Ameliorative Effects of Curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on Learning and Memory in Aged Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
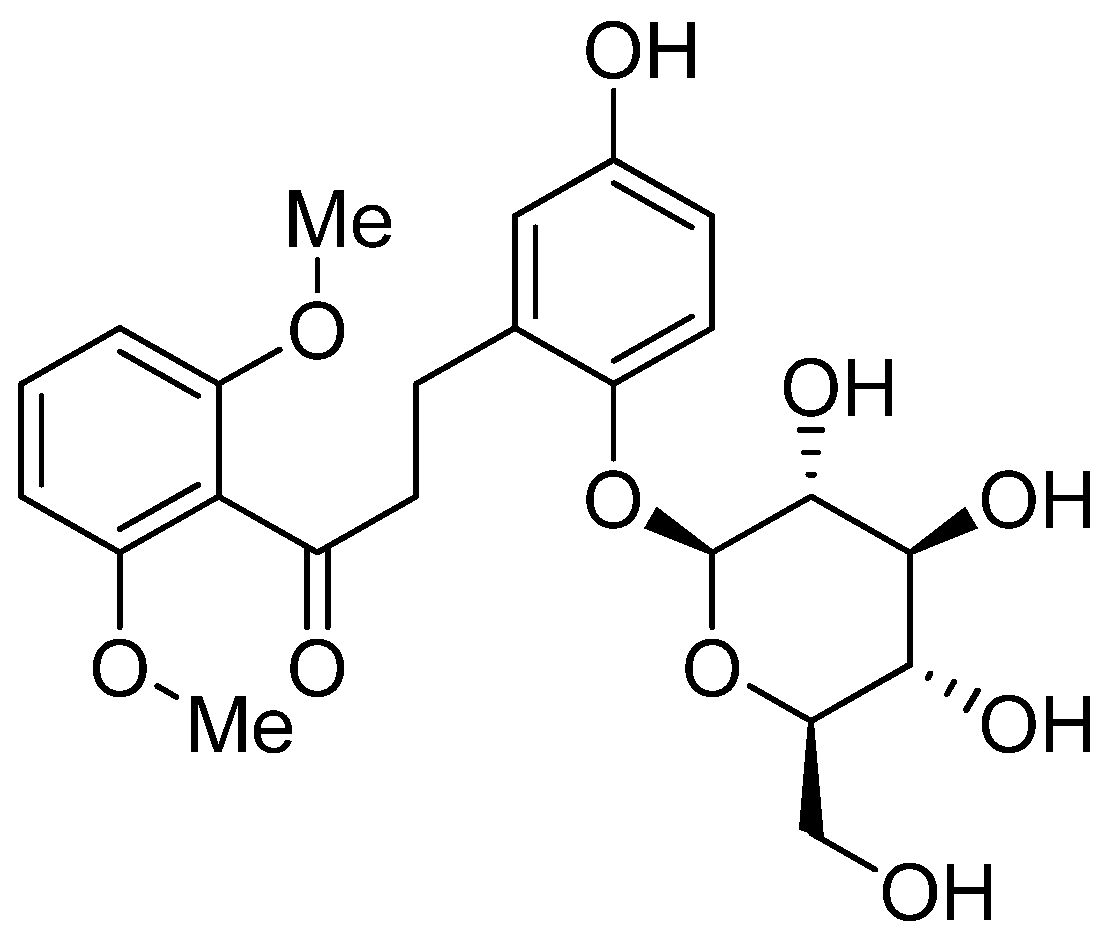
2. Results and Discussion
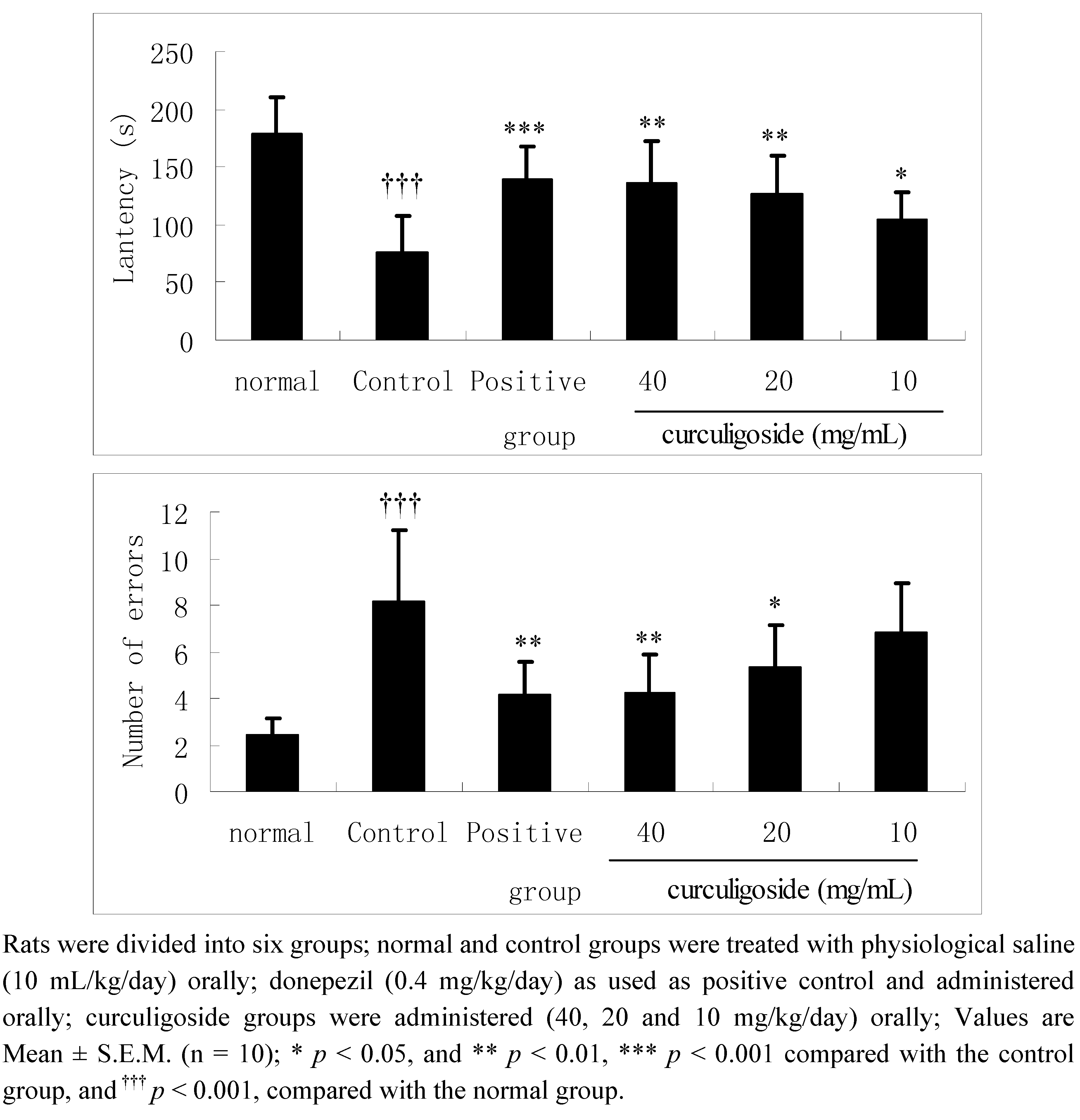
2.1. Effects of Curculigoside on Learning Performances in Aged Rats in the Step-Down Test
2.2. Effects of Curculigoside on Learning Performances in Aged Rats in the Y-Maze Test

2.3. Effects of Curculigoside on Cerebral Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.4. Effect of Curculigoside on Expressions of BACE1


2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Animals
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Drugs and Chemicals
3.5. Analysis of Curculigoside
3.6. Protocols
3.7. Preparation of AD Model Rats and Grouping
3.8. Step-Down Test
3.9. Y-maze Test
3.10. Measurement of AchE Activity
3.11. Western Blotting for Determination of BACE1Expression
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of interest
References
- Um, M.Y.; Choi, W.H.; Aan, J.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Ha, T.Y. Protective effect of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb on amyloid β-peptide 25–35 induced cognitive deficits in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankner, B.A. Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1996, 16, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirths, O.; Multhaup, G.; Bayer, T.A. A modified beta-amyloid hypothesis: intraneuronal accumulation of the beta-amyloid peptide-the first step of a fatal cascade. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.P.; Han, G.C.; Feng, X.M.; Sun, J.Y.; Duan, Y.; Lei, H.X. Concerted perturbation observed in a hub network in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40498. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.G.; Zhu, X.; Castellani, R.J.; Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Amyloidbeta in Alzheimer disease: The null versus the alternate hypothesis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2009 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzherimers Dement 2009, 5, 234–270. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Yang, X.L.; Cai, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, X.X.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.P.; Zhao, X.; et al. Proanthocyanidins from Grape Seeds Modulate the NF-κB Signal Transduction Pathways in Rats with TNBS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Molecules 2011, 16, 6721–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Han, T.; Xin, W.B.; Zhang, X.G.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jia, M.; Qin, L.P. Comparative research of chemical constituents and bioactivities between petroleum ether extracts of the aerial part and the rhizome of Atractylodes macrocephala. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafna, A.R.; Mishra, S.H. Immunostimulatory effect of methanol extract of Curculigo orchioides on immunosuppressed mice. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanarayana, K.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Chandrashekhar, K.S.; Subrahmanyama, E.V.S. Evaluation of estrogenic activity of alcoholic extract of rhizomes of Curculigo orchioides. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, P.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Kumar, N.S.; Nema, N.K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Fukui, H. Mast cell stabilization and antihistaminic potentials of Curculigo orchioides rhizomes. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Pandey, K.; Puri, A.; Saxena, R.P.; Saxena, K.C. Immunostimulant principles from Curculigo orchioides. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Hong, Y.J.; Wei, M.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.Q.; Chen, R.Z.; Chen, H.Z. Curculigoside attenuates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by H2O2. J.Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cheng, X.W.; Lei, G.Q.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, J.K.; Zhou, T.S. Effect of Curculigoside on free radical scavenging. Chin. JMAP 2007, 24, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Fu, F.; Tian, J.; Zhu, H.; Hou, J. Curculigoside A ateenuates experimental cerebral ischemia injury in vitro and vivo. Neuron 2011, 192, 572–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, H.; Prvulovic, D.; Teipel, S.; Jessen, F.; Luckhaus, C.; Frolich, L.; Riepe, M.W.; Dodel, R.; Leyhe, T.; Bertram, L.; et al. The future of Alzheimer’s disease: The next 10 years. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, T.; Yu, C.H.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.P.; Peng, C. Ameliorating effects of essential oil from Acori graminei rhizoma on learning and memory in aged rats and mice. J.Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrindast, M.R.; Khalilzadeh, A.; Malekmohammadi, N.; Fazli-Tabaei, S. Influence of morphine- or apomorphine-induced sensitization on histamine state-dependent learning in the step-down passive avoidance test. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 171, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.; Shearer, J.; Ritchie, C.W.; Zajicek, J.P. Model-Based Economic Evaluation in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Methods Available to Model Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Value Health 2011, 14, 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Myhrer, T. Neurotransmitter systems involved in learning and memory in the rat: A meta-analysis based on studies of four behavioral tasks. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 41, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelheber, A.M.; Sarter, M.; Bruno, J.P. Increases in cortical acetylcholine release during sustained attention performance in rats. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2000, 9, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, R.; Uehara, Y. Physostigmine and recent memory: Effects in young and aged nonhuman primates. Science 1979, 206, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, G.; Heyes, C.; Iversen, S. Pharmacological mechanisms and animal models of cognition. Behav. Pharmacol. 1992, 3, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. Overeview of Chinese research on senile dementia in mainland China. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9s, s6–s12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Xu, H.X. Molecular and cellular mechanisms for Alzheimer’s disease: Understanding APP metabolism. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.E.; Wang, W.Y.; Song, L.X.; Lee, J.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Wong, G. Measuring human β-secretase (BACE1) activity using homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 319, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Roberds, S.L.; Anderson, J.; Basi, G.; Bienkowski, M.J.; Branstetter, D.G.; Chen, K.S.; Freedman, S.; Frigon, N.L.; Games, D.; Hu, K.; et al. BACE knockout mice are healthy despite lacking the primary beta-secretase activity in brain: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.X.; Lei, G.Q.; Cheng, X.W.; Chen, J.K.; Zhou, T.S. Curculigoside C, a new phenolic glucoside from Rhizomes of Curculigo orchioides. Acta Bot. Sin. 2004, 4, 621–624. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not Available.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.-Y.; Li, J.-Z.; Guo, J.-Z.; Hou, B.-Y. Ameliorative Effects of Curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on Learning and Memory in Aged Rats. Molecules 2012, 17, 10108-10118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910108
Wu X-Y, Li J-Z, Guo J-Z, Hou B-Y. Ameliorative Effects of Curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on Learning and Memory in Aged Rats. Molecules. 2012; 17(9):10108-10118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910108
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiu-Ying, Jian-Zhong Li, Jian-Zheng Guo, and Bao-Yuan Hou. 2012. "Ameliorative Effects of Curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on Learning and Memory in Aged Rats" Molecules 17, no. 9: 10108-10118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910108
APA StyleWu, X.-Y., Li, J.-Z., Guo, J.-Z., & Hou, B.-Y. (2012). Ameliorative Effects of Curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on Learning and Memory in Aged Rats. Molecules, 17(9), 10108-10118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910108



