MicroRNA miR-491-5p Targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL Induces Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Mitochondria Mediated Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
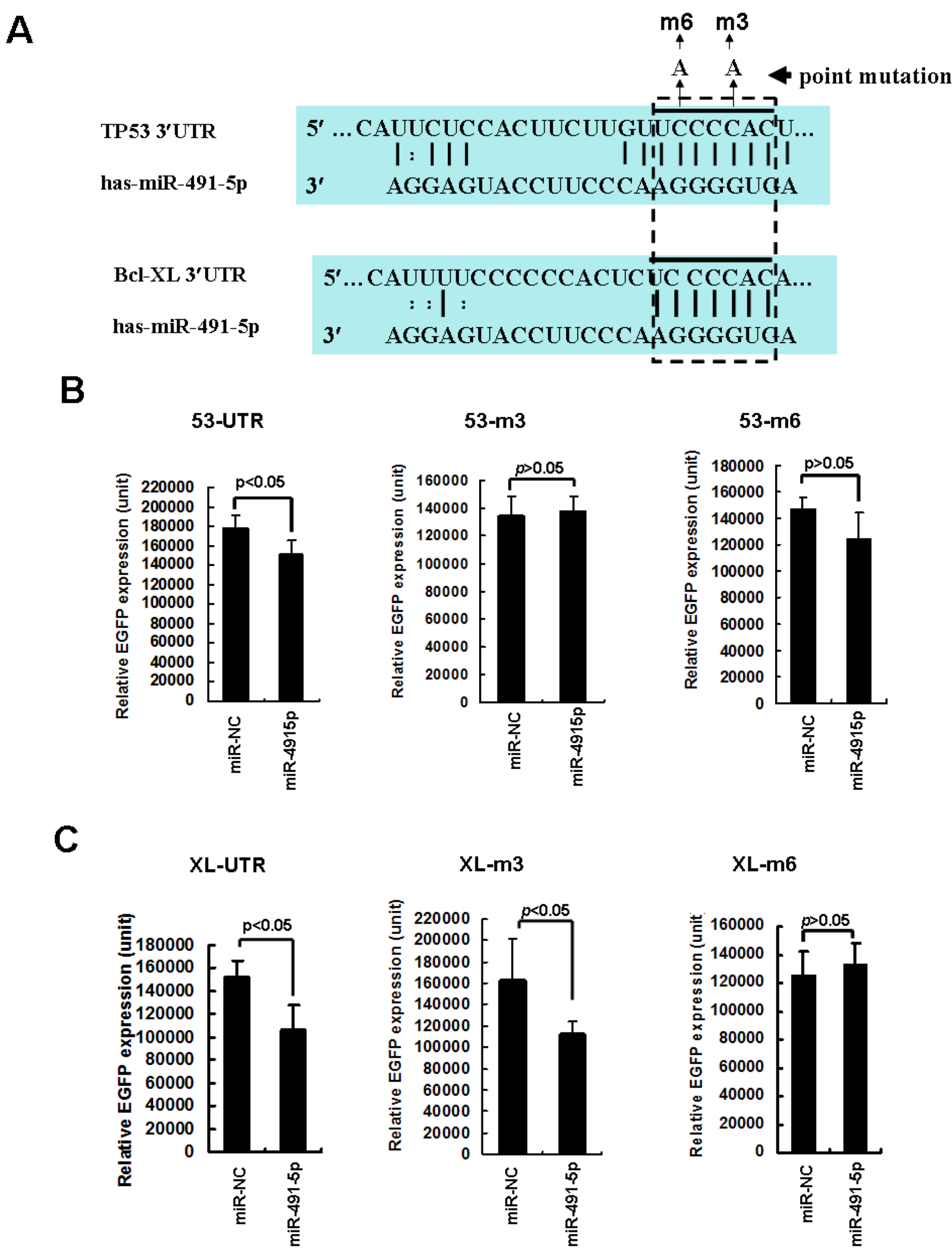
2.1. The Expression Profile of miR491-5p and Its Targeting Site Prediction
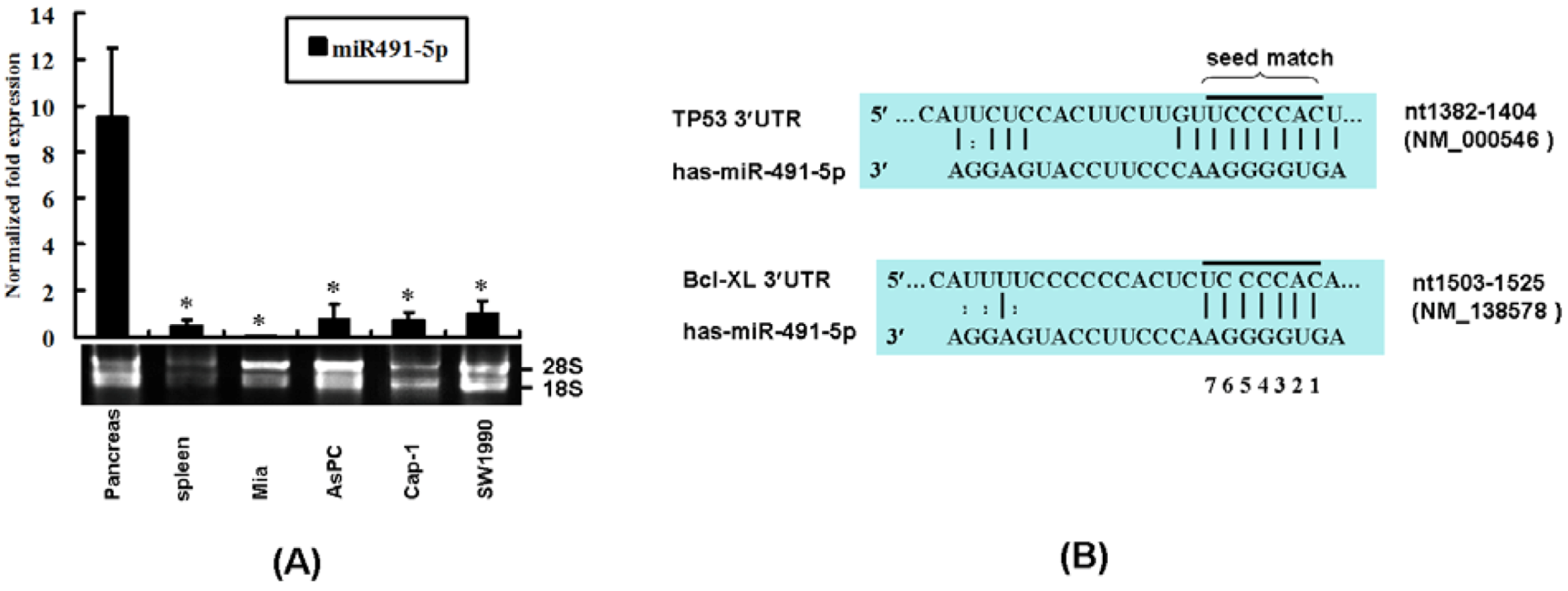
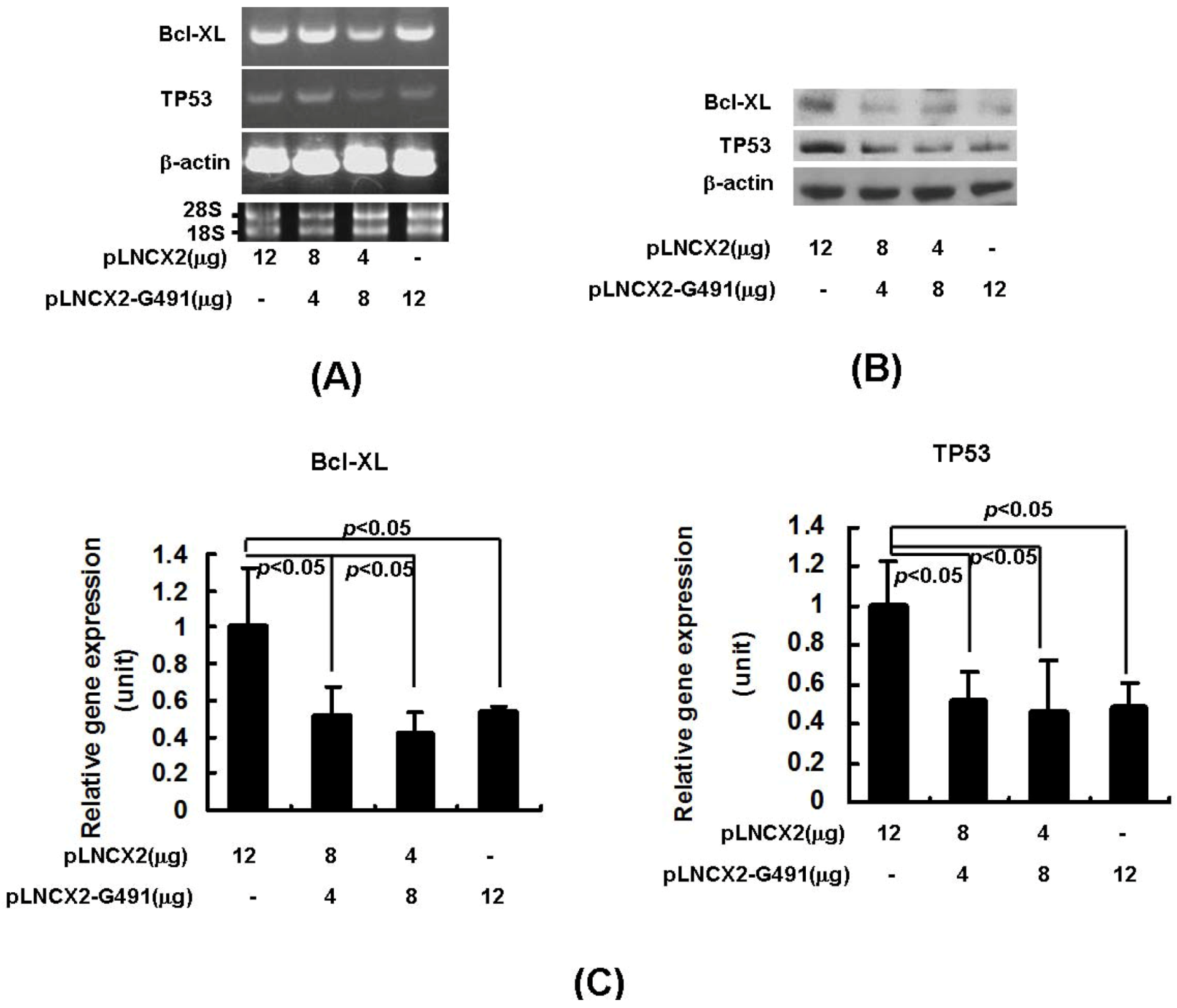
2.2. miR491-5p Effectively Downregulated TP53 and Bcl-XL Gene Expressions in Pancreatic Cancer Cells SW1990

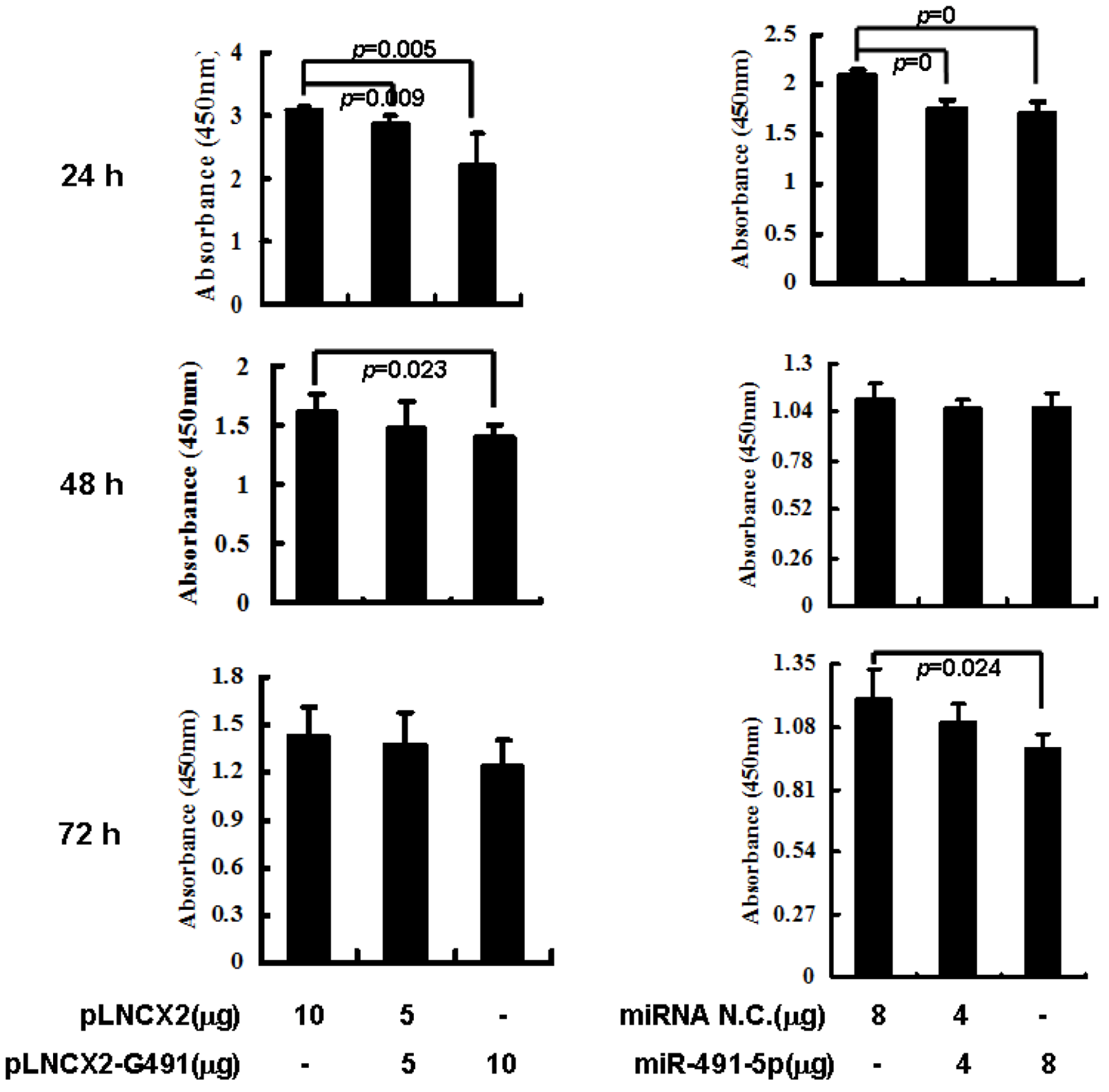
2.3. Overexpression of miR491-5p Inhibited Cell Proliferation and Promoted Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Cells
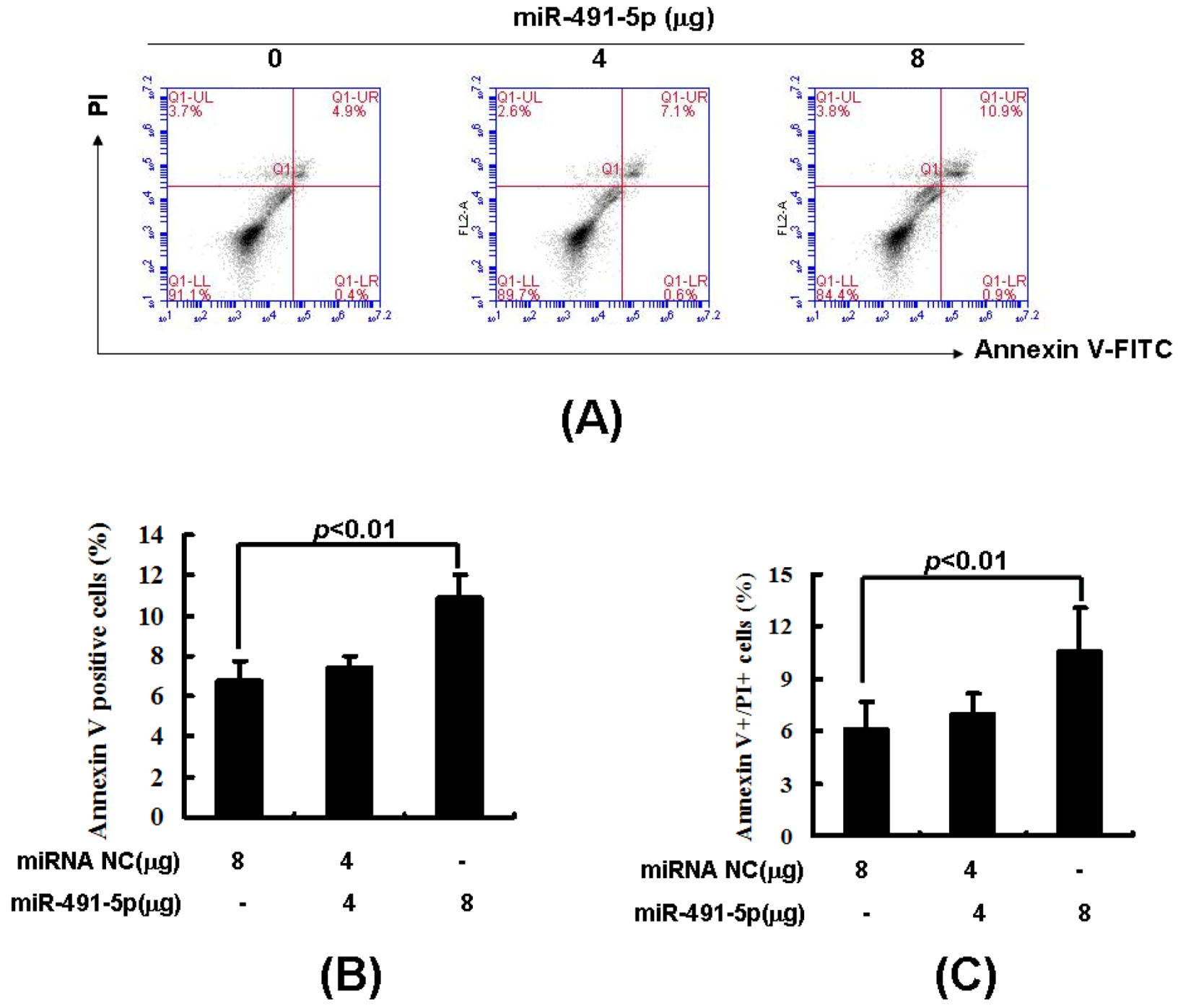
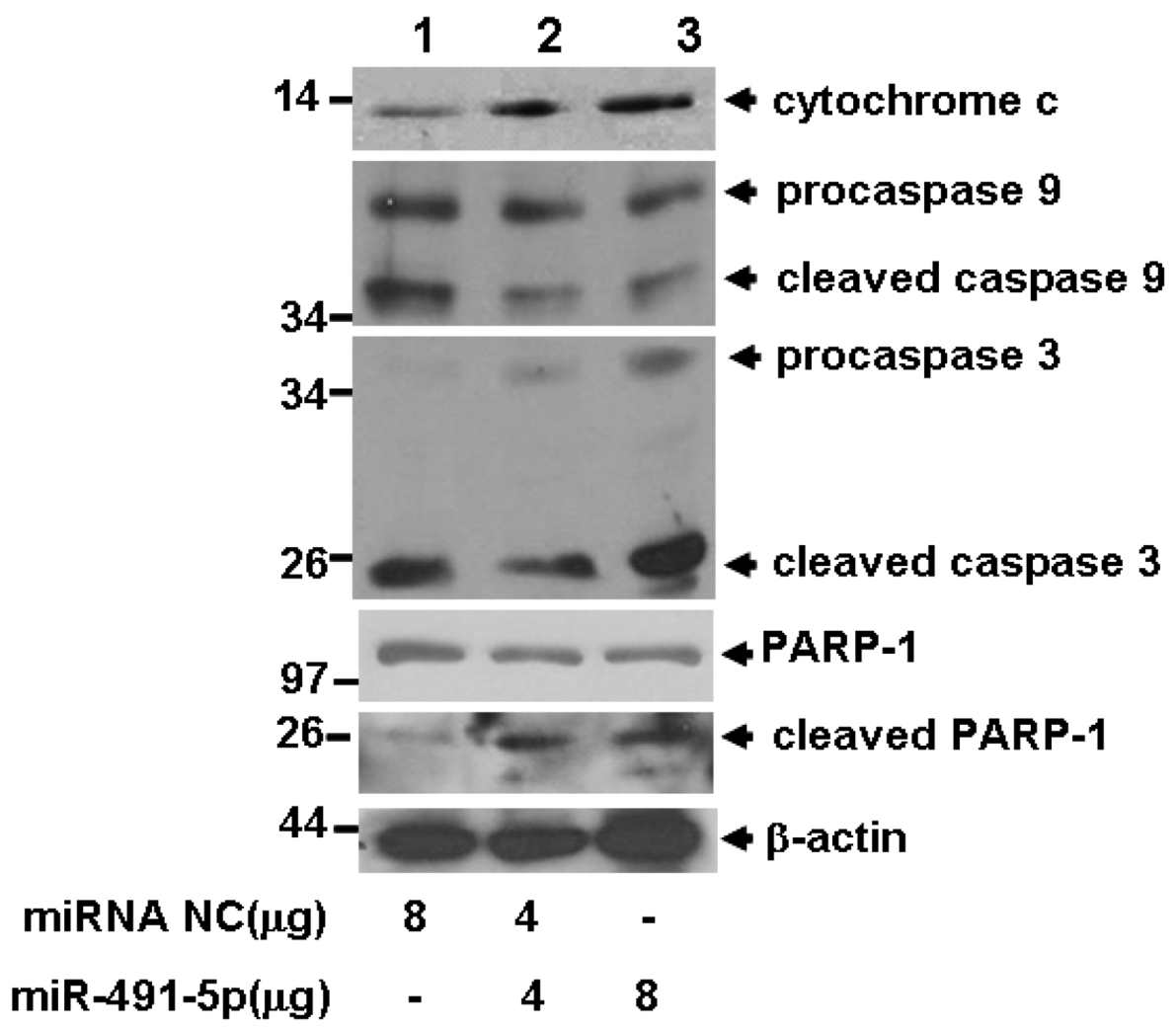
2.4. miR491-5p Effectively Activated Intrinsic Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway
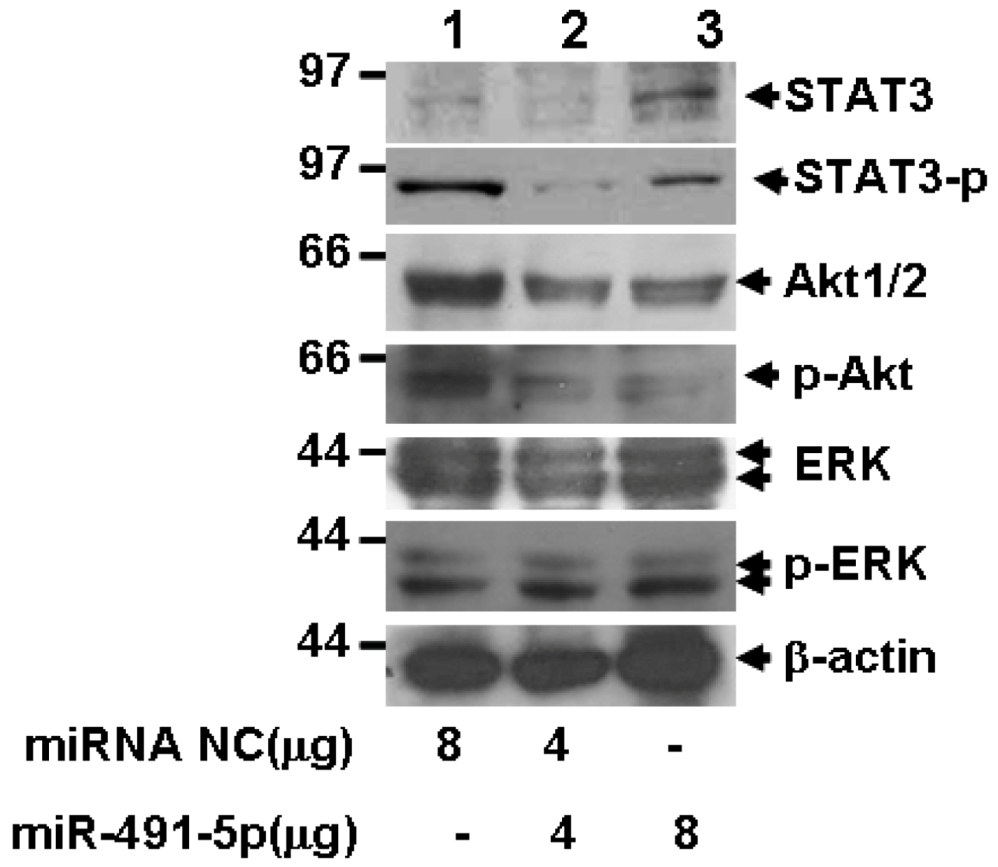
2.5. miR491-5p Inhibited both STAT3 and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways
3. Experimental
3.1. Cell Lines, Antibodies and Chemical Reagents
3.2. The Construction of microRNA Expression Plasmid
3.3. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Real Time Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
| Gene name | GenBank ID | forward primer(5'→3') | reverse primer(5'→3') | Size of product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-acti n + | bc009275 | cacactgtgcccatctacga | ctgcttgctgatccacatct | 600 |
| Bcl-X L + | z23115.1 | ggtggttgactttctctcct | gcatctccttgtctacgctt | 454 |
| TP53 + | NM_000546.4 | atcacactggaagactccag | ctgacgcacacctattgcaa | 741 |
| β-actin-R ++ | bc009275 | tccatcatgaagtgtgacgt | ctcaggaggagcaatgatct | 161 |
| Bcl-XL-R ++ | z23115.1 | ggtggttgactttctctcct | ggcctcagtcctgttctctt | 87 |
| TP53-R ++ | NM_000546.4 | atcacactggaagactccag | agattctcttcctctgtgcg | 103 |
3.4. Transient Transfection
3.5. Western Blot Analysis
3.6. Apoptotic Assay by Flow Cytometric Analysis
3.7. Cell Proliferation assay by Cell-Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chen, C.Z. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ow, Y.-L.P.; Green, D.R.; Hao, Z.; Mak, T.W. Cytochrome c: Functions beyond respiration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1999, 33, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.E.; Krammer, P.H. The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acehan, D.; Jiang, X.; Morgan, D.G.; Heuser, J.E.; Wang, X.; Akey, C.W. Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: Implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, S.N.; Fletcher, J.I.; Kaufmann, T.; van Delft, M.F.; Chen, L.; Czabotar, P.E.; Ierino, H.; Lee, E.F.; Fairlie, W.D.; Bouillet, P.; et al. Apoptosis initiated when BH3 ligands engage multiple Bcl-2 homologs, not Bax or Bak. Science 2007, 315, 856–859. [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Gazouli, M.; Manta, A.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. A review on the role of microRNA in biology, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2012, 41, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11549–11556. [Google Scholar]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- Krejs, G.J. Pancreatic cancer: Epidemiology and risk factors. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P. Epidemiology and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 20, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA functional network in pancreatic cancer: From biology to biomarkers of disease. J. Biosci. 2011, 36, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, N.A.; Werner, J.; Willenbrock, H.; Roslind, A.; Giese, N.; Horn, T.; Wojdemann, M.; Johansen, J.S. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and ampullary adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomston, M.; Frankel, W.L.; Petrocca, F.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Liu, C.G.; Bhatt, D.; Taccioli, C.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007, 297, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Szafranska, A.E.; Davison, T.S.; John, J.; Cannon, T.; Sipos, B.; Maghnouj, A.; Labourier, E.; Hahn, S.A. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.R.; Frampton, A.E.; Jacob, J.; Pellegrino, L.; Krell, J.; Giamas, G.; Tsim, N.; Vlavianos, P.; Cohen, P.; Ahmad, R.; et al. MicroRNAs targeting oncogenes are down-regulated in pancreatic malignant transformation from benign tumors. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32068. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Saleh, H.; Sethi, S.; Sarkar, F.H.; Philip, P.A. MicroRNA profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of MicroRNAs in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer and Its Prognostic Significance. Pancreas 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Miyazawa, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yoshida, T. Functional screening identifies a microRNA, miR-491 that induces apoptosis by targeting Bcl-X(L) in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, M.; Orzaez Mdel, M.; Delgado-Soler, L.; Perez, J.J.; Rubio-Martinez, J. Rational design of new class of BH3-mimetics as inhibitors of the Bcl-xL protein. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Yang, J.S.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.R.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.M.; De, W. Functional and biological analysis of Bcl-xL expression in human osteosarcoma. Bone 2010, 47, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Page, C.; Beidler, D.R.; Wicha, M.S.; Nunez, G. Overexpression of Bcl-x(L) promotes chemotherapy resistance of mammary tumors in a syngeneic mouse model. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grad, J.M.; Zeng, X.R.; Boise, L.H. Regulation of Bcl-xL: A little bit of this and a little bit of STAT. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2000, 12, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Downes, C.P.; Whetton, A.D.; Owen-Lynch, P.J. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and specific protein kinase B isoforms in the suppression of apoptosis mediated by the Abelson protein-tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13142–13148. [Google Scholar]
- Catlett-Falcone, R.; Landowski, T.H.; Oshiro, M.M.; Turkson, J.; Levitzki, A.; Savino, R.; Ciliberto, G.; Moscinski, L.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L.; Nunez, G.; et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 1999, 10, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnauskas, R.; Niu, Q.; Talapatra, S.; Plas, D.R.; Greene, M.E.; Crispino, J.D.; Rudin, C.M. Bcl-x(L) and Akt cooperate to promote leukemogenesis in vivo. Oncogene 2003, 22, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zou, Y.; Rahman, J.S.; Lu, B.; Massion, P.P. Synergy between phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and Bcl-xL in the control of apoptosis in adenocarcinoma cells of the lung. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Chen, Y.T.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, D. The cell growth suppressor, mir-126, targets IRS-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, M.; Miyazono, Y.; Sasamoto, K.; Ohkura, Y.; Ueno, K. A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 1997, 44, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds pLNCX2-G491 are available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.-Y.; Liu, B.; Hou, S.-Q.; Liu, L. MicroRNA miR-491-5p Targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL Induces Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Mitochondria Mediated Pathway. Molecules 2012, 17, 14733-14747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214733
Guo R, Wang Y, Shi W-Y, Liu B, Hou S-Q, Liu L. MicroRNA miR-491-5p Targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL Induces Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Mitochondria Mediated Pathway. Molecules. 2012; 17(12):14733-14747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214733
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Rong, Yi Wang, Wei-Ye Shi, Bin Liu, Sheng-Qi Hou, and Li Liu. 2012. "MicroRNA miR-491-5p Targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL Induces Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Mitochondria Mediated Pathway" Molecules 17, no. 12: 14733-14747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214733
APA StyleGuo, R., Wang, Y., Shi, W.-Y., Liu, B., Hou, S.-Q., & Liu, L. (2012). MicroRNA miR-491-5p Targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL Induces Cell Apoptosis in SW1990 Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Mitochondria Mediated Pathway. Molecules, 17(12), 14733-14747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171214733




