Cloning, Phylogenetic Analysis and 3D Modeling of a Putative Lysosomal Acid Lipase from the Camel, Camelus dromedarius
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning of the cLIPA and Sequence Identity

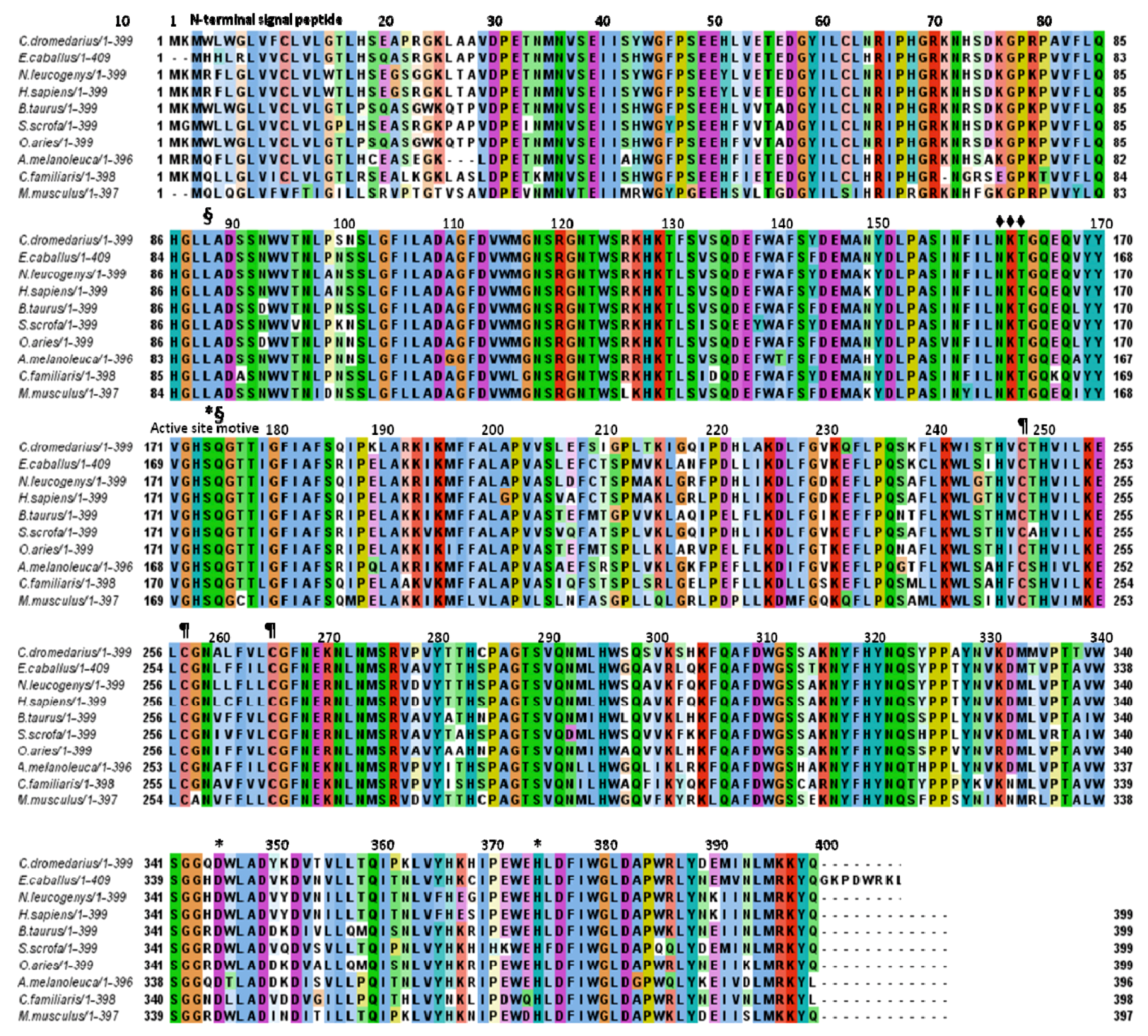
2.2. Aminoacid Composition of cLIPA, Sequence Identity and Phylogenetic Analysis
| Amino Acid | Number count | % by weight | % by frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ala (A) | 22 | 3.43 | 5.51 |
| Cys (C) | 6 | 1.36 | 1.50 |
| Asp (D) | 19 | 4.80 | 4.76 |
| Glu (E) | 16 | 4.53 | 4.01 |
| Phe (F) | 23 | 7.43 | 5.76 |
| Gly (G) | 26 | 3.25 | 6.52 |
| His (H) | 17 | 5.12 | 4.26 |
| Ile (I) | 20 | 4.97 | 5.01 |
| Lys (K) | 26 | 7.31 | 6.52 |
| Leu (L) | 39 | 9.68 | 9.77 |
| Met (M) | 12 | 3.45 | 3.01 |
| Asn (N) | 21 | 5.26 | 5.26 |
| Pro (P) | 21 | 4.47 | 5.26 |
| Gln (Q) | 16 | 4.50 | 4.01 |
| Arg (R) | 9 | 3.08 | 2.26 |
| Ser (S) | 30 | 5.73 | 7.52 |
| Thr (T) | 19 | 4.21 | 4.76 |
| Val (V) | 27 | 5.87 | 6.77 |
| Trp (W) | 15 | 6.13 | 3.76 |
| Tyr (Y) | 15 | 5.37 | 3.76 |
| Charged aminoacids (RKHYCDE) | 108 | 31.57 | 27.07 |
| Acidic (DE) | 35 | 9.33 | 8.77 |
| Basic (KR) | 35 | 10.40 | 8.77 |
| Polar (NCQSTY) | 107 | 26.43 | 26.82 |
| Hydrophobic (AILFWV) | 146 | 37.51 | 36.59 |
| APEX1 | (Ref. Seq) | Aminoacid Residues | Total score | Identity (%) | Positive (%) | Gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camelus dromedarius | AEG75815 | 399 | 835 | 100 | 100 | 0 |
| Nomascus leucogenys | XP_003255244 | 399 | 716 | 85 | 91 | 0 |
| Homo sapiens | AAB60328 | 399 | 716 | 84 | 90 | 0 |
| Equus caballus | XP_001503012 | 409 | 714 | 86 | 91 | 0 |
| Bos taurus | DAA14963 | 399 | 697 | 82 | 89 | 0 |
| Sus scrofa | NP_001116606 | 399 | 693 | 84 | 91 | 0 |
| Ovis aries | NP_001119818 | 399 | 692 | 81 | 89 | 0 |
| Ailuropoda melanoleuca | XP_002914448 | 398 | 679 | 79 | 88 | 3 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | XP_003639974 | 398 | 664 | 77 | 89 | 1 |
| Mus musculus | NP_067435 | 397 | 652 | 76 | 86 | 0 |
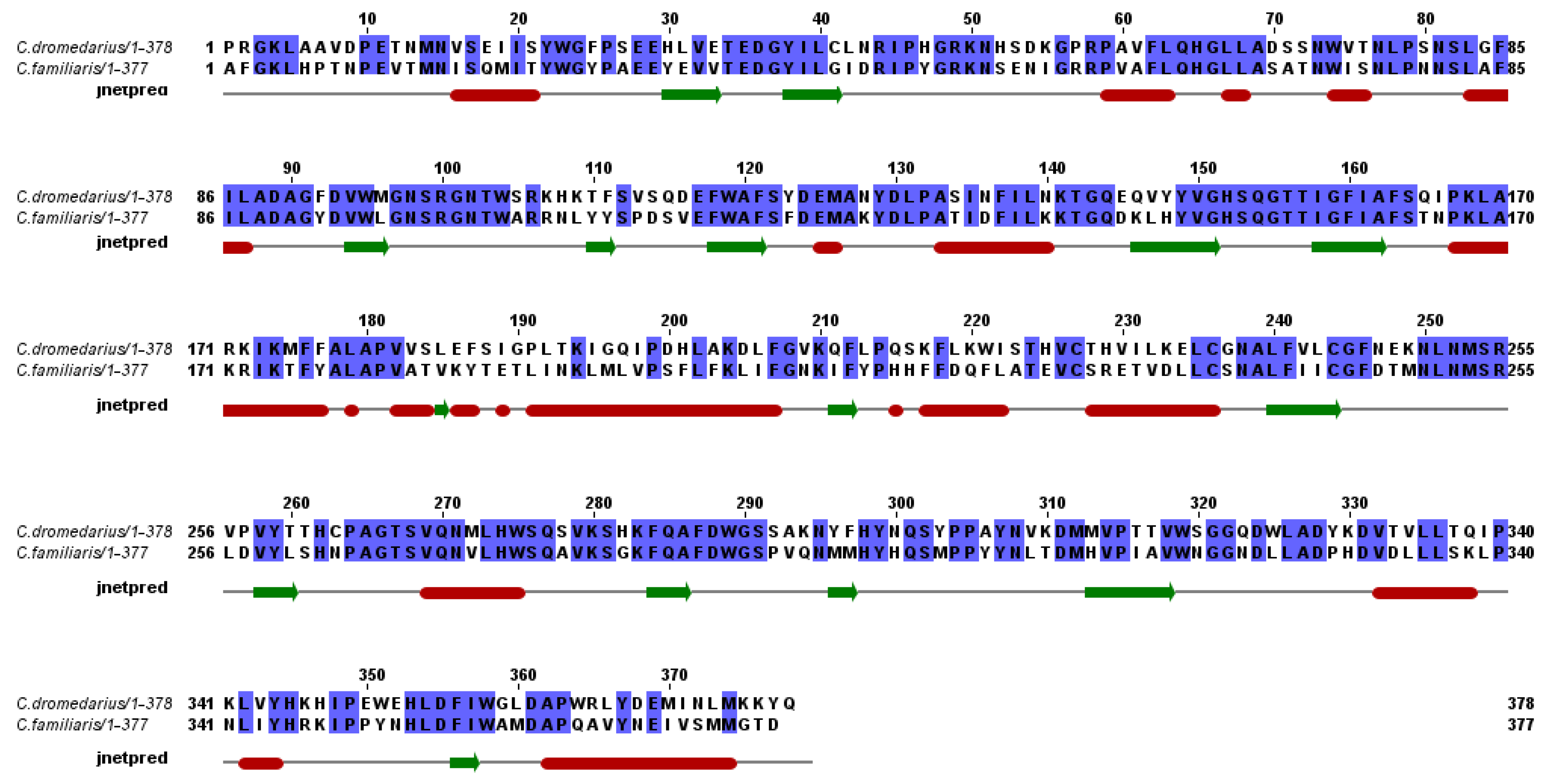
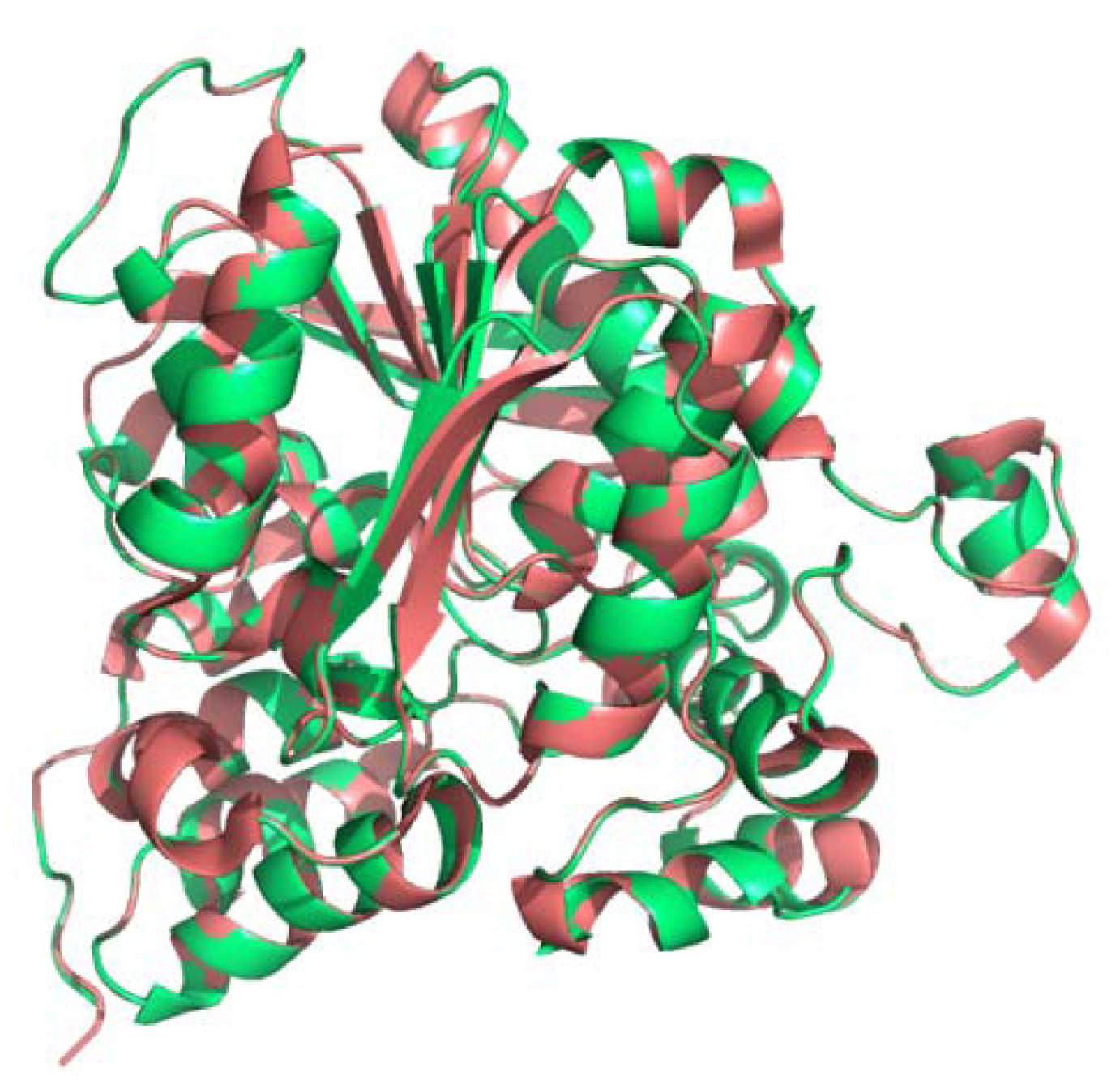
2.3. Secondary and 3D Structure Modeling of cLIPA Compared with Human and Dog Gastric Lipase
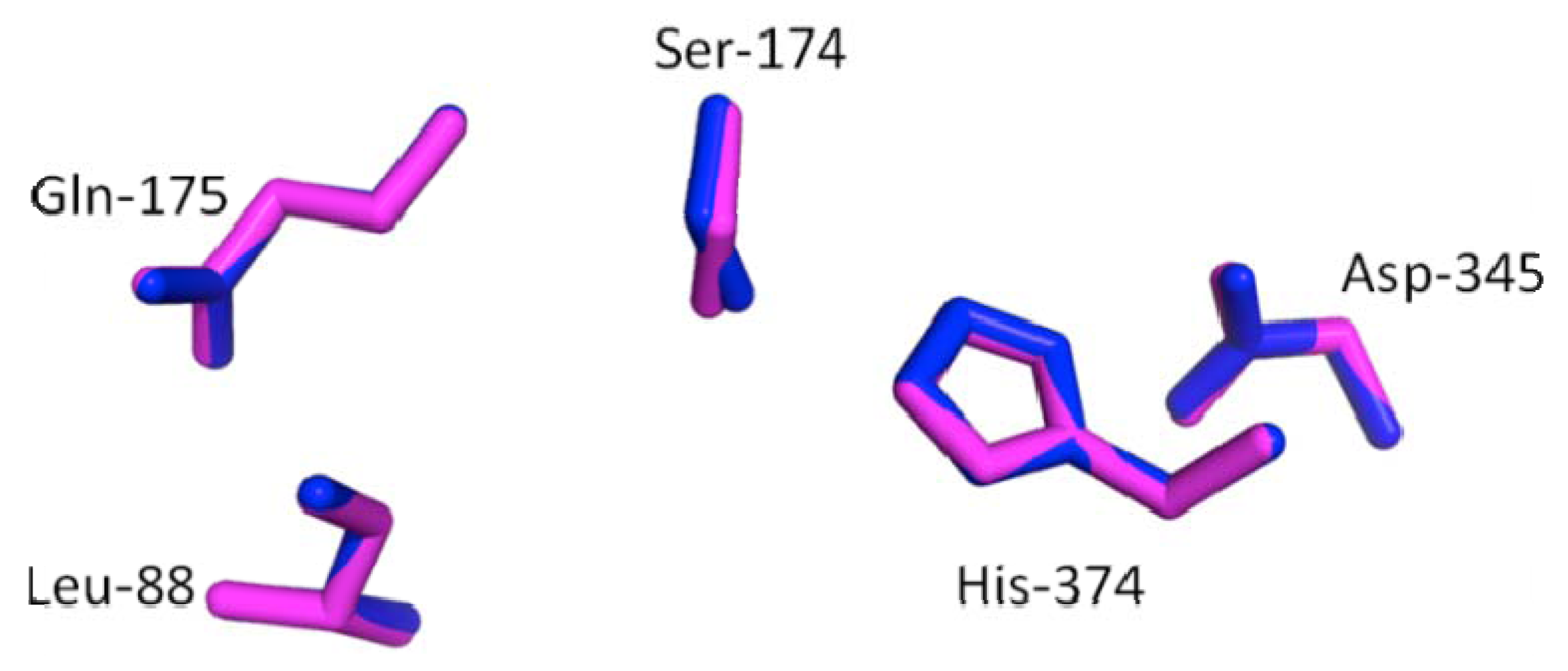
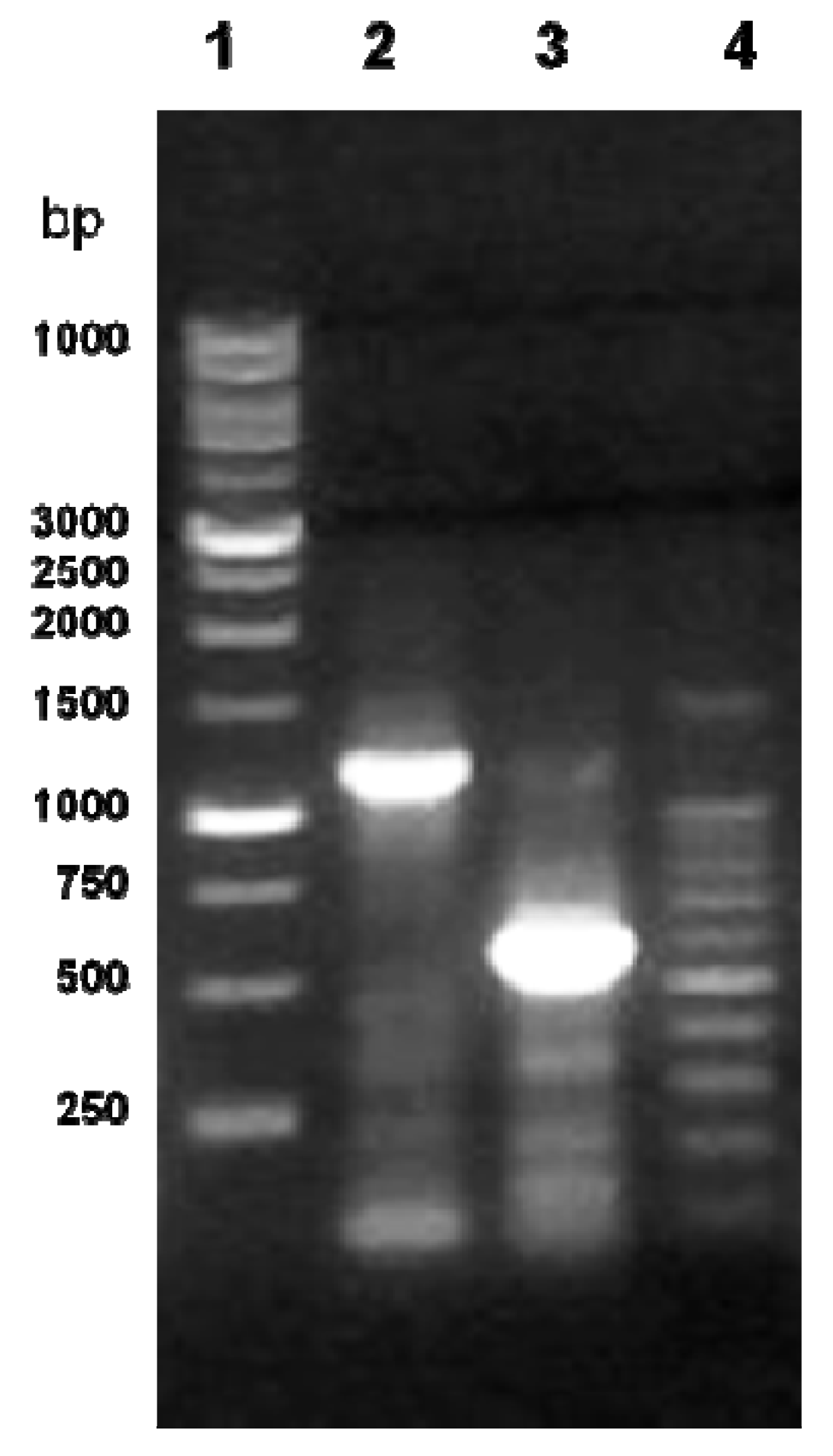
2.4. The Level of cLIPA Expression
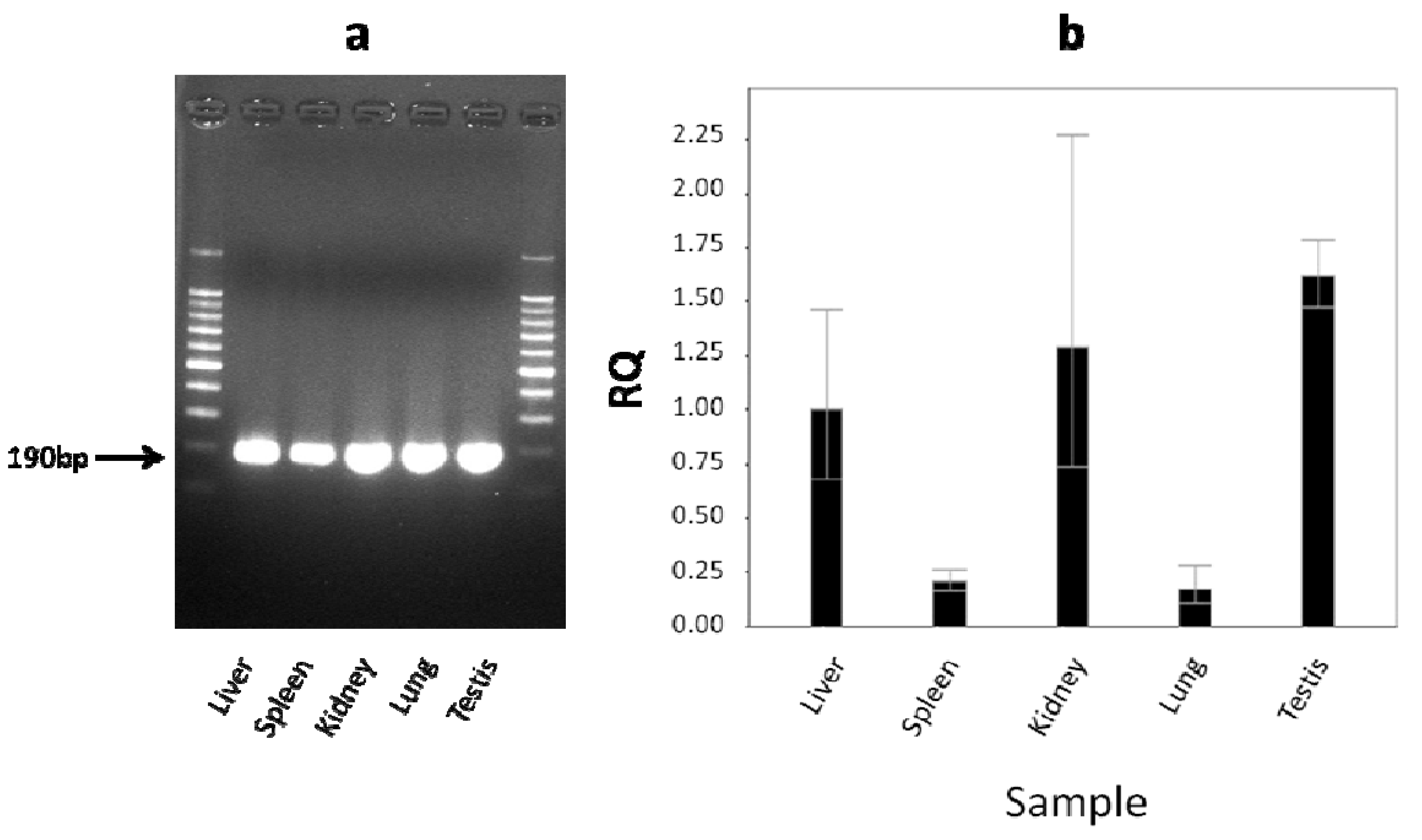
3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Oligonucleotide Design
| Primer couple | Primer | Primer sequence | Product (bp) | Annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full coding region | LALF1 | ATGAAAATGTGGCTCTGGGGTTTG | 1200 | 55 |
| LALR1 | AAGCTTTCACTGGTACTTCTTCATTAG | |||
| Internal primers | LALF2 | GAGATGGCAAATTATGACCTACCC | 540 | 55 |
| LALR2 | ATGACCCCCGCTCCAGACAG | |||
| qPCR | LALqF | CTTTGCCTTAACCGAATCCCTCAT | 190 | 57 |
| LALqR | TGTTCCCCTGCTATTCCCCATCC |
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. PCR and Cloning
4.4. Gene Expression
4.5. DNA Sequencing and Prediction of Aminoacid Sequence
4.6. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Analysis of Phylogenetic Relationship
4.7. Secondary and Prediction of the 3D Structure of cLIPA
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Holmes, R.S.; Cox, L.A.; VandeBerg, J.L. Comparative studies of mammalian acid lipases: Evidence for a new gene family in mouse and rat (Lipo). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genomics Proteomics 2010, 5, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, H.; Gargouri, Y.; Lecat, D.; Junien, J.L.; Verger, R. Screening of preduodenal lipases in several mammals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 959, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénicourt, C.; Blanchard, C.; Carrière, F.; Verger, R.; Junien, J.L. Potential use of a recombinant dog gastric lipase as an enzymatic supplement to pancreatic extracts in cystic fibrosis. In Clinical Ecology of Cystic Fibrosis; Escobar, H., Baquero, C.F., Suárez, L., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Carrière, F.; Moreau, H.; Raphel, V.; Laugier, R.; Benicourt, C.; Junien, J.L.; Verger, R. Purification and biochemical characterization of dog gastric lipase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 202, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, M.E. Structure and function of pancreatic lipase and colipase. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1977, 46, 897–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, G.; Seedorf, U. Acid lipase deficiency: Wolman disease and cholesteryl ester storage disease. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Childs, B., Kinzler, K., Vogelstein, B., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 3551–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Kadim, I.T.; Mahgoub, O.; Purchas, R.W. A review of the growth, and of the carcass and meat quality characteristics of the one-humped camel (Camelus dromedaries). Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, A.; Canaan, S.; Egloff, M.P.; Rivière, M.; Dupuis, L.; Verger, R.; Cambillau, C. Crystal structure of human gastric lipase and model of lysosomal acid lipase, two lipolytic enzymes of medical interest. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16995–16702. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, A.; Miled, N.; Berti-Dupuis, L.; Rivière, M.; Spinelli, S.; Berna, P.; Gruber, V.; Verger, R.; Cambillau, C. Crystal structure of the open form of dog gastric lipase in complex with a phosphonate inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, S.; Ohno, K.; Suzuki, T.; Sakuraba, H. Structural bases of Wolman disease and cholesteryl ester storage disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 105, 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ataya, F.S.; Fouad, D.; Malik, A.; Saeed, H.M. Molecular cloning and 3D structure modeling of APEX1, DNA base excision repair enzyme from the camel, Camelus dromedarius. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8578–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataya, F.S.; Fouad, D.; Al-Olayan, E.; Malik, A. Molecular cloning, characterization and predicted structure of a putative copper-zinc SOD1 from the camel, Camelus dromedarius. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 879–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataya, F.S.; Alanazi, M.; Fouad, D.; Saeed, H.M.; Bazzi, M.D. Molecular cloning and characterization of a putative OGG_N domain from the camel, Camelus dromedarius. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 7803–7811. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, M.S.; Saeed, H.M.; Ataya, F.S.; Bazzi, M.D. Molecular characterization of the Camelus dromedarius putative cytochrome P450s genes. Protein J. 2010, 29, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seqman, version 5.07; Matching nucleotide sequences; DNASTAR Inc: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- PROTEAN, version 5.07; Molecular analysis of protein; DNASTAR Inc: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- MAFFT, version 6.864; Multiple Sequence Alignment program; Computational Biology Research Center (CBRC): Tokyo, Japan, 2011.
- Jalview, version 2.3; Multiple Sequence Alignment; University of Dundee: Scotland, UK, 2011.
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PyMOL, version 0.99; Superimposition of 3D protein structure; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2006.
- EMBL-EBI. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/ssm/cgi-bin/ssmserver (accessed on 9 August 2012).
- Zschenker, O.; Oezden, D.; Ameis, D. Lysosomal acid lipase as a preproprotein. J. Biochem. 2004, 136, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleat, D.E.; Zheng, H.; Qian, M.; Lobel, P. Identification of sites of mannose 6-phosphorylation on lysosomal proteins. Mol. Cell Prot. 2006, 5, 686–701. [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda, Z.S.; Derewenda, U. Relationships among serine hydrolases: Evidence for a common structural motif in triacylglyceride lipases and esterases. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1991, 69, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameis, D.; Merkel, M.; Eckerskorn, C.; Greten, H. Purification, characterization and molecular cloning of human hepatic lysosomal acid lipase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 219, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J.; et al. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Dana, S.E.; Faust, J.R.; Beaudet, A.L.; Brown, M.S. Role of lysosomal acid lipase in the metabolism of plasma low density lipoprotein. Observations in cultured fibroblasts from a patient with cholesteryl ester storage disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, 8487–8495. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science 1976, 191, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Wahala, K.; Adlercreutz, H.; Ikonen, E.; Tikkanen, M.J. Role of lysosomal acid lipase in the intracellular metabolism of LDL-transported dehydroepiandrosterone-fatty acyl esters. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrin. Metab. 2008, 295, E1455–E1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargouri, Y.; Moreau, H.; Verger, R. Gastric lipases: Biochemical and physiological studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1006, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, F.; Pariyarath, R.; Stuani, C.; Garcia, R.; Baralle, F.E. Cysteine residues in human lysosomal acid lipase are involved in selective cholesteryl esterase activity. Biochem. J. 1997, 326, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R.S.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Cox, L.A. Genomics and proteomics of vertebrate cholesterol ester lipase (LIPA) and cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H). 3 Biotech 2011, 1, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Witte, D.P.; Grabowski, G.A. Tissue and cellular specific expression of murine lysosomal acid lipase mRNA and protein. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 937–949. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.; Manaiatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ataya, F.S. Cloning, Phylogenetic Analysis and 3D Modeling of a Putative Lysosomal Acid Lipase from the Camel, Camelus dromedarius. Molecules 2012, 17, 10399-10413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910399
Ataya FS. Cloning, Phylogenetic Analysis and 3D Modeling of a Putative Lysosomal Acid Lipase from the Camel, Camelus dromedarius. Molecules. 2012; 17(9):10399-10413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910399
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtaya, Farid Shokry. 2012. "Cloning, Phylogenetic Analysis and 3D Modeling of a Putative Lysosomal Acid Lipase from the Camel, Camelus dromedarius" Molecules 17, no. 9: 10399-10413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910399
APA StyleAtaya, F. S. (2012). Cloning, Phylogenetic Analysis and 3D Modeling of a Putative Lysosomal Acid Lipase from the Camel, Camelus dromedarius. Molecules, 17(9), 10399-10413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910399





