Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Methyl Salicylate Glycosides Isolated from Gaultheria yunnanensis (Franch.) Rehder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
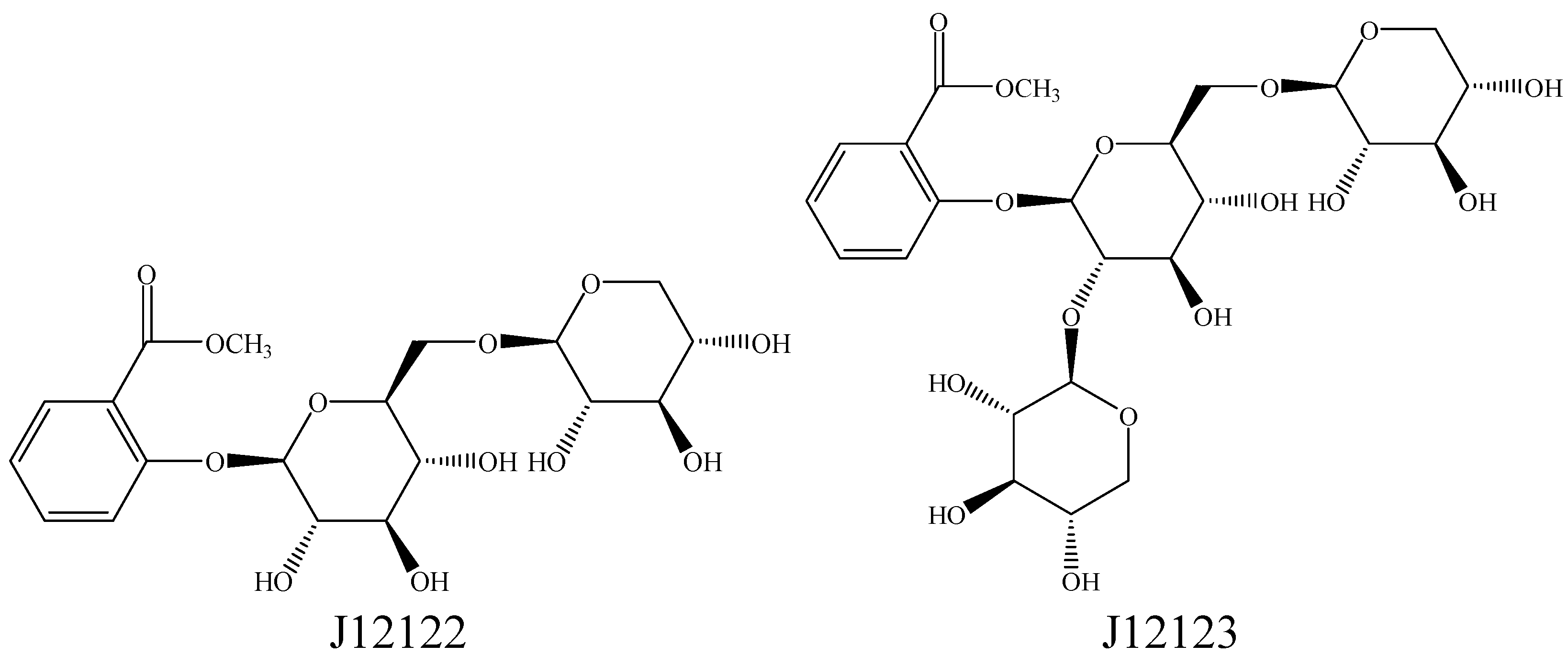
2.1. Compounds
2.2. Production of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
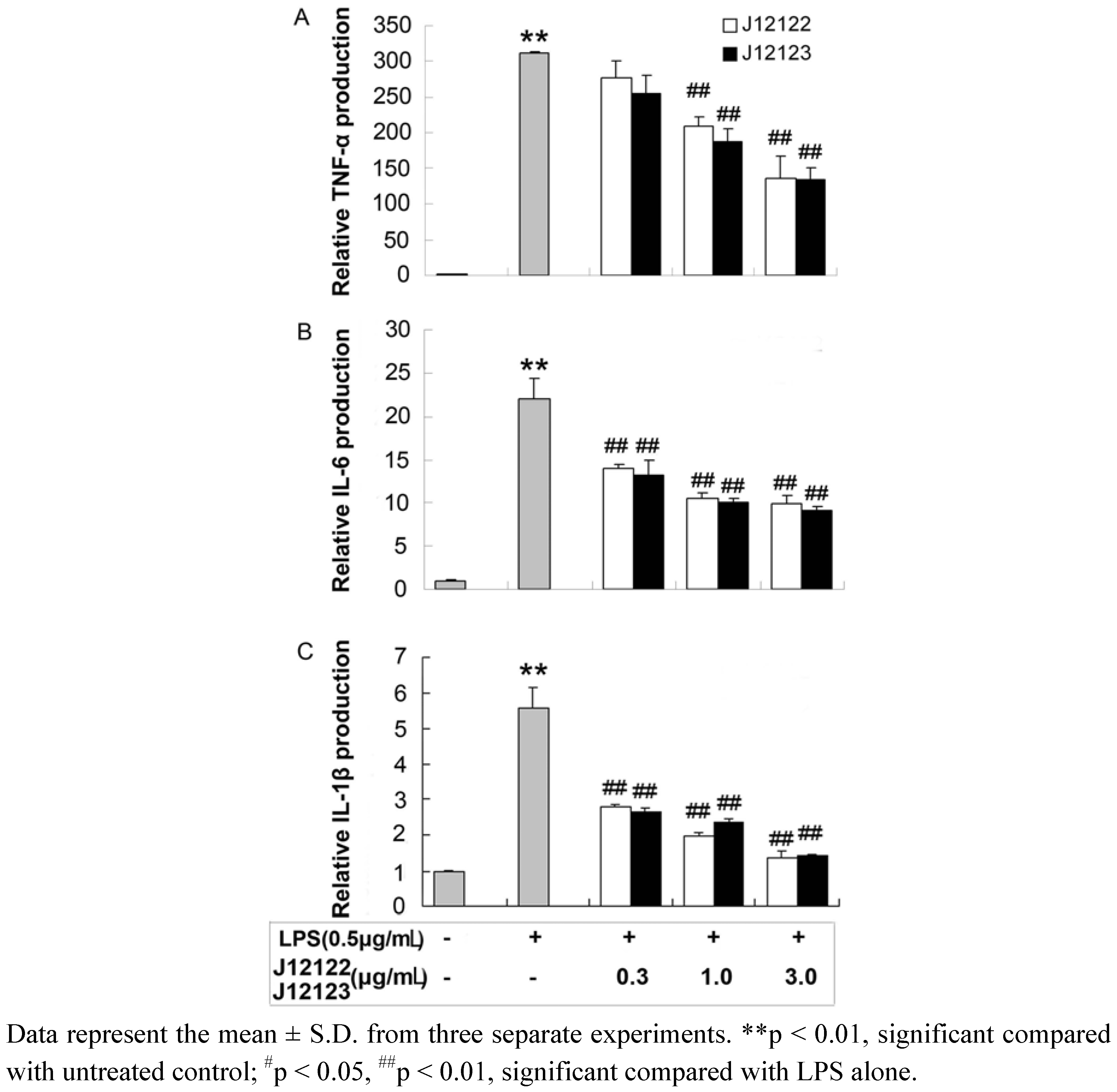
| Pro-inflammatory cytokine | Inhibition of J12122 (%) | Inhibition of J12123 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 μg/mL | 1.0 μg/mL | 3.0 μg/mL | 0.3 μg/mL | 1.0 μg/mL | 3.0 μg/mL | |
| TNF-α | 11.21 ± 2.08 | 32.69 ± 3.29 | 56.46 ± 2.98 | 18.37 ± 2.44 | 39.92 ± 3.09 | 57.16 ± 6.32 |
| IL-1β | 53.58 ± 3.56 | 64.40 ± 7.34 | 75.67 ± 8.02 | 54.47 ± 6.98 | 56.93 ± 4.51 | 74.33 ± 7.86 |
| IL-6 | 61.81 ± 4.01 | 71.26 ± 6.46 | 73.15 ± 4.37 | 39.83 ± 5.42 | 53.92 ± 6.72 | 58.73 ± 6.78 |
2.3. Effects of NO Production

2.4. Effect of Reactive Oxygen Species Production

3. Experimental
3.1. Chemical and Biological Materials
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Plant Material
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay

3.6. Measurement of NO Release (by Griess assay)

3.7. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)

3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Lawrence, T.; Willoughby, D.A.; Gilroy, D.W. Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution of inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loetscher, P.; Seitz, M.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. Activation of NK cells by CC chemokines. Chemotaxis, Ca2+ mobilization, and enzyme release. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Igonin, A.A.; Armstrong, V.W.; Shipkova, M.; Lazareva, N.B.; Kukes, V.G.; Oellerich, M. Circulating cytokines as markers of systemic inflammatory response in severecommunity-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 204–209. [Google Scholar]
- Teplyakov, A.I.; Pryschepova, E.V.; Kruchinsky, N.G.; Chegerovaet, T.I. Cytokines and soluble cell adhesion molecules. Possible markers of inflammatory response in atherosclerosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 902, 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.S.; Grange, R.W.; Isotani, E.; Sarelius, I.H.; Kamm, K.E.; Huang, P.L. nNOS and eNOS modulate cGMP formation and vascular response in contracting fast-twitch skeletal muscle. Physiol. Genomics 2000, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, G.P.; Ford-Hutchinson, A.W. Expression of mRNA for cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1993, 330, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: What have we learned? Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, A.; Nakae, S.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1beta, but not IL-1alpha, is required for antigen-specific T cell activation and the induction of local inflammation in the delayed-type hypersensitivity responses. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 701–712. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.H.; Shin, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Jung, H.J.; Koh, D.J.; Jo, B.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, K.; Lee, K.T. Anti-inflammatory effects of Madecassic acid via the suppression of NF-kB pathway in the LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, C.; Strehlow, I. Cytokines and STAT signalling. Adv. Pharmacol. 2000, 47, 113–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, S.F.; Serrano, A.; Hernanz-Falcon, P.; Martin de Ana, A.; Monterrubio, M.; Martinez, C.; Rodriguez-Frade, J.M. Mellado, M. Chemokines integrate JAK/STAT and G-protein pathways during chemotaxis and calcium flux responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shacter, E.; Weitzman, S.A. Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Huntingt) 2002, 16, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Kirschenbaum, A.; Lu, M.; Yao, S.; Klausner, A.; Preston, C.; Holland, J.F.; Levineet, A.C. Prostaglandin E (2) stimulates prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia cell growth through activation of the interleukin-6/GP130/STAT-3 signalling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.J.; Zheng, J.H.; Chen, X.Z. Studies on resources of ethnomedicine Gaultheria leucocarpa var. yunnanensis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2001, 26, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, D.; Li, C.; Zheng, J.; Koike, K.; Jia, Z.; Nikaido, T.J. Two diterpenoids from the roots of gaultheria yunnanensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriveau, C.C.; Danner, R.L. Endotoxin as a therapeutic target in septic shock. Infect. Agents Dis. 1993, 2, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.A.; Seatter, S.C.; Bellingham, J.; Clair, L. Mechanisms of reprogrammed macrophage endotoxin signal transduction after lipopolysaccharide pretreatment. Surgery 1995, 118, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, X.L.; Ding, Y.; Du, G.H. Gaultherin, a natural salicylate derivative from Gaultheria yunnanensis: Towards a better non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drug. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 530, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggard, E. Nitric oxide: mediator, murderer, and medicine. Lancet 1994, 343, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, C.F.; Hibbs, J.B., Jr. Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1991, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Macmicking, J.; Xie, Q.W.; Nathan, C. Nitric oxide and macrophage function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 323–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkimalla, V.B.; Blunder, M.; Bauer, R.; Efferth, T. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase by bis(helenalinyl)glutarate in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert, H.; Schwarz, P.M.; Forstermann, U. Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 1343–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Victor, V.M.; Rocha, M.; De la Fuente, M. Immune cells: Free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjigogos, K. The role of free radicals in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Panminerva. Med. 2003, 45, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.B.; Wahl, L.M. Oxidative stress augments the production of matrix metalloproteinase-1, cyclooxygenase-2, and prostaglandin E2 through enhancement of NF-kappa B activity in lipopolysaccharide-activated human primary monocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5423–5429. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, G.; Varsaldi, F.; Miglio, G.; Papini, M.G.; Battaglia, A.; Canonico, P.L. Cabergoline prevents necrotic neuronal death in an in vitro model of oxidative stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 457, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkimalla, V.B.; Blunder, M.; Korn, B.; Soomro, S.A.; Jansen, H.; Chang, W.; Posner, G.H.; Bauer, R.; Efferth, T. Effect of artemisinins and other endoperoxides on nitric oxide-related signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells. Nitric. Oxide 2008, 19, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominacini, L.; Pasini, A.F.; Garbin, U.; Davoli, A.; Tosetti, M.L.; Campagbola, M.; Rigoni, A.; Pastorino, A.M.; Cascio, V.L.; Sawamura, T. Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) binding to ox-LDL receptor-1 in endothelial cells induces the activation of NF-kappa B through an increased production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12633–12638. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples available from the authors.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Liu, R.; Sun, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.-M.; Zhang, T.-T.; Du, G.-H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Methyl Salicylate Glycosides Isolated from Gaultheria yunnanensis (Franch.) Rehder. Molecules 2011, 16, 3875-3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16053875
Zhang D, Liu R, Sun L, Huang C, Wang C, Zhang D-M, Zhang T-T, Du G-H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Methyl Salicylate Glycosides Isolated from Gaultheria yunnanensis (Franch.) Rehder. Molecules. 2011; 16(5):3875-3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16053875
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dan, Rui Liu, Lan Sun, Chao Huang, Chao Wang, Dong-Ming Zhang, Tian-Tai Zhang, and Guan-Hua Du. 2011. "Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Methyl Salicylate Glycosides Isolated from Gaultheria yunnanensis (Franch.) Rehder" Molecules 16, no. 5: 3875-3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16053875
APA StyleZhang, D., Liu, R., Sun, L., Huang, C., Wang, C., Zhang, D.-M., Zhang, T.-T., & Du, G.-H. (2011). Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Methyl Salicylate Glycosides Isolated from Gaultheria yunnanensis (Franch.) Rehder. Molecules, 16(5), 3875-3884. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16053875





