Sikokianin D, A New C-3/C-3"-Biflavanone from the Roots of Wikstroemia indica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
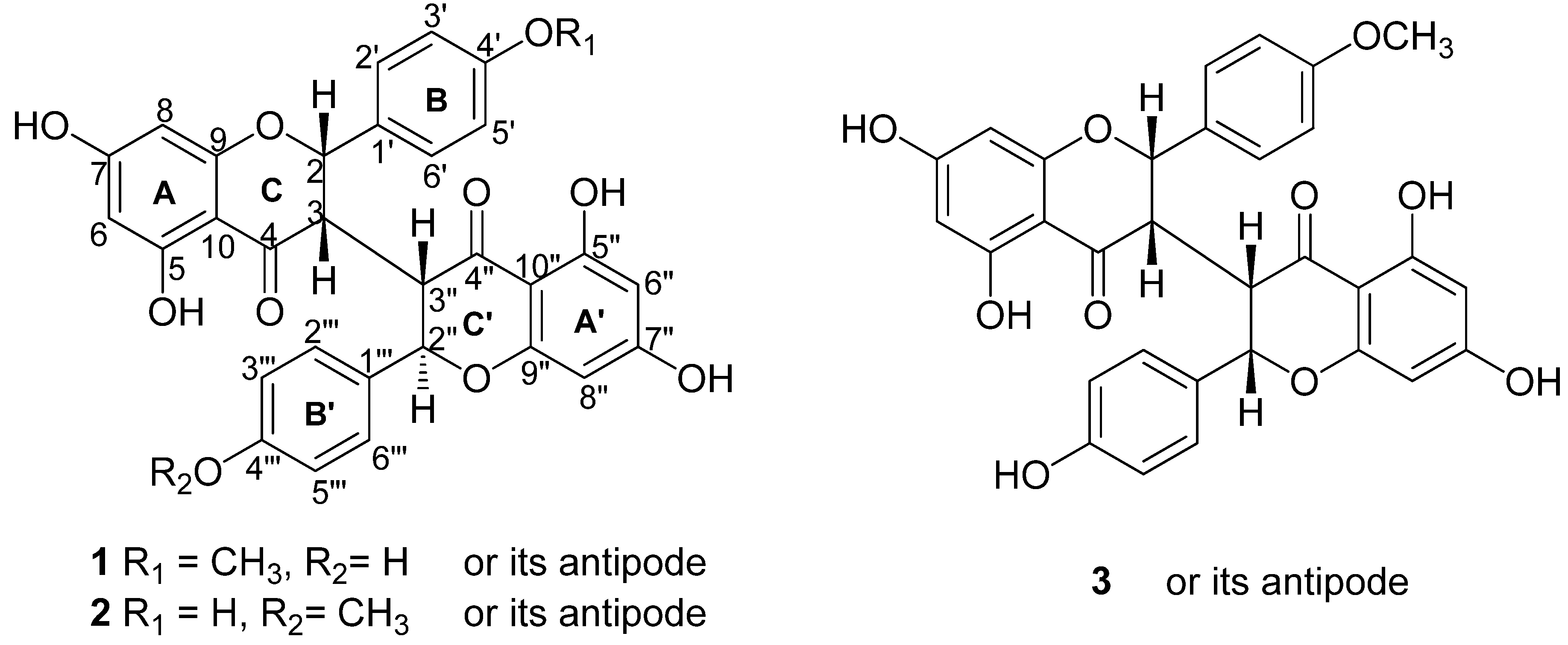
2. Results and Discussion
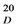 : + 231). The HR-ESI-MS of 1 exhibited a quasi-molecular-ion peak ([M+H]+) at m/z 557.1442 (calc. 557.1448), corresponding to the molecular formula C31H24O10. Moreover, this compound showed positive reaction with HCl-Mg reagent, indicating that it is a flavonoid. The 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 (Table 1) displayed signals of one methoxyl group (δH 3.79, s, 3H), two H-atoms corresponding to H-2 (δH 5.57, 1H, d, J = 5.0 Hz) and H-2" (δH 5.19, 1H, d, J = 9.5 Hz), and two H-atoms corresponding to H-3 (δH 3.19, 1H, br s) and H-3" (δH 3.26, 1H, dd, J = 9.5, 3.0 Hz) at the rings C and C' of the biflavanone. In the 1H- and 13C-NMR established by 1H-1H COSY and HMQC experiments (Table 1), the spectra showed its structural fragments to include two sets of typical 5,7-dioxygenated A rings (δH 5.74, 5.77, each 1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz; δH 5.78, 5.98, each 1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), and two sets of para-oxygenated B rings (δH 7.22, 6.90, each 2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz; δH 6.93, 6.63, each 2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz). From the 13C-NMR data (Table 1), two carbonyl groups (δC 198.5, 196.1) were also observed. These structural fragments were connected to form the given carbon framework of 1 as a dimer of flavanonol derivatives. The partial (-CH-CH-CH-CH-) structure inferred from the 1H-1H COSY spectrum (bold line in Figure 2) suggested that the linkage of the two flavanones was possible only at the C-3 and C-3" positions, which was supported by the comparison of the 1H- and 13C-NMR data of 1 with those of known 3,3"-biflavanones [4,6,8,10], and further confirmed by the HMBC correlations of H-2 (δH 5.57) with C-3" (δC 51.0). The B ring could be located at C-2, based on the observation of the clear cross-peaks of H-2' and H-6' (δH 7.22) with C-2 (δC 81.2). In the same way, linkage of the B' ring to C-2" of the C' ring was deduced by the correlations of H-2"'and H-6"'(δH 6.93) with C-2" (δC 83.3). The HMBC cross-peak between the methoxyl group and C-4' on the B ring indicated that the methoxyl group was connected to C-4'.
: + 231). The HR-ESI-MS of 1 exhibited a quasi-molecular-ion peak ([M+H]+) at m/z 557.1442 (calc. 557.1448), corresponding to the molecular formula C31H24O10. Moreover, this compound showed positive reaction with HCl-Mg reagent, indicating that it is a flavonoid. The 1H-NMR spectrum of 1 (Table 1) displayed signals of one methoxyl group (δH 3.79, s, 3H), two H-atoms corresponding to H-2 (δH 5.57, 1H, d, J = 5.0 Hz) and H-2" (δH 5.19, 1H, d, J = 9.5 Hz), and two H-atoms corresponding to H-3 (δH 3.19, 1H, br s) and H-3" (δH 3.26, 1H, dd, J = 9.5, 3.0 Hz) at the rings C and C' of the biflavanone. In the 1H- and 13C-NMR established by 1H-1H COSY and HMQC experiments (Table 1), the spectra showed its structural fragments to include two sets of typical 5,7-dioxygenated A rings (δH 5.74, 5.77, each 1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz; δH 5.78, 5.98, each 1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz), and two sets of para-oxygenated B rings (δH 7.22, 6.90, each 2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz; δH 6.93, 6.63, each 2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz). From the 13C-NMR data (Table 1), two carbonyl groups (δC 198.5, 196.1) were also observed. These structural fragments were connected to form the given carbon framework of 1 as a dimer of flavanonol derivatives. The partial (-CH-CH-CH-CH-) structure inferred from the 1H-1H COSY spectrum (bold line in Figure 2) suggested that the linkage of the two flavanones was possible only at the C-3 and C-3" positions, which was supported by the comparison of the 1H- and 13C-NMR data of 1 with those of known 3,3"-biflavanones [4,6,8,10], and further confirmed by the HMBC correlations of H-2 (δH 5.57) with C-3" (δC 51.0). The B ring could be located at C-2, based on the observation of the clear cross-peaks of H-2' and H-6' (δH 7.22) with C-2 (δC 81.2). In the same way, linkage of the B' ring to C-2" of the C' ring was deduced by the correlations of H-2"'and H-6"'(δH 6.93) with C-2" (δC 83.3). The HMBC cross-peak between the methoxyl group and C-4' on the B ring indicated that the methoxyl group was connected to C-4'.| No. | δH Mult (J = Hz) | δC |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.57 d (5.0) | 81.2 d |
| 3 | 3.19 br s | 49.3 d |
| 4 | - | 198.5 s |
| 5 | - | 165.0 s |
| 6 | 5.74 d (2.0) | 96.0 d |
| 7 | - | 168.1 s |
| 8 | 5.77 d (2.0) | 97.0 d |
| 9 | - | 165.0 s |
| 10 | - | 103.6 s |
| 1' | - | 130.0 s |
| 2' | 7.22 d (8.5) | 128.4 d |
| 3' | 6.90 d (8.5) | 114.9 d |
| 4' | - | 160.9 s |
| 5' | 6.90 d (8.5) | 114.9 d |
| 6' | 7.22 d (8.5) | 128.4 d |
| 2'' | 5.19 d (9.5) | 83.3 d |
| 3'' | 3.26 dd (9.5, 3.0) | 51.0 d |
| 4'' | - | 196.1 s |
| 5'' | - | 165.3 s |
| 6'' | 5.78 d (2.0) | 97.0 d |
| 7'' | - | 167.9 s |
| 8'' | 5.98 d (2.0) | 96.4 d |
| 9'' | - | 163.9 s |
| 10'' | - | 105.1 s |
| 1''' | - | 128.9 s |
| 2''' | 6.93 d (8.5) | 130.3 d |
| 3''' | 6.63 d (8.5) | 116.1 d |
| 4''' | - | 158.9 s |
| 5''' | 6.63 d (8.5) | 116.1 d |
| 6''' | 6.93 d (8.5) | 130.3 d |
| 4'-OCH3 | 3.79 s | 55.7 q |
3. Experimental
3.1. General
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
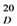 : +231 (c = 0.48, MeOH); IR (KBr, cm−1): 3362, 1643; 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR data, see Table 1; HR-ESI-MS: m/z 557.1442 [M+H]+, calcd for C31H25O10, 557.1448.
: +231 (c = 0.48, MeOH); IR (KBr, cm−1): 3362, 1643; 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR data, see Table 1; HR-ESI-MS: m/z 557.1442 [M+H]+, calcd for C31H25O10, 557.1448.4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Ko, F.N.; Chang, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Teng, C.M. Daphnoretin, a new protein kinase C activator isolated from Wikstroemia indica C. A. Mey. Biochem. J. 1993, 295, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Tagahara, K.; Suzuki, H.; Wu, R.Y.; Haruna, H.; Hall, I.H.; Huang, H.C.; Ito, K.; Iida, T.; Lai, J.S. Antitumor agents. 49 tricin, kaempferol-3-beta-D-glucopyranoside and (+)-nortrachelogenin, antileukemic principles from Wikstroemia indica. J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Dong, A.; Iwasaki, S.; Yao, X. Antifungal, antimitotic and anti-HIV-1 agents from the roots of Wikstroemia indica. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunome, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Otoguro, K.; Kiyohara, H.; Yamada, H.; Omura, S. In vitro antimalarial activity of biflavonoids from Wikstroemia indica. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Unehara, T.; Kitanaka, S. Anti-inflammatory activity of new guaiane type sesquiterpene from Wikstroemia indica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Ye, W.C.; Ooi, V.E.C.; Chung, H.Y.; Li, Y.L. Antiviral biflavonoids from radix Wikstroemiae (Liaogewanggen). Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.S.; Xue, J.Y.; Sun, S.S.M.; Ooi, V.E.C.; Li, Y.L. Antiviral activity of daphnoretin isolated from Wikstroemia indica. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, M.; Jiang, P.F.; Hirata, Y. Two new C-3/C-3"-biflavanones from Wikstroemia sikokiana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 3631–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, W.W.; Sun, L.X.; Wang, Q.; Qi, W.; Yu, H. A new coumarin from Wikstroemia indica (L.) C. A. Mey. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Hu, J.L.; Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Li, X.R. A new C-3/C-3"-biflavanone from the roots of Stellera chamaejasme L. Molecules 2011, 16, 6465–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, O.; Lopez, J.; Vergara, A. Isoflavans and a Stilbene from Wood of the Decay-Resistant Tropical Tree Diphysa robinioides. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.Q.; Recio, M.C.; Máñez, S.; Giner, R.M.; Cerdá-Nicolás, M.; Ríos, J.L. Isolation of two triterpenoids and a biflavanone with anti-inflammatory activity from Schinus molle fruits. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Cheung, F.W.K.; Liu, B.P.L.; Li, C.M.; Ye, W.C.; Che, C.T. Involvement of p21 and FasL in Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Neochamaejasmin A in Human Prostate LNCaP Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.H.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Sun, M.L.; Sang, H.R.; Zhou, C.H.; An, T.Y.; Hu, L.H.; Ye, R.D.; Wang, M.W. Stereospecific Induction of Nuclear Factor-κB Activation by Isochamaejasmin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Lu, L.-Y.; Zeng, L.-H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.-L.; Li, X.-R. Sikokianin D, A New C-3/C-3"-Biflavanone from the Roots of Wikstroemia indica. Molecules 2012, 17, 7792-7797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17077792
Li J, Lu L-Y, Zeng L-H, Zhang C, Hu J-L, Li X-R. Sikokianin D, A New C-3/C-3"-Biflavanone from the Roots of Wikstroemia indica. Molecules. 2012; 17(7):7792-7797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17077792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Lin-Yan Lu, Ling-Hui Zeng, Chong Zhang, Jia-Lei Hu, and Xiang-Rong Li. 2012. "Sikokianin D, A New C-3/C-3"-Biflavanone from the Roots of Wikstroemia indica" Molecules 17, no. 7: 7792-7797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17077792
APA StyleLi, J., Lu, L.-Y., Zeng, L.-H., Zhang, C., Hu, J.-L., & Li, X.-R. (2012). Sikokianin D, A New C-3/C-3"-Biflavanone from the Roots of Wikstroemia indica. Molecules, 17(7), 7792-7797. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17077792




