestep? Epilepsy Res. 2013, 104, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullakhandam, R.; Palika, R.; Ghosh, S.; Reddy, G.B. Contrasting effects of type 2 and type 1 diabetes on plasma RBP4 levels: The significance of transthyretin. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, U.; Kopelman, M.; Mokady, S.; Shinitzky, M. Binding affinities of retinol and related compounds to retinol binding proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 65, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheves, M.; Makover, A.; Edelstein, S. Photo-affinity label for cellular retinol-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 122, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, H.L. Regulation of vitamin D metabolism. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, J.G. Plasma vitamin D-binding protein (Gc-globulin): Multiple tasks. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 53, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebanjo, O.A.; Moonga, B.S.; Haddad, J.G.; Huang, C.L.; Zaidi, M. A possible new role for vitamin D-binding protein in osteoclast control: Inhibition of extracellular Ca2+ sensing at low physiological concentrations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboven, C.; Rabijns, A.; de Maeyer, M.; van Baelen, H.; Bouillon, R.; de Ranter, C. A structural basis for the unique binding features of the human vitamin D-binding protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.R.; Holick, M.F. The role of sunlight in the cutaneous production of vitamin D3. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1988, 8, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, R.P.; Kutner, A.; Schnoes, H.K.; DeLuca, H.F. Photoaffinity labeling of serum vitamin D binding protein by 3-deoxy-3-azido-25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 3957–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.A.; DeLuca, H.F. Photoaffinity labeling of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3 receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1073, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.A.; DeLuca, H.F. Sites of phosphorylation and photoaffinity labeling of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 286, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Holick, S.A.; Hanafin, N.; Holick, M.F. Photoaffinity labeling of the rat plasma vitamin D binding protein with [26,27-3H]-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 3 beta-[N-(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)glycinate]. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 4729–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Bouillon, R.; van Baelen, H.; Holick, M.F. Synthesis of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 3 beta-3'-[N-(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)amino]propyl ether, a second-generation photoaffinity analogue of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3: Photoaffinity labeling of rat serum vitamin D binding protein. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 4809–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Bouillon, R.; van Baelen, H.; Holick, M.F. Photoaffinity labeling of human serum vitamin D binding protein and chemical cleavages of the labeled protein: Identification of an 11.5-kDa peptide containing the putative 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 binding site. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7638–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, N.; Dutta, A.; Ray, R. Roles of the structure and orientation of ligands and ligand mimics inside the ligand-binding pocket of the vitamin D-binding protein. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 7432–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, J.K.; Ray, R. Synthesis and binding-analysis of 5E-[19-(2-bromoacetoxy)methyl]25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 5E-25-hydroxyvitamin D3-19-methyl[(4-azido-2-nitro)phenyl]glycinate: Novel C19-modified affinity and photoaffinity analogs of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Steroids 1998, 63, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, J.K.; Swamy, N.; Ray, R. The C(19) position of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) faces outward in the vitamin D sterol-binding pocket of vitamin D-binding protein. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentiev, A.A.; Moldogazieva, N.T. Structural and functional mapping of alpha-fetoprotein. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2006, 71, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, D.W.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Carlson, K.E. Photoaffinity labeling of rat alpha-fetoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 10359–10367. [Google Scholar]
- Kassab, D.; Pichat, S.; Chambon, C.; Blachere, T.; Rolland de Ravel, M.; Mappus, E.; Grenot, C.; Cuilleron, C.Y. Photoaffinity labeling of homologous Met-133 and Met-139 amino acids of rabbit and sheep sex hormone-binding globulins with the unsubstituted Delta 6-testosterone photoreagent. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 14088–14097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, C. Sex hormone binding globulin: Origin, function and clinical significance. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 27 (Pt 6), 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Grishkovskaya, I.; Avvakumov, G.V.; Hammond, G.L.; Muller, Y.A. Resolution of a disordered region at the entrance of the human sex hormone-binding globulin steroid-binding site. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 318, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A., Jr.; Smith, H.E.; Danzo, B.J. Characterization of androgen binding protein in rat epididymal cytosol using a photoaffinity ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 7769–7773. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.A., Jr.; Smith, H.E.; Danzo, B.J. Photoaffinity labeling of rat androgen binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenot, C.; de Montard, A.; Blachere, T.; de Ravel, M.R.; Mappus, E.; Cuilleron, C.Y. Characterization of Met-139 as the photolabeled amino acid residue in the steroid binding site of sex hormone binding globulin using delta 6 derivatives of either testosterone or estradiol as unsubstituted photoaffinity labeling reagents. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 7609–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, G.L.; Underhill, D.A.; Smith, C.L.; Goping, I.S.; Harley, M.J.; Musto, N.A.; Cheng, C.Y.; Bardin, C.W. The cDNA-deduced primary structure of human sex hormone-binding globulin and location of its steroid-binding domain. FEBS Lett. 1987, 215, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchinfuso, W.P.; Hammond, G.L. Steroid-binding and dimerization domains of human sex hormone-binding globulin partially overlap: Steroids and Ca2+ stabilize dimer formation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 10622–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, A.; Egloff, M.; Gerard, H.; el Harate, A.; Domingo, M.; Gueant, J.L.; Dang, C.D.; Degrelle, H. Internalization of human sex steroid-binding protein in the monkey epididymis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1990, 5, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, A.; Nya, A.E.; Egloff, M.; Domingo, M.; Degrelle, H.; Gerard, H. Endocytosis of human sex steroid-binding protein in monkey germ cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 637, 258–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felden, F.; Leheup, B.; Fremont, S.; Bouguerne, R.; Egloff, M.; Nicolas, J.P.; Grignon, G.; Gueant, J.L. The plasma membrane of epididymal epithelial cells has a specific receptor which binds to androgen-binding protein and sex steroid-binding protein. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 42, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, C.; Bennat, D.; Delolme, F.; Dessalces, G.; Blachere, T.; Rolland de Ravel, M.; Mappus, E.; Grenot, C.; Cuilleron, C.Y. Photoaffinity labeling of human sex hormone-binding globulin using 17alpha-alkylamine derivatives of 3beta-androstanediol substituted with azidonitrophenylamido, azidonitrophenylamino, or trifluoroazidonitrophenylamino chromophores. Localization of Trp-84 in the vicinity of the steroid-binding site. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 15424–15435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klieber, M.A.; Underhill, C.; Hammond, G.L.; Muller, Y.A. Corticosteroid-binding globulin, a structural basis for steroid transport and proteinase-triggered release. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29594–29603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumer-Bayraktar, Z.; Kolarich, D.; Campbell, M.P.; Ali, S.; Packer, N.H.; Thaysen-Andersen, M. N-glycans modulate the function of human corticosteroid-binding globulin. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, M111.009100. [Google Scholar]
- Gardill, B.R.; Vogl, M.R.; Lin, H.Y.; Hammond, G.L.; Muller, Y.A. Corticosteroid-binding globulin: Structure-function implications from species differences. PLoS One 2012, 7, e52759. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, A.; Wei, Z.; Stanley, P.L.; Read, R.J.; Stein, P.E.; Carrell, R.W. The S-to-R transition of corticosteroid-binding globulin and the mechanism of hormone release. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 380, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marver, D.; Chiu, W.; Wolff, M.E.; Edelman, I.S. Photoaffinity site-specific covalent labeling of human corticosteroid-binding globulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 4462–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenot, C.; Blachere, T.; Rolland de Ravel, M.; Mappus, E.; Cuilleron, C.Y. Identification of Trp-371 as the main site of specific photoaffinity labeling of corticosteroid binding globulin using delta 6 derivatives of cortisol, corticosterone, and progesterone as unsubstituted photoreagents. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 8969–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.O.; Rundle, S.; Leavitt, W.W. Purification and partial characterization of a corticosteroid-binding globulin from hamster serum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 926, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, W.; Oekonomopulos, R.; Punter, J.; Summ, H.D. Direct photoaffinity labeling of the putative sulfonylurea receptor in rat beta-cell tumor membranes by [3H]glibenclamide. FEBS Lett. 1988, 229, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, W.; Girbig, F.; Leipe, I.; Petzoldt, E. Direct photoaffinity labelling of binding proteins for beta-lactam antibiotics in rabbit intestinal brush border membranes with [3H]benzylpenicillin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzato, F.; Margreth, A.; Volpe, P. Direct photoaffinity labeling of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum with [14C]doxorubicin. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 13252–13257. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.; Horwitz, S.B.; Ringel, I. Direct photoaffinity labeling of tubulin with taxol. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Covell, D.G.; Taylor, G.F.; Kepler, J.A.; Copeland, T.D.; Nguyen, N.Y.; Pettit, G.R.; Hamel, E. Direct photoaffinity labeling by dolastatin 10 of the amino-terminal peptide of beta-tubulin containing cysteine 12. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30731–30740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.; Knipling, L.; Cahnmann, H.J.; Palumbo, G. Direct photoaffinity labeling of tubulin with colchicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, M.F.; Morris, D.P.; Edwards, B.M. [3H]forskolin. Direct photoaffinity labeling of the erythrocyte D-glucose transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 5978–5984. [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan, M.F.; Cytochalasin, B. A natural photoaffinity ligand for labeling the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 7290–7293. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.P.; Lipshutz, G.M.; Denney, G.H. Direct photoaffinity labeling of the high affinity nitrendipine-binding site in subcellular membrane fractions isolated from canine myocardium. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 5384–5387. [Google Scholar]
- Petzinger, E.; Honscha, W.; Schenk, A.; Follmann, W.; Deutscher, J.; Zierold, K.; Kinne, R.K. Photoaffinity labeling of plasma membrane proteins involved in the transport of loop diuretics into hepatocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 208, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsler, K.; Kinne, R. Photoinactivation of sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport in LLC-PK1/Cl 4 cells by bumetanide. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 250, C799–C806. [Google Scholar]
- Bowling, A.C.; DeLorenzo, R.J. Photoaffinity labeling of a novel benzodiazepine binding protein in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1987, 135, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Fukuda, H.; Chuang, V.T.; Yamasaki, K.; Kawahara, K.; Nakayama, H.; Suenaga, A.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Subdomain IIIA of dog albumin contains a binding site similar to site II of human albumin. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, V.T.G.; Otagiri, M. Photoaffinity Labeling of Plasma Proteins. Molecules 2013, 18, 13831-13859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113831
Chuang VTG, Otagiri M. Photoaffinity Labeling of Plasma Proteins. Molecules. 2013; 18(11):13831-13859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113831
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Victor Tuan Giam, and Masaki Otagiri. 2013. "Photoaffinity Labeling of Plasma Proteins" Molecules 18, no. 11: 13831-13859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113831
APA StyleChuang, V. T. G., & Otagiri, M. (2013). Photoaffinity Labeling of Plasma Proteins. Molecules, 18(11), 13831-13859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181113831






