Nanofabrication of Nonfouling Surfaces for Micropatterning of Cell and Microtissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cell Patterning Techniques
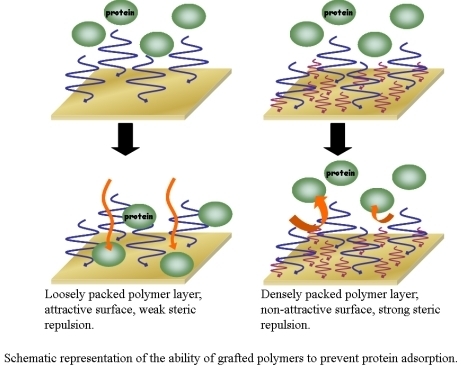
3. The Basis of Cellular Patterning; Non-Fouling Surface Chemistries
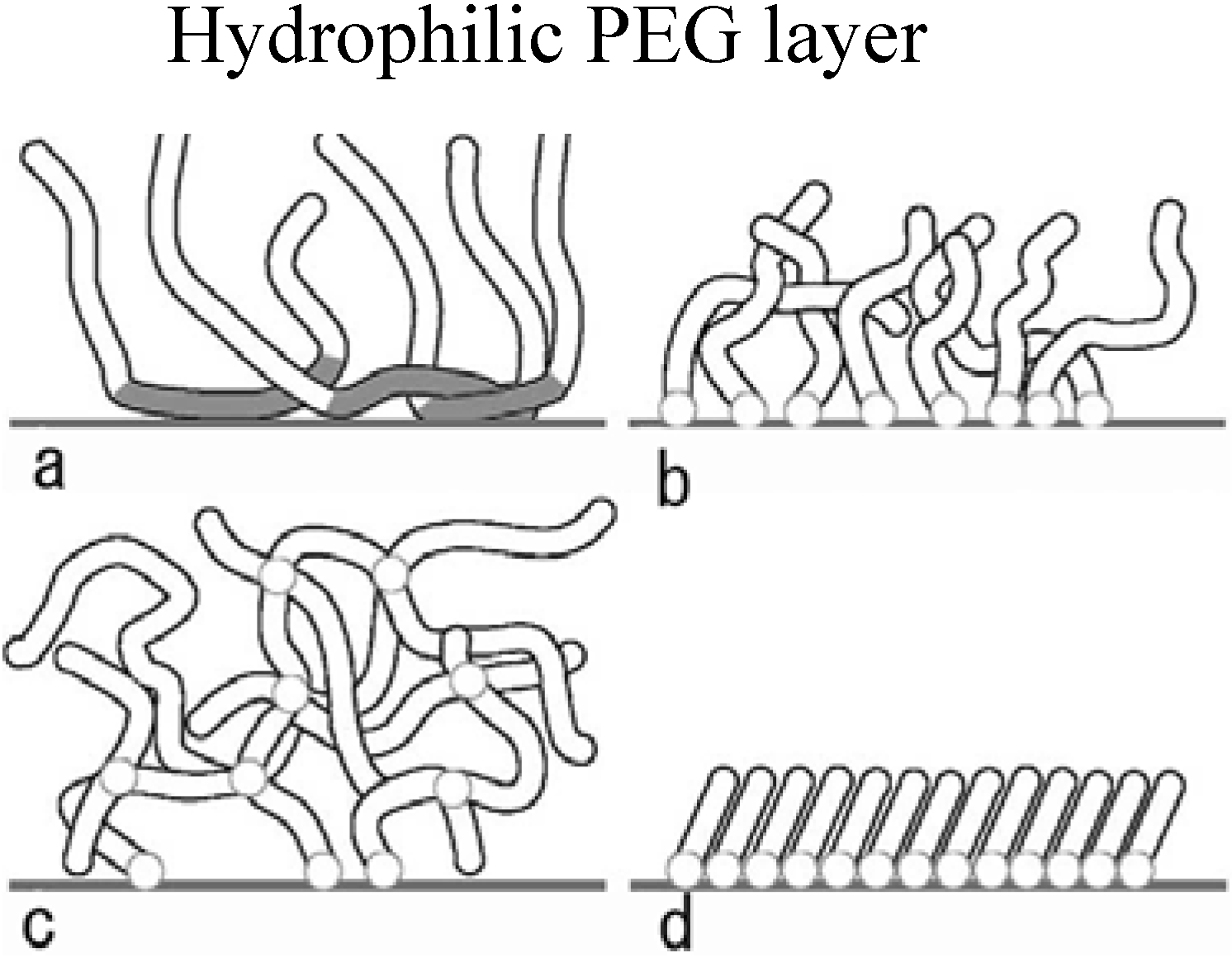
 |

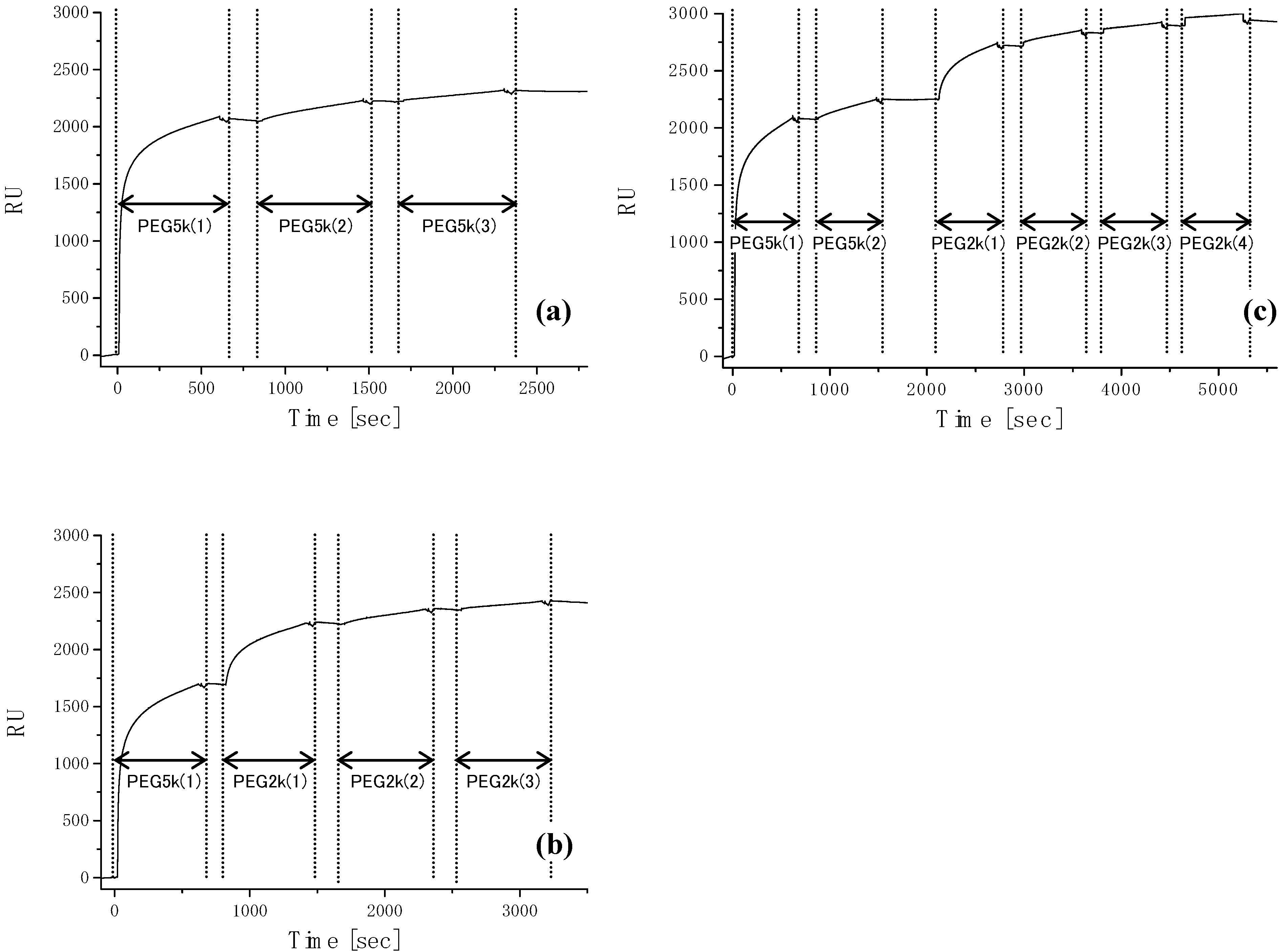

4. Patterned 3D-Microorganized Cells Using Dry Etching (Plasma Etching)
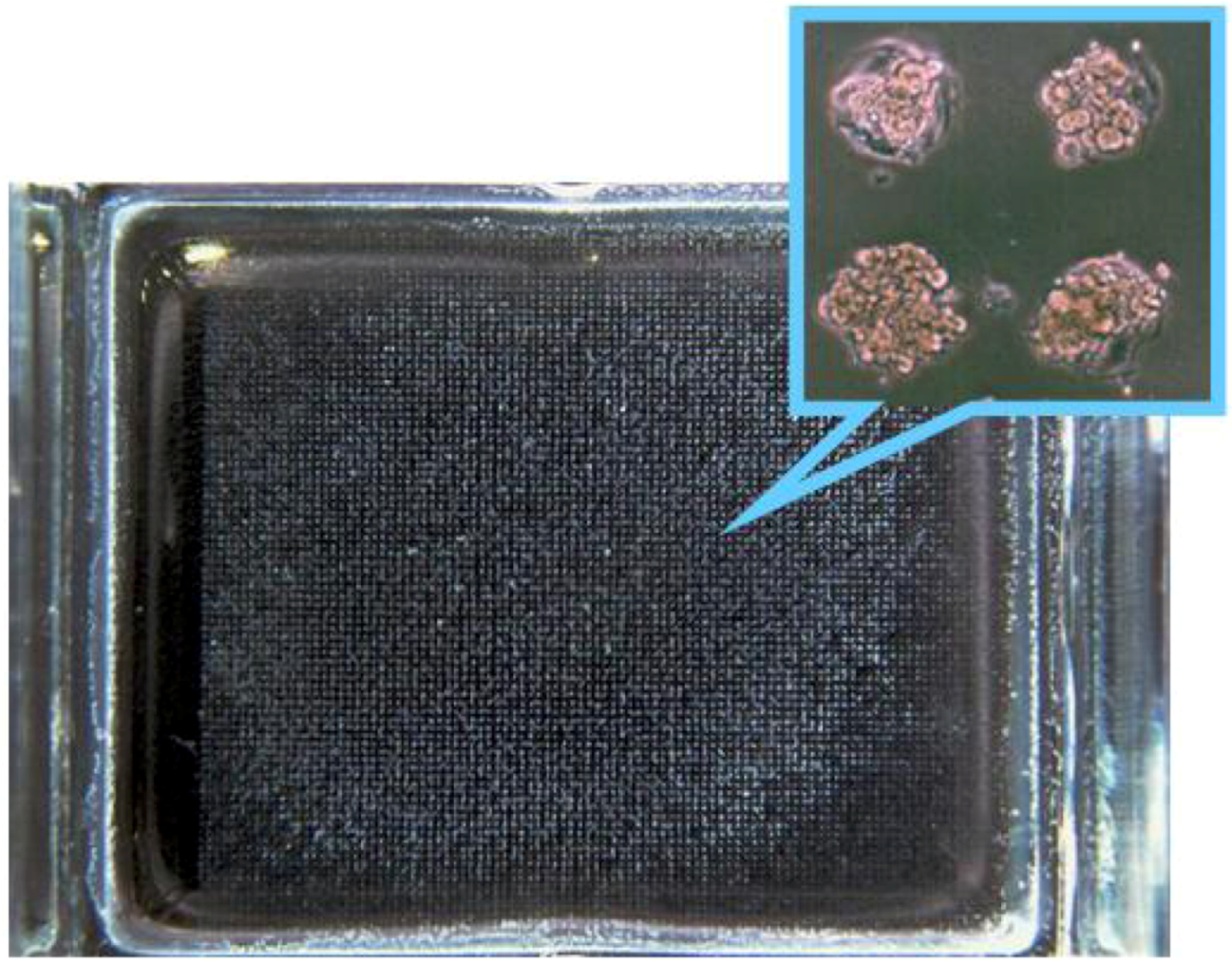

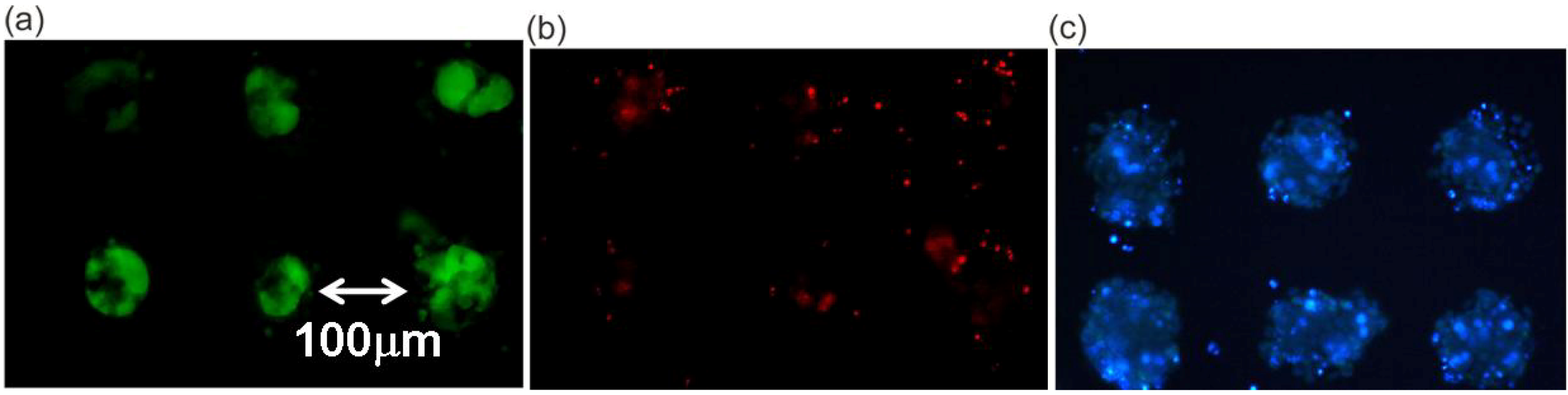
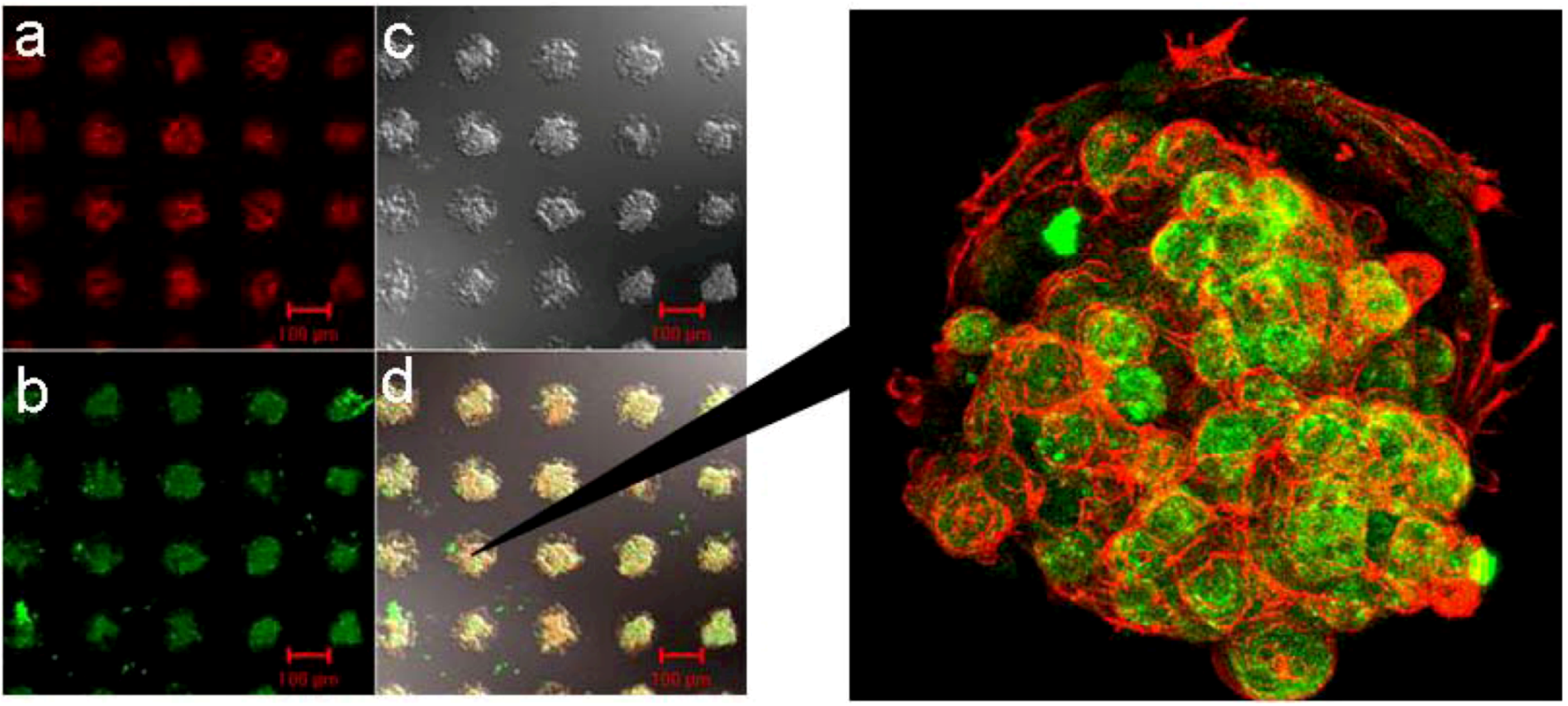
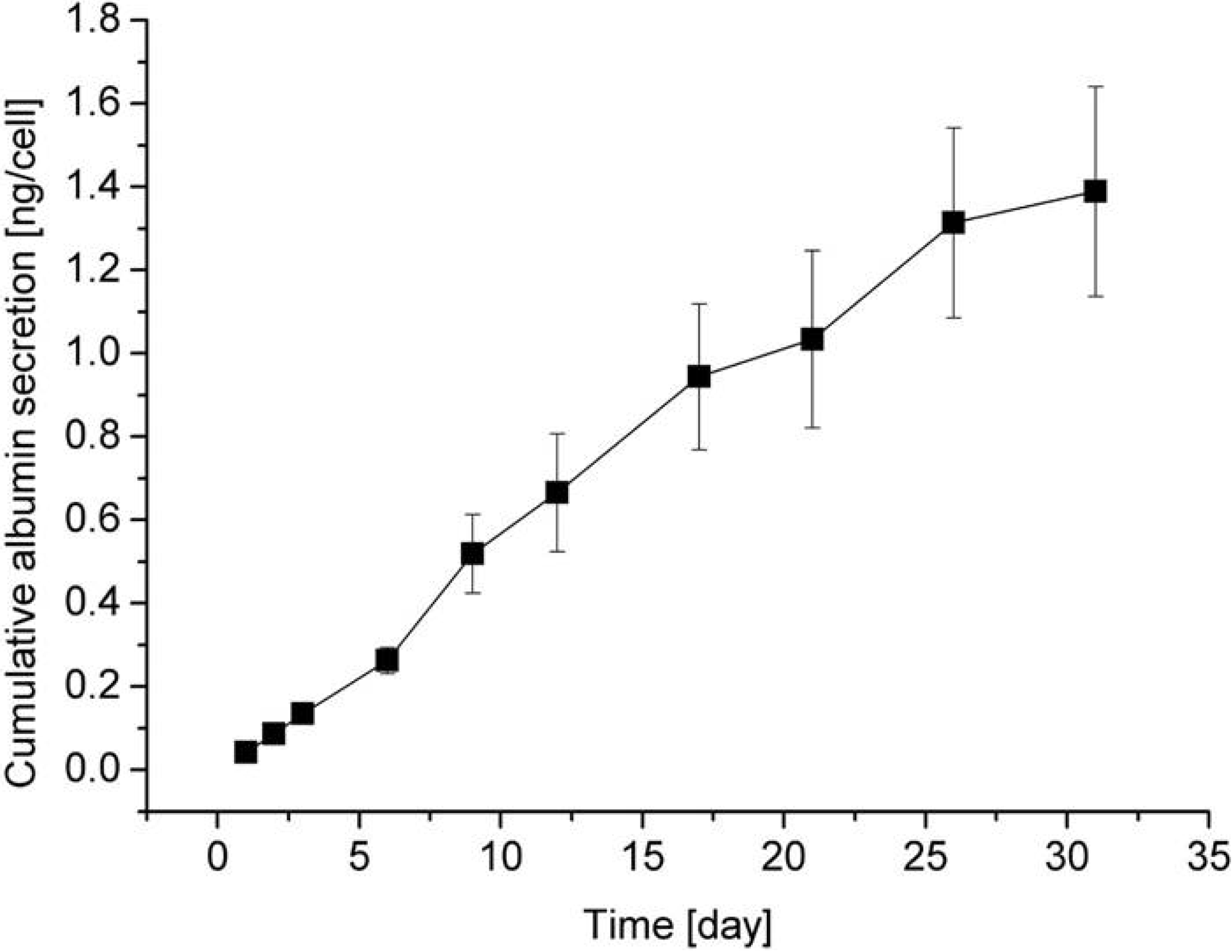
5. Cell Assembly for Tissue Engineering
6. Photolithography
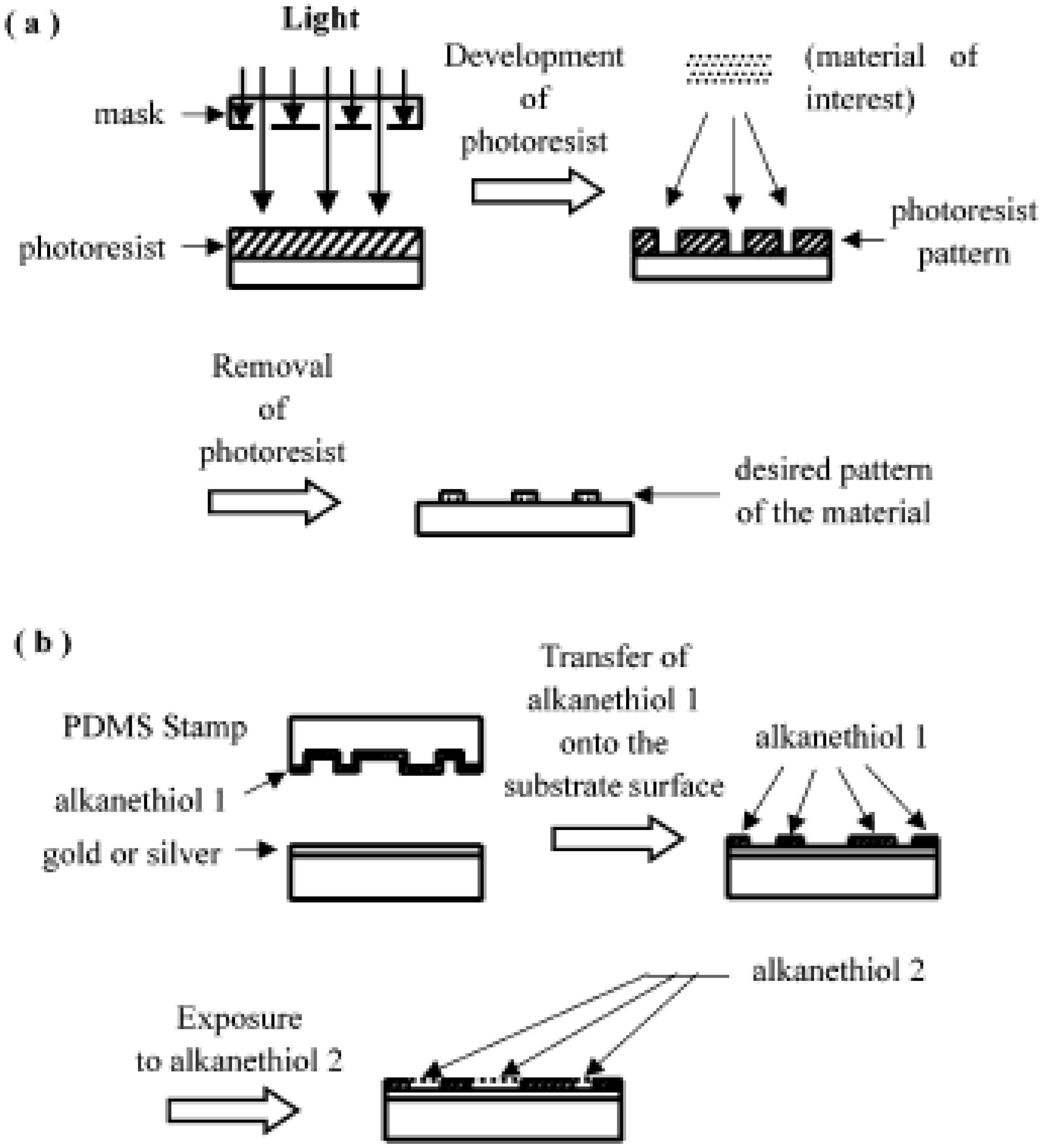
7. Microcontact Printing
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Takayama, S.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373. [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N.L.; Baskaran, H.; Detringer, S.K.W.; Whitesides, G.M.; Van de Water, L.; Toner, M. Nuetrophil chemotazis in linear and complex gradients of interleukin-8 formed in a microfabricated device. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 826–830. [Google Scholar]
- Britland, S.; Clark, P.; Connolly, P.; Moores, G. Micropatterned substrateum adhesiveness: Amodel for morphogenetic cues controlling cell behavior. Ex. Cell Res. 1992, 198, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, K.E.; Lom, B.; Hockberger, P.E. Spatial distribution of mammalian cells dictated by material surface chemistry. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.J.; Bhatia, S.K.; Quong, J.N.; Shoen, P.; Stenger, D.A. Rational pattern design for in vitro cellular networks using surface photochemistry. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1994, 12, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekos, E.J.; Ranien, J.P.; Aebischer, P.; Gardella, J.A.; Bnght, F.V. Structural-changes of bovine serum-albumin upon adsorption to modified fluoropolymer substrates used for neural cell attachmentstudies. Langmuir 1995, 11, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, R.; Kumar, A.; Lopez, G.P.; Stehanopoulos, G.N.; Wan, D.I.C. Engineering cell shape and function. Science 1994, 264, 696–698. [Google Scholar]
- Spargo, B.J.; Testoff, M.A.; Nielsen, T.B.; Stenger, D.A.; Hickman, J.J.; Rudolph, A.A. Spatially controlled adhesion, spreading, and differentiation of endothelial cells on self-assembled molecular monolayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11070–11074. [Google Scholar]
- Stenger, D.A.; Georger, J.H.; Dulcey, C.S.; Hickman, J.J.; Rudolph, A.S.; Nielsen, T.B.; McCort, S.M.; Calvert, J.H. Coplanar molecular assemblies of amino- and perfluorinated alkylsilanes: Characterization and geometric definition of mammalian cell adhesion and growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8435–8442. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, A.; Lammerink, T.S.J. Micro total analysis systems: Microfluidic aspects, integration concept and applications. Microsyst. Technol. Chem. Life Sci. 1998, 194, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, A.; Graber, N.; Widmer, H.M. Miniaturized total chemical analysis system: A novel concept for chemical sensing. Sens. Actuat. B. Chem. 1990, 1, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, P.S.; Manz, A. Lab-on-a-chip: Microfluidics in drug discovery. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, S.N.; Balis, U.J.; Yarmush, M.L.; Toner, M. Effect of cell-cell interactions in preservation of cellular phenotype: Cocultivation of hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, A.; Toner, M. Microengineering of cellular interactions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, V.L.; Bhatia, S.N. Tree-dimensional tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britland, S.; Clark, P.; Connolly, P.; Moores, G. Micropatterned substrateum adhesiveness: Amodel for morphogenetic cues controlling cell behavior. Ex. Cell Res. 1992, 198, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Mrksich, M.; Huang, S.; Whitesides, G.M.; Ingber, D.E. Genometric control of life and death. Science 1997, 276, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, E.; Z. Katz, B.; Aota, K.M.; Yamada, K.M.; Geiger, B.; Kam, Z. Molecular diversity of cell-matrix adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, B.; Bershadsky, A.; Pankov, R.; Yamada, K.M. transmembrane crosstalk between the cytoskeleton. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.; Firth, J.D.; Uitto, V.J.; Brunette, D.M. Substratum surface topography alter cell shape and regulates fibronectin mRNA level, mRNA stability, secretion and assembly in human fibroblas. J. Cell. Sci. 1995, 108, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, P.; Connolly, P.; Curtis, A.S.G.; Dow, J.A.T.; Wilkinson, C.D.W. Topographical control of cell behavior: II. multiple grooved substrate. Development 1990, 108, 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Stenger, D.A.; Gross, G.W.; Keefer, E.W.; Shaffer, K.M.; Andreadis, J.D.; Ma, W.; Pancrazio, J. Detection of physiologically active compounds using cell-based biosensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kononen, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Kallioniemi, A.; Barlund, M.; Schraml, P.; Leighton, S.; Torhorst, J.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P. Tissue microarrays. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 844–847. [Google Scholar]
- Ziauddin, J.; Sabatini, D.M. microarrays of cells expressing defined cDNAs. Nature 2001, 411, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulos, G.K.; DeFrances, M.C. Liver Regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.G.; Levenberg, S.; Langer, R. Nanoliter-scale synthesis of arrayed biomaterials and application to human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 863–866. [Google Scholar]
- Revzin, A.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Surface engineering with poly(ethylene glycol) photolithography to create high- density cell arrays on glass. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9855–9862. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, H.; Hirano, A.; Nagasaki, Y.; Okano, T.; Horiike, Y.; Kataoka, K. Two-dimensional multiarray formation of hepatoytes sphroids on a microfabricated PEG-brush surface. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Hill, J.P.; Lee, M.V.; Vinu, A.; Charvet, R.; Acharya, S. Challenges and breakthroughs in recent research on self-assembly. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 014109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Darder, M.; Aranda, P.; Ariga, K. Advances in biomimetic and nanostructured biohybrid materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, Y.Y.; Kato, M.; Mrksich, M. Self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates presenting mannitol groups are inert to protein adsorption and cell attachment. Langmuir 2000, 16, 9604–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.M.; Raghavan, S.; Tan, J.L.; Chen, C.S. Degradation of micropatterned surface by cell-dependent and independent processes. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Ratner, B.D.; Bryant, S.J. Biomaterials: Where we have been and where we are going. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 6, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M. Poly(ethylene glycol) Chemistry. Biotechnical and Biomedical Applications; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Martic, P.A.; Tan, J.S. Protein adsorption on pluronic copolymer-coated polystyrene particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 131, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kopecek, J.; Andrade, J.; Biomed, J. Protein-resistant surfaces prepared by PEO-containing block copolymer surfactants. Mater. Res. 1989, 23, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.S.; Martic, P.A. Protein adsorption and conformational change on small polymer particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 136, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lshihara, K.; Ziats, N.; Tierney, B.; Nakabayashi, N.; Anderson, J. Protein adsorption from human plasma is reduced on phospholipid polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Hubbell, J. Solution technique to incorporate polyethylene oxide and other water-soluble polymers into surfaces of polymeric biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombotz, W.; Guanghui, W.; Horbett, T.; Hoffman, A. Protein adsorption to poly(ethylene oxide) surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.K.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Min, B.G.; Cho, H.I. Negative cilia concept for thromboresistance: Synergistic effect of PEO and sulfonate groups grafted onto polyurethanes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.; Park, K. Prevention of protein adsorption and platelet adhesion on surfaces by PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, K.; Holmberg, K.; Safranj, A.; Hoffman, A.; Edgell, M.; Kozlowski, A.; Hovanes, B.; Harris, J. Reduction of fibrinogen adsorption on PEG-coated polystyrene surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterberg, E.; Bergstr6m, K.; Holmberg, K.; Riggs, J.; Alstine, J.V.; Schuman, T.; Burns, N.; Harris, J. Comrarison of polysaccharide and poly(ethylene glycol) coating for reduction of protein adsorption on polystyrene surfaces. Colloid. Surf. A 1993, 77, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Inoue, H.; Ikada, Y. Protein adsorption and platelet adhesion onto polyurethane grafted with methoxy-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate by plasma technique. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1993, 27, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, G.; Sefton, M. Immobilization of poly(ethylene glycol) onto a poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel: 2. evaluation of thrombogenicity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 27, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hlady, V.; Goander, C. The surface density gradient of grafted poly(ethylene glycol): Preparation, characterization and protein adsorption. Colloid. Surface B 1994, 3, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, T.B.; Lee, S.J.; Park, K. Analysis of the Prevention of Protein Adsorption by Steric Repulsion Theory. In Proteins at Interfaces II; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pasche, S.; Vörös, J.; Griesser, H.J.; Spencer, N.D.; Textor, M. Effects of lonic strength and surface charge on protein adsorption at PEGylated surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 17545–17552. [Google Scholar]
- 50. Pasche, S.; De Paul, S.M.; Vörös, J.; Spencer, N.D.; Textor, M. Poly(L-lysine)-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) assembled monolayers on niobium oxide surfaces: a quantitative study of the influence of polymer interfacial architecture on resistance to protein adsorption by ToF-SIMS and in situ OWLS. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9216–9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.S.; Pasche, S.; Castner, D.G.; Textor, M. Characterization of poly(L-lysine)-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) assembled monolayers on niobium pentozide substrates using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry and multivariate analysis. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, C.; Attwood, D. Effects of block architecture and composition on the association properties of poly(oxyalkylene) copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 501–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.R.; Loh, W. Investigation of Self-Assembly and Micelle Polarity for a Wide Range of Ethylene Oxide−Propylene Oxide−Ethylene Oxide Block Copolymers in Water. Langmuir 1998, 14, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Holzwarthf, J.F.; Hatton, T.A. Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers in aqueous-soltions – Thermodynamics of copolymer association. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 2414–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M.Y.; Melik-Nubarov, N.S.; Batrakova, E.V.; Kabanov, A.V. Relationship between pluronic block copolymer structure, critical micellization concentration and partitioning coeffecientsof low molecular mass solutions. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanka, G.; Hoffmann, H.; Ulbricht, W. Phase diagrams and aggregation behavior of poly(oxyethylene)-poly(oxypropylene)-poly(oxyethylene) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Hatton, T.A. Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly8ethylene oxide) block sopolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloid. Surf. A 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thissen, H.; Hayes, J.P.; Kingshott, P.; Johnson, G.; Harvey, E.C.; Griesser, H.J. Nanometer thickness laser ablation for spatial control of cell attachment. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Caldwell, K.D. Plasma protein interactions with PluronicTM-treated colloids. Colloid. Surf. B 1996, 7, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.A.; Tresco, P.A.; Caldwell, K.D. Surface modification for controlled studies of cell-ligand interactions. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2377–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.M.; Park, K.J. Analysis on the surface adsorption of PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers by radiolabelling and fluorescence techniques. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 52, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.; Park, K. Prevention of protein adsorption and platelet adhesion on surfaces by PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, V.A.; Jastromb, W.E.; Bhatia, S.N. Engineering protein and cell adhesivity using PEO-terminated triblock polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Surface characterization of functionalized polylactide through the coating with heterobifunctional poly(ethylene glycol)/polylactide block copolymer. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Akiyama, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Quantitative and reversible lectin-induced association of gold nanoparticles modified with α-Lactosyl-ω-mercapto-(ethylene glycol). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8226–8230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, R.G.; Allara, D.L. Absorption of bifunctional organic disulfides on gold surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 4481–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, E.; Chapman, R.G.; Liang, M.N.; Meluleni, G.; Pier, G.; Ingber, D.E. Self-assembled monolayers that resist the adsorption of proteins and the adhesion of bacterial and mammalian cells. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6336–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, E.; Chapman, R.G.; Holmlin, R.E.; Takayama, S.; Whitesides, G.M. A survey of structure-property relationships of surfaces that resist the adsorption of protein. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5605–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendel, D.; Dahint, R.; Herrwerth, S.; Schloerholz, M.; Eck, W.; Grunze, M. Temperature dependence of the protein resistance of poly-and oligo(ethylene glycol)-terminated alkanethiolate monolayers. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5717–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Biebuyck, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning self-assembled monolayers – applications in materials science. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1498–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrksich, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning self-assembled monolayers using microcontact printing: a new technology for biosensors? Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Use of controlled reactive spreading of liquid alkanethiol on gold modify the size of features produced by microcontact printing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 3274–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, R.J.; Wilbur, J.L.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of submicrometer features on curved substrates by microcontact printing. Science 1995, 269, 664–666. [Google Scholar]
- Britland, S.; Clark, P.; Connolly, P.; Moores, G. Micropatterned substrateum adhesiveness: amodel for morphogenetic cues controlling cell behavior. Ex. Cell Res. 1992, 198, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulcey, C.S.; Georger, J.H.; krauthamer, V.; Strenger, D.A.; Fare, T.L.; Calvert, J.M. Deep UV photochemistry of chemisorbed monolayers: Patterned soplanar molecular assemblies. Science 1991, 252, 551–554. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfeld, D.; Kahler, K.H.; Hockber, P.E. Controlled outgrowth of dissociated neurons on patterned substrates. J. Neurosci. 1988, 4098–4120. [Google Scholar]
- Frisbie, C.D.; Wollma, E.W.; Wrighton, M.S. High Lateral Resolution Imaging by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry of Photopatterned Self-Assembled Monolayers Containing Aryl Azide. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2563–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.J.; Bhatia, S.K.; Quong, J.N.; Shoen, P.; Stenger, D.A. Rational pattern design for in vitro cellular networks using surface photochemistry. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1994, 12, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfisch, M.H.; Pemberton, J.E. Air stability of alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers on silver and gold surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4502–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearinger, J.P.; Terrettaz, S.; Michel, R.; Tirelli, N.; Vogel, H.; Textor, M. Chemisorbed poly(propylene sulphide)-based copolymers resist biomolecular interactions. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.A.; Golledge, S.L.; Castner, D.G.; Healy, K.E. Peptide-modified p(AAm-co-EG/AAc) IPNs grafted to bulk titanium modulate osteoblast behavior in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 64A, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearinger, J.P.; Castner, D.G.; Healy, K.E. Biomolcular modification of p(AAm-co-EG/AA) IPNs supports osteoblast adhesion and phenotypic exression. J. Biomater. Sci.-Poly. Ed. 1998, 9, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revzin, A.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Surface engineering with poly(ethylene glycol) photolithography to create high-density cell arrays on glass. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9855–9862. [Google Scholar]
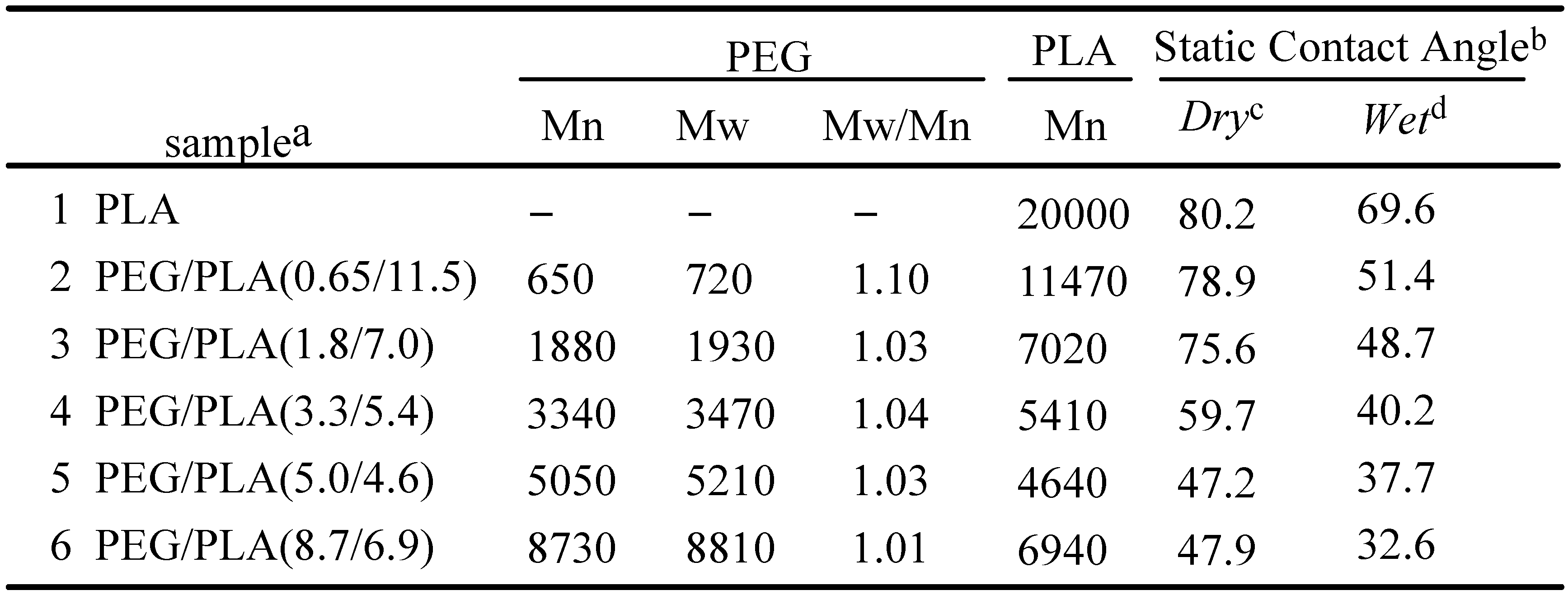
- Satomi, T.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Otsuka, H.; Kataoka, K. Density control of poly (ethylene glycol) layer to regurate cellular attachment. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6609–6703. [Google Scholar]
- Satomi, T.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Tateishi, T.; Otsuka, H. Physicochemical characterization of densely packed poly (ethylene glycol) layer for minimizing nonspecific protein adsorption. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Rossant, J.; Zaret, K.S. Liver organogenesis promoted by endothelial cells prior to vascular function. Science 2001, 294, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, K.S. Regulatory pheases of early liver development: Paradigms of organogenesis. Nature Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Couter, J.; Moritz, D.R.; Li, B.; Phillips, G.L.; Liang, H.; Gerber, H.P.; Hillan, K.J.; Ferrara, N. Angiogenesis-independent endothelial protection of liver: Role of VEGFR-1. Science 2003, 299, 890–893. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nature Med. 2003, 6, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Tzanakakis, E.S.; Hansen, L.K.; Hu, W.S. The role of actin filaments and microtubules in hepatocyte spheroid self-assembly. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 2001, 48, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, J.M.; Fussenegger, M. Microscale tissue engineering using gravity-enforced cell assembly. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Yamato, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Okano, T. Cell sheet engineering for myocardial tissue reconstruction. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, N.; Paquet, S.; Labbe, R.; Germain, L.; Auger, F.A. A completely biological tissue-engineered human blood vessel. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, J.; Mizumoto, H.; Nakazawa, K.; Kajiwara, T.; Funatsu, K. Hepatocyte organoid culture in elliptic hollow fibers to develop a hybrid artificial liver. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2004, 27, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Khademhosseini, A.; Yeh, J.; Jon, S.; Eng, G.; Suh, K.Y.; Burdick, J.A.; Langer, R. Cell bocking inside microwells sithin reversibly sealed microfluidic channels for fabrivcating multipherotype cell arrays. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britland, S.; Clark, P.; Moores, G. Micropatterned substratum adhesiveness: A model for morphogenetic cues controlling cell behavior. Exp. Cell. Res. 1992, 198, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinfeld, D.; Kahler, K.H.; Hockberger, P.E. Controlled outgrowth of dissociated neurons on patterned substrates. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 4098–4120. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, S. N.; Yarmush, M. L.; Toner, M. Controlling cell interactions by micropatterning in co-cultures: Hpetocytes and 3T3 fibroblasts. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1997, 34, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarback, J.A.; Palm, S.L.; Furcht, L.T.; Letourneau, P.C. Guidance of neurite outgrowth by pathways of substratum-adsorbed laminin. J. Neurosci. Res. 1985, 13, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, K.E.; Thomas, C.H.; Rezania, A.; Kim, J.E.; McKeown, P.J.; Lom, B.; Hockberger, P.E. Kinetics of bone cell organization and mineralization on materials with patterne surface chemistry. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinfeld, D.; Kahler, K.H.; Hockberger, P.E. Controlled outgrowth of dissociated neurons on patterned substrates. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 4098–4120. [Google Scholar]
- Britland, S.; Perez-Arnaud, E.; Clark, P.; McGinn, B.; Connolly, P.; Moores, G. Micropatterning proteins and synthetic peptides on solid supports: A novel application for microelectronics fabrication technology. Biotechnol. Prog. 1992, 8, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lom, B.; Healy, K.E.; Hockberger, P.E. A versatile technique for patterning biomolecules onto glass coverslips. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1993, 50, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, A.; Toner, M. Microengineering of cellular interactions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.; Takayama, S.; Ostuni, E.; Ingber, D.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterning proteins and cells using soft lithography. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Polymer microstructures formed by moulding in capillaries. Nature 1995, 376, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Whitesides, G.M. features of gold having micrometer to centimenter dimensions can be formed thorugh a combination of stamping with an elastometric stamp and an alkaneethiol ”ink”. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 273, 347–349. [Google Scholar]
- Jackman, R.; Wilbur, J.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of submicrometer features on curved substrates by microcontact printing. Science 1995, 269, 664–666. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, G.P.; Albers, M.W.; Schreiber, S.L.; Carroll, R.; Peralta, E.; Whitesides, G.M. convernient methods for patterning the adhesion of mammalian cells to surfaces using self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on gold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 5877–5878. [Google Scholar]
- Mrksich, M.; Chen, C.S.; Xia, Y.; Dike, L.E.; Ingber, D.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Controling cell attachment on contoured surfaces with self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on gold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10775–10778. [Google Scholar]
- Mrksich, M.; Dike, L.E.; Tien, J.; Ingber, D.E.; Whitesides, G.M. Using microcontact printing to pattern the attachment of mammalian cells to self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on transparent films of gold and silver. Exp. Cell. Res. 1997, 235, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.F. Microchemical systems: Status, challenges, and opportunities . AIChE J. 1999, 45, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.A.; Kim, S. Microfluidics: Basic issue, applications and challenges. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Otsuka, H. Nanofabrication of Nonfouling Surfaces for Micropatterning of Cell and Microtissue. Molecules 2010, 15, 5525-5546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085525
Otsuka H. Nanofabrication of Nonfouling Surfaces for Micropatterning of Cell and Microtissue. Molecules. 2010; 15(8):5525-5546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085525
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtsuka, Hidenori. 2010. "Nanofabrication of Nonfouling Surfaces for Micropatterning of Cell and Microtissue" Molecules 15, no. 8: 5525-5546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085525
APA StyleOtsuka, H. (2010). Nanofabrication of Nonfouling Surfaces for Micropatterning of Cell and Microtissue. Molecules, 15(8), 5525-5546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085525