The Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Steroidal Saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through Enhanced Immunostimulation in Experimental Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Induction of Apoptosis in the A549 Cell Line
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Chemical Components
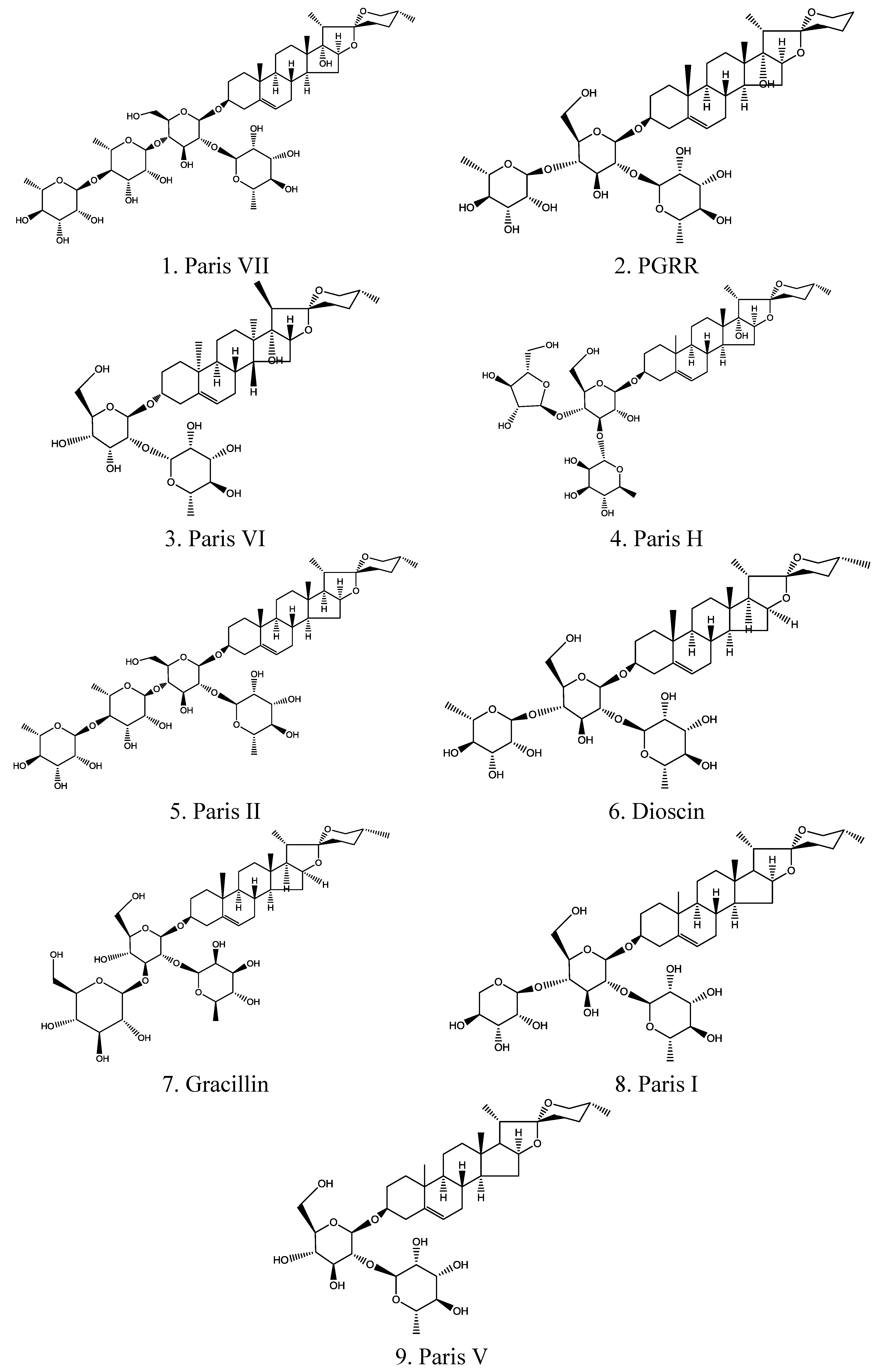
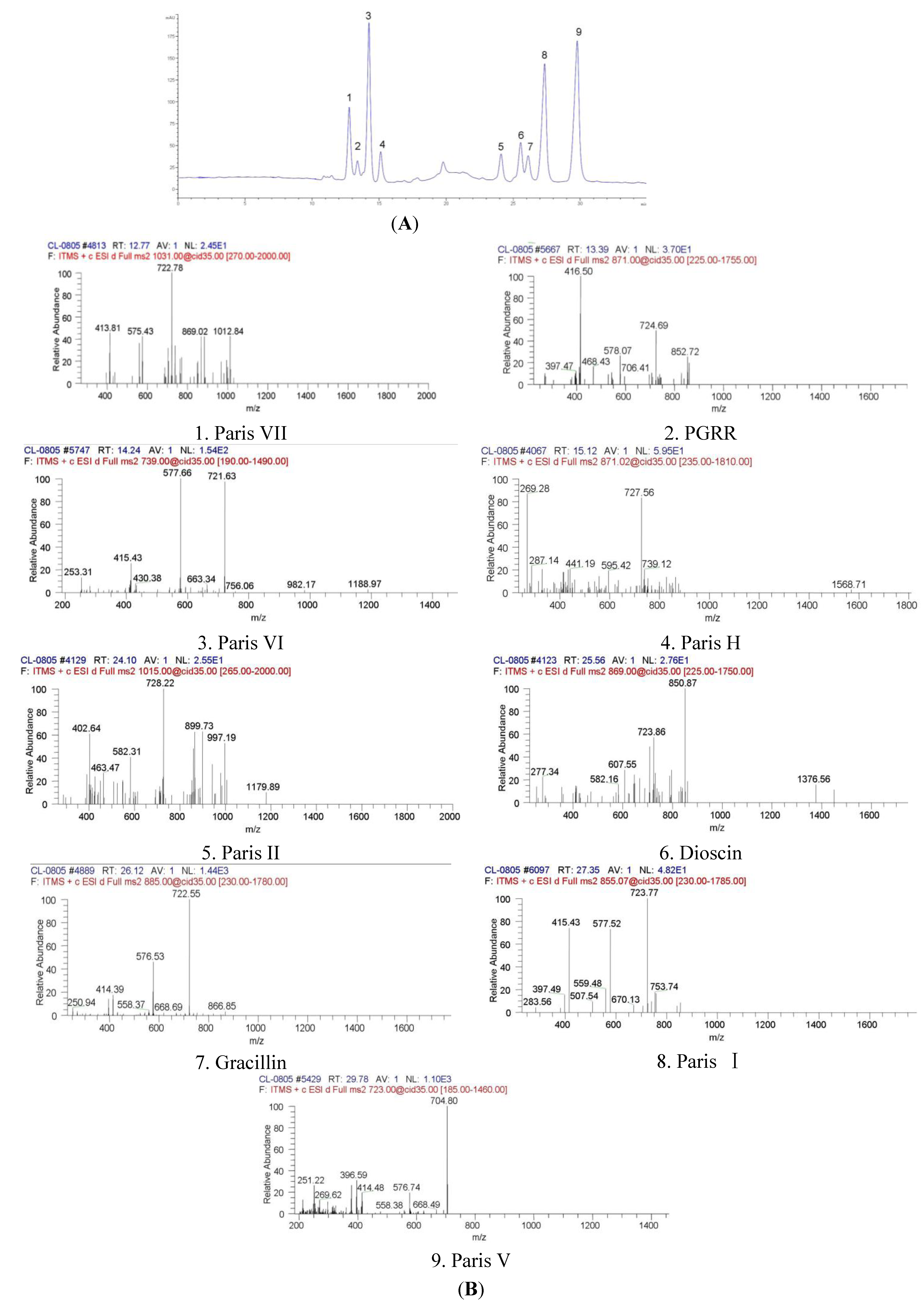
| No. | Compound | Chemical nomenclature | TR (min) | (+)ESI-MS m/z | UVmax (nm) | (+)ESI-MS m/z (ion fragments) | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paris VII | 25(R) Pennogenin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→4) -α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)]- β-D-glucopyranoside | 12.774 | 1031.18 | 200, 280 | 1012.84, 869.02, 722.78, 575.43, 413.81 | C51H82O21 |
| 2 | PGRR | 25(R)-5-en-spirost-3β, 17α-diol-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→4)]-β-D-glucopyranoside | 13.390 | 871.02 | 205, 280 | 852.72, 724.69, 578.07, 416.50 | C44H70O17 |
| 3 | Paris VI | 25(R) pennogenin-3-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosyl (1→2) –β-D-glucopyranoside | 14.248 | 738.90 | 200, 285 | 721.63, 577.66, 415.43 | C39H62O13 |
| 4 | Paris H | 25(R) pennogenin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl(1→4) [α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)] -β-D-glucopyranoside | 15.122 | 871.02 | 203 | 727.56, 595.42, 441.19, 287.14 | C44H70O17 |
| 5 | Paris II | 25(R) diosgenin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→4) -α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→4)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)]- β-D-glucopyranoside | 24.103 | 1015.18 | 200 | 997.19, 899.73, 728.22, 582.31, 402.64 | C51H82O20 |
| 6 | Dioscin | 25(R) diosgenin bis-α-L -rhamnopyranosyl)-(1→2 and 1→4)- β-D-glucopyranoside | 25.562 | 869.04 | 205 | 850.87, 723.86, 607.55, 277.34 | C45H72O16 |
| 7 | Gracillin | 25(R) diosgenin bis-α-L -rhamnopyranosyl)-(1→2 and 1→3)- β-D-glucopyranoside | 26.125 | 885.04 | 200 | 722.55, 576.53, 414.39 | C45H72O17 |
| 8 | Paris I | 25(R) diosgenin-3-O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl(1→4) -[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2)] –β-D-glucopyranoside | 27.352 | 855.07 | 200, 280 | 723.77, 577.52, 415.43 | C44H70O16 |
| 9 | Paris V | 25(R) diosgenin-3-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosyl (1→2) –β-D-glucopyranoside | 29.786 | 722.90 | 200 | 704.80, 576.74, 396.59, 251.22 | C39H62O12 |
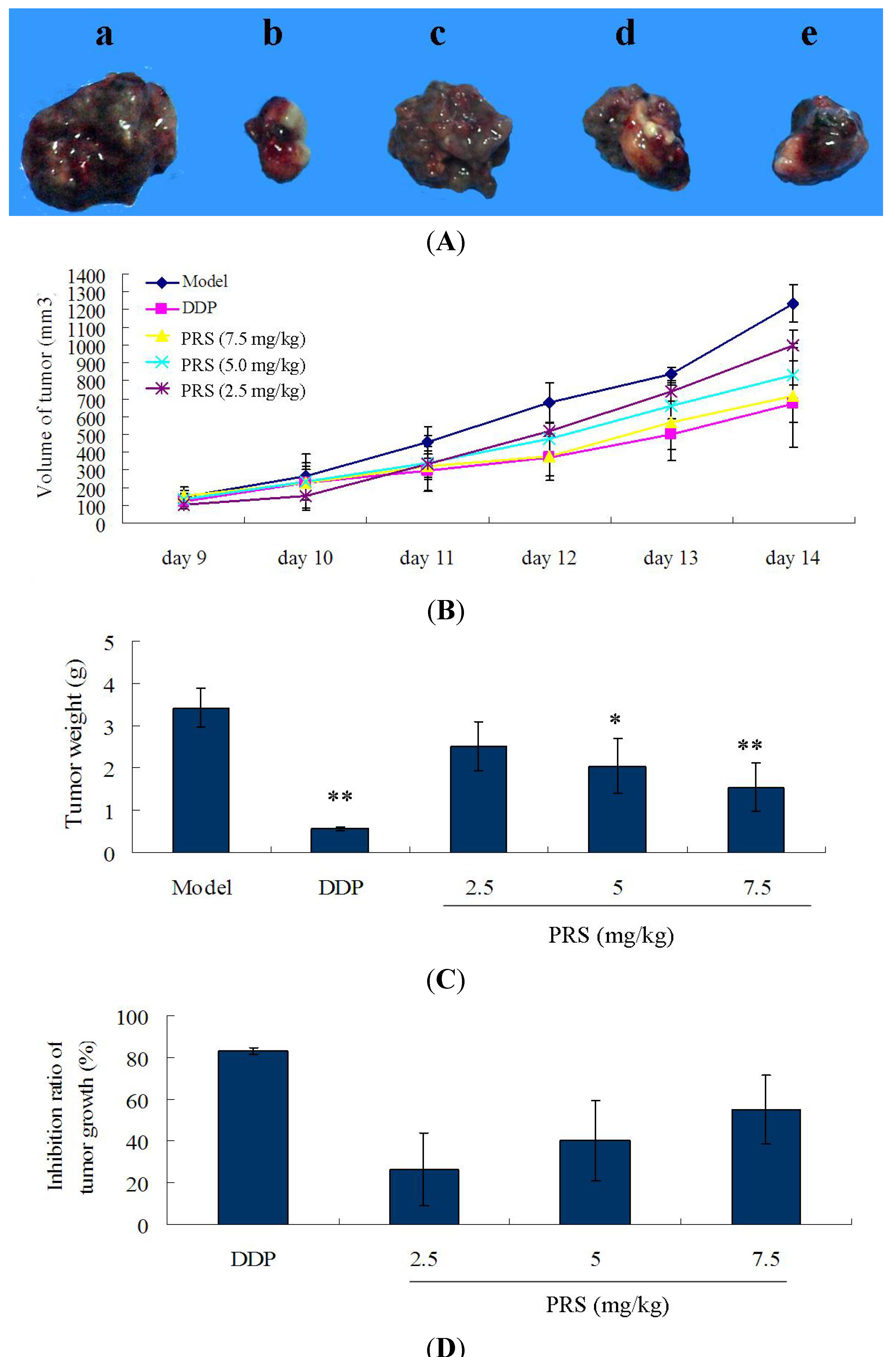
2.2. Effect of PRS on Tumor Growth, Tumor Volume, Tumor Weight in C57BL/6 Mice
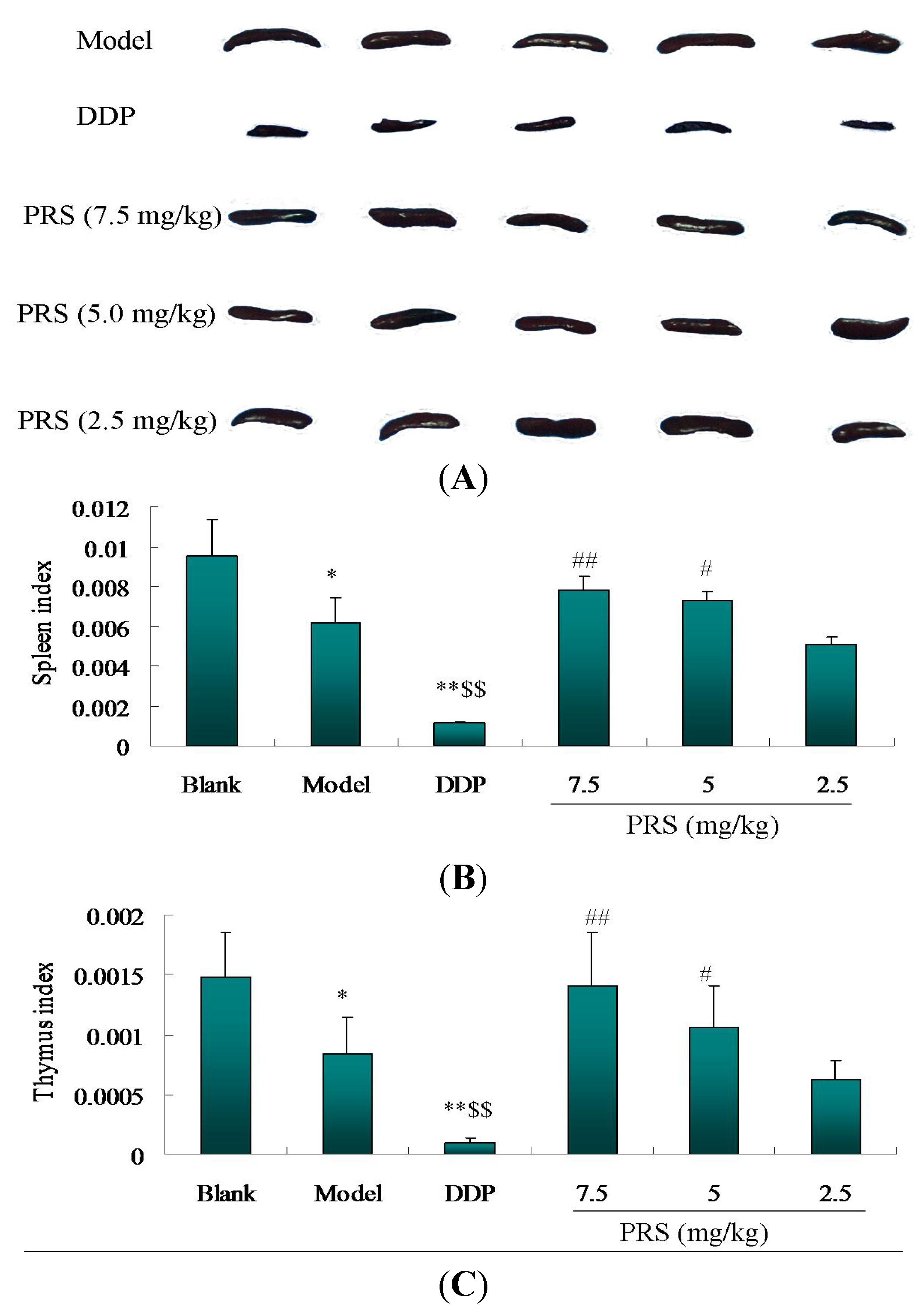
2.3. Immunomodulatory Effects of PRS on Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice
2.4. PRS Decreased TNF-α, IL-8 and IL-10 Levels of Serum in C57BL/6 Mice
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg/day) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | IL-8 (pg/mL) | IL-10 (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | − | 71.1 ± 8.2 | 45.8 ± 8.4 | 44.7 ± 5.7 |
| Model | − | 106.2 ± 6.7 ** | 85.4 ± 10.3 ** | 77.3 ± 6.8 ** |
| DDP | 20 | 91.7 ± 9.3 # | 58.5 ± 5.5 # | 53.9 ± 4.2 # |
| PRS | 7.5 | 74.8 ± 11.5 ## | 64.7 ± 6.8 # | 59.0 ± 8.5 # |
| 5 | 77.3 ± 5.3 # | 71.7 ± 7.2 # | 68.3 ± 11.4 | |
| 2.5 | 83.9 ± 6.6 | 82.6 ± 4.6 | 76.5 ± 10.6 | |
| Standard curve | − | Y = 0.0006x + 0.0304 (R2 = 0.9824) | Y = 0.0037x + 0.1800 (R2 = 0.9110) | Y = 0.0001x + 0.0960 (R2 = 0.9977) |
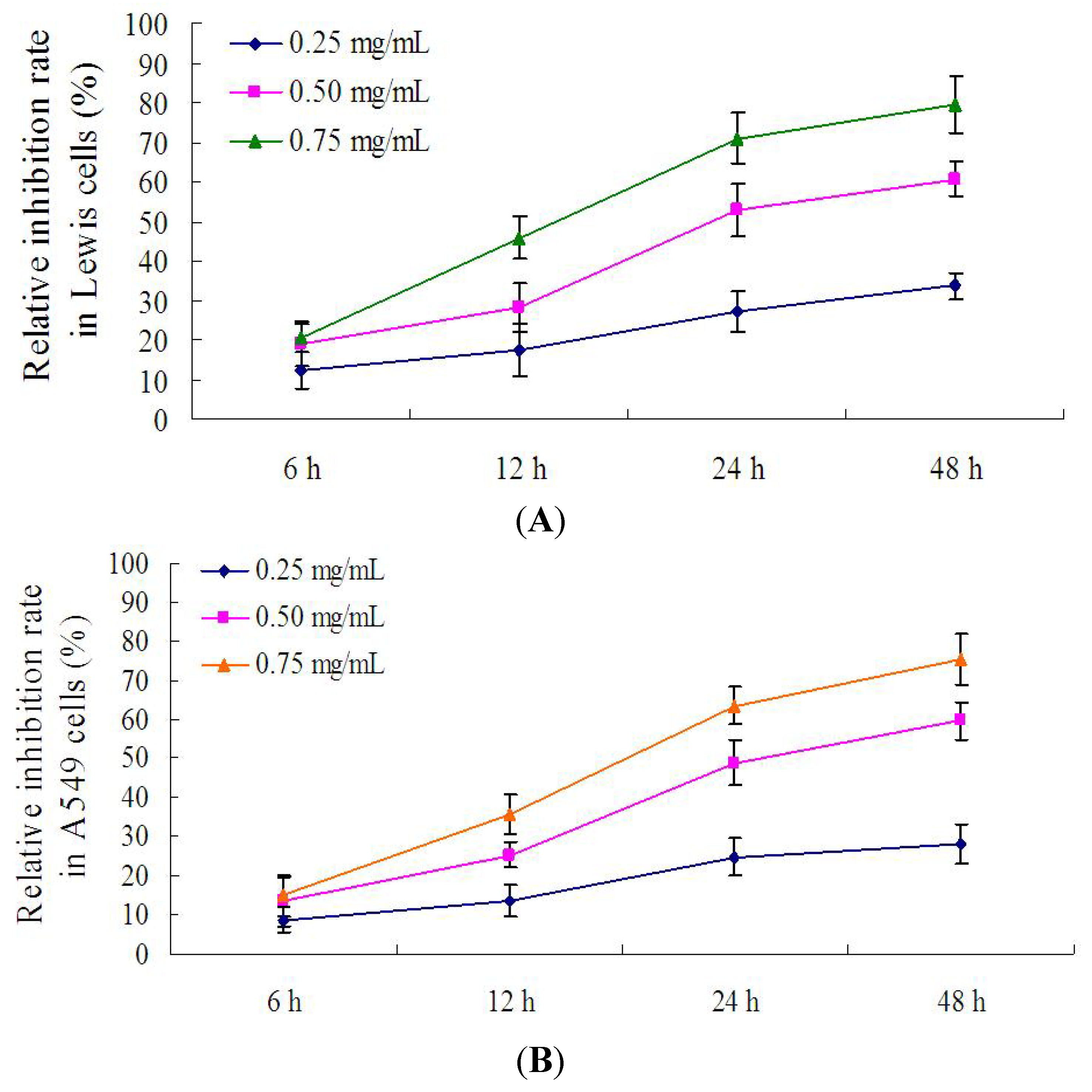
2.5. Effect of PRS on the Proliferation of Lewis Cells and A549 Cells
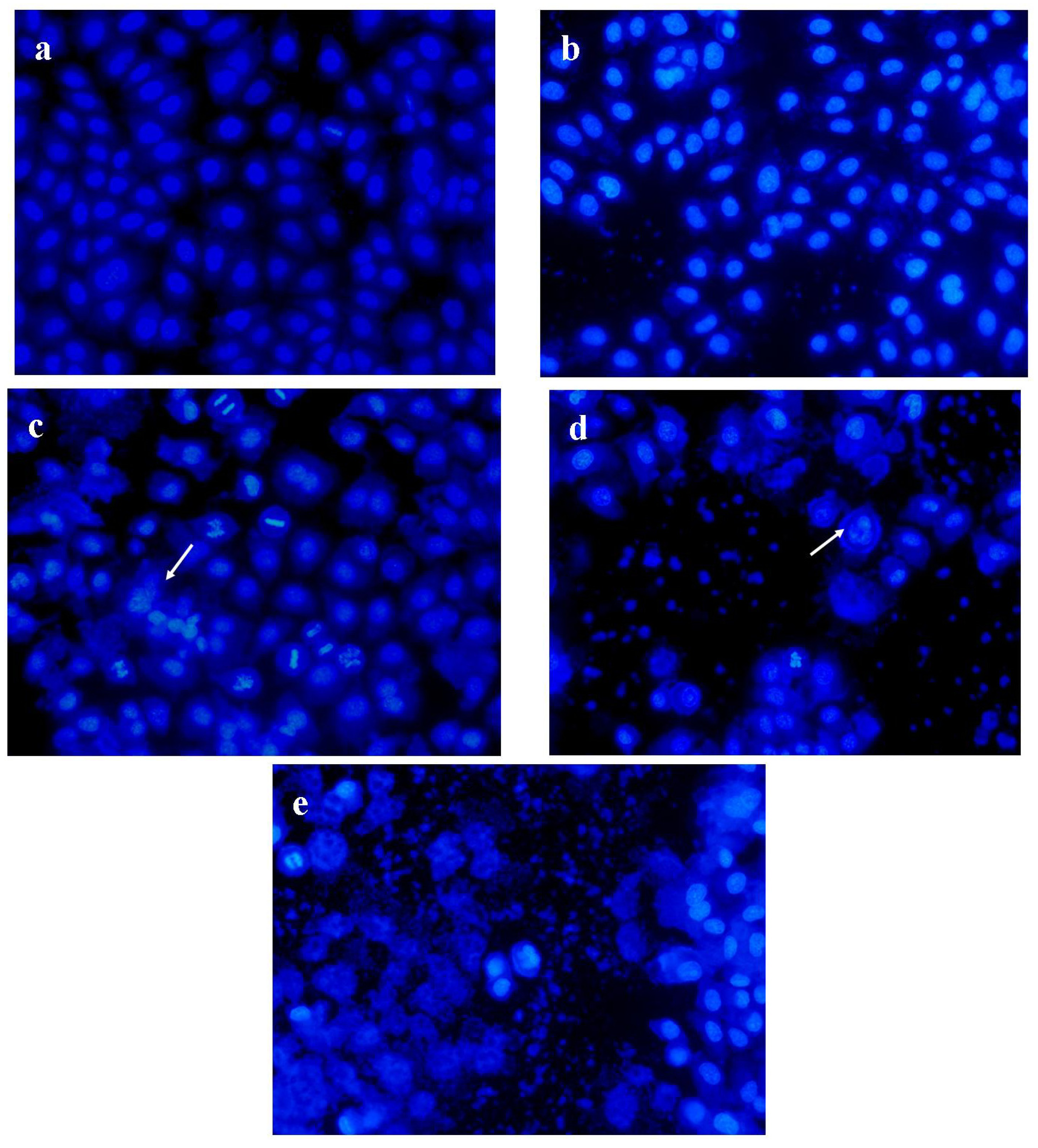
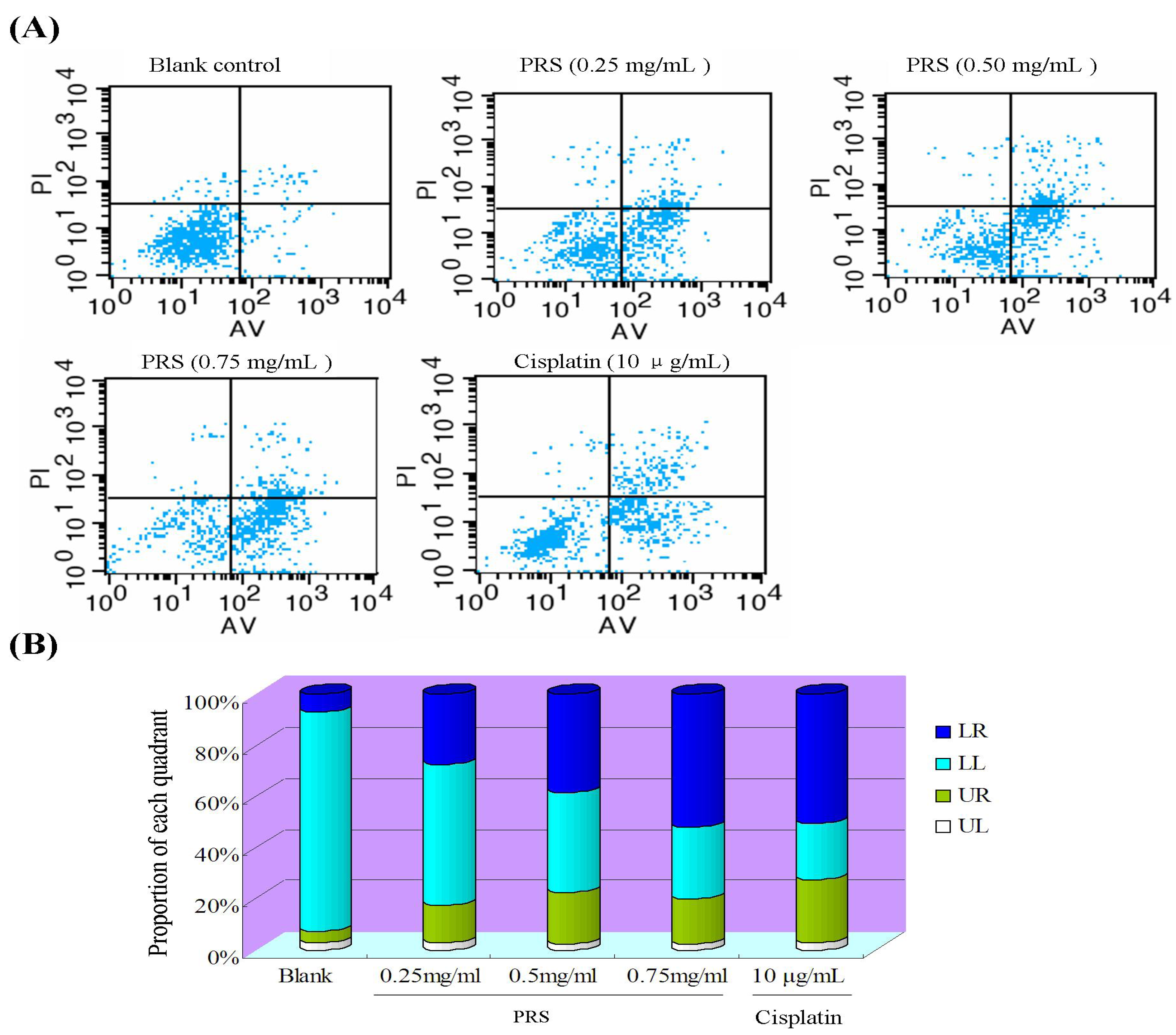
2.6. PRS induced Apoptosis of A549 Cells
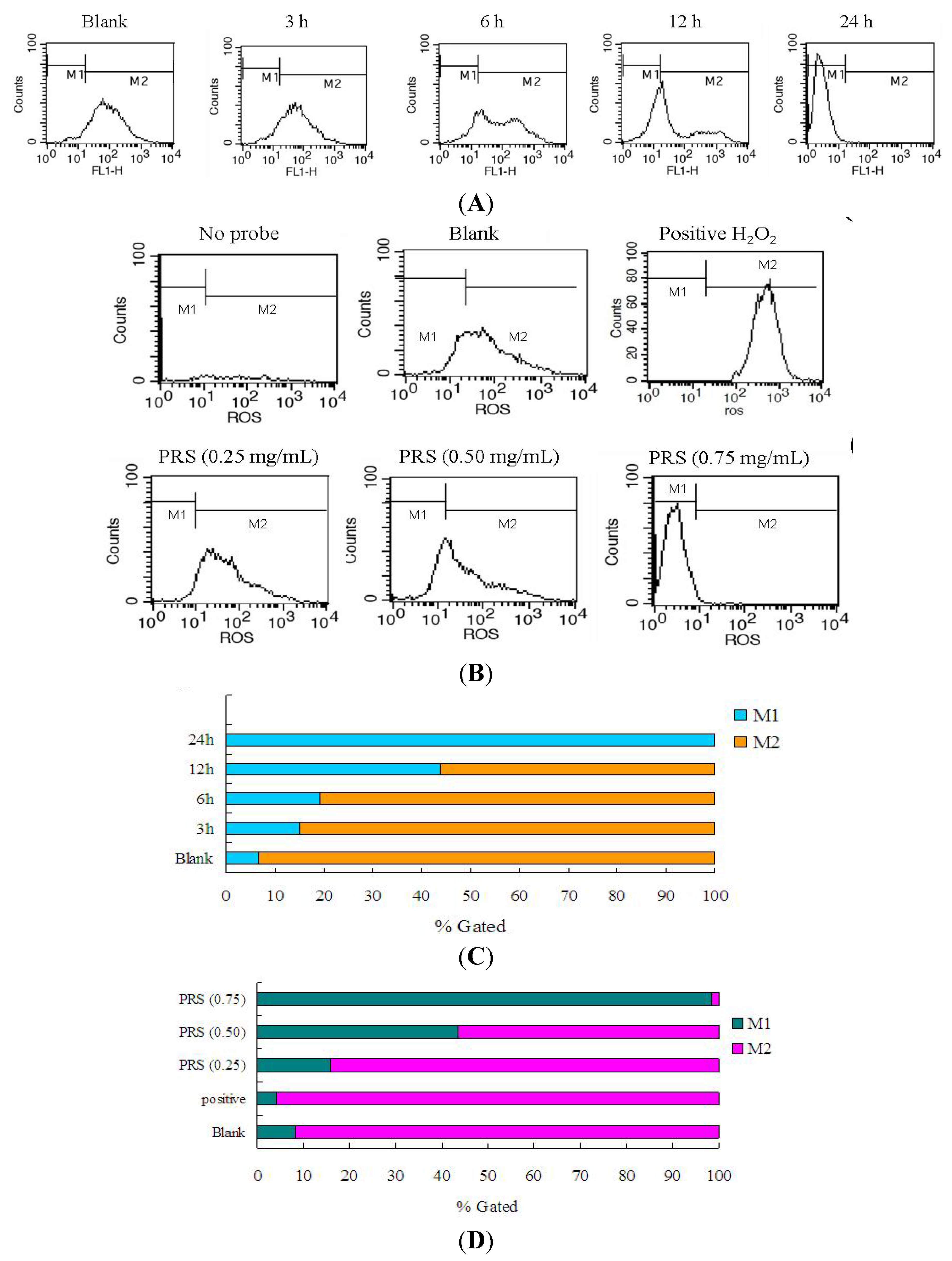
2.7. PRS Reduced ROS Generation of A549 Cells
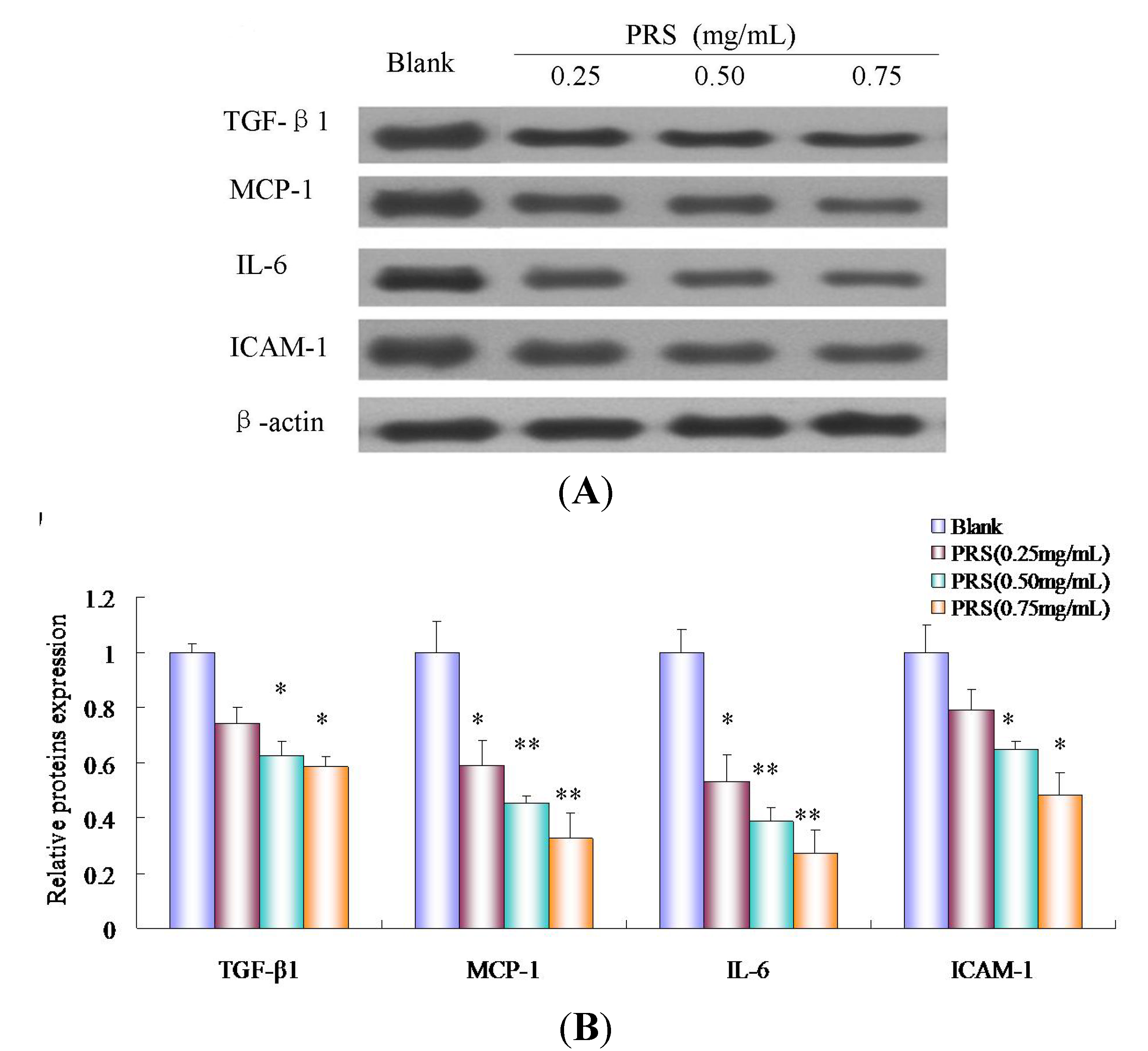
2.8. PRS Decreased the Expressions of Inflammation-Related Proteins
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Preparation of PRS Extract
3.3. HPLC and LC/MS/MS Analysis
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Treatment
3.6. ELISA Assay for Inflammatory Cytokines
3.7. Hoechst 33342 Staining
3.8. Annexin-V/PI Double-Staining
3.9. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
3.10. Western Blotting Analysis
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Palladino, G.P.; Lacedonia, D.; Koutelou, A.; Orlando, S. Foschino-Barbaro MP. Neutrophilic airways inflammation in lung cancer: The role of exhaled LTB-4 and IL-8. BMC Cancer 2011, 7, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Umekawa, K.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; Suzumura, T.; Oka, T.; Nagata, M.; Mitsuoka, S.; Matsuura, K.; Nakai, T.; Yoshimura, N.; et al. Plasma RANTES, IL-10 and IL-8 levels in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-TKIs. BMC. Res. Notes 2013, 6, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Cho, B.C.; Bae, M.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, I.K.; Kim, D.J.; Ahn, S.V.; Chung, K.Y. Preoperative C-reactive protein levels are associated with tumor size and lymphovascular invasion in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, T.; Ichiki, Y.; Yamada, S.; Shigematsu, Y.; Baba, T.; Nagata, Y.; Mizukami, M.; Sugaya, M.; Takenoyama, M.; Hanagiri, T.; et al. Cytokine production of lung cancer cell lines: Correlation between their production and the inflammatory/immunological responses both in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Eichhorn, T.; Dapat, E.; Yu, H.S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, C.Q.; Liu, C.; Efferth, T.; Ma, B.P. Polyhydroxylated steroidal glycosides from Paris polyphylla. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.R.; Jiao, P.; Yao, S.T.; Sang, H.; Qin, S.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.B.; Gao, L.L. Paris polyphylla Smith extract induces apoptosis and activates cancer suppressor gene connexin26 expression. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kang, L.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Liang, Y.G.; Tan, D.W.; Yu, Z.Y.; Cong, Y.W.; Ma, B.P. Steroidal saponins from the rhizome of Paris polyphylla and their cytotoxic activities. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, B.R.; Hu, W.J.; Yu, L.X.; Qian, X.P. In vitro anticancer activity of aqueous extracts and ethanol extracts of fifteen traditional Chinese medicines on human digestive tumor cell lines. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.L.; Gao, W.Y; Zhang, Y.J.; Ma, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.W. Paridis saponins inhibiting carcinoma growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Fan, J.; Dong, A.; Cheng, H.; Xu, R. Effects of polyphyllin I on growth inhibition of human non-small lung cancer cells and in xenograft. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2010, 42, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Lu, H.X.; Xu, L.S.; Xiao, W. Polyphyllin D exerts potent anti-tumour effects on Lewis cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, F.M.; Ma, D.L.; Cheung, Y.W.; Lok, C.N.; Yan, K.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Xu, S.; Ko, B.C.; He, Q.Y.; et al. Proteomic and transcriptomic study on the action of a cytotoxic saponin (Polyphyllin D): Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathways. Proteomics 2008, 8, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Dai, Y.; Ye, W.C.; Li, Y.L. Steroidal saponins from Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Phytochemistry 2012, 81, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Gao, W.Y.; Man, S.L.; Wang, Y. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of steroid saponins of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Exp. Oncol. 2009, 31, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jadus, M.R.; Natividad, J.; Mai, A.; Ouyang, Y.; Lambrecht, N.; Szabo, S.; Ge, L.; Hoa, N.; Dacosta-Iyer, M.G. Lung cancer: A classic example of tumor escape and progression while providing opportunities for immunological intervention. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 160724. [Google Scholar]
- Ronan, J.K.; James, L.G.; Giuseppe, G. Immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2010, 11, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikemu, A.; Umar, A.; Yusup, A.; Upur, H.; Berké, B.; Bégaud, B.; Moore, N. Immunomodulatory and antitumour effects of abnormal Savda Munziq on S180 tumour-bearing mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Genetic single-nucleotide polymorphisms of inflammation-related factors associated with risk of lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, J.; Kowalska, M.; Kotowicz, B.; Fuksiewicz, M.; Glogowski, M.; Wojcik, E.; Chechlinska, M.; Steffen, J. Pretreatment serum levels of cytokines and cytokine receptors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, and correlations with clinicopathological features and prognosis. M-CSF—An independent prognostic factor. Oncology 2006, 70, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishodia, S.; Koul, D.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor celecoxib abrogates TNF-induced NF-kappa B activation through inhibition of activation of I kappa B alpha kinase and Akt in human non-small cell lung carcinoma: correlation with suppression of COX-2 synthesis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.F.; Cui, Y.; Huang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Nie, Z.; Wang, L.F.; Yan, B.Z.; Tang, Y.L.; Liu, Y. Immuno-stimulating properties of diosgenyl saponins isolated from Paris polyphylla. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2408–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Jia, X.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Y.; Shi, F. Chemoprevention by Prunella vulgaris L. extract of non-small cell lung cancer via promoting apoptosis and regulating the cell cycle. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Suchaoin, W.; Chanvorachote, P. Caveolin-1 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage to lung carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Uneri, C.; Sari, M.; Bağlam, T.; Polat, S.; Yüksel, M. Effects of vitamin E on cigarette smoke induced oxidative damage in larynx and lung. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetriou, C.A.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Loft, S.; Møller, P.; Vermeulen, R.; Palli, D.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Xun, W.W.; Vineis, P. Biomarkers of ambient air pollution and lung cancer: A systematic review. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, N.; Manti, R.; Birocco, N.; Pugliese, M.; Brignardello, E.; Ciuffreda, L.; Catalano, M.G.; Aragno, M.; Boccuzzi, G. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress/antioxidant parameters characterize the bio-humoral profile of early cachexia in lung cancer patients. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Panieri, E.; Gogvadze, V.; Norberg, E.; Venkatesh, R.; Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Reactive oxygen species generated in different compartments induce cell death, survival, or senescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 57, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, C.; Hayashi, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Oike, M. Endothelium-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tumor cells: Exclusive roles of transforming growth factor β1 and β2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4470–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirino, V.; Camerlingo, R.; Bifulco, K.; Irollo, E.; Montella, R.; Paino, F.; Sessa, G.; Carriero, M.V.; Normanno, N.; Rocco, G.; et al. TGF-β1 exposure induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition both in CSCs and non-CSCs of the A549 cell line, leading to an increase of migration ability in the CD133+ A549 cell fraction. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzgo-Martínez, S.; Pilares-Ortega, L.; Alvarez-Rodríguez, L.; Aranzamendi-Zaldunbide, M.; Padilla, D.; Icardo, J.M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human lung epithelial cells during Rhodococcus equi infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Mim, H.J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, H. P-selectin-mediated platelet activation promotes adhesion of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells on vascular endothelial cells under flow. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Tai, H.H. Thromboxane A2 receptor-mediated release of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) induces expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) by activation of protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.T.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Hsieh, P.W.; Yang, C.M. Protective effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate against TNF-α-induced lung inflammation via ROS-dependent ICAM-1 inhibition. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Jia, X.B.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Tan, X.B.; Shi, F. Combination of active components enhances the efficacy of Prunella in prevention and treatment of lung cancer. Molecules 2010, 15, 7893–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Zheng, G.B.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gao, H.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dai, C.Y.; Huang, L.; Meng, X.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; et al. Dracorhodin perchlorate induced human breast cancer MCF-7 apoptosis through mitochondrial pathways. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Bai, J.P.; Xie, Y.; Yu, J.Z.; Ma, C.G. The triterpenoid pristimerin induces U87 glioma cell apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Koarai, A.; Sugiura, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Kanda, M.; Tanaka, R.; Akamatsu, K.; Hirano, T.; Matsunaga, K.; Minakata, Y.; et al. Oxidative stress augments toll-like receptor 8 mediated neutrophilic responses in healthy subjects. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Gu, J.-F.; Zou, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.-H.; Jiang, J.; Qin, D.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Liu, B.-X.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-T.; et al. The Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Steroidal Saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through Enhanced Immunostimulation in Experimental Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Induction of Apoptosis in the A549 Cell Line. Molecules 2013, 18, 12916-12936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012916
Li Y, Gu J-F, Zou X, Wu J, Zhang M-H, Jiang J, Qin D, Zhou J-Y, Liu B-X-Z, Zhu Y-T, et al. The Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Steroidal Saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through Enhanced Immunostimulation in Experimental Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Induction of Apoptosis in the A549 Cell Line. Molecules. 2013; 18(10):12916-12936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012916
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu, Jun-Fei Gu, Xi Zou, Jian Wu, Ming-Hua Zhang, Jun Jiang, Dong Qin, Jin-Yong Zhou, Bao-Xin-Zi Liu, Yun-Tao Zhu, and et al. 2013. "The Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Steroidal Saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through Enhanced Immunostimulation in Experimental Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Induction of Apoptosis in the A549 Cell Line" Molecules 18, no. 10: 12916-12936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012916
APA StyleLi, Y., Gu, J.-F., Zou, X., Wu, J., Zhang, M.-H., Jiang, J., Qin, D., Zhou, J.-Y., Liu, B.-X.-Z., Zhu, Y.-T., Jia, X.-B., Feng, L., & Wang, R.-P. (2013). The Anti-Lung Cancer Activities of Steroidal Saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var. chinensis (Franch.) Hara through Enhanced Immunostimulation in Experimental Lewis Tumor-Bearing C57BL/6 Mice and Induction of Apoptosis in the A549 Cell Line. Molecules, 18(10), 12916-12936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012916




