Analysis of the Main Nucleosides in Cordyceps Sinensis by LC/ESI-MS
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion
Optimization of chromatographic conditions
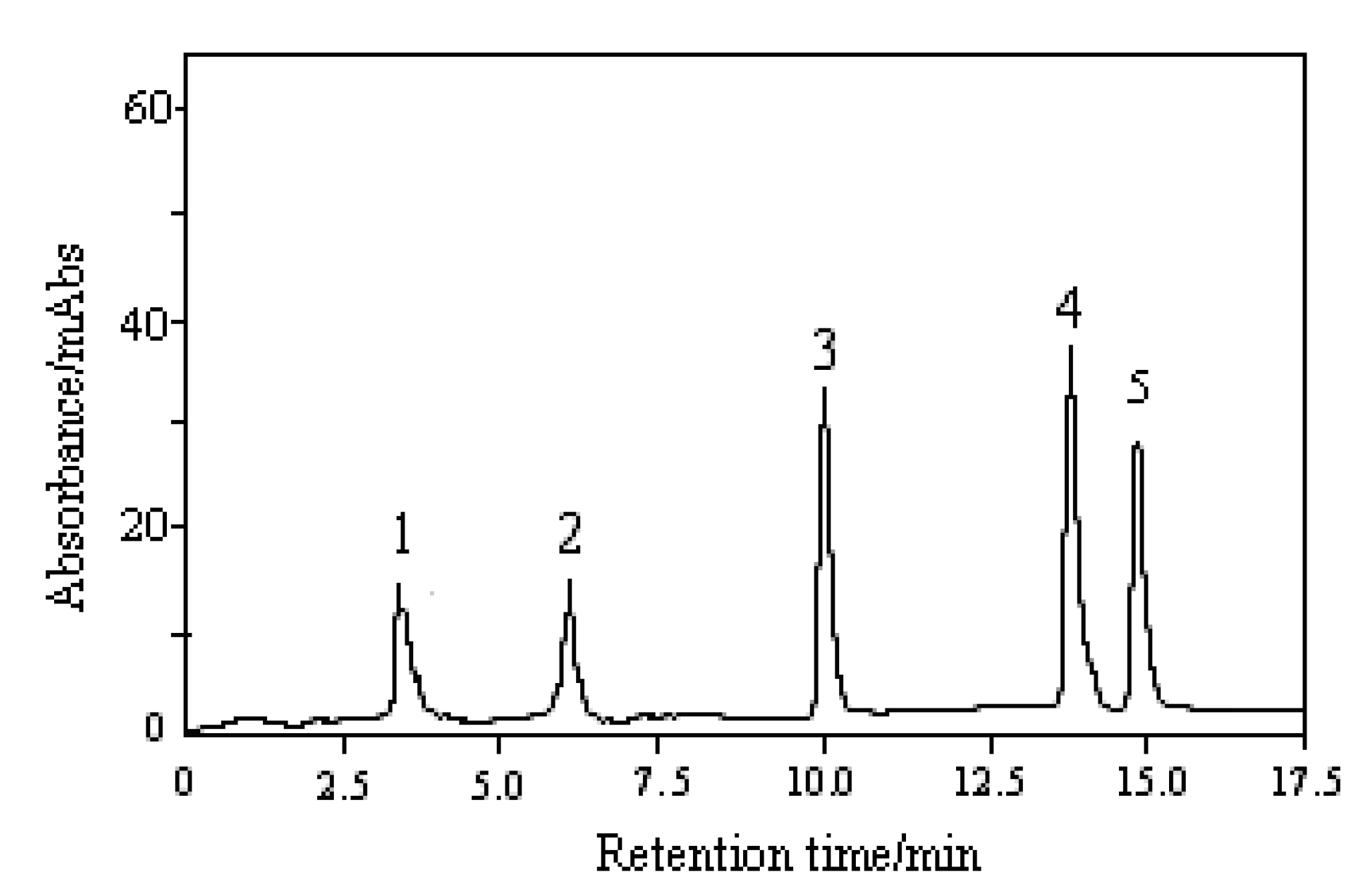
| Peak number | Compound | tR/min | UVλmax /nm | [M+H]+/m/z | [M+Na]+/m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thymine | 3.49 | 203, 264 | 127 | |
| 2 | Adenine | 5.92 | 207, 261 | 136 | |
| 3 | Adenosine | 10.12 | 206, 260 | 268 | 290 |
| 4 | Cordycepin | 13.75 | 207, 260 | 252 | 274 |
Optimization of the ESI-MS conditions
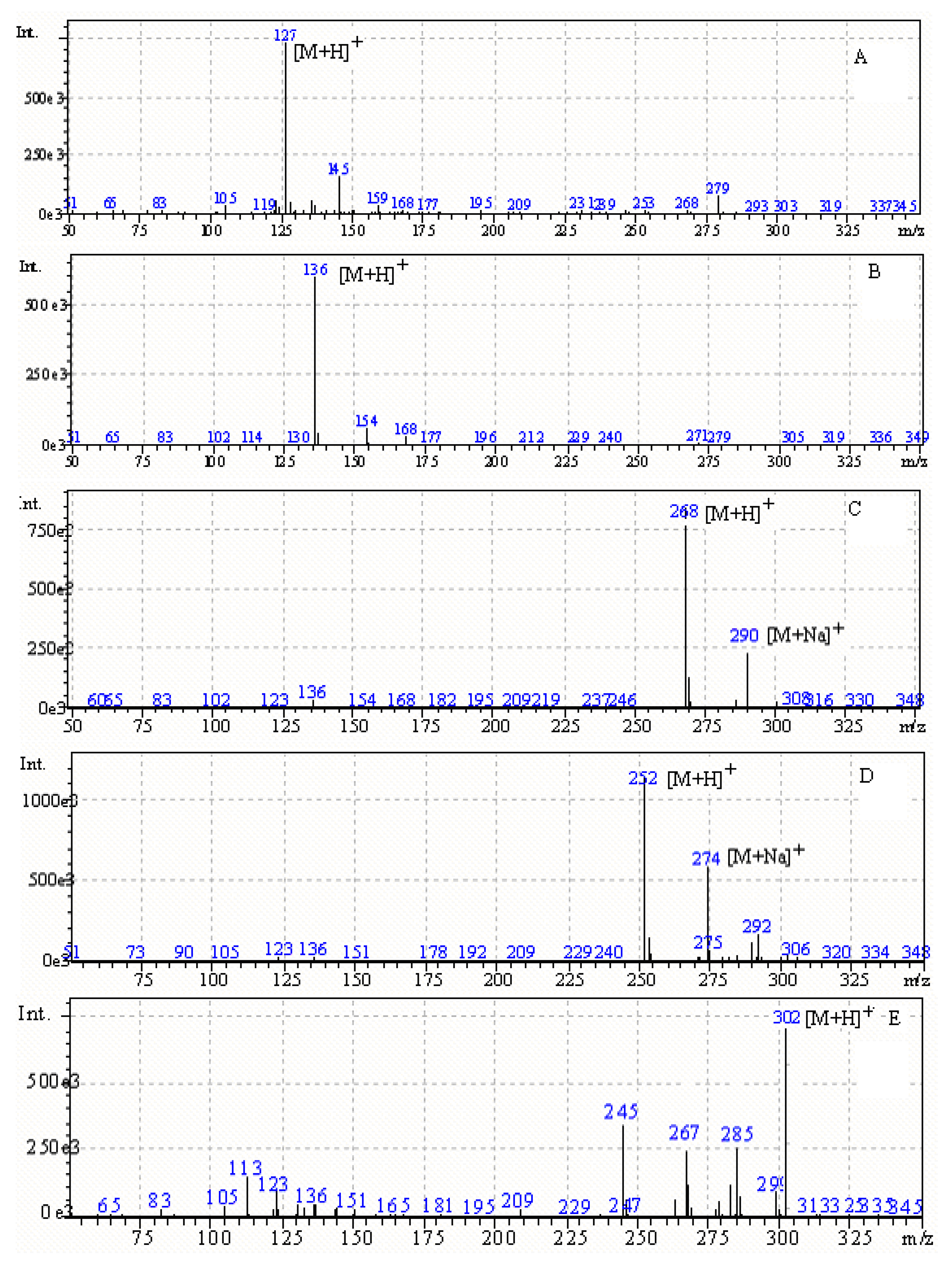
Method validation
| Compound name | Regression equation | R | Liner range/µg·mL-1 | Limit of detection/µg·mL-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymine | Y = 0.06537X + 0.00614 | 0.9984 | 1.0~117.5 | 0.2 |
| Adenine | Y = 0.1438X + 0.0136 | 0.9981 | 1.8~127.0 | 0.6 |
| Adenosine | Y = 0.1292X + 0.0113 | 0.9991 | 0.6~114.0 | 0.1 |
| Cordycepin | Y = 0.2146X + 0.0194 | 0.9993 | 0.5~107.5 | 0.1 |
| Analyte | Concentration added/µg·mL-1 | Concentration found/µg·mL-1 | RE/% | RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymine | 2.0 | 2.06 | 3.0 | 6.3 |
| 20.0 | 19.7 | -1.5 | 3.2 | |
| 100.0 | 101.6 | 1.6 | 1.4 | |
| 4.0a | 3.94 | -1.5 | 4.2 | |
| Adenine | 2.0 | 1.93 | -3.5 | 5.4 |
| 20.0 | 20.4 | 2.0 | 3.1 | |
| 100.0 | 99.3 | -0.7 | 1.6 | |
| 2.0 a | 1.95 | -2.5 | 2.9 | |
| Adenosine | 2.0 | 1.96 | -2.0 | 5.4 |
| 20.0 | 20.3 | 1.5 | 3.4 | |
| 100.0 | 99.1 | -0.9 | 1.7 | |
| 2.5 a | 2.47 | -1.2 | 3.8 | |
| Cordycepin | 2.0 | 2.08 | 4.0 | 6.1 |
| 20.0 | 20.4 | 2.0 | 2.9 | |
| 100.0 | 99.3 | -0.7 | 1.9 | |
| 2.0 a | 2.07 | 3.5 | 5.7 |
| Analyte | Concentration added/µg·mL-1 | Concentration found/µg·mL-1 | RE/% | RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymine | 2.0 | 2.08 | 4.0 | 6.7 |
| 20.0 | 19.4 | -3.0 | 4.2 | |
| 100.0 | 98.6 | 1.4 | 1.8 | |
| 4.0a | 4.10 | -2.5 | 3.8 | |
| Adenine | 2.0 | 1.91 | -4.5 | 6.2 |
| 20.0 | 20.6 | 3.0 | 3.7 | |
| 100.0 | 98.7 | -1.3 | 1.9 | |
| 2.0 a | 2.04 | 2.0 | 5.4 | |
| Adenosine | 2.0 | 1.94 | -3.0 | 6.4 |
| 20.0 | 20.7 | 3.5 | 3.8 | |
| 100.0 | 98.1 | -1.9 | 2.1 | |
| 2.5 a | 2.58 | 3.2 | 5.3 | |
| Cordycepin | 2.0 | 1.92 | -4.0 | 6.5 |
| 20.0 | 20.6 | 3.0 | 3.9 | |
| 100.0 | 98.2 | -1.8 | 1.6 | |
| 2.0 a | 1.94 | -3.0 | 6.2 |
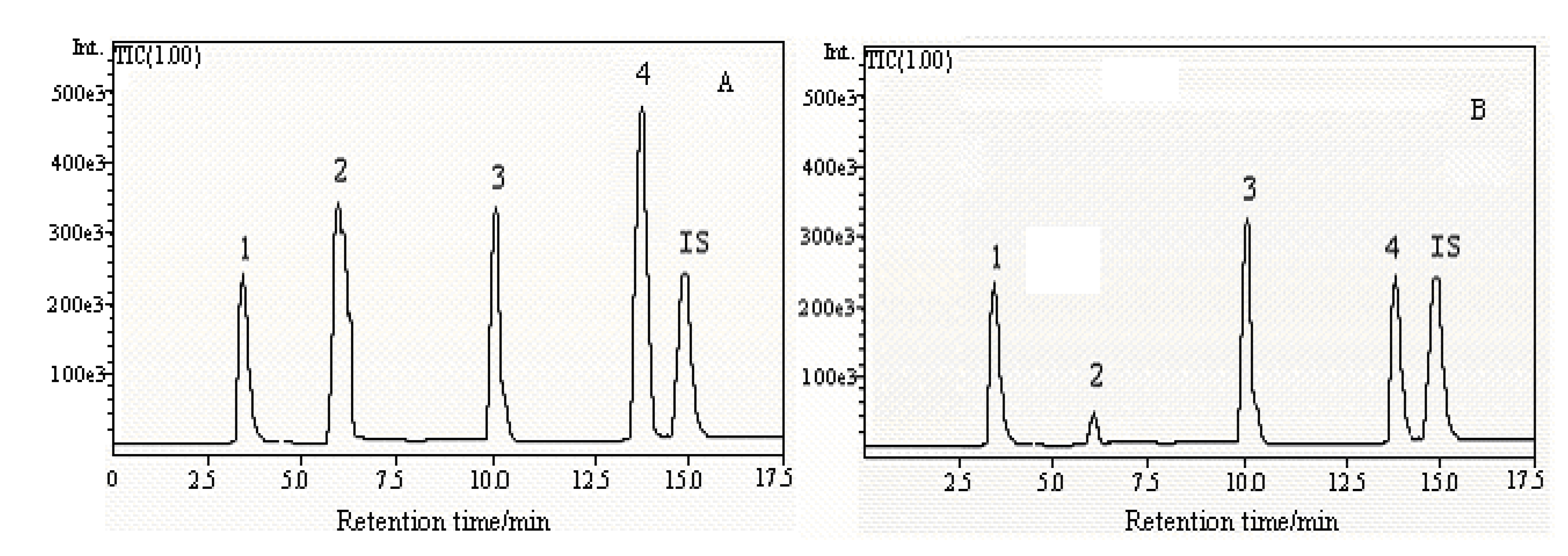
Application
| Source | Thymine/µg·g-1 | Adenine/µg·g-1 | Adenosine/µg·g-1 | Cordycepin/µg·g-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qinghai | 174.2 | 29.7 | 186.5 | 91.2 |
| Tibet | 138.5 | 38.1 | 79.6 | 48.7 |
| Sichuan | 142.6 | 20.4 | 126.1 | 31.3 |
Experimental
Apparatus
Materials and standards
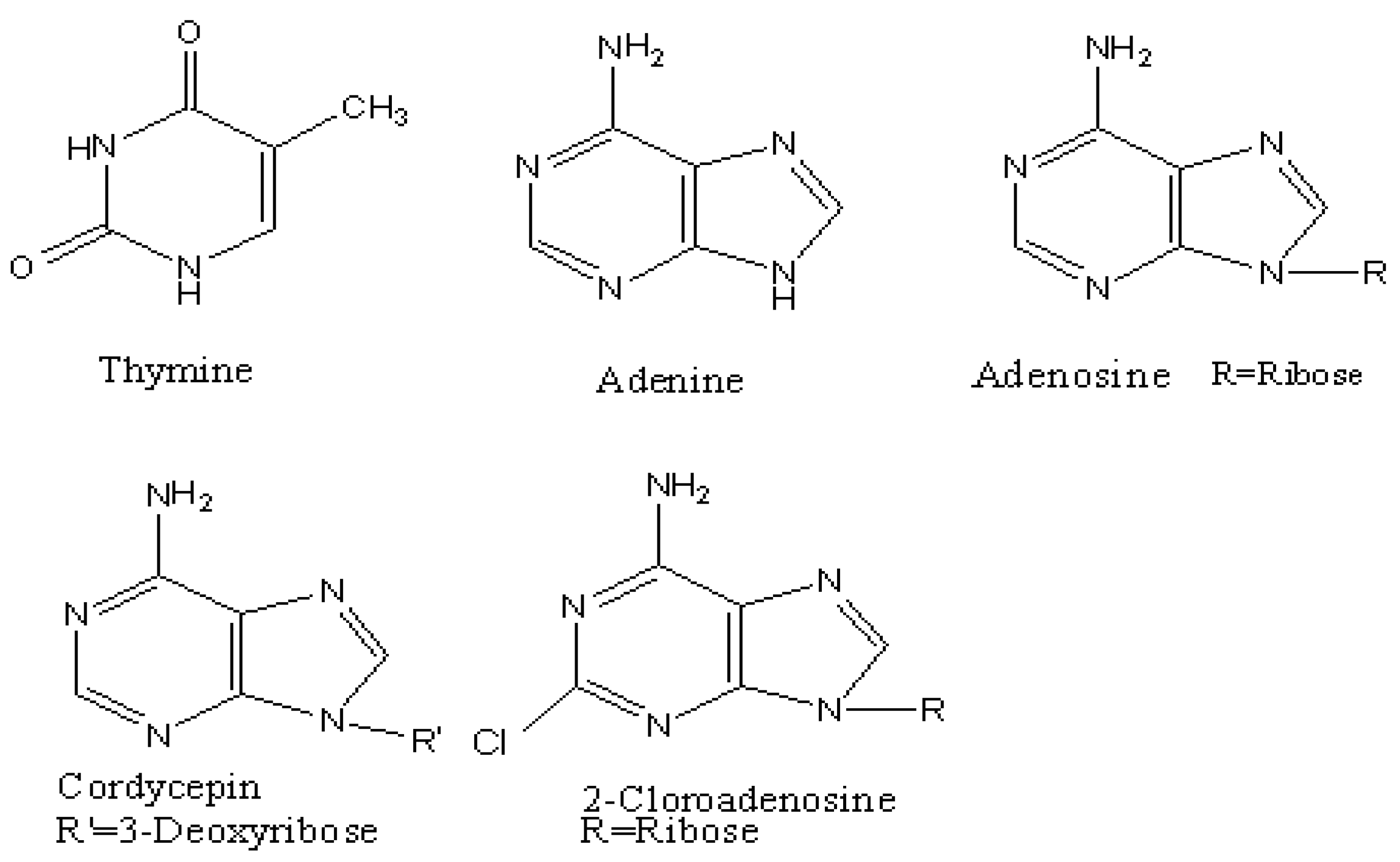
Sample preparation
Chromatographic conditions
| Step | Time/min | Ammonium acetate (40 mM, pH=5.2)/% | Methanol/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 85 | 15 |
| 2 | 6 | 85 | 15 |
| 3 | 12 | 80 | 20 |
| 4 | 17 | 80 | 20 |
| 5 | 20 | 95 | 5 |
Mass spectrometric detection conditions
Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Zhu, J.S.; Halpern, G.M.; Jones, K. The scientific rediscovery of an ancient Chinese herbal medicine: Cordyceps sinensis: part I. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 1998, 4, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.S.; Halpern, G.M.; Jones, K. The scientific rediscovery of a precious ancient Chinese herbal regimen: Cordyceps sinensis: part II. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 1998, 4, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.Z.; Dong, Z.H.; Yu, Q. Modern Study of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Xue Yuan Press: Beijing, China, 1999; Volume 6, pp. 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Determination of nucleosides in Cordyceps sinensis preparation by dual-wavelength TLC-scanning. China Pharm. 2008, 20, 2375–2377. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Fang, D.S. Comparison of Cordyceps Sinensis and solid fermentation of Cordyceps Militaris by TLC. China Pharm. 2008, 19, 1180–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.J. Determination of adenosine and 3-deoxyadenosine in Cordyceps militaris (L.) Link by HPLC. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1998, 23, 236–237. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.N; Hua, Y.Y.; Lin, H.L. Research on rapid and simultaneous determination of functional factor in Cordyceps by HPLC-PDA method. Strait J. Prev. Med. 2008, 14, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.F.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, D.J.; Jin, B.Q. Determination of cordycepin from cultured cordyceps sinensis by HPLC-DAD. Food Sci. 2008, 40, 352–354. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Lu, H.C. Determination of adenosine content in Cordyceps militaris(L.) Link by HPLC. J. Guangdong Coll. Pharm. 2008, 24, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Sun, G.X.; Jin, Y. Quality control of traditional Chinese medicines by the capillary electrophoresis fingerprint and capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2008, 26, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Feng, C.Q.; Ni, X.M.; Zhang, W.S. Determination of nucleosides of natural Cordyceps sinensis in Qinghai Province by capillary electrophoresis. Chin. Pharm. J. 2008, 43, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.F.; Liang, Y.Z.; Guo, F.Q.; Zhou, Z.F.; Cheng, B.M. Simultaneous separation and determination of active components in Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militarris by LC/ESI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the extracts from Cordyceps sinensis are available from the authors.
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.-W.; Huang, L.-F.; Hu, W.; He, Y.-B.; Wong, K.P. Analysis of the Main Nucleosides in Cordyceps Sinensis by LC/ESI-MS. Molecules 2010, 15, 305-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15010305
Xie J-W, Huang L-F, Hu W, He Y-B, Wong KP. Analysis of the Main Nucleosides in Cordyceps Sinensis by LC/ESI-MS. Molecules. 2010; 15(1):305-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15010305
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Jian-Wei, Lan-Fang Huang, Wei Hu, Yun-Biao He, and Kin Ping Wong. 2010. "Analysis of the Main Nucleosides in Cordyceps Sinensis by LC/ESI-MS" Molecules 15, no. 1: 305-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15010305
APA StyleXie, J.-W., Huang, L.-F., Hu, W., He, Y.-B., & Wong, K. P. (2010). Analysis of the Main Nucleosides in Cordyceps Sinensis by LC/ESI-MS. Molecules, 15(1), 305-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15010305




