Antiproliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells by Ethanolic Extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxicity Effects of EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells
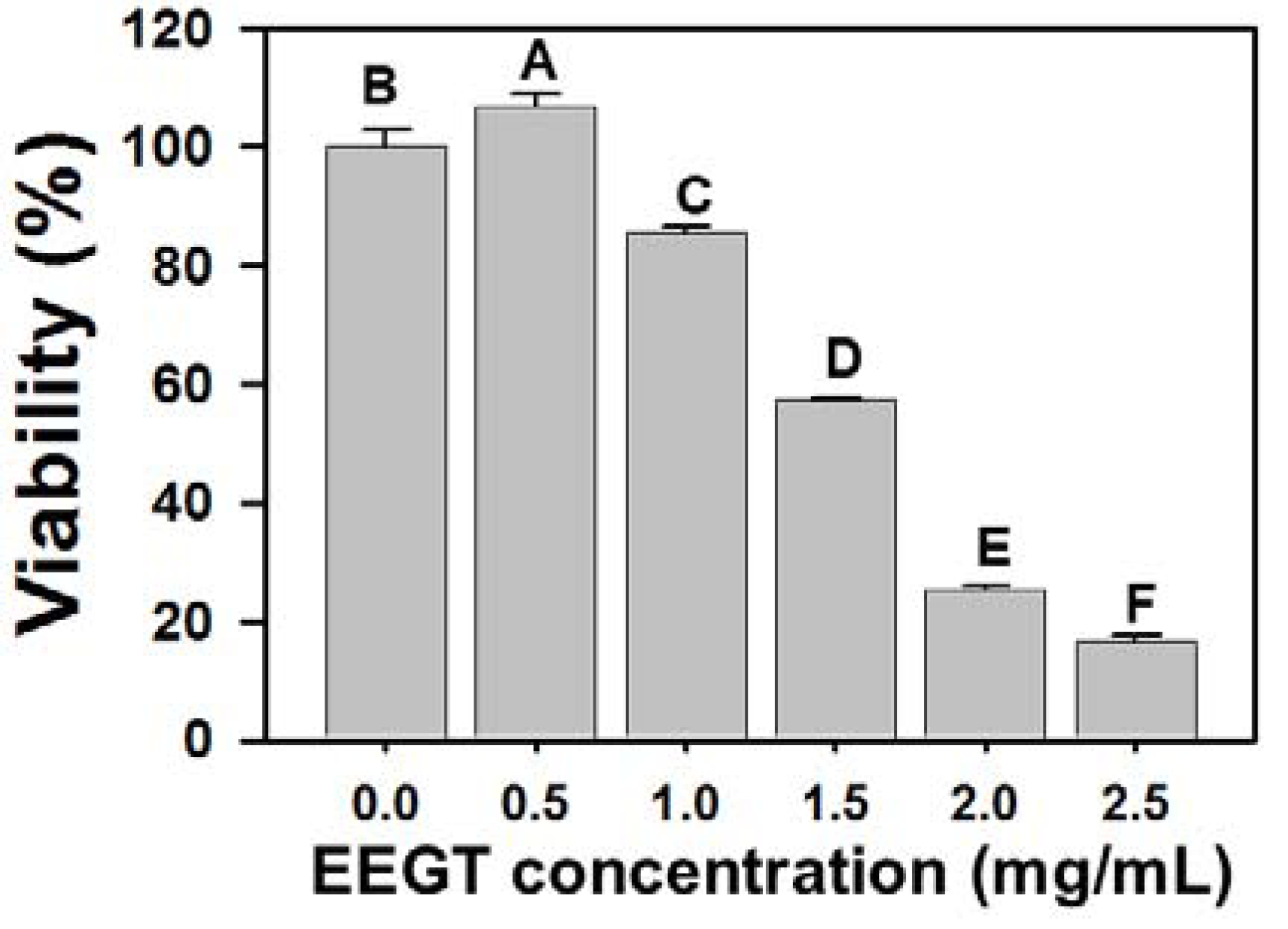
2.2. Apoptosis Induction of EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cells

2.3. Activation of Pan-Caspase in EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells
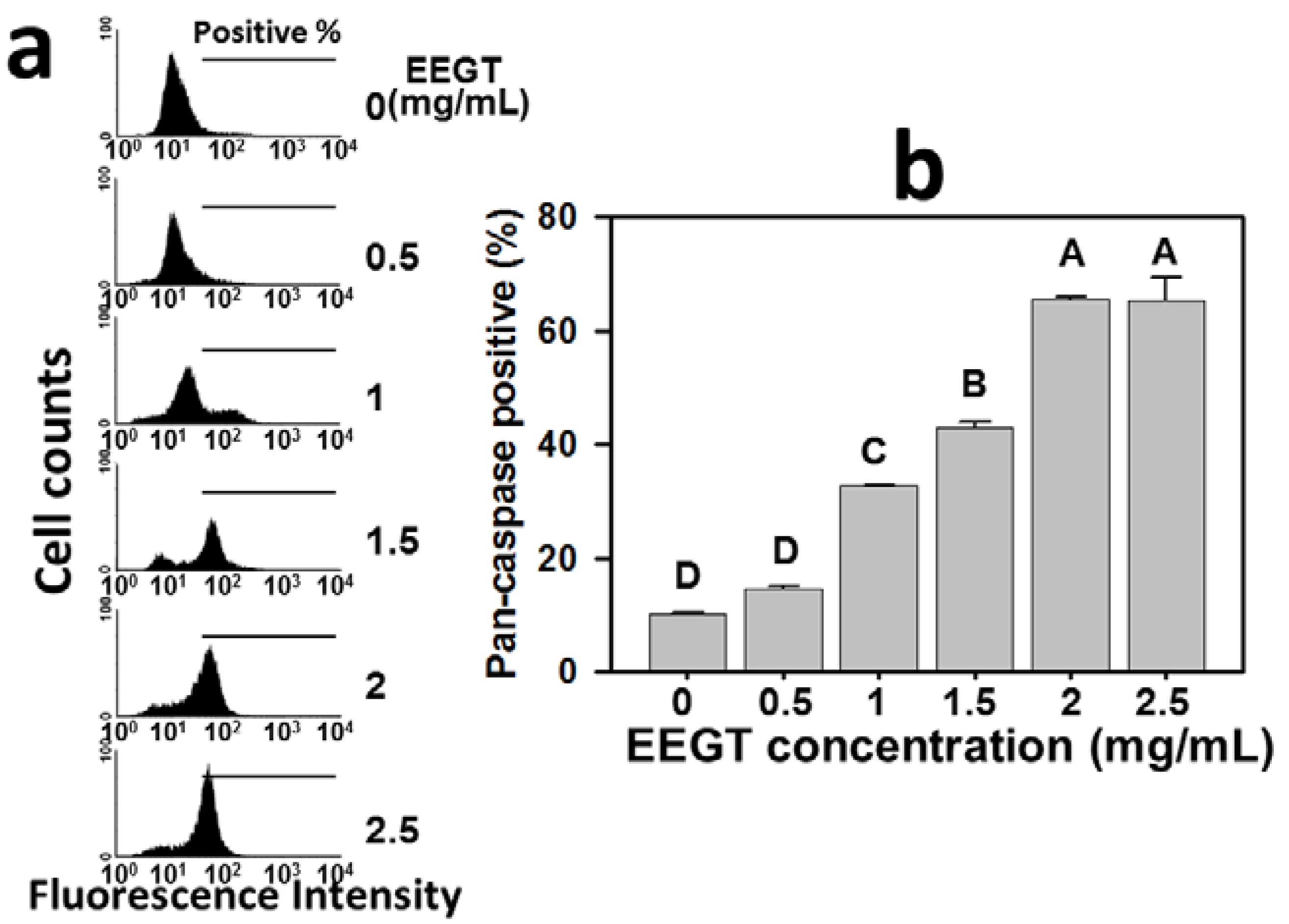
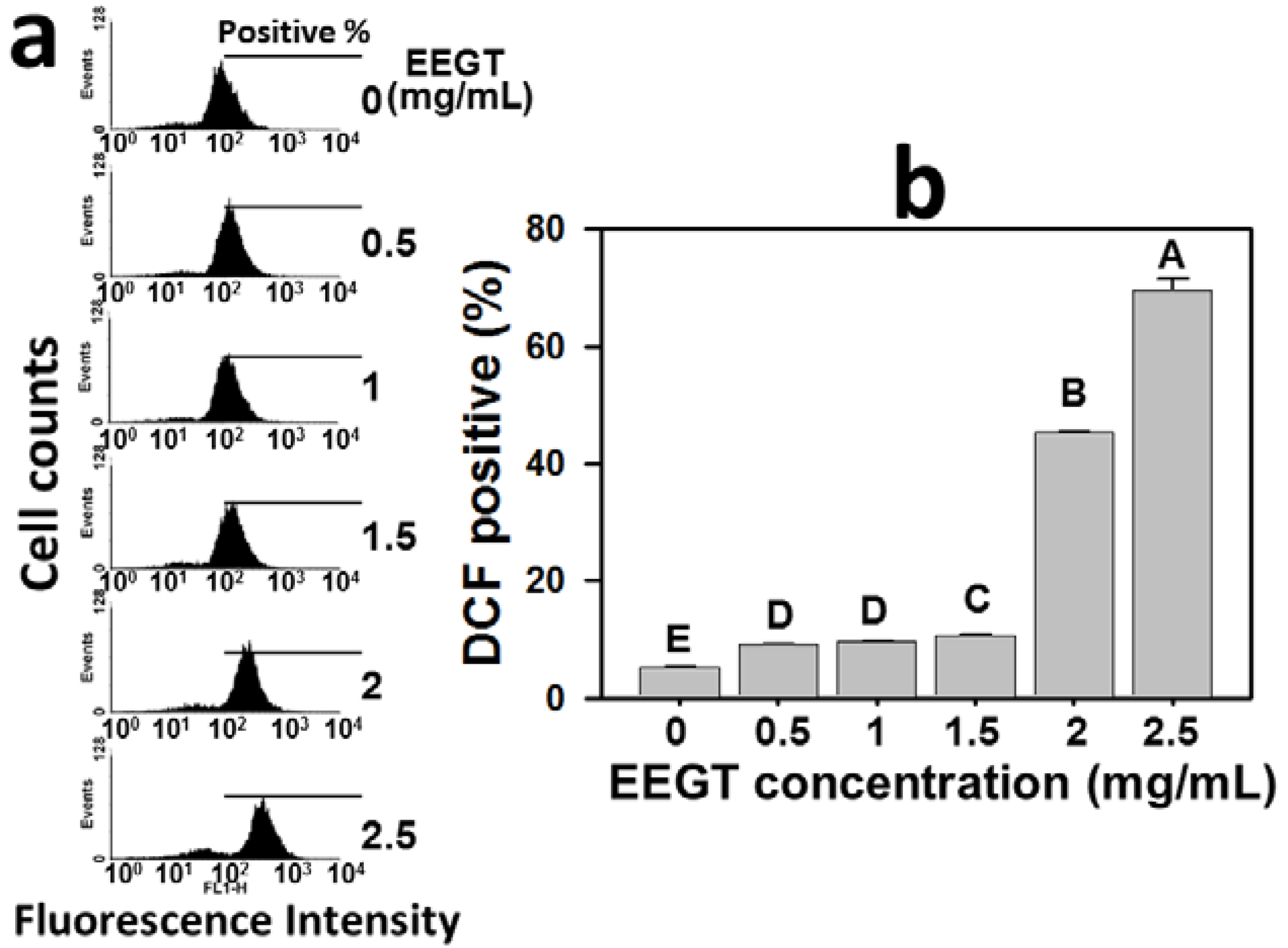
2.4. Induction of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells
2.5. Depletion of Intracellular Reduced Glutathione (GSH) in EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells
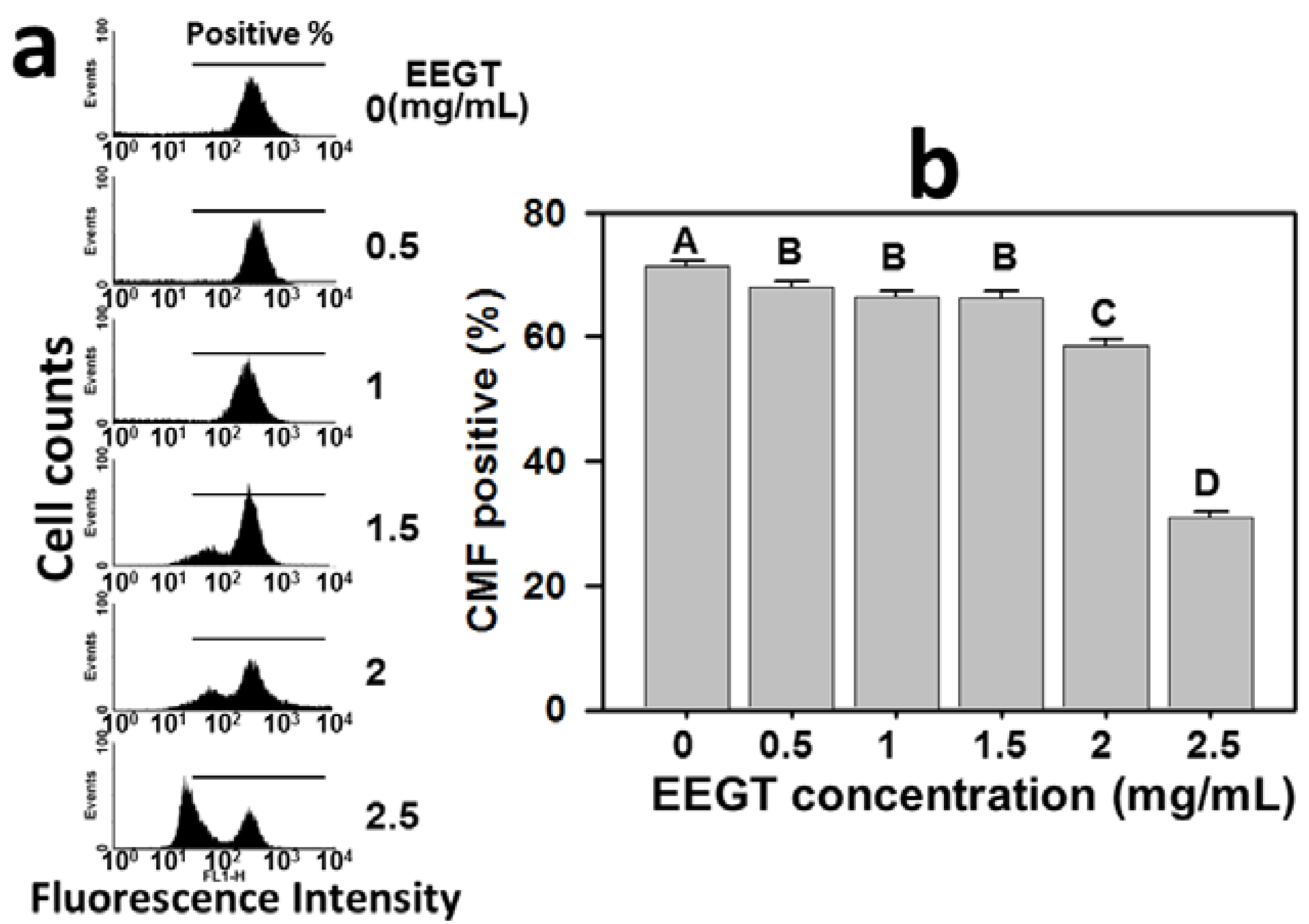
2.6. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Decrease in EEGT-Treated Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells
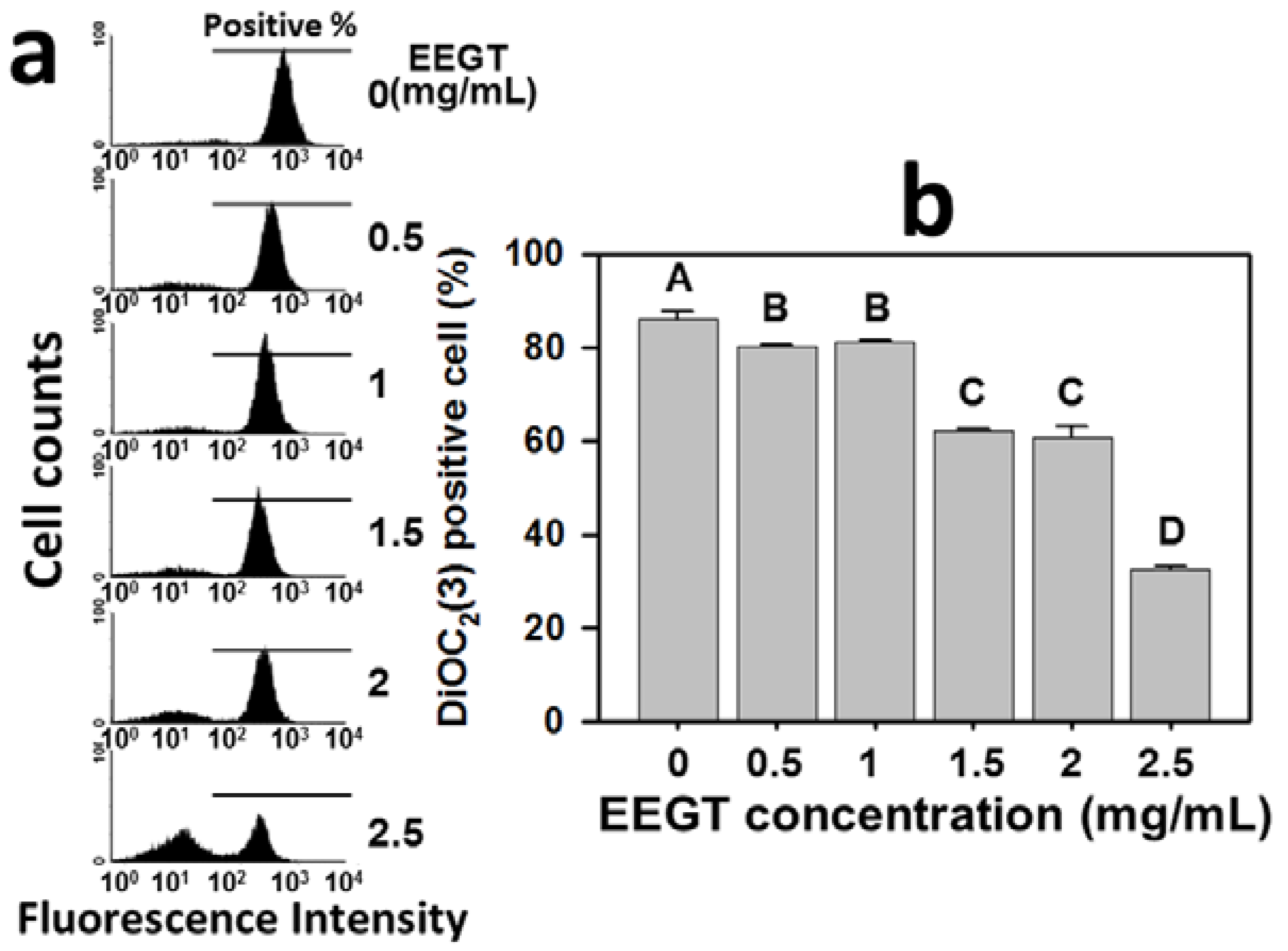
2.7. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Raw Materials and Ethanol Extract Preparation
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
3.4. Apoptosis Assay
3.5. Pan-Caspase Activity Assay
3.6. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
3.7. Intracellular Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Assay
3.8. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.W.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Gupta, P.C.; Dimba, E.; Chindia, M.; Otoh, E.C.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Califano, J.; Kowalski, L. Global oral health inequalities in incidence and outcomes for oral cancer: Causes and solutions. Adv. Dent. Res. 2011, 23, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, C.; Bagan, J. Oral squamous cell carcinoma overview. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myoung, H.; Hong, S.P.; Yun, P.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.J. Anti-cancer effect of genistein in oral squamous cell carcinoma with respect to angiogenesis and in vitro invasion. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.K. Marine antitumor drugs: Status, shortfalls and strategies. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2702–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Jimenez, G.M.; Burgos-Hernandez, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: Sources from marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajisaka, T.; Chiang, Y.M. Recent status of Gracilaria cultivation in Taiwan. Hydrobiologia 1993, 260/261, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.L.; Falcao Hde, S.; Lima, G.R.; Montenegro Cde, A.; Lira, N.S.; de Athayde-Filho, P.F.; Rodrigues, L.C.; de Souza Mde, F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Batista, L.M. Bioactivities from marine algae of the genus gracilaria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 4550–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.I.; Yeh, C.C.; Lee, J.C.; Yi, S.C.; Huang, H.W.; Tseng, C.N.; Chang, H.W. Aqueous extracts of the edible Gracilaria tenuistipitata are protective against H2O2-induced DNA damage, growth inhibition, and cell cycle arrest. Molecules 2012, 17, 7241–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravan, J.; Mosafa, F.; Soudmand, N.; Taghiabadi, E.; Razavi, B.M.; Karimi, G. Protective effects of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Portulaca oleracea L. aerial parts on H2O2-induced DNA damage in lymphocytes by comet assay. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2011, 4, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Li, R.X.; Chuang, L.Y. Antioxidant activity of various parts of Cinnamomum cassia extracted with different extraction methods. Molecules 2012, 17, 7294–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang extract inhibits MCF-7 cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle G2/M arrest. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 579–586. [Google Scholar]
- Bechelli, J.; Coppage, M.; Rosell, K.; Liesveld, J. Cytotoxicity of algae extracts on normal and malignant cells. Leukemia Res. Treat. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szliszka, E.; Czuba, Z.P.; Domino, M.; Mazur, B.; Zydowicz, G.; Krol, W. Ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) enhances the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in cancer cells. Molecules 2009, 14, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Tsang, S.F.; Chyuan, J.H.; Hsu, H.Y. Induction of apoptosis by ethanolic extract of Corchorus olitorius leaf in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells via a mitochondria-dependent pathway. Molecules 2012, 17, 9348–9360. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Morgan, W.A.; Sanchez-Medina, A.; Corcoran, O. The ethanol extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and the active compounds induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis including upregulation of p53 and Bax in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, J.; Ma, A.G.; Zhang, P.H.; Bi, S.L.; Shi, D.Y. Effect of ethanol extract of alga Laurencia supplementation on DNA oxidation and alkylation damage in mice. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16 (Suppl. 1), 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Madkour, F.F.; Khalil, W.F.; Dessouki, A.A. Protective effect of ethanol extract of Sargassum dentifolium (Phaeophyceae) in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 637–641. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y. Apoptosis-based anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Lipinski, M.; Yuan, J.; Kroemer, G. Cell death assays for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 221–237. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.C.; Yang, J.I.; Lee, J.C.; Tseng, C.N.; Chan, Y.C.; Hseu, Y.C.; Tang, J.Y.; Chuang, L.Y.; Huang, H.W.; Chang, F.R.; et al. Anti-proliferative effect of methanolic extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata on oral cancer cells involves apoptosis, DNA damage, and oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.H.; Li, C.M.; Yang, Z.Y.; Che, D.H.; Cao, J.Y.; Yu, Y. Luffa echinata Roxb. induces human colon cancer cell (HT-29) death by triggering the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Molecules 2012, 17, 5780–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Chang, H.W.; Chuang, D.W.; Chang, F.R.; Chang, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.S.; Tsai, M.T.; Chen, W.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Wang, C.K.; et al. Fern plant-derived protoapigenone leads to DNA damage, apoptosis, and G(2)/m arrest in lung cancer cell line H1299. DNA Cell Biol. 2009, 28, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, J.Y.; Hwang, C.C.; Hseu, Y.C.; Yang, H.L.; Lee, A.Y.; Tsai, M.T.; Guo, Z.L.; et al. 4beta-Hydroxywithanolide E from Physalis peruviana (golden berry) inhibits growth of human lung cancer cells through DNA damage, apoptosis and G2/M arrest. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Gu, C.; Wang, W.; Yao, L.; Efferth, T. Dryofragin, a phloroglucinol derivative, induces apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 199, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T.; Lu, C.C.; Yang, J.S.; Chiang, J.H.; Li, T.C.; Ip, S.W.; Hsia, T.C.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, J.G.; Wood, W.G.; et al. Berberine induced apoptosis via promoting the expression of caspase-8, -9 and -3, apoptosis-inducing factor and endonuclease G in SCC-4 human tongue squamous carcinoma cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4063–4070. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Haung, R.W.; Yeh, C.C.; Huang, K.J.; Chang, K.F.; Hseu, Y.C.; Chang, F.R.; Chang, H.W.; Wu, Y.C. Antiproliferative effects of goniothalamin on Ca9-22 oral cancer cells through apoptosis; DNA damage and ROS induction. Mutat. Res. 2012, 747, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, S. Targeting apoptosis: Selected anticancer strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 971–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.D.; Kim, J.Y. Essential oil from Cryptomeria japonica induces apoptosis in human oral epidermoid carcinoma cells via mitochondrial stress and activation of caspases. Molecules 2012, 17, 3890–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cordero, C.; Leon-Gonzalez, A.J.; Calderon-Montano, J.M.; Burgos-Moron, E.; Lopez-Lazaro, M. Pro-oxidant natural products as anticancer agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1006–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, A.J.; Jassem, J. Cellular redox pathways as a therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Drugs 2011, 71, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondrak, G.T. Redox-directed cancer therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms and opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2009, 11, 3013–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Yi, F.; Rasul, A.; Li, T.; Wang, N.; Gao, H.; Gao, R.; Ma, T. Alantolactone induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells via GSH depletion, ROS generation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, P. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and rapid depletion of mitochondrial glutathione by beta-phenethyl isothiocyanate: Mechanisms for anti-leukemia activity. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2011, 15, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, P.L.; Weng, B.C.; Lu, F.J.; Lin, M.L.; Chang, T.T.; Hung, R.P.; Chen, C.H. The anticancer effect of protein-extract from Bidens alba in human colorectal carcinoma SW480 cells via the reactive oxidative species- and glutathione depletion-dependent apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Huang, Y.T.; Wu, M.L.; Huang, T.C.; Ho, C.T.; Pan, M.H. Induction of apoptosis by vitamin D2, ergocalciferol, via reactive oxygen species generation, glutathione depletion, and caspase activation in human leukemia cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2996–3005. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.A.; Kim, J.J.; Choi, E.S.; Shim, J.H.; Ryu, M.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Park, H.M.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lim, D.W.; et al. In vitro apoptotic effects of methanol extracts of Dianthus chinensis and Acalypha australis L. targeting specificity protein 1 in human oral cancer cells. Head Neck 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Liu, P.L.; Huang, K.J.; Wang, H.M.; Chang, K.F.; Chou, C.K.; Chang, F.R.; Chong, I.W.; Fang, K.; Chen, J.S.; et al. Goniothalamin inhibits growth of human lung cancer cells through DNA damage, apoptosis, and reduced migration ability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4288–4293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-N.; Yang, J.-I.; Huang, H.-W.; Fang, Y.; Tang, J.-Y.; Chang, F.-R.; Chang, H.-W. Antiproliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells by Ethanolic Extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Molecules 2012, 17, 10916-10927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910916
Yeh C-C, Tseng C-N, Yang J-I, Huang H-W, Fang Y, Tang J-Y, Chang F-R, Chang H-W. Antiproliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells by Ethanolic Extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Molecules. 2012; 17(9):10916-10927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910916
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Chi-Chen, Chao-Neng Tseng, Jing-Iong Yang, Hurng-Wern Huang, Yi Fang, Jen-Yang Tang, Fang-Rong Chang, and Hsueh-Wei Chang. 2012. "Antiproliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells by Ethanolic Extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata" Molecules 17, no. 9: 10916-10927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910916
APA StyleYeh, C.-C., Tseng, C.-N., Yang, J.-I., Huang, H.-W., Fang, Y., Tang, J.-Y., Chang, F.-R., & Chang, H.-W. (2012). Antiproliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Ca9-22 Oral Cancer Cells by Ethanolic Extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Molecules, 17(9), 10916-10927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910916





