A Method of Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC is Established for Screening Potential Active Components in Chinese Medicines—Probing Herba Artemisiae Scopariae as an Exemplifying Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Detection of Bifendate after Hepatocyte Extraction
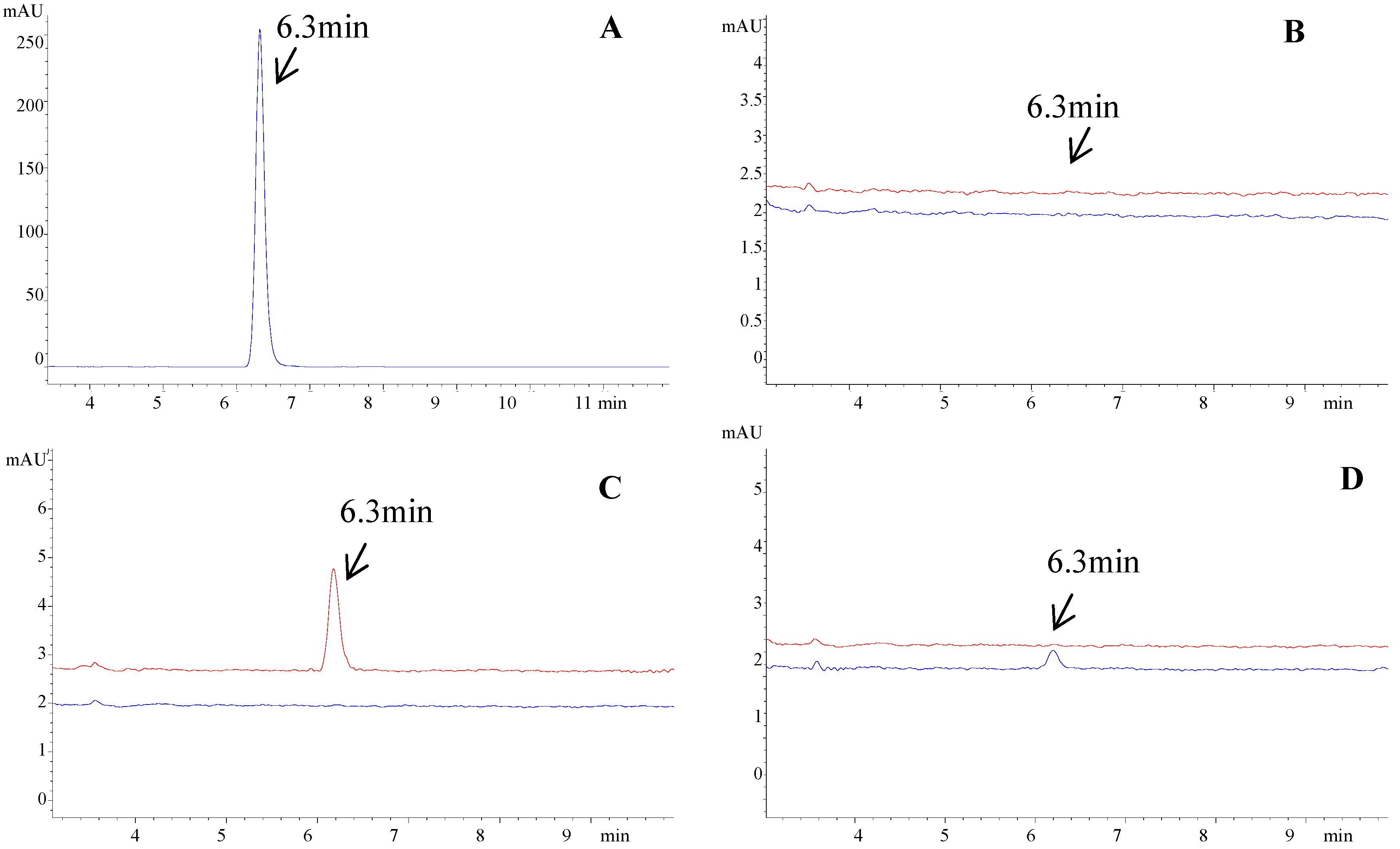
2.2. Identification of Potential Active Components in the A. scopariae Extract by HE-HPLC
2.2.1. HPLC-DAD Analysis on the Fingerprint of A. scopariae Extract
2.2.1.1. Selection of Suitable Chromatographic Conditions

2.2.1.2. Method Validation
2.2.1.3. Fingerprint of the A. scopariae Extract
| Number of peaks | Relative retention time (RRT) | Relative peak area (RPA) | Percentage of total peak area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.160 | 1.496 | 5.35 |
| 2 | 0.195 | 0.440 | 1.57 |
| 3 | 0.233 | 0.399 | 1.42 |
| 4 | 0.300 | 1.671 | 5.98 |
| 5 | 0.325 | 0.422 | 1.51 |
| 6 | 0.348 | 2.480 | 8.87 |
| 7 | 0.401 | 1.371 | 4.90 |
| 8 | 0.514 | 2.403 | 8.59 |
| 9 | 0.544 | 1.879 | 6.72 |
| 10 | 0.581 | 2.042 | 7.30 |
| 11 | 0.633 | 4.968 | 17.76 |
| 12 | 0.697 | 0.356 | 1.27 |
| 13 | 0.747 | 0.482 | 1.72 |
| 14 | 0.880 | 1.334 | 4.77 |
| 15 | 0.900 | 0.834 | 2.98 |
| 16 | 0.918 | 0.517 | 1.85 |
| 17 * | 1 | 1 | 3.58 |
| 18 | 1.139 | 0.445 | 1.59 |
| 19 | 1.486 | 0.399 | 1.43 |
2.2.2. Detection of the Components in A. scopariae after Extraction by Hepatocytes
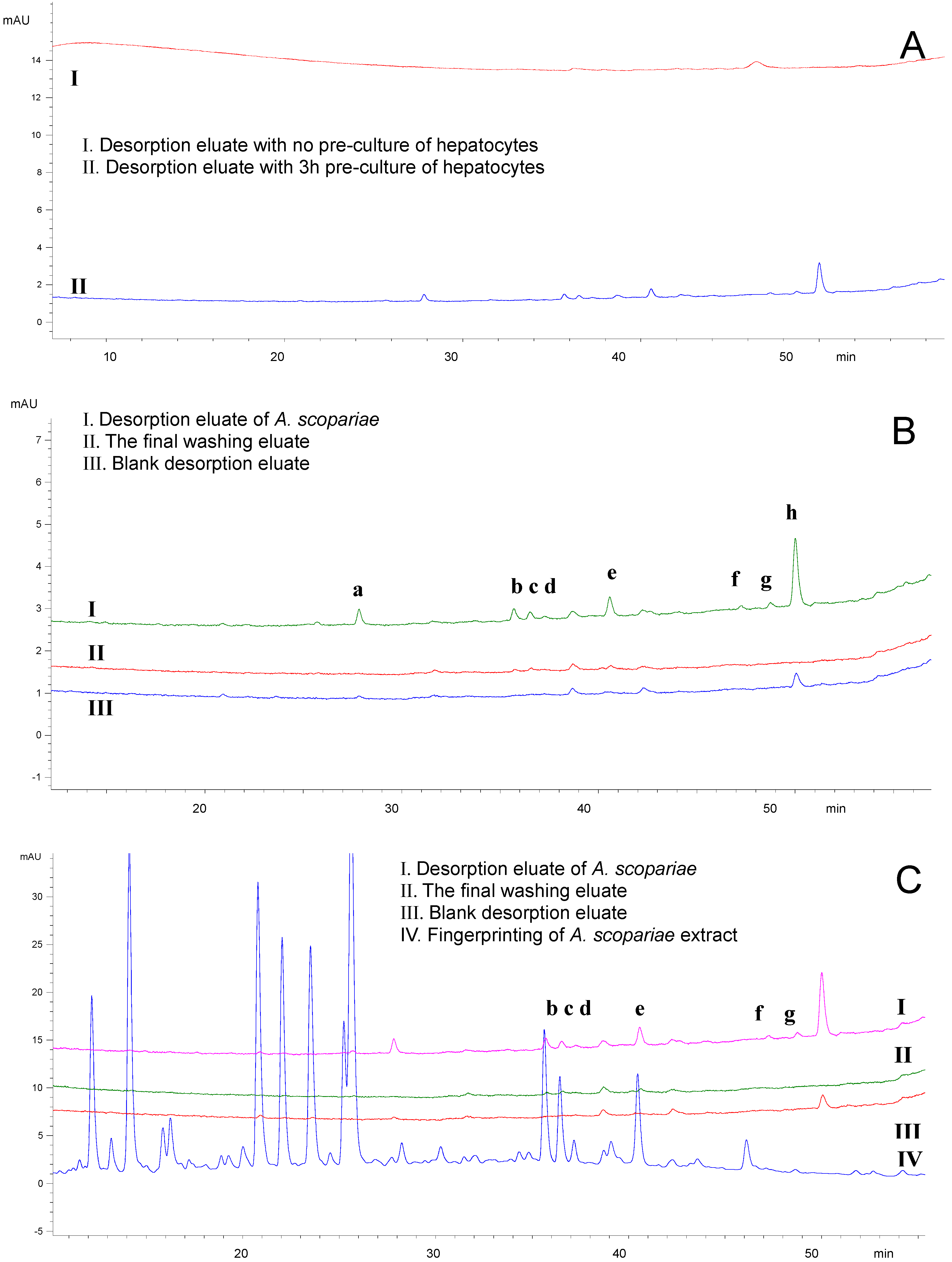
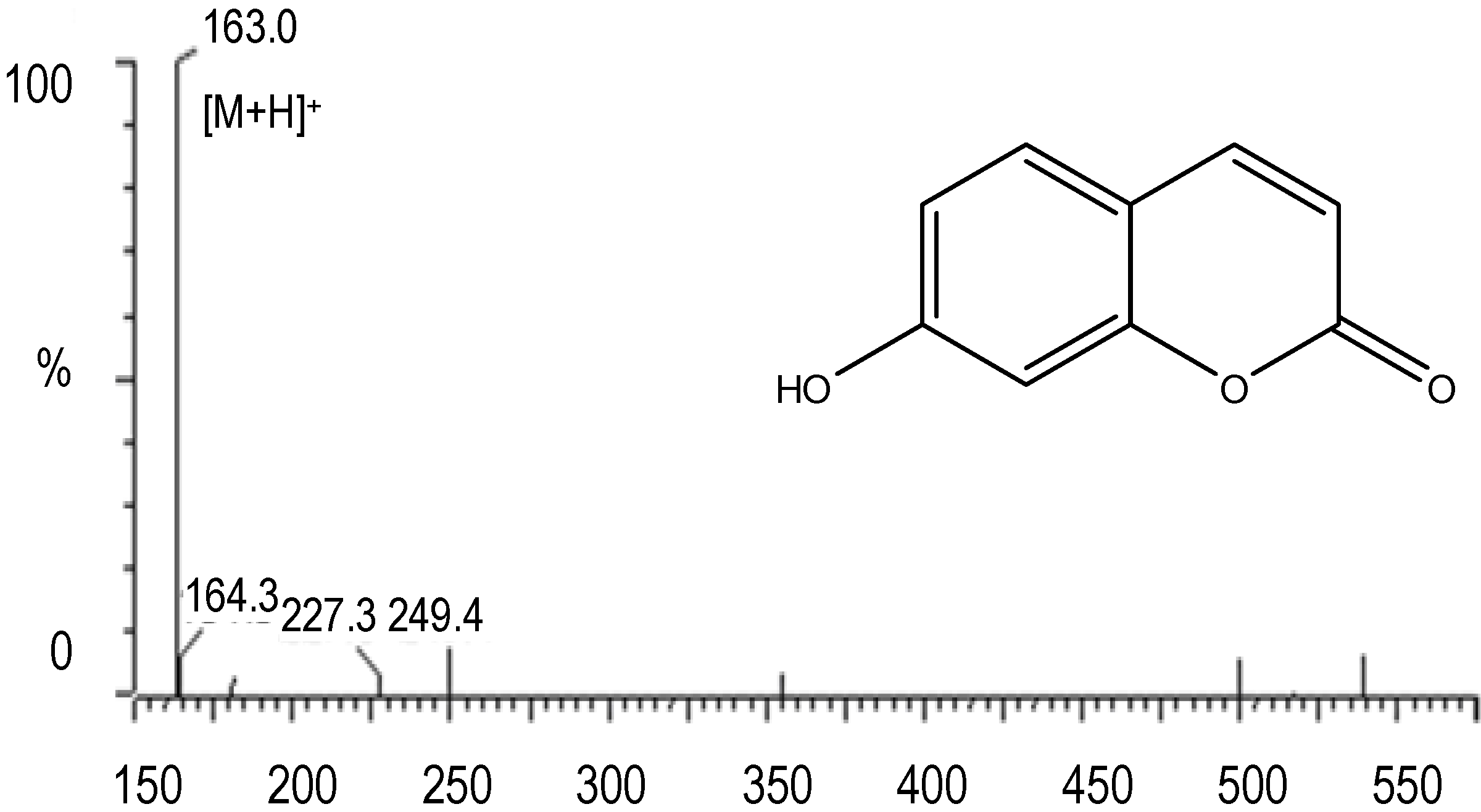
2.2.3. Extraction and Identification of Compounds “b”, “c” and “e”

2.2.4. Extraction and Purification of Compounds Extracted by HE-HPLC

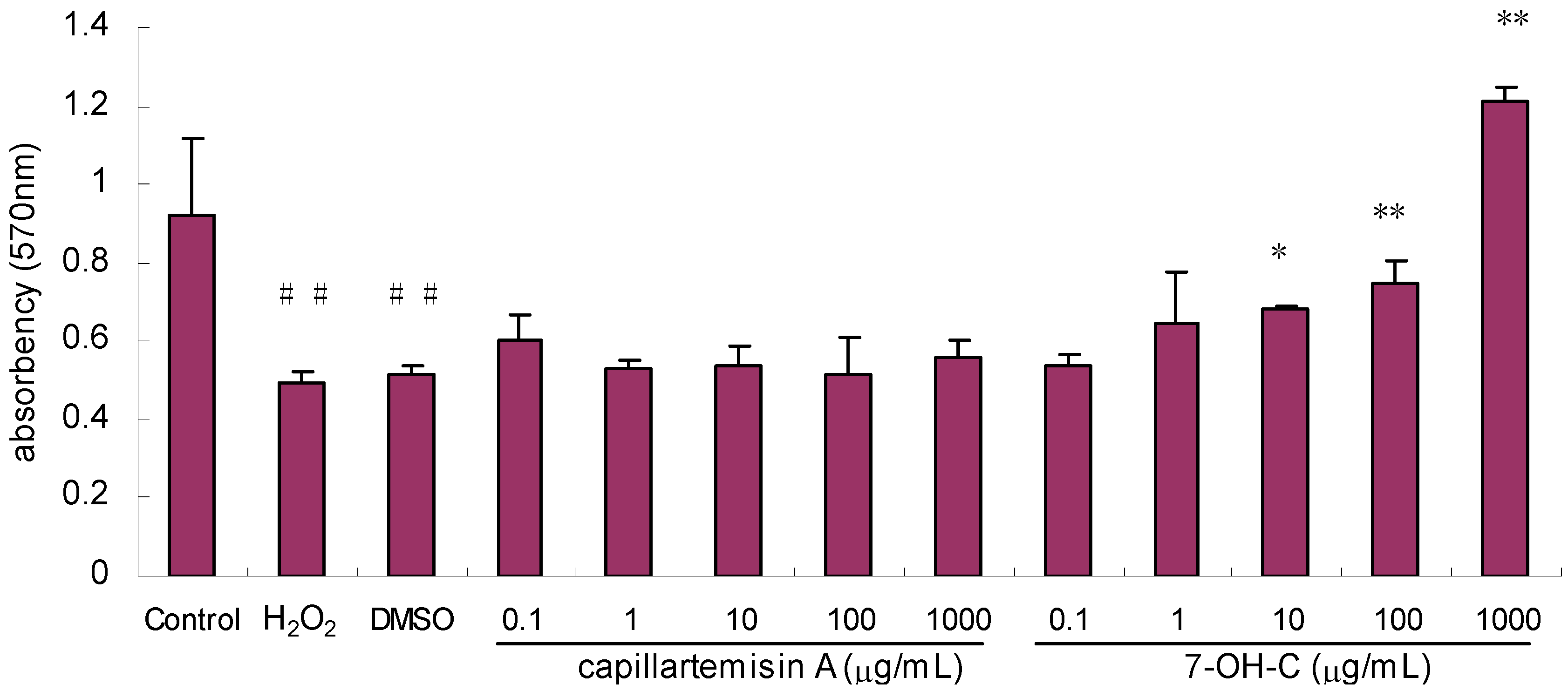
2.2.5. Effect of Compounds on Proliferation/Viability of HL-7702 Hepatocytes
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Samples and Solutions
3.3. Isolation and Culture of the Rat Primary Hepatocytes
3.4. Method for Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC (HE-HPLC)
3.4.1. Extracting Bifendate or the Components in A. scopariae Extract by Hepatocytes
3.4.2. HPLC-DAD Analysis of Bifendate or the Components in the A. scopariae Extract
3.5. Mass Spectrometry
3.6. Evaluation of HL-7702 Hepatocyte Proliferation/Viability by MTT Assay
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Cui, S.; Wang, M.; Fan, G. Anti-HBV efficacy of bifendate in treatment of chronic hepatitis b, a primary study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 82, 538–540. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.Y.; Yang, R.; Dong, H.; Yu, Z.L.; Ko, K.M. Bifendate treatment attenuates hepatic steatosis in cholesterol/bile salt- and high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 552, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Zhu, J.B.; Chen, H.X.; Xiao, Y.Y. A simple hplc method for the determination of bifendate: Application to a pharmacokinetic study of bifendate liposome. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 857, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Song, Y.H.; Xia, W.J.; Jin, M.W. Aqueous extract of yin-chen-hao decoction, a traditional chinese prescription, exerts protective effects on concanavalin a-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibition of nf-kappab. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.P.; Kung, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Jong, M.S.; Chen, T.J.; Chen, F.J.; Hwang, S.J. Frequency and pattern of chinese herbal medicine prescriptions for chronic hepatitis in taiwan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, P.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, L.; Dou, S.; et al. Metabolic urinary profiling of alcohol hepatotoxicity and intervention effects of yin-chen-hao-tang in rats using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadruple time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Chang, H.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Lin, H.C. Yin-chen-hao-tang ameliorates obstruction-induced hepatic apoptosis in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Li, T.L.; Sun, H. Hepatoprotective effects of yin-chen-hao-tang and its constituent absorbed into blood after oral administration. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao 2004, 20, 239–240. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, I.; Uchida, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sakurawi, K. Studies on choleretic constituents in artemisia capillaris thunb. Chem. Pharm. Bull.(Tokyo) 1988, 36, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazihan, N.; Ataoğlu, H.; Yener, B.; Aydin, C. Erythropoietin attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced damage of hepatocytes. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 18, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, U.S.; Steffen, B.; Siegers, C.P. Antitumor-activities of coumarin, 7-hydroxy-coumarin and its glucuronide in several human tumor cell lines. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1998, 99, 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.; Ma, H.Y.; Zhu, Q. Establishment of hepatocyte extraction combined with hplc (he-hplc) and application in analysis of active components in the fruits of gardenia jasminoides extract. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2009, 34, 450–453. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Qian, Z.Y.; Liu, T.Z.; Rao, S.Y.; Qu, B. Comparative studies on hepatic protective and choleretic effect of geniposide and crocetin. Zhongguo Xin Yao Za Zhi 2003, 12, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.J.; Wang, S.W.; Lin, J.K. Suppressive effect of geniposide on the hepatotoxicity and hepatic DNA binding of aflatoxin b1 in rats. Cancer Lett. 1991, 60, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seglen, P.O. Protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes is inhibited by ammonia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1975, 66, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds b and c are available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, M.; Ma, H.-Y.; Wu, X.-R.; Hua, Y.-Q.; Zhu, Q.; Fan, H.-W. A Method of Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC is Established for Screening Potential Active Components in Chinese Medicines—Probing Herba Artemisiae Scopariae as an Exemplifying Approach. Molecules 2012, 17, 1468-1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17021468
Hong M, Ma H-Y, Wu X-R, Hua Y-Q, Zhu Q, Fan H-W. A Method of Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC is Established for Screening Potential Active Components in Chinese Medicines—Probing Herba Artemisiae Scopariae as an Exemplifying Approach. Molecules. 2012; 17(2):1468-1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17021468
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Min, Hong-Yu Ma, Xiang-Rui Wu, Yong-Qing Hua, Quan Zhu, and Hong-Wei Fan. 2012. "A Method of Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC is Established for Screening Potential Active Components in Chinese Medicines—Probing Herba Artemisiae Scopariae as an Exemplifying Approach" Molecules 17, no. 2: 1468-1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17021468
APA StyleHong, M., Ma, H.-Y., Wu, X.-R., Hua, Y.-Q., Zhu, Q., & Fan, H.-W. (2012). A Method of Hepatocyte Extraction Conjugated with HPLC is Established for Screening Potential Active Components in Chinese Medicines—Probing Herba Artemisiae Scopariae as an Exemplifying Approach. Molecules, 17(2), 1468-1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17021468




