Small Molecule Inhibitors as Countermeasures for Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Crystal Structures of Botulinum Neurotoxins
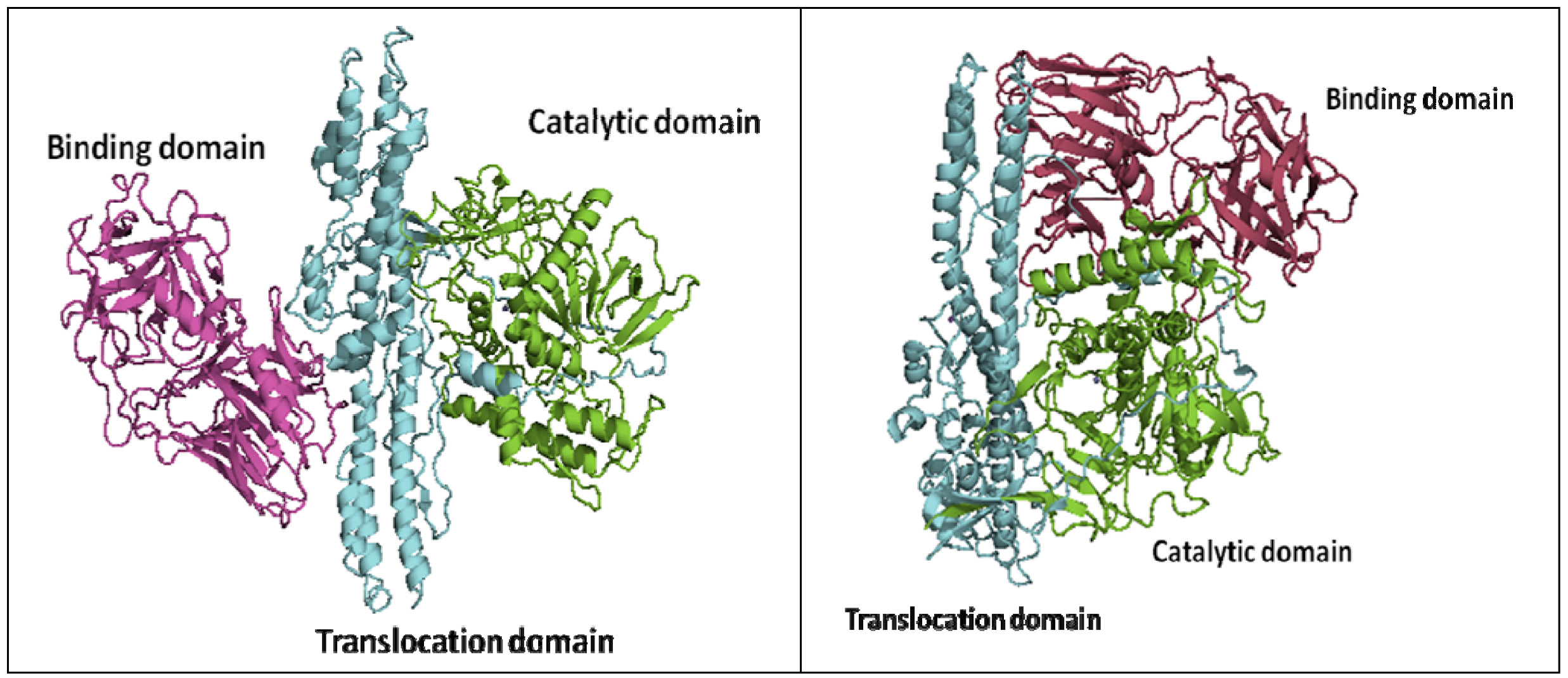
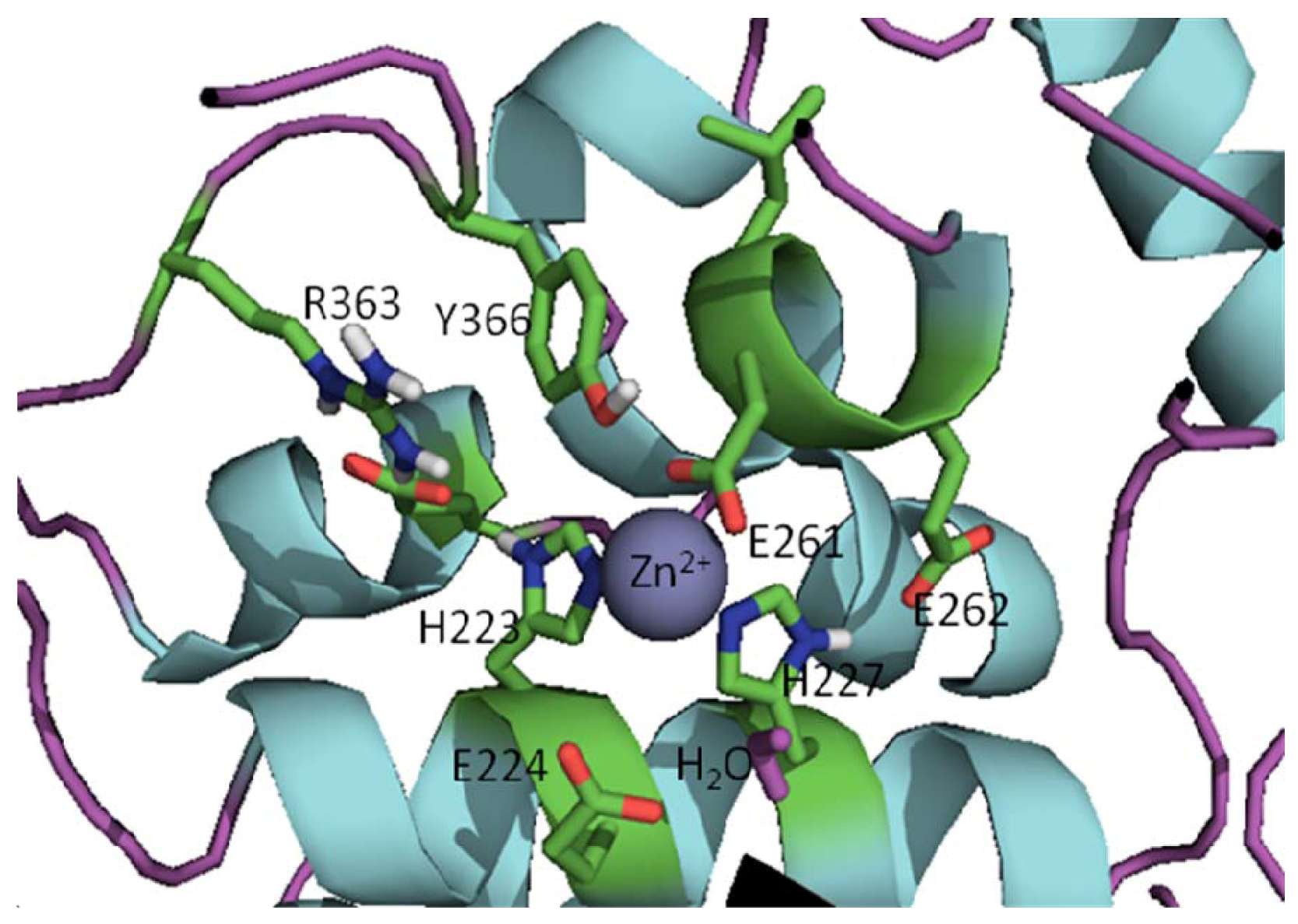
3. Approaches to BoNT Inhibition
4. Broad-Spectrum Small Molecule BoNT Inhibitors
5. Small Molecule BoNT/A LC Inhibitors
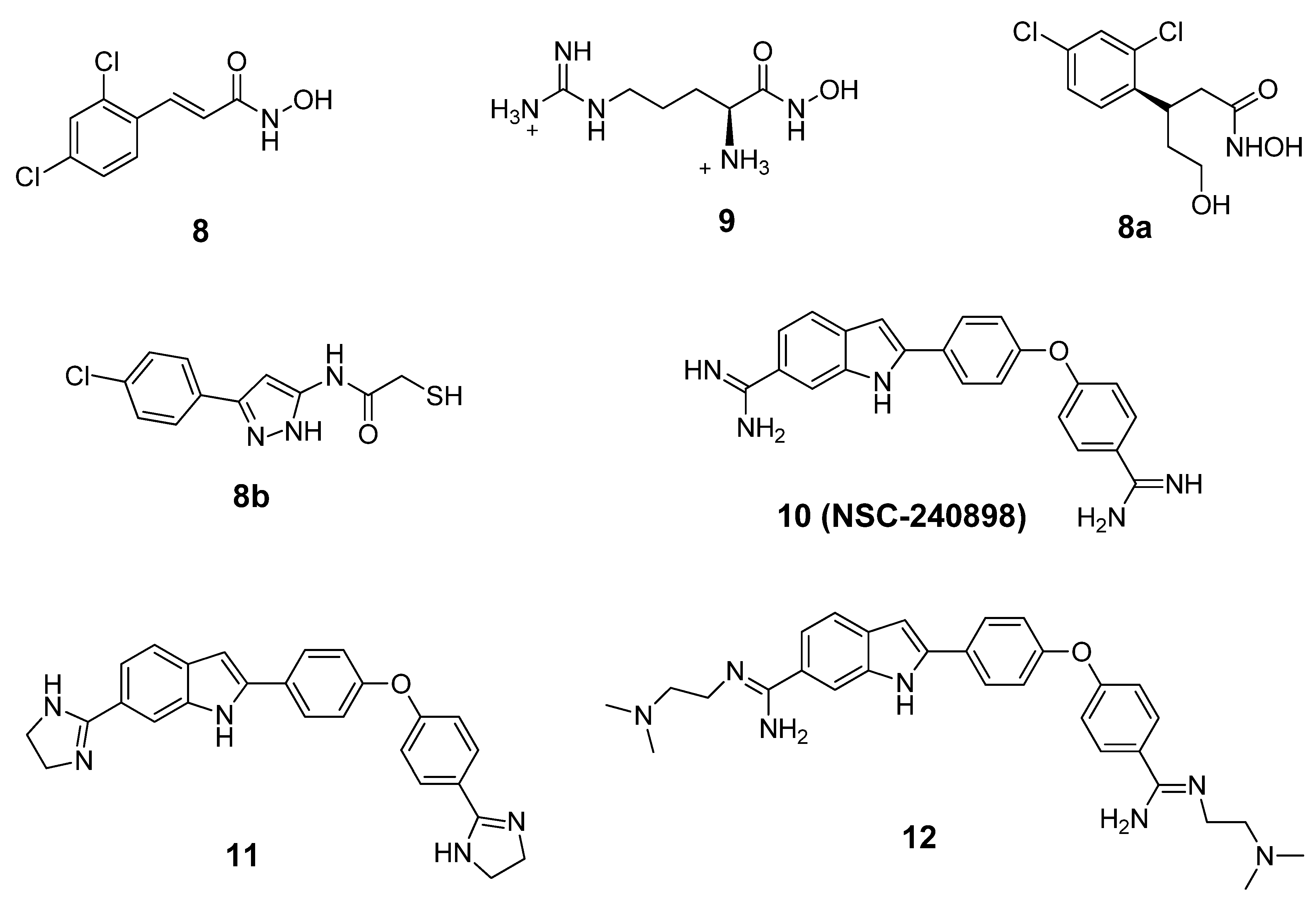
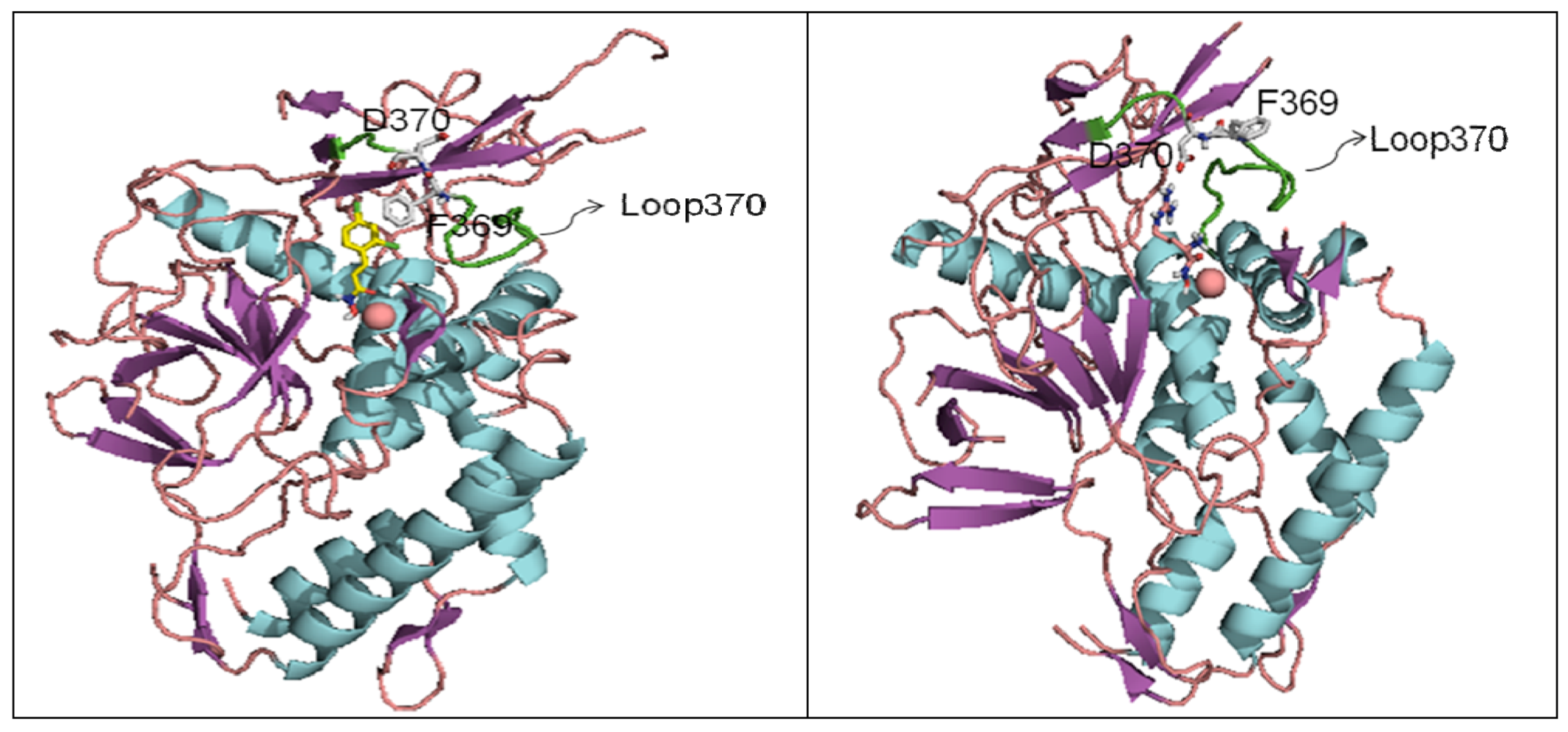
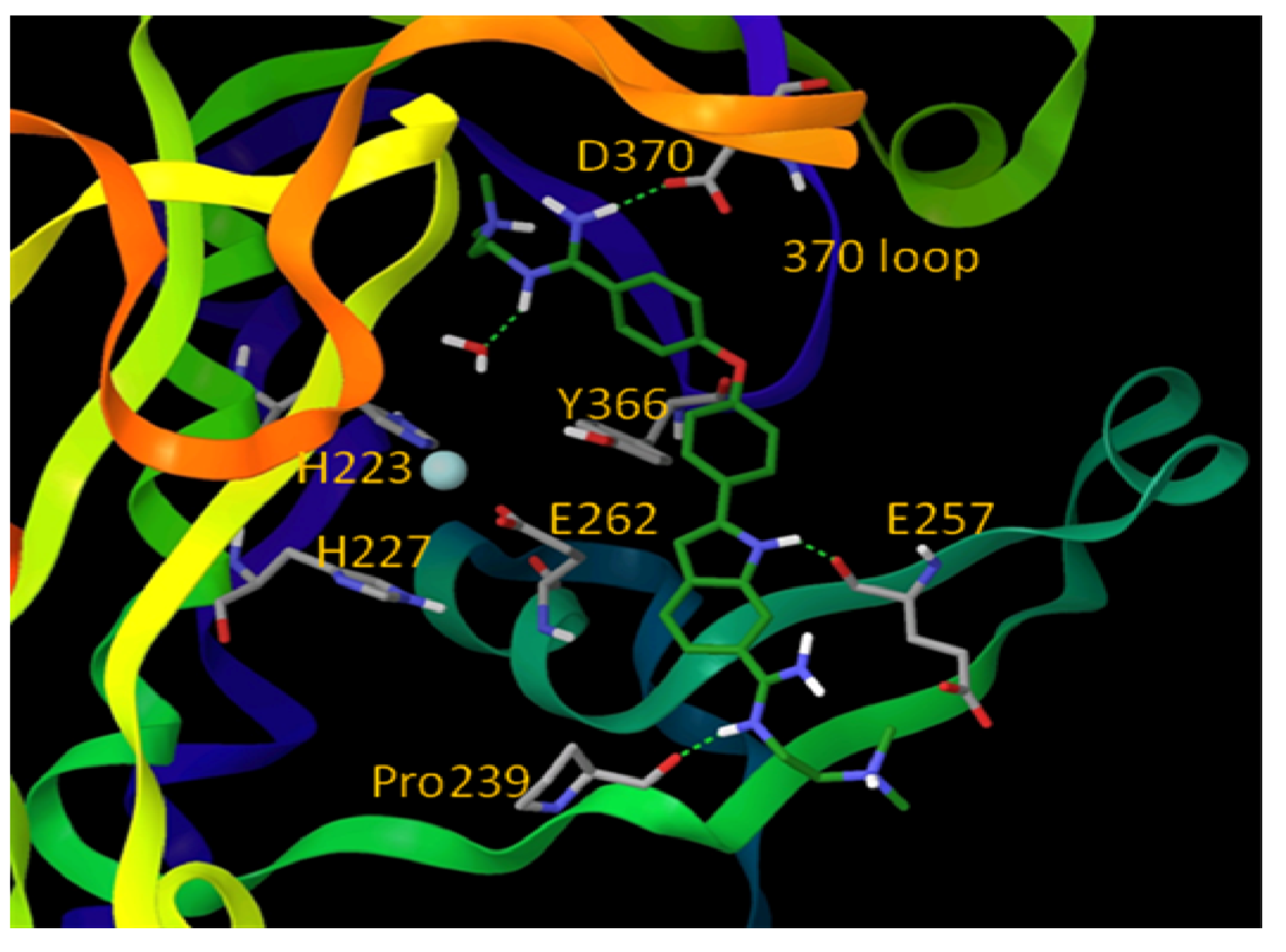
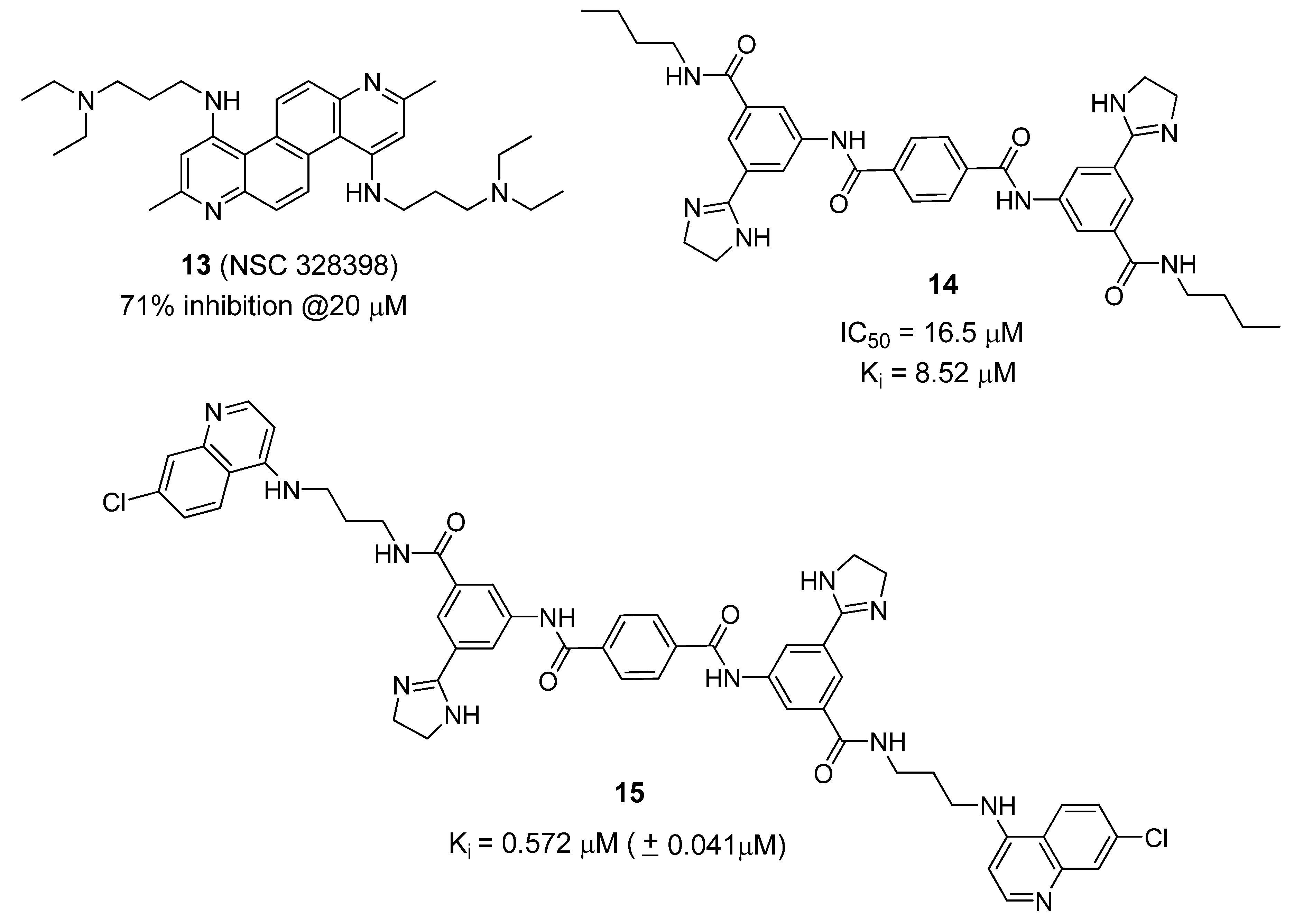
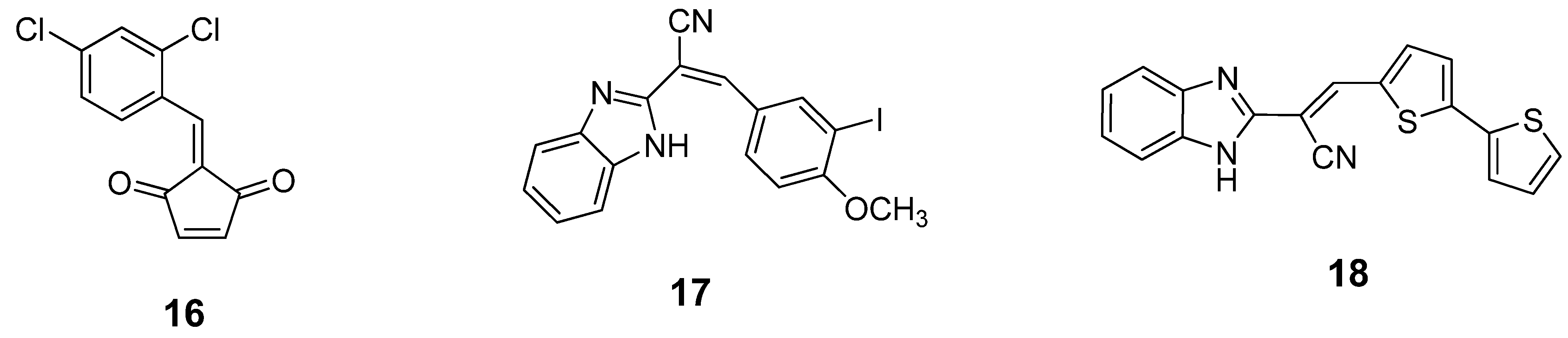

6. Small Molecule BoNT/B LC Inhibitors
7. Summary
References
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; Lillibridge, S.; Osterholm, M.T.; O'Toole, T.; Parker, G.; Perl, T.M.; Russell, P.K.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Tonat, K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Paddle, B.M. Therapy and prophylaxis of inhaled biological toxins. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2003, 23, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Henchal, E.A.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Bavari, S. The evolving field of biodefense: Therapeutic developments and diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Schmidt, J.J.; McGrath, C.F.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Panchal, R.G.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Kodukula, K.; Zaharevitz, D.W.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Conformational sampling of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A light chain: Implications for inhibitor binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Josko, D. Botulin toxin: A weapon in terrorism. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 17, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.C. Bacteria as potential tools in bioterrorism, with an emphasis on bacterial toxins. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 62, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, R.P.; Hartell, M.G.; Nichols, D.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.K.; van Hamont, J.E. Skillman, D.R. The medicinal chemistry of botulinum, ricin and anthrax toxins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Henchal, E.A.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Bavari, S. The evolving field of biodefense: Therapeutic developments and diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, H.D.; Sharma, S.K. Clostridium botulinum: A bug with beauty and weapon. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 31, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comella, C.L.; Pullman, S.L. Botulinum toxins in neurological disease. Muscle Nerve 2004, 29, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogau, R.G. Review of the use of botulinum toxin for hyperhidrosis and cosmetic purposes. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18 (6 Suppl.), S191–S197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.D. Medical aspects of biologic toxins. Anesthesiol. Clin. N. Amer. 2004, 22, 509–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Molgo, J. Botulinal neurotoxins: Revival of an old killer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhidayasiri, R.; Truong, D.D. Expanding use of botulinum toxin. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 235, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, H.; Rummel, A. Medical aspects of toxin weapons. Toxicology 2005, 214, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A. A new wrinkle on pain relief: Re-engineering clostridial neurotoxins for analgesics. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, T.R.; Mohan, A.K.; Polder, J.A.; Walton, M.K.; Braun, M.M. Botulinum toxin type A injections: Adverse events reported to the US Food and Drug Administration in therapeutic and cosmetic cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, S.S.; Schechter, R.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; Lillibridge, S.; Osterholm, M.T.; O'Toole, T.; Parker, G.; Perl, T.M.; Russell, P.K.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Tonat, K. Botulinum toxin as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Foran, P.G.; Mohammed, N.; Lisk, G.O.; Nagwaney, S.; Lawrence, G.W.; Johnson, E.; Smith, L.; Aoki, K.R.; Dolly, J.O. Evaluation of the therapeutic usefulness of botulinum neurotoxins B, C1, E, and F compared with the long lasting type A. Basis for distinct durations of inhibition of exocytosis in central neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, R.A.; Brown, B.R.; Hutchins, J.B.; Iandolo, J.J.; Jackson, R.; Slater, L.N.; Bronze, M.S. Microbiological, biological, and chemical weapons of warfare and terrorism. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 323, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, M.; Leikin, J.B.; Vogel, S.N.; Chaudry, Z.A. Biological and chemical agents: A brief synopsis. Am. J. Ther. 2002, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F.A.; Lisk, G.; Sesardic, D.; Dolly, J.O. Dynamics of motor nerve terminal remodeling unveiled using SNARE-cleaving botulinum toxins: the extent and duration are dictated by the sites of SNAP-25 truncation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 22, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, D.B.; Tepp, W.; Cohen, A.C.; DasGupta, B.R.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.L. Identification of the major steps in botulinum toxin action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.R. Intimate details of the most poisonous poison. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, K.; Chaddock, J.A.; Acharya, K.R. Botulinum and tetanus neurotoxins: Structure, function and therapeutic utility. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binz, T.; Blasi, J.; Yamasaki, S.; Baumeister, A.; Link, E.; Sudhof, T.C.; Jahn, R.; Niemann, H. Proteolysis of SNAP-25 by types E and A botulinal neurotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Stafford, R.G. Fluorogenic substrates for the protease activities of botulinum neurotoxins, serotypes A, B, and F. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, G.; Malizio, C.; Trimble, W.S.; Polverino de Laureto, P.; Milan, G.; Sugiyama, H.; Johnson, E.A.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum G neurotoxin cleaves VAMP/synaptobrevin at a single Ala-Ala peptide bond. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20213–20216. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Benfenati, F.; Poulain, B.; Rossetto, O.; de Polverino, L.P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature 1992, 359, 832–835. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Rossetto, O.; Catsicas, S.; de Polverino, L.P.; DasGupta, B.R.; Benfenati, F.; Montecucco, C. Identification of the nerve terminal targets of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A, D, and E. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23784–23787. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Shone, C.C.; Rossetto, O.; Alexander, F.C.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype F is a zinc endopeptidase specific for VAMP/synaptobrevin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11516–11519. [Google Scholar]
- Blasi, J.; Chapman, E.R.; Yamasaki, S.; Binz, T.; Niemann, H.; Jahn, R. Botulinum neurotoxin C1 blocks neurotransmitter release by means of cleaving HPC-1/syntaxin. EMBO.J. 1993, 12, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, S.; Eswaramoorthy, S. Structural analysis of the catalytic and binding sites of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin B. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Furey, W.; Navaza, J.; Sax, M.; Swaminathan, S. Domain organization in Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type E is unique: Its implication in faster translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, J.E.; Schmidt, J.J.; Fenn, T.; Burnett, J.C.; Arac, D.; Gussio, R.; Stafford, R.G.; Badie, S.S.; Bavari, S.; Brunger, A.T. A potent peptidomimetic inhibitor of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A has a very different conformation than the SNAP-25 substrate. Structure 2008, 16, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaggi, N.R.; Wilson, D.; Tzipori, S.; Allen, K.N. Catalytic features of the botulinum neurotoxin A light chain revealed by high resolution structure of an inhibitory peptide complex. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 5736–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidenbach, M.A.; Brunger, A.T. Substrate recognition strategy for botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Nature 2004, 432, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, M.A.; Stevens, R.C. Co-crystal structure of synaptobrevin-II bound to botulinum neurotoxin type B at 2.0 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Binz, T.; Swaminathan, S. Structural analysis of botulinum neurotoxin type E catalytic domain and its mutant Glu212-->Gln reveals the pivotal role of the Glu212 carboxylate in the catalytic pathway. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 6637–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Binz, T.; Swaminathan, S. Structural analysis of botulinum neurotoxin serotype F light chain: implications on substrate binding and inhibitor design. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11758–11765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.W.; Yu, W.; Bi, F.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type G light chain: Serotype divergence in substrate recognition. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9574–9580. [Google Scholar]
- Arndt, J.W.; Chai, Q.; Christian, T.; Stevens, R.C. Structure of botulinum neurotoxin type D light chain at 1.65 Å resolution: repercussions for VAMP-2 substrate specificity. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucco, C.; Schiavo, G. Structure and function of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1995, 28, 423–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieglstein, K.G.; DasGupta, B.R.; Henschen, A.H. Covalent structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A: Location of sulfhydryl groups, and disulfide bridges and identification of C-termini of light and heavy chains. J. Protein. Chem. 1994, 13, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagane, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kouguchi, H.; Sunagawa, H.; Inoue, K.; Fujinaga, Y.; Oguma, K.; Ohyama, T. Dichain structure of botulinum neurotoxin: Identification of cleavage sites in types C, D, and F neurotoxin molecules. J. Protein. Chem. 1999, 18, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, N.; Smith, L.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Light chain separated from the rest of the type a botulinum neurotoxin molecule is the most catalytically active form. PLoS One 2010, 5, e12872. [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo, G.; Shone, C.C.; Bennett, M.K.; Scheller, R.H.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum neurotoxin type C cleaves a single Lys-Ala bond within the carboxyl-terminal region of syntaxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10566–10570. [Google Scholar]
- Lebeda, F.J.; Cer, R.Z.; Mudunuri, U.; Stephens, R.; Singh, B.R.; Alder, M. The zinc-dependent protease activity of the botulinum neurotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 978–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.P.; Hartell, M.G.; Nichols, D.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.K.; van Hamont, J.E.; Skillman, D.R. The medicinal chemistry of botulinum, ricin and anthrax toxins. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.; Eubanks, L.M.; Dickerson, T.J.; Janda, K.D. The strange case of the botulinum neurotoxin: Using chemistry and biology to modulate the most deadly poison. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8360–8379. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Schmidt, J.J.; Stafford, R.G.; Panchal, R.G.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; McGrath, C.F.; Lane, D.J.; Sausville, E.A.; Zaharevitz, D.W.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Novel small molecule inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin A metalloprotease activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Opsenica, D.; Sriraghavan, K.; Panchal, R.G.; Ruthel, G.; Hermone, A.R.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kenny, T.A.; Lane, D.J.; McGrath, C.F.; Schmidt, J.J.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Gussio, R.; Solaja, B.A.; Bavari, S. A refined pharmacophore identifies potent 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline-based inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Pai, R.; Cardinale, S.C.; Butler, M.M.; Peet, N.P.; Moir, D.T.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2264–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Silvaggi, N.R.; Boldt, G.E.; Hixon, M.S.; Kennedy, J.P.; Tzipori, S.; Janda, K.D.; Allen, K.N. Structures of clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotype A light chain complexed with small-molecule inhibitors highlight active-site flexibility. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Bostian, K.A. Proteolysis of synthetic peptides by type Abotulinum neurotoxin. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, S.C.; Butler, M.M.; Ruthel, G.; Nuss, J.E.; Wanner, L.M.; Li, B.; Pai, R.; Peet, N.P.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Novel benzimidazole inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin/A display enzyme and cell based potency. The Botulinum J. 2010, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.B.; Simpson, L.L. Progress toward development of an inhalation vaccine against botulinum toxin. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.P.; Smith, L.A. Development of vaccines for prevention of botulism. Biochimie 2000, 82, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, A.; Karnath, T.; Henke, T.; Bigalke, H.; Binz, T. Synaptotagmins I and II act as nerve cell receptors for botulinum neurotoxin G. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30865–30870. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Richards, D.A.; Goodnough, M.C.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptotagmins I and II mediate entry of botulinum neurotoxin B into cells. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, N.; Kamata, Y.; Simpson, L.L. Lectins from Triticumvulgaris and Limaxflavus are universal antagonists of botulinum neurotoxin and tetanus toxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 258, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.-Z.; Zhou, J.; Miao, W.-Y.; Ding, F.-H.; Meng, J.-Y.; Jia, G.-R.; Li, J.-F.; Ye, H.-J.; He, X.-Y.; Chen, M.-Y.; Huang, Z.-M. Therapeutic effect of toosendanin on animal botulism. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 1982, 13, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Li, M.-F. Biological effects of toosendanin, a triterpenoid extracted from Chinese traditional medicine. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-F. Cure of experimental botulism and antibotulismic effect of toosendanin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Miao, W.-Y.; Ding, F.-H.; Meng, J.-Y.; Ye, H.-J.; Jia, G.-R.; He, X.-Y.; Sun, G.-Z.; Li, P.-Z. The effect of toosendanin on monkey botulism. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1985, 5, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Nakai, Y.; Eubanks, L.M.; Clancy, C.M.; Tepp, W.H.; Pellett, S.; Dickerson, T.J.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D.; Montal, M. Bimodal modulation of the botulinum neurotoxin protein-conducting channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Tepp, W.H.; Dickerson, T.J.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Function-oriented synthesis applied to the anti-botulinum natural product toosendanin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, Y.; Pellett, S.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Toosendanin: Synthesis of the AB-ring and investigations of its anti-botulinum properties (Part II). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, P.A.; Verma, V.A.; Paxton, T.J.; Pillow, T.H. Function-oriented synthesis, step economy, and drug design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.L. The interaction between aminoquinolines and presynaptically acting neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1982, 222, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L.L. Ammonium chloride and methylamine hydrochloride antagonize clostridial neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 225, 546–552. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L.L.; Coffield, J.A.; Bakry, N. Inhibition of vacuolar adenosine triphosphatase antagonizes the effects of clostridial neurotoxins but not phospholipase A2 neurotoxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 269, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks, L.M.; Silhar, P.; Salzameda, N.T.; Zakhari, J.S.; Xiaochuan, F.; Barbieri, J.T.; Shoemaker, C.B.; Hixon, M.S.; Janda, K.D. Identification of a natural product antagonist against the botulinum neurotoxin light chain protease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silhar, P.; Capkova, K.; Salzameda, N.T.; Barbieri, J.T.; Hixon, M.S.; Janda, K.D. Botulinum neurotoxin A protease: Discovery of natural product exosite inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2868–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Stowe, G.N.; Silhar, P.; Hixon, M.S.; Silvaggi, N.R.; Allen, K.N.; Moe, S.T.; Jacobson, A.R.; Barbieri, J.T.; Janda, K.D. Chirality holds the key for potent inhibition of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype a protease. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, S.T.; Thompson, A.B.; Smith, G.M.; Fredenburg, R.A.; Stein, R.L.; Jacobson, A.R. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A inhibitors: Small molecule mercaptoacetamide analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Ruthel, G.; Stegmann, C.M.; Panchal, R.G.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Stafford, R.G.; Lane, D.J.; Kenny, T.A.; McGrath, C.F.; Wipf, P.; Stahl, A.M.; Schmidt, J.J.; Gussio, R.; Brunger, A.T.; Bavari, S. Inhibition of metalloproteasebotulinum serotype A from a pseudo-peptide binding mode to a small molecule that is active in primary neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5004–5014. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, J.C.; Wang, C.; Nuss, J.E.; Nguyen, T.L.; Hermone, A.R.; Schmidt, J.J.; Gussio, R.; Wipf, P.; Bavari, S. Pharmacophore-guided lead optimization: The rational design of a non-zinc coordinating, sub-micromolar inhibitor of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5811–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Widom, J.; Petronijevic, F.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.E.; Bavari, S.; Gussio, R.; Wipf, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of inhibitors of botulinum neurotoxin metalloprotease. Heterocycles 2009, 79, 487–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M. M.; Cardinale, S. C.; Li, B.; Pai, R.; Ruthel, G.; Nuss, J. E.; Wanner, L. M.; Park, J.-B.; Rich, C.; Basu, A.; Mills, D.; Williams, J.D.; Peet, N.P.; Moir, D.; Bavari, S.; Bowlin, T.L. Unpublished results.
- Roxas-Duncan, V.; Enyedy, I.; Montgomery, V.A.; Eccard, V.S.; Carrington, M.A.; Lai, H.; Gul, N.; Yang, D.C.H.; Smith, L.A. Identification and biochemical characterization of small molecule inhibitors of clostridium botulinum neurotoxin seroptype A. Antimicro. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3478–3486. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.; Feng, M.; Roxas-Duncan, V.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Smith, L. A.; Yang, D.C.H. Quinolinol and peptide inhibitors of zinc protease in botulinum neurotoxin A: Effects of zinc ion and peptides on inhibition. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 491, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Vummenthala, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Park, J.G.; Wang, S.; Davis, J.; Millard, C.B.; Schmidt, J.J. Potent new small molecule inhibitor of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A endopeptidase developed by synthesis-based computer-aided molecular design. PLos One 2009, 4, e7730. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.-P.; Davis, J.; Wang, S.; Park, J.G.; Nambiar, M.P.; Schmidt, J.J.; Millard, C.B. Small molecules showing significant protection of mice against botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10129. [Google Scholar]
- Hermone, A.R.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.E.; Tressler, L.E.; Nguyen, T.L.; Solaja, B.A.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Schmidt, J.J.; Wipf, P.; Bavari, S.; Gussio, R. Three-dimensional database mining identifies a unique chemotype that unites structurally diverse botulinum neurotoxin serotype A inhibitors in a three-zone pharmacophore. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuss, J.E.; Dong, Y.; Wanner, L.M.; Ruthel, G.; Wipf, P.; Gussio, R.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Bavari, S.; Burnett, J.C. Pharmacophore refinement guides the rational design of nanomolar-range inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A metalloprotease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaja, B.A.; Opsenica, D.; Smith, K.S.; Milhous, W.K.; Terzic, N.; Opsenica, I.; Burnett, J.C.; Nuss, J.; Gussio, R.; Bavari, S. Novel 4-aminoquinolines active against chloroquine-resistant and sensitive P. falciparum strains that also inhibit botulinum serotype A. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4388–4391. [Google Scholar]
- Capkova, K.; Hixon, M.S.; Pellett, S.; Barbieri, J.T.; Johnson, E.A.; Janda, K.D. Benzylidene cyclopentenediones: First irreversible inhibitors against botulinum neurotoxin A's zinc endopeptidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaramoorthy, S.; Kumaran, D.; Swaminathan, S. A novel mechanism for clostridium botulinum neurotoxin inhibition. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 9795–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Nicholson, J.D.; Cornille, F.; Hackley, B.E., Jr. Efficacy of a novel metalloprotease inhibitor on botulinum neurotoxin B activity. FEBS Lett. 1998, 429, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Peet, N.P.; Butler, M.M.; Burnett, J.C.; Moir, D.T.; Bowlin, T.L. Small Molecule Inhibitors as Countermeasures for Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication. Molecules 2011, 16, 202-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16010202
Li B, Peet NP, Butler MM, Burnett JC, Moir DT, Bowlin TL. Small Molecule Inhibitors as Countermeasures for Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication. Molecules. 2011; 16(1):202-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16010202
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bing, Norton P. Peet, Michelle M. Butler, James C. Burnett, Donald T. Moir, and Terry L. Bowlin. 2011. "Small Molecule Inhibitors as Countermeasures for Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication" Molecules 16, no. 1: 202-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16010202
APA StyleLi, B., Peet, N. P., Butler, M. M., Burnett, J. C., Moir, D. T., & Bowlin, T. L. (2011). Small Molecule Inhibitors as Countermeasures for Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication. Molecules, 16(1), 202-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16010202



