Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Gallic Acid, a Major Component of Toona sinensis Leaf Extract, on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
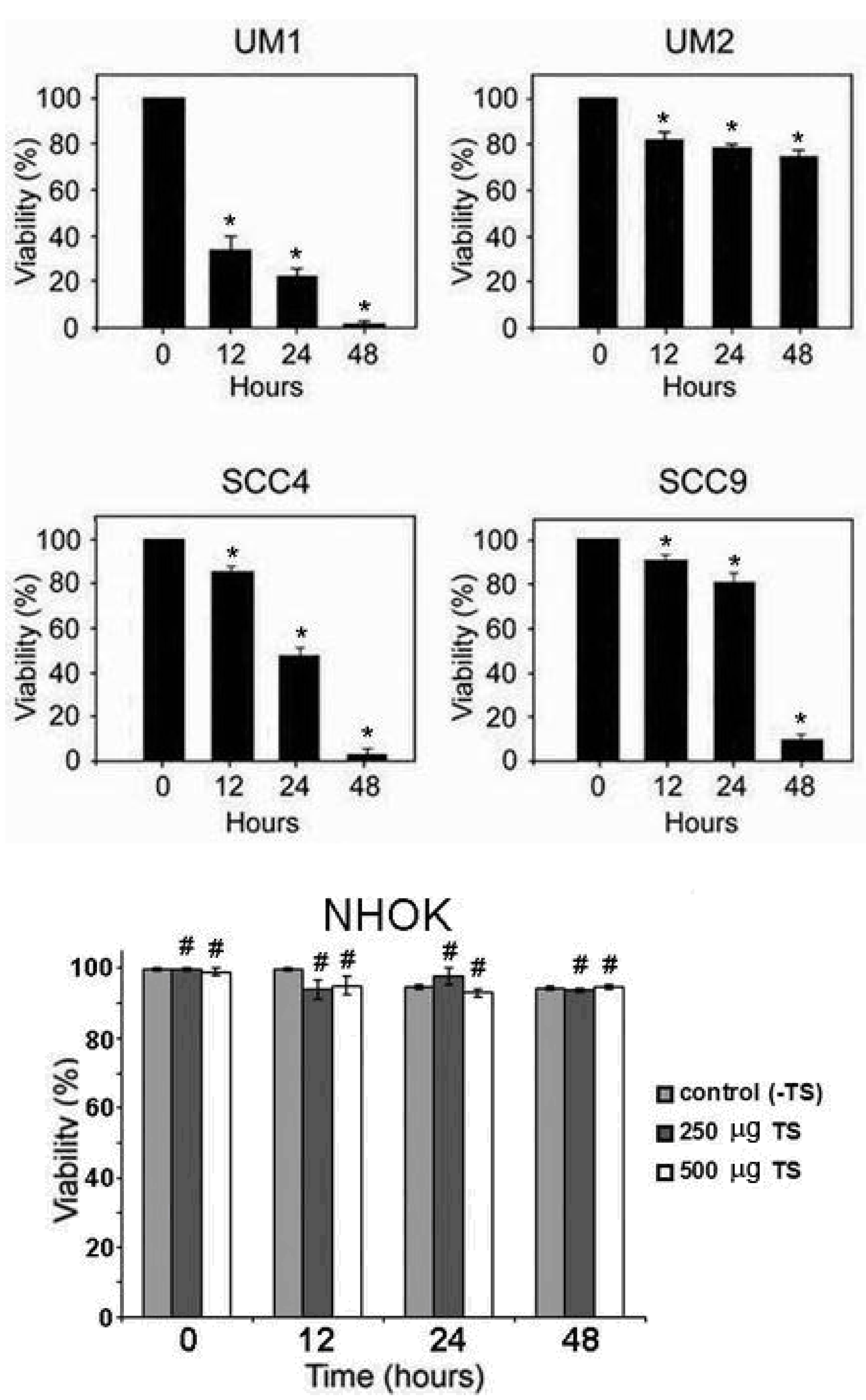
2.1. Toona sinensis leaf extract (TSL-1) has inhibitory effects on oral squamous cell carcinoma
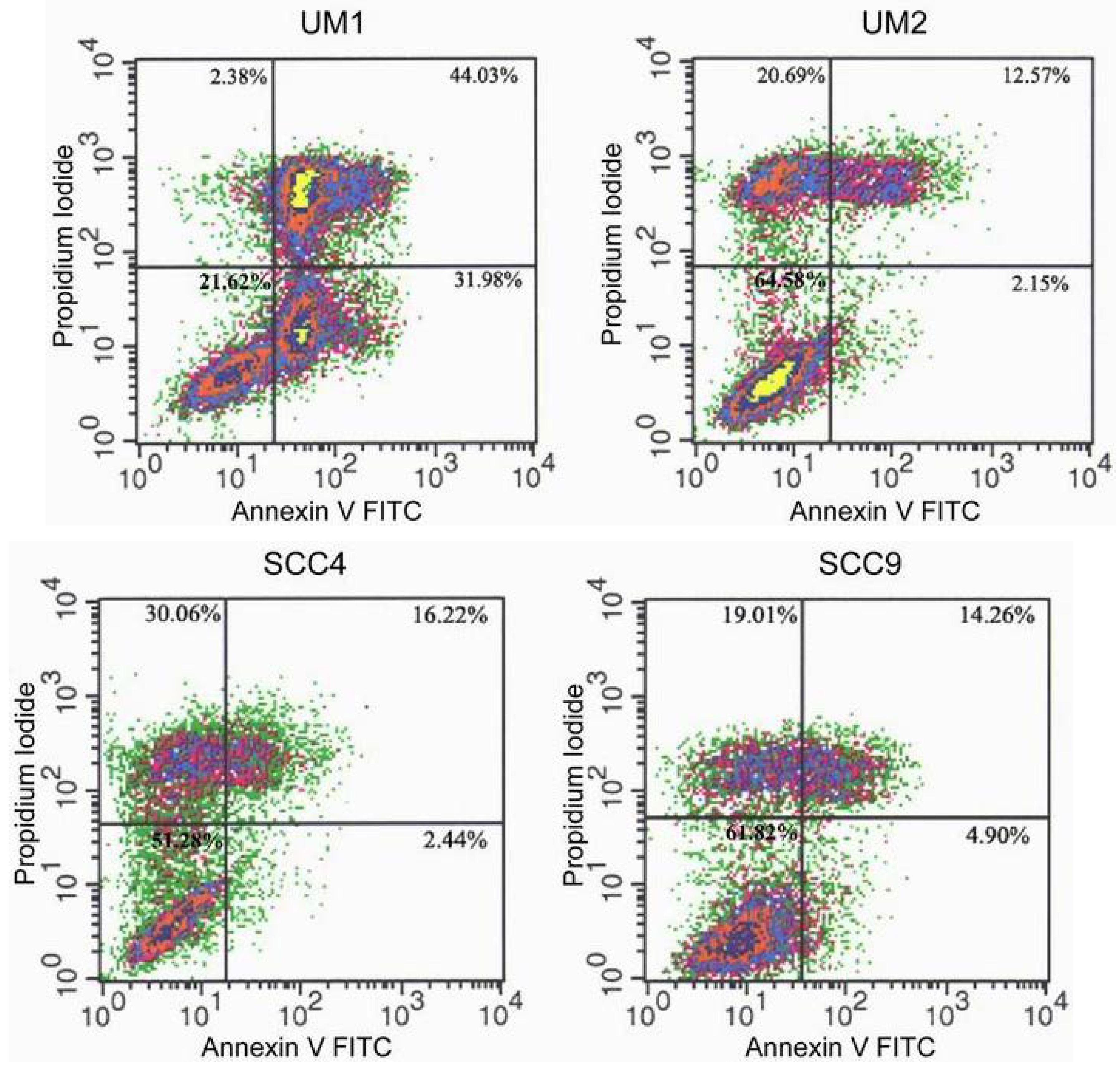
2.2. TSL-1 induces apoptosis in HOSCC
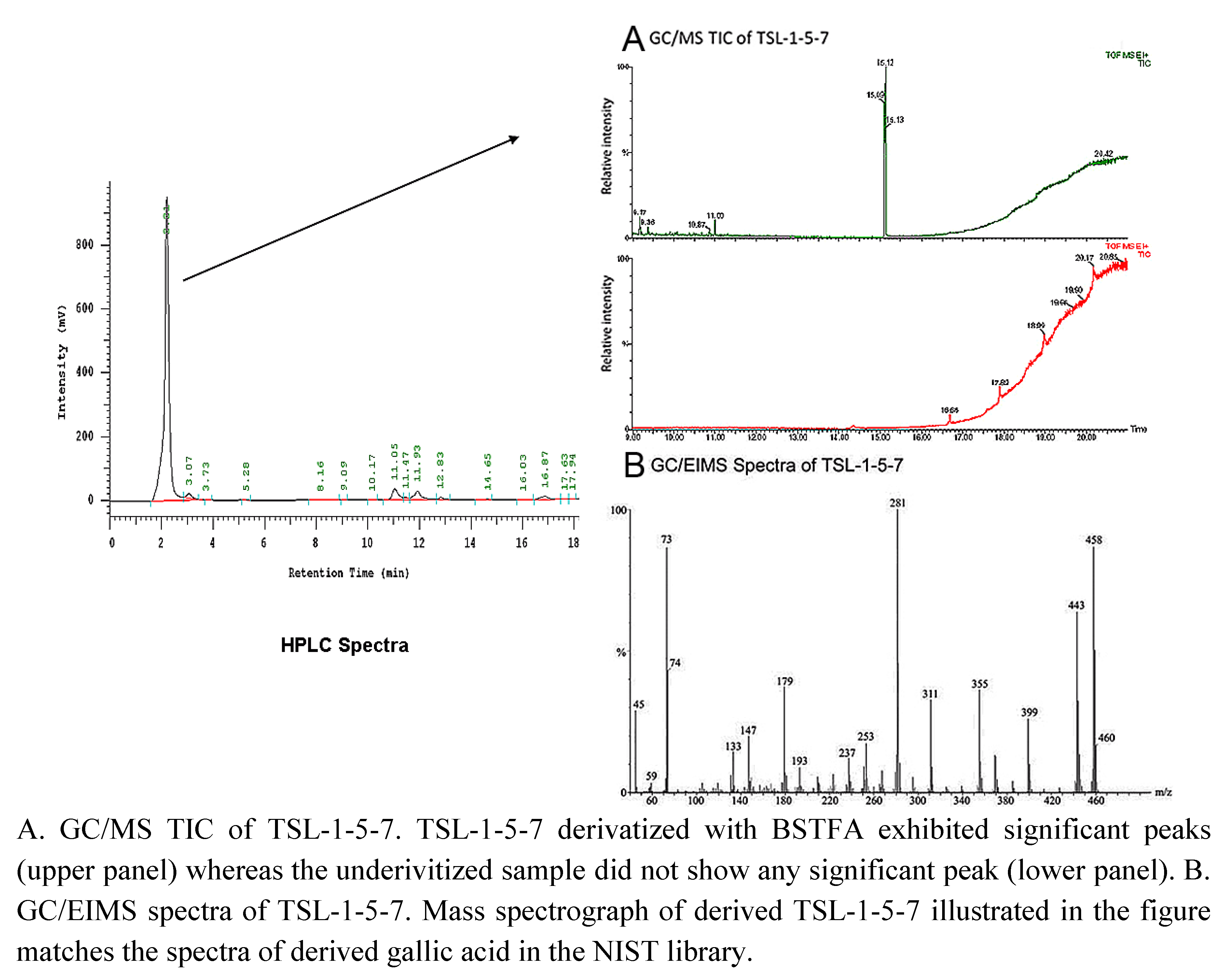
2.3. 3 4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid (gallic acid) is a major bioactive component of TSL-1
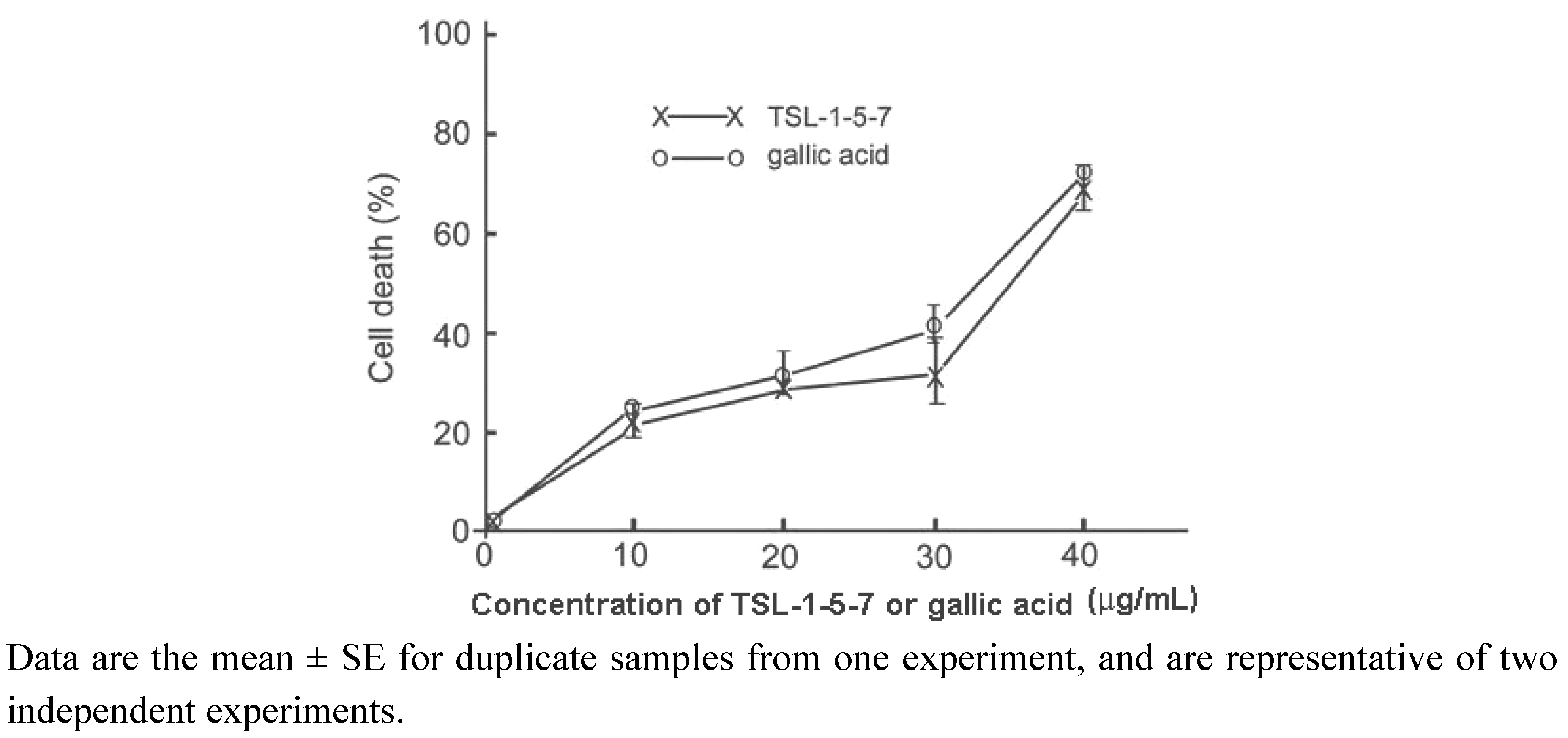
2.4. The presence of gallic acid in TSL-1 exerts anti-tumor activity
2.5. TSL-1-5-7 and gallic acid both up-regulate pro-apoptotic genes and down-regulate anti-apoptotic genes

2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Cell culture and chemical reagents
3.2. Toona sinensis leaf extract preparation
3.3. Viability and IC50 assays
3.4. Flow cytometry analysis
3.5. Semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
3.6. GC/EIMS analysis
3.7. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Samples Availability: Samples of Toona sinensis are available for experimental purposes only from Dr. Yi-Chen Chia.
References and Notes
- Edmonds, J.M.; Staniforth, M. Toona sinensis (Meliaceae). Curtis's Bot. Mag. 1998, 15, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.K.; Yang, Y.C.; Wang, J.H.; Hong, S.J. Effects of Toona sinensis leaf extract on lipolysis in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2003, 19, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.J.; Liu, T.Z.; Chia, Y.C.; Chern, C.L.; Lu, F.J.; Chuang, M.C.; Mau, S.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Syu, Y.H.; Chen, C.H. Protective effect of methyl gallate from Toona sinensis (Meliaceae) against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in MDCK cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Hsu, H.K.; Hwang, J.H.; Hong, S.J. Enhancement of glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by Toona sinensis leaf extract. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2003, 19, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Michaelis, M.; Hsu, H.K.; Tsai, C.C.; Yang, K.D.; Wu, Y.C.; Cinatl, J., Jr.; Doerr, H.W. Toona sinensis Roem tender leaf extract inhibits SARS coronavirus replication. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, S.L.; Leu, S.F.; Hsu, H.K.; Liu, M.Y.; Huang, B.M. Regulatory mechanism of Toona sinensis on mouse leydig cell steroidogenesis. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1473–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Hung, W.C.; Huang, M.S.; Hsu, H.K. Extract from the leaves of Toona sinensis roemor exerts potent antiproliferative effect on human lung cancer cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2002, 30, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Lin, K.H.; Yang, C.J.; Tsai, J.R.; Hung, J.Y.; Wang, P.H.; Hsu, H.K.; Huang, M.S. Toona sinensis extracts induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the human lung large cell carcinoma. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.S.; Wang, P.H.; Hung, J.Y.; Wang, T.H.; Hsu, H.K.; Huang, H.W.; Kumar, S.P.; Huang, M.S.; Weng, C.F. Antiproliferative and antitumorigenic activity of Toona sinensis leaf extracts in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Med. Food. 2010, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Huang, Y.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, P.H.; Hsu, H.K.; Tsai, M.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Bharath, K.V.; Huang, M.S.; Weng, C.F. Antiproliferative effect of Toona sinensis leaf extract on non-small-cell lung cancer. Transl. Res. 2010, 155, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Chen, H.N.; Wang, C.J.; Tseng, W.C.; Hsu, H.K.; Weng, C.F. Toona sinensis Roem (Meliaceae) leaf extract alleviates liver fibrosis via reducing TGFβ1 and collagen. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Tsai, M.J.; Hsu, C.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsu, H.K.; Weng, C.F. Toona sinensis Roem (Meliaceae) leaf extract alleviates hyperglycemia via altering adipose glucose transporter 4. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2554–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.L.; Hsu, H.K.; Su, J.H.; Wang, P.H.; Chung, Y.F.; Chia, Y.C.; Tsai, L.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Yuan, S.S. The fractionated Toona sinensis leaf extract induces apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in a murine xenograft model. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 102, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Chang, W.H.; Chia, Y.C.; Huang, C.J.; Lu, F.J.; Hsu, H.K.; Hseu, Y.C. Toona sinensis extracts induces apoptosis via reactive oxygen species in human premyelocytic leukemia cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Chia, Y.C.; Chang, F.R.; Hsu, H.K.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Yuan, S.S. Gallic acid, a major component of Toona sinensis leaf extracts, contains a ROS-mediated anti-cancer activity in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Taraphdar, A.K.; Roy, M.; Bhattacharya, R.K. Natural products as inducers of apoptosis: implication for cancer therapy and prevention. Curr. Sci. 2001, 80, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Zhu, C.F.; Iwamoto, H.; Chen, J.S. Genistein inhibits invasive potential of human hepatocellular carcinoma by altering cell cycle, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6512–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.C.; Yu, Y.B.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Ok, K.D. Phenolic compounds from the rachis of Cedrela sinensis. Korea J. Pharmacognosy 1996, 27, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Chang, W.H.; Chen, C.S.; Liao, J.W.; Huang, C.J.; Lu, F.J.; Chia, Y.C.; Hsu, H.K.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, H.L. Antioxidant activities of Toona Sinensis leaves extracts using different antioxidant models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L. Naturally occurring food toxicants: phenolic substances of plant origin common in foods. Adv. Food Res. 1981, 27, 149–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, H.U.; Perchellet, E.M.; Perchellet, J.P. Inhibition of tumor promoter-induced ornithine decarboxylase activity by tannic acid and other polyphenols in mouse epidermis, in vivo. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 2820–2825. [Google Scholar]
- Gali, H.U.; Perchellet, E.M.; Klish, D.S.; Johnson, J.M.; Perchellet, J.P. Antitumor-promoting activities of hydrolyzable tannins in mouse skin. Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Suzuki, R.; Sakaguchi, N.; Li, Z.; Takeda, T.; Ogihara, Y.; Jiang, B.Y.; Chen, Y. Selective induction of cell death in cancer cells by gallic acid. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Sakaguchi, N.; Isuzugawa, K.; Tani, H.; Ogihara, Y. Role of reactive oxygen species in gallic acid-induced apoptosis. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T.; Volm, M. Pharmacogenetics for individualized cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 107, 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Takemura, G.; Toyota, M.; Watanabe, M.; Yasuda, N.; Xinbin, Q.; Maruyama, R.; Akao, S.; Gotou, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara, H. Induction of apoptosis by gallic acid in lung cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 1999, 10, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Sasaki, A.; Mese, H.; Alcalde, R.E.; Matsumura, T. Establishment of high and low metastasis cell lines derived from a human tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Invasion Metastasis 1999, 18, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G. Molecular mechanism of TNF signaling and beyond. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradham, C.A.; Qian, T.; Streetz, K.; Trautwein, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Lemasters, J.J. The mitochondrial permeability transition is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis and cytochrome C release. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6353–6364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Baldwin, A.S. TNF-α and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB. Science 1996, 274, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Kajino, S.; Takahashi, N.; Kanazawa, S.; Imai, K.; Hibi, Y.; Ohara, H.; Itoh, M.; Okamoto, T. 53BP2 induces apoptosis through the mitochondria death pathway. Genes Cells 2005, 10, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Ji, J.; Jin, S.; Li, X.; Fan, W.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhan, Q. Gad45a expression induces Bim dissociation from the cytoskeleton and translocation to mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4488–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc-Brude, O.P.; Mesri, M.; Wall, N.R.; Plescia, J.; Dohi, T.; Altieri, D.C. Therapeutic targeting of the surviving pathway in cancer: Initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Roy, N.; Stennicke, H.R.; Van Arsdale, T.; Zhou, Q.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Salvesen, G.S.; Reed, J.C. IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome C by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Palacios, C.; Roy, G.; Cespon, C.; Villar, M.L.; Nocito, M.; Gonzales-Poreque, P. Derivatives of gallic acid induce apoptosis in tumoral cells and inhibit lymphocyte proliferation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 350, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F. Antioxidants in food and food antioxidants. Nahrung 2000, 44, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, N.; Inoue, M.; Ogihara, Y. Reactive oxygen species and intracellular Ca+, common signals for apoptosis induced by gallic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kawada, M.; Ohno, Y.; Ri, Y.; Ikoma, T.; Yuugetu, H.; Asai, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yasuda, N.; Akao, S.; Takemura, G.; Minatoguchi, S.; Gotoh, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Fukuda, K. Anti-tumor effect of gallic acid on LL-2 lung cancer cells transplanted in mice. Anticancer Drugs 2001, 12, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.C.; Ridolpho, P. Use of a trypan blue assay to measure the deoxyribonucleic acid content and radioactive labeling of viable cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1980, 28, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, Z.; Poirot, O.; Fenoglio, I.; Ghiazza, M.; Daniere, M.C.; Terzetti, F.; Darne, C.; Coulais, C.; Matekovits, I.; Fubini, B. Surface reactivity, cytotoxic, and morphological transforming effects of diatomaceous earth products in syrian hamster embryo cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 91, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chia, Y.-C.; Rajbanshi, R.; Calhoun, C.; Chiu, R.H. Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Gallic Acid, a Major Component of Toona sinensis Leaf Extract, on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Molecules 2010, 15, 8377-8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15118377
Chia Y-C, Rajbanshi R, Calhoun C, Chiu RH. Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Gallic Acid, a Major Component of Toona sinensis Leaf Extract, on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Molecules. 2010; 15(11):8377-8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15118377
Chicago/Turabian StyleChia, Yi-Chen, Ranjan Rajbanshi, Colonya Calhoun, and Robert H. Chiu. 2010. "Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Gallic Acid, a Major Component of Toona sinensis Leaf Extract, on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells" Molecules 15, no. 11: 8377-8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15118377
APA StyleChia, Y.-C., Rajbanshi, R., Calhoun, C., & Chiu, R. H. (2010). Anti-Neoplastic Effects of Gallic Acid, a Major Component of Toona sinensis Leaf Extract, on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Molecules, 15(11), 8377-8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15118377