Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Crude Oil from Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida) Seed Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content and Fatty Acid Composition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
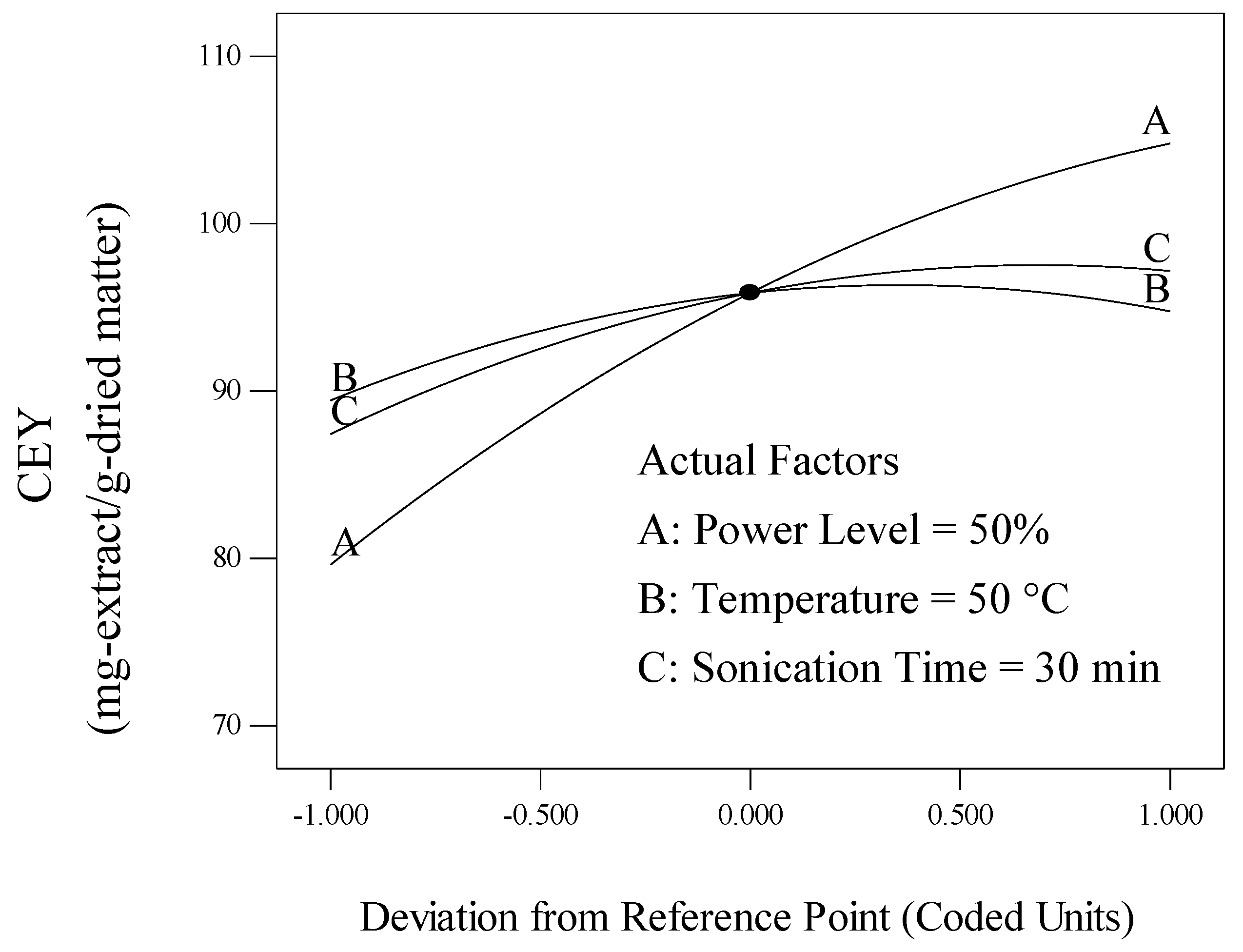
2.1. Effect of the Process Variables on Crude Extract Yield
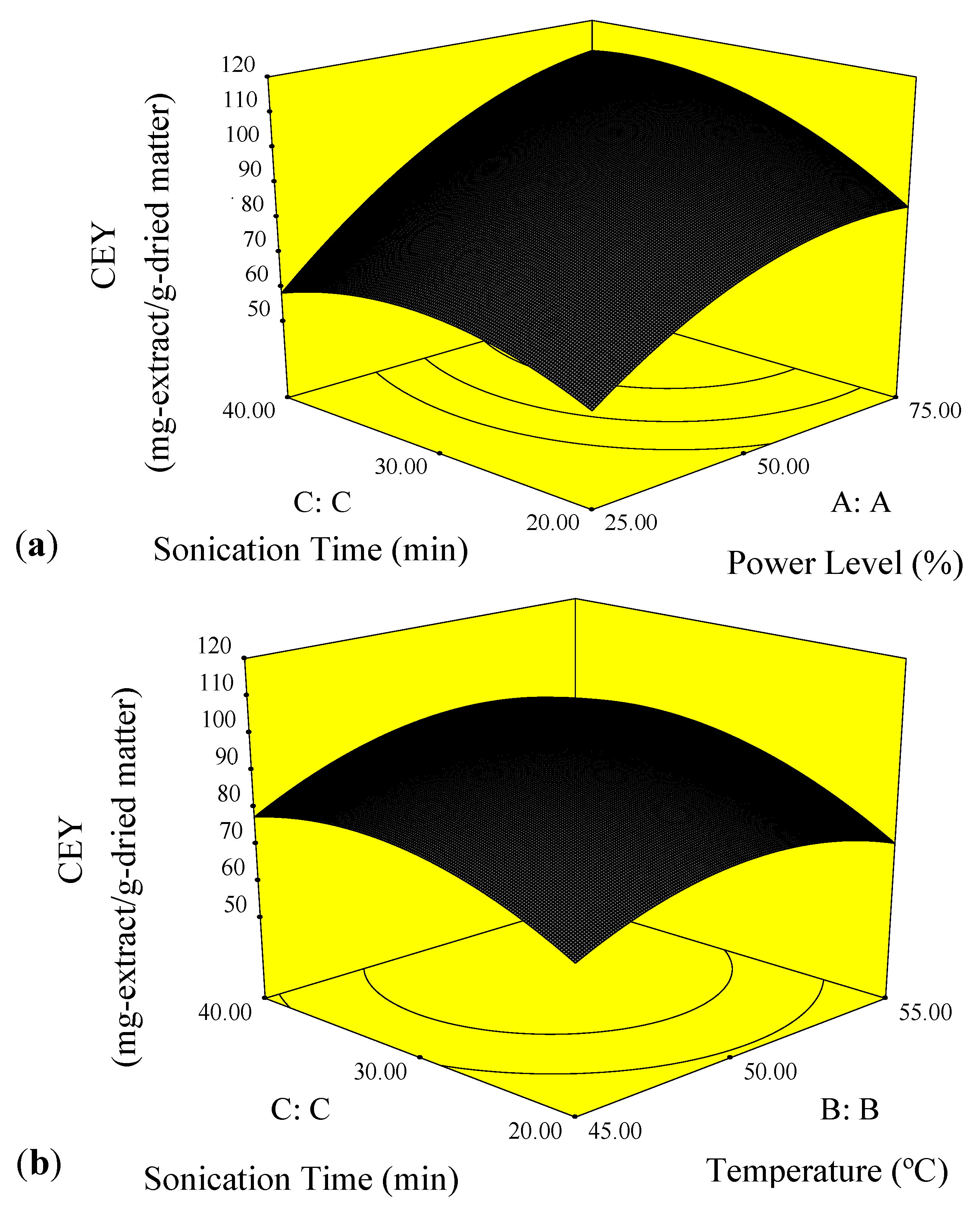
2.2. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Conditions and Verification of the Model
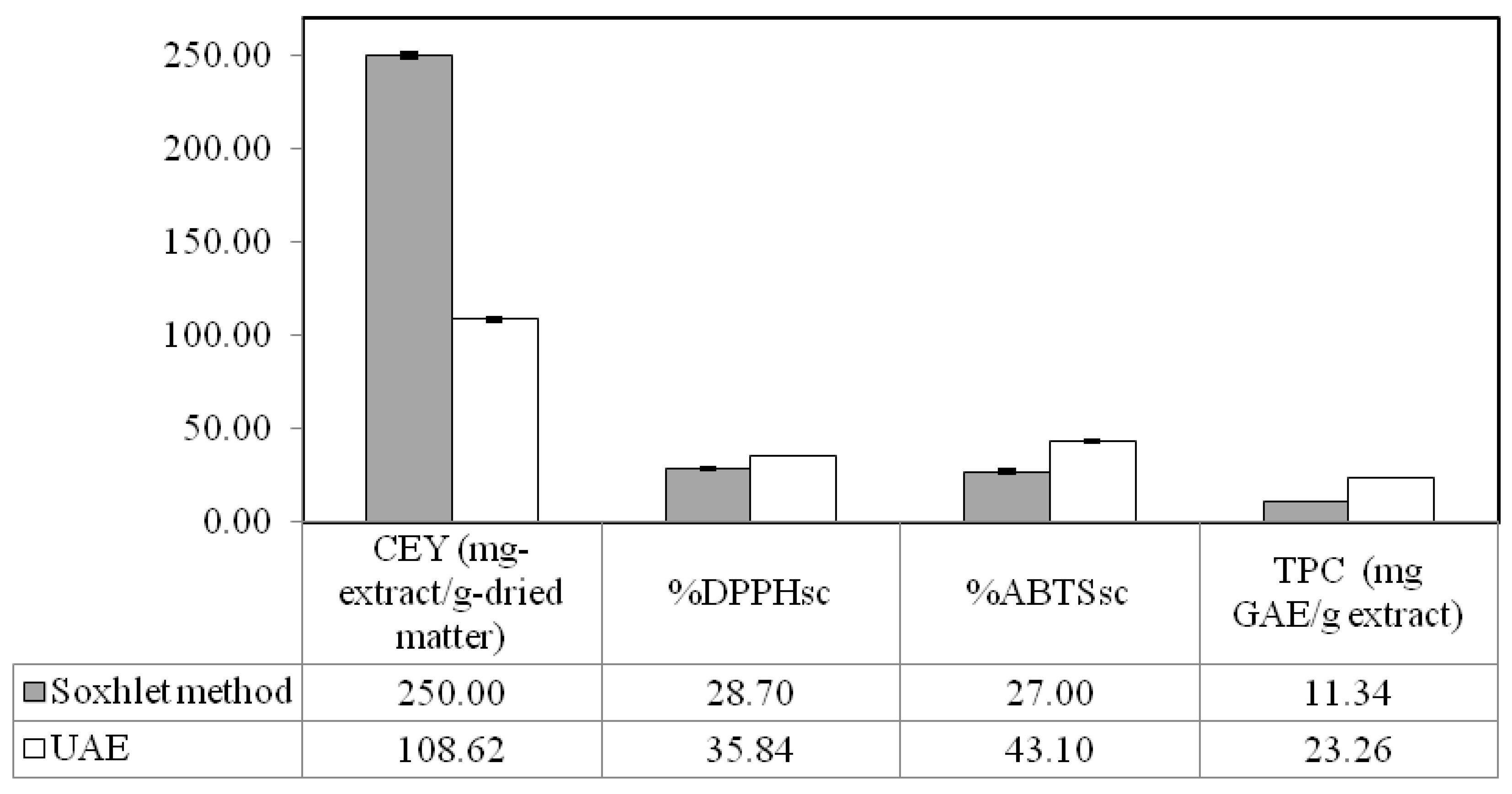
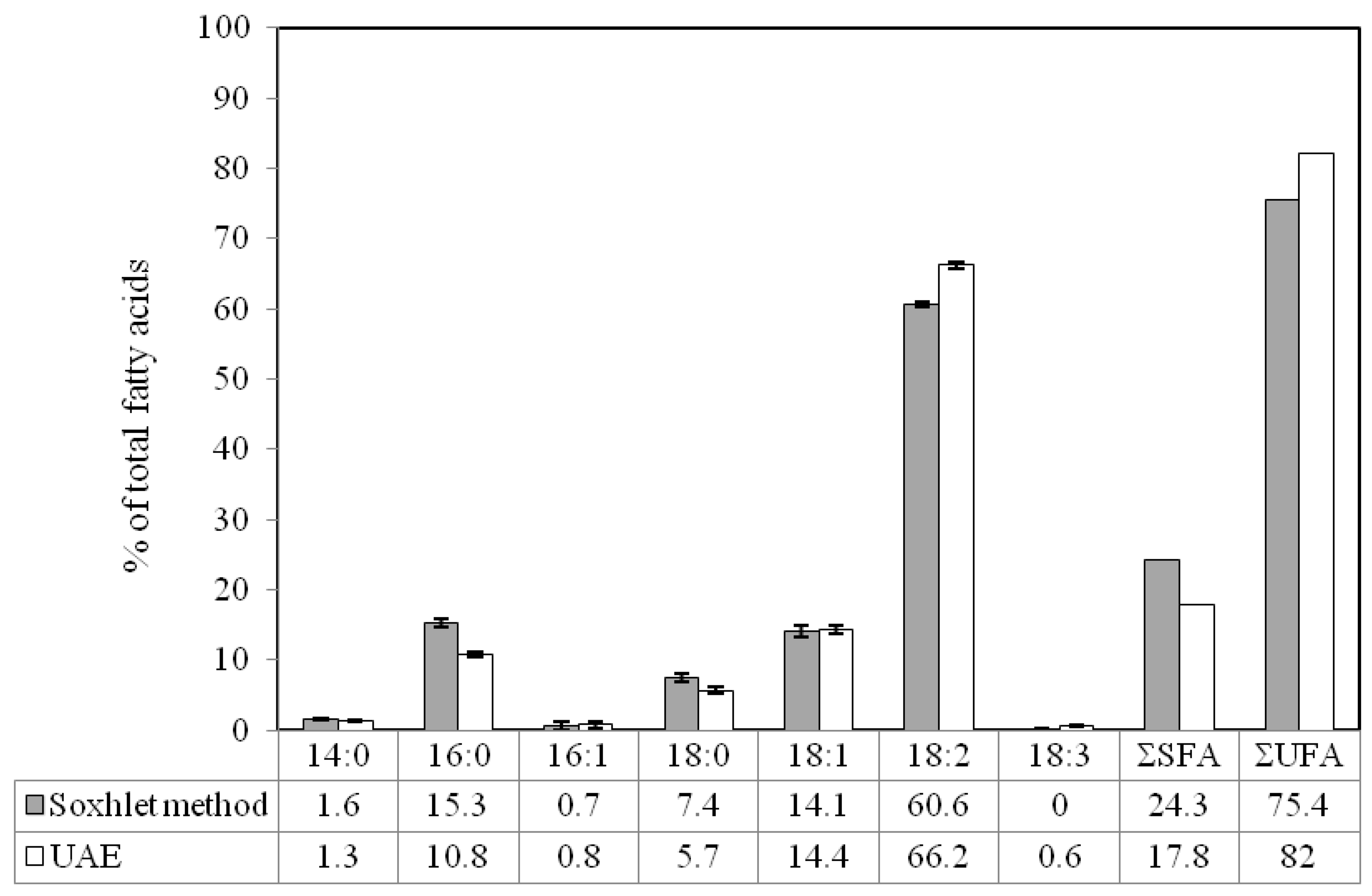
2.3. Comparison of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction with Soxhlet Method
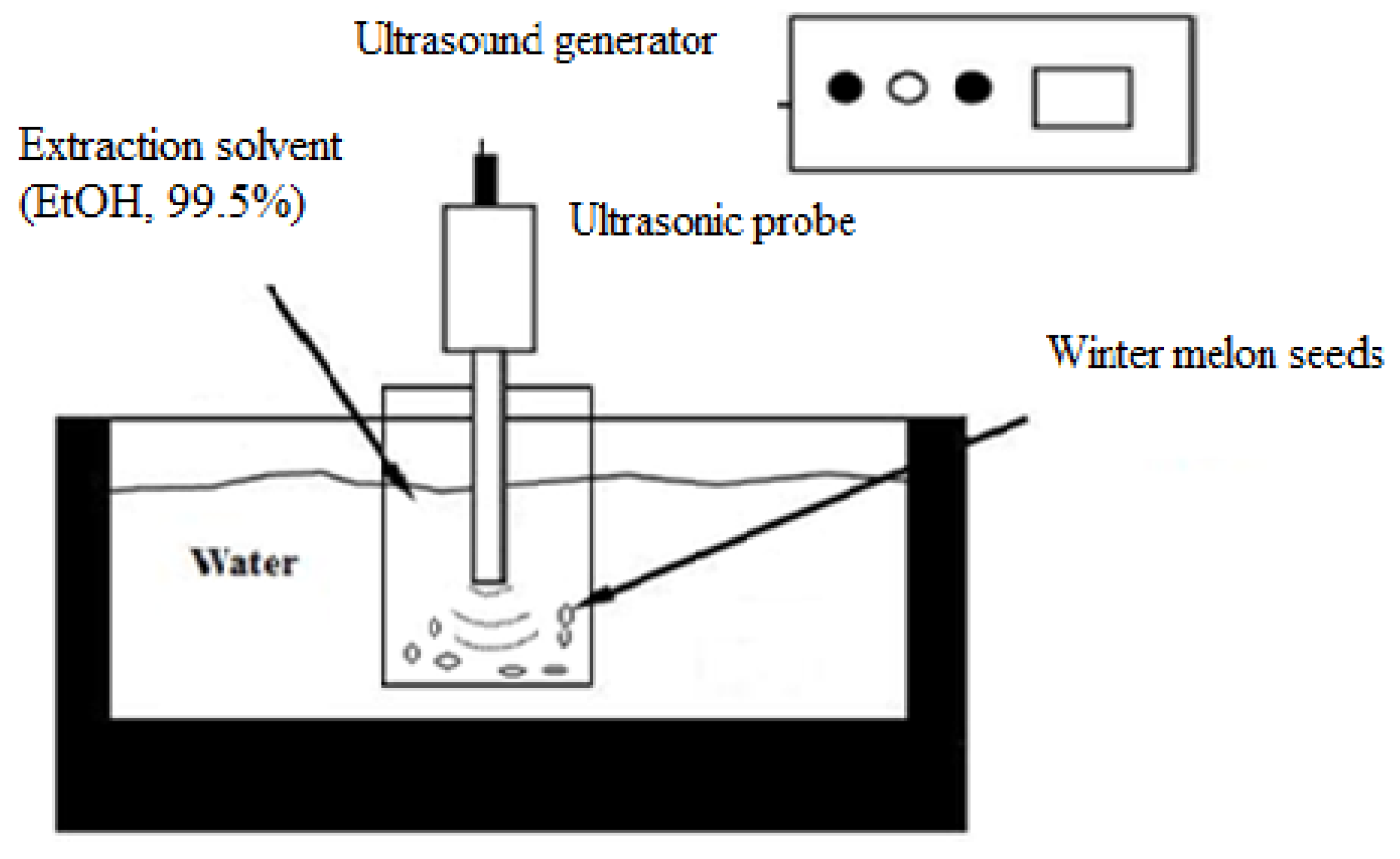
3. Experimental
3.1. Material
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction
3.4. Soxhlet Method
3.5. Crude Extract Yield Measurement
3.6. Determination of Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.1. Determination of DPPH˙ Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.2. Determination of ABTS˙+ Radical Scavenging Activity
3.7. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
3.8. Preparation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
3.9. Gas Chromatography Analysis
3.10. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Morton, J.F. The Wax Gourd, Year-Round Florida Vegetable with Unusual Keeping Quality; State Horticultural Society: Miami, FL, USA, 1971; Volume 84, pp. 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Zaini, N.A.; Anwar, F.; Abdul Hamid, A.; Saari, N. Kundur [Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn.]: A potential source for valuable nutrients and functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2011, 14, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendra, R.K.; Martin, P. Ethnomedicinal Plants; Agrobios: Jodhpur, India, 2006; pp. 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yagnik, B.; Jitendra, V.; Nurudin, J.; Nilesh, K.; Rameshvar, P.; Natavarlal, P. Antioxidant activity of Benincasa hispida on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharmacology online 2009, 1, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Stevigny, C.; Rolle, L.; Valentini, N.; Zeppa, G. Optimization of extraction of phenolic content from hazelnut shell using response surface methodology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimakr, M.; Russly, A.R.; Farah, S.T.; Noranizan, M.A.; Zaidul, I.S.; Ganjloo, A. Antioxidant activity of winter melon (Benincasa Hispida) seeds using conventional soxhlet extraction technique. Food Res. Int. 2012, 19, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, K.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.H. Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from grape (Vitis labrusca B.) peel by using response surface methodology. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Tomao, V.; Virot, M. Ultrasound-assisted Extraction in Food Analysis. In Handbook of Food Analysis Instruments; Semih, O., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 85–103. [Google Scholar]
- Cuoco, G.; Mathe, C.; Archier, P.; Chemat, F.; Vieillescazes, C. A multivariate study of the performance of an ultrasound-assisted madder dyes extraction and characterization by liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat, F.; Grondin, I.; Costes, P.; Moutoussamy, L.; Sing, A.S.C.; Smadja, J. High power ultrasound effects on lipid oxidation of refined sunflower oil. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2004, 11, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Weller, C.L. Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, M.; Zenker, V.H.; Knorr, D. Application of ultrasound-assisted thermal processing for preservation and quality retention of liquid foods. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinatoru, M.; Toma, M.; Mason, T.J. Advances in Sonochemistry; JAI Press: Greenwich, CT, USA, 1999; Volume 5, pp. 209–248. [Google Scholar]
- Romdhane, M.; Gourdan, C. Investigation in solid-liquid extraction: Influence of ultrasound. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 87, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinatoru, M. An overview of ultrasonically assisted extraction of bioactive principles from herbs. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Huma, A.; Kamran Khan, M. Application of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, Preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, K.A.; Saad, E.B.; Wilhelm, H.M.; Ramos, L.P. Optimization of the ethanolysis of Raphanus sativus (L. Var.) crude oil applying the response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.F.; Yang, X.H.; Zhao, L.D.; Wang, Y. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of epimedin C from fresh leaves of Epimedium and extraction mechanism. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.B.; Wang, M.; Gan, R.Y.; Ling, W.H. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins from mulberry, Using response surface methodology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3006–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veličković, D.T.; Milenović, D.M.; Ristić, M.S.; Veljković, V.B. Ultrasonic extraction of waste solid residues from the Salvia sp. essential oil hydrodistillation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patist, A.; Bates, D. Ultrasonic innovations in the food industry: From the laboratory to commercial production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2008, 9, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Brunton, N.P.; Patras, A.; Tiwari, B.; Donnell, C.P.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Barry-Rayan, C. Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) using response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Xie, C.; Gongjian, F.; Gu, Z.; Han, Y. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of melanin from Auricularia auricular fruit bodies. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.A.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Yue, X.F.; Fan, X.H.; Li, T.; Chen, S.F. Response surface optimization of ultrasound-assisted oil extractionfrom autoclaved almond powder. Food Chem. 2009, 11, 6513–6518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Wang, L.J.; Li, D.; Jiao, S.S.; Chen, X.D.; Mao, Z.H. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from flaxseed. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, D.; Rekha, B.N.; Gogate, P.R.; Ratho, V.K. Extraction of vanillin from vanilla pods: A comparison study of conventional soxhlet and ultrasound assisted extraction. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Pan, B.; Xu, J.; Sheng, J.; Shi, Y. Effects of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction conditions on yields and antioxidant activity of Chlorella pyrenoidosa extracts. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaei, A.; Barzegar, M.; Yamini, Y. Supercritical fluid extraction of tea seed oil and its comparison with solvent extraction. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcel, J.A.; Benedito, J.; Rosselló, C.; Mulet, A. Influence of ultrasound intensity on mass transfer in apple immersed in a sucrose solution. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Guler, G.O.; Aktumsek, A. In vitro antioxidant capacities and fatty acid compositions of three Centaurea species collected from Central Anatolia region of Turkey. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2638–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Luo, Q.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2157–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Meth. Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, S.C.; Tan, C.P.; Mirhosseini, H.; Lai, O.M.; Long, K.; Baharin, B.S. Optimization of ultrasound extraction condition of phospholipids from palm-pressed fiber. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Lin, C.W. Studies on the optimum models of the dairy product Kou Woan Lao using response surface methodology. Asian Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 14, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y.J. Effects of pulsed-vacuum and ultrasound on the osmodehydration kinetics and microstructure of apples (Fuji). J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the winter melon oil, extracted by UAE and by Soxhlet method, are available from the authors. |

| Run | Process Variables | CEY (mg-extract/g-dried matter) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Level (%) (X1) | Temperature (°C) (X2) | Sonication Time (min) (X3) | ||
| 1 | 34.69 (−1) | 46.94 (−1) | 36.12 (+1) | 72.10 |
| 2 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 95.44 |
| 3 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 96.24 |
| 4 | 65.31 (+1) | 53.06 (+1) | 23.88 (−1) | 92.81 |
| 5 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 96.43 |
| 6 | 65.31 (+1) | 46.94 (−1) | 23.88 (−1) | 89.18 |
| 7 | 34.69 (−1) | 46.94 (−1) | 23.88 (−1) | 68.18 |
| 8 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 94.60 |
| 9 | 34.69 (−1) | 53.06 (+1) | 36.12 (+1) | 77.50 |
| 10 | 34.69 (−1) | 53.06 (+1) | 23.88 (−1) | 72.00 |
| 11 | 65.31 (+1) | 46.94 (−1) | 36.12 (+1) | 100.1 |
| 12 | 65.31 (+1) | 53.06 (+1) | 36.12 (+1) | 108.2 |
| 13 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 20.00 (−1.63) | 77.23 |
| 14 | 75.00 (+1.63) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 106.5 |
| 15 | 25.00 (−1.63) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 65.33 |
| 16 | 50.00 (0) | 55.00 (+1.63) | 30.00 (0) | 90.11 |
| 17 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 40.00 (+1.63) | 95.15 |
| 18 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 96.43 |
| 19 | 50.00 (0) | 45.00 (−1.63) | 30.00 (0) | 81.20 |
| 20 | 50.00 (0) | 50.00 (0) | 30.00 (0) | 96.17 |
| Source | df | CEY (mg-extract/g-dried matter) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Sum of Squares | p-value | ||
| Model | 8 | 3,028.59 | <0.0001 | |
| Const. | 95.86 | |||
| X1 | 1 | 12.59 | 2,112.73 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | 1 | 2.66 | 94.52 | <0.0001 |
| X3 | 1 | 4.87 | 316.81 | <0.0001 |
| X12 | 1 | −3.65 | 176.22 | <0.0001 |
| X22 | 1 | −3.76 | 186.87 | <0.0001 |
| X32 | 1 | −3.56 | 167.47 | <0.0001 |
| X1X2 | 1 | - | - | - |
| X1X3 | 1 | 2.11 | 35.66 | <0.0001 |
| X2X3 | 1 | 0.76 | 4.58 | 0.0395 |
| Residual | 10 | 8.16 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 6 | 6.03 | 0.2810 | |
| Pure Error | 4 | 2.13 | ||
| Total | 19 | 3,036.76 | ||
| R2 | 0.997 | |||
| Adjusted-R2 | 0.995 | |||
| E (%) | 0.550 | |||
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bimakr, M.; Rahman, R.A.; Taip, F.S.; Adzahan, N.M.; Sarker, M.Z.I.; Ganjloo, A. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Crude Oil from Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida) Seed Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content and Fatty Acid Composition. Molecules 2012, 17, 11748-11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011748
Bimakr M, Rahman RA, Taip FS, Adzahan NM, Sarker MZI, Ganjloo A. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Crude Oil from Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida) Seed Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content and Fatty Acid Composition. Molecules. 2012; 17(10):11748-11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011748
Chicago/Turabian StyleBimakr, Mandana, Russly Abdul Rahman, Farah Saleena Taip, Noranizan Mohd Adzahan, Md. Zaidul Islam Sarker, and Ali Ganjloo. 2012. "Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Crude Oil from Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida) Seed Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content and Fatty Acid Composition" Molecules 17, no. 10: 11748-11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011748
APA StyleBimakr, M., Rahman, R. A., Taip, F. S., Adzahan, N. M., Sarker, M. Z. I., & Ganjloo, A. (2012). Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Crude Oil from Winter Melon (Benincasa hispida) Seed Using Response Surface Methodology and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolic Content and Fatty Acid Composition. Molecules, 17(10), 11748-11762. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171011748




