Separation, Characterization and Dose-Effect Relationship of the PPARγ-Activating Bio-Active Constituents in the Chinese Herb Formulation ‘San-Ao Decoction’
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of the different fraction from SAD on PPARγ

2.2. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS analysis of the fraction activiting of PPARγ in SAD
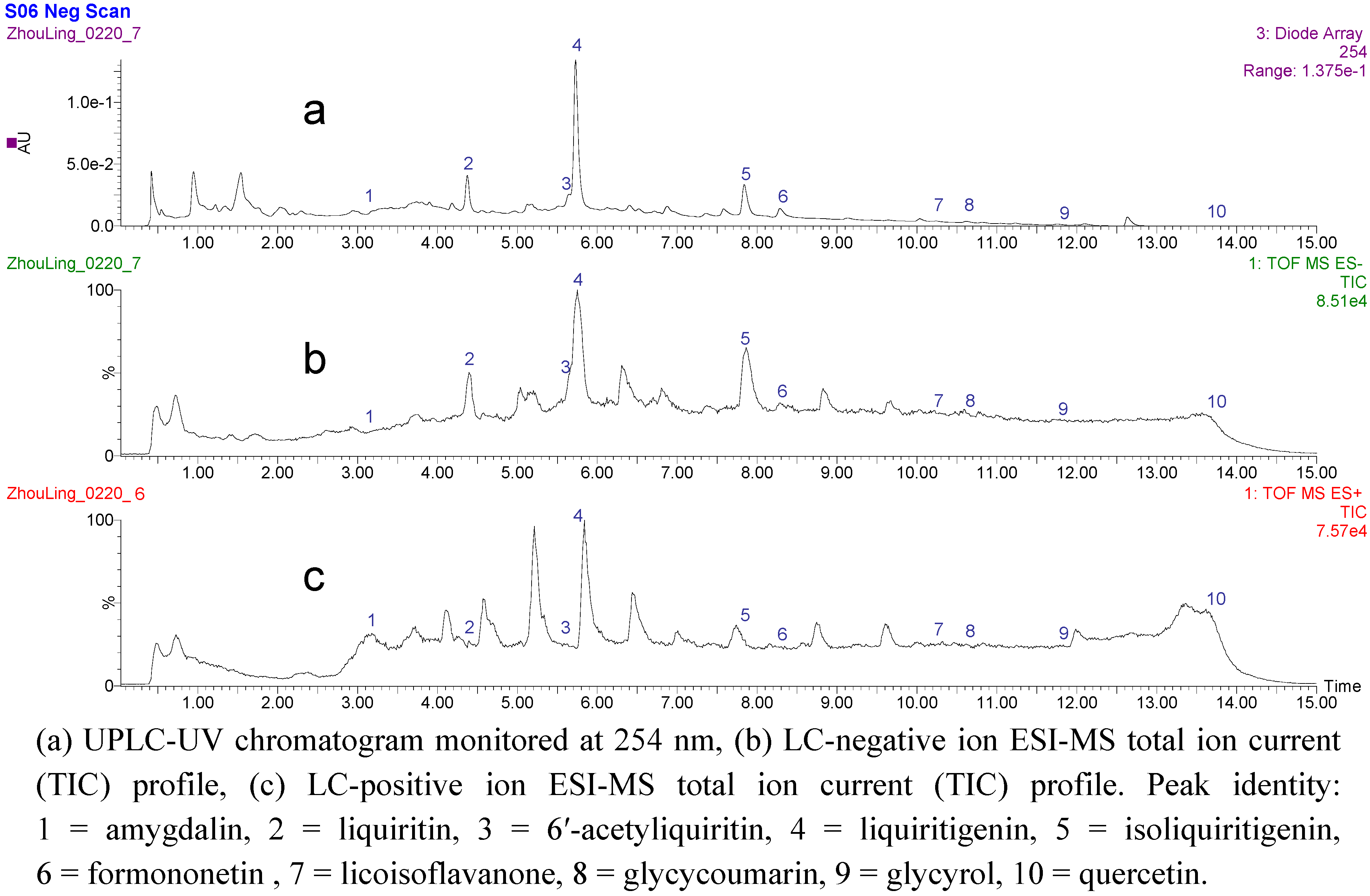
| Peak no. | Retention time (min) | MS2 of fragment Ions | ESI-mass spectra[M-H]- | Maximum absorption wavelength λmax (nm) | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.59 | 385.14, 340.18, 237.08, 187.09, 165.05 | 456.15 | 210, 252, 263, 269 | amygdalin |
| 2 | 4.39 | 417.11, 366.11, 255.06, 151.04, 135.00 | 418.15 | 241, 275, 327 | liquiritin |
| 3 | 5.73 | 417.11, 255.06, 135.00 | 469.13 | 230, 258, 277, 320 | 6′-acetyliquiritin |
| 4 | 5.75 | 135.01 | 255.07 | 236, 272, 315 | liquiritigenin |
| 5 | 7.68 | 135.01 | 255.06 | 240, 330, 395 | isoliquiritigenin |
| 6 | 8.29 | 255.06, 135.01 | 267.06 | 248, 300 | formononetin |
| 7 | 10.17 | 297.20, 269.08 | 353.10 | 227, 260, 330 | licoisoflavanone |
| 8 | 10.59 | 353.11, 329.22, 183.02, 141.02 | 367.11 | 236, 327, 370, 384 | glycycoumarin |
| 9 | 11.79 | 335.10, 267.04 | 365.10 | 229, 286, 351, 382 | glycyrol |
| 10 | 13.57 | 227.16 | 301.16 | 254, 312 | quercetin |

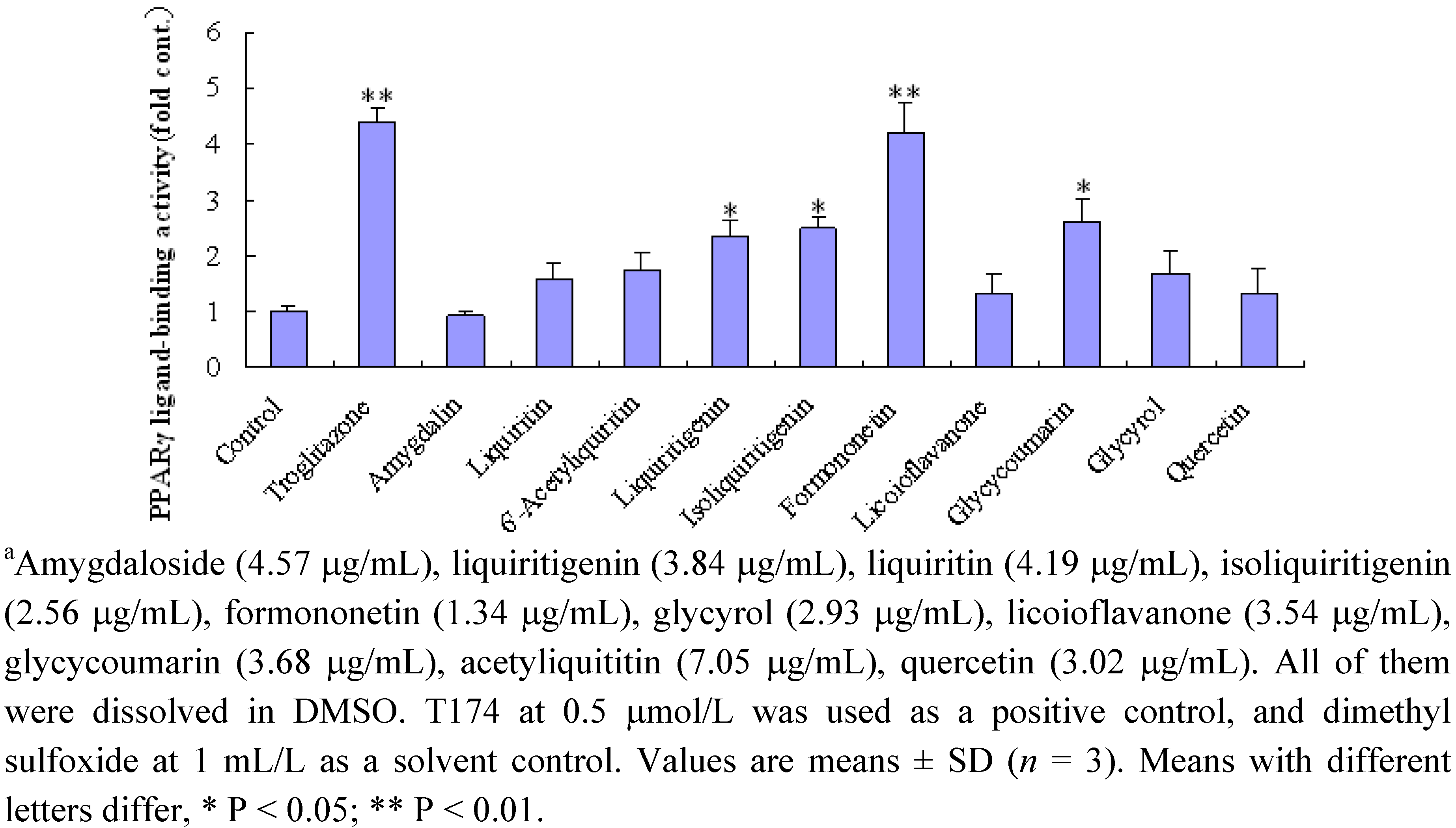
2.3. Effect of ten compounds from EtOAc fraction on PPARγ
2.4. Dose-effect relationship of formononetin in EtOAc fraction of SAD
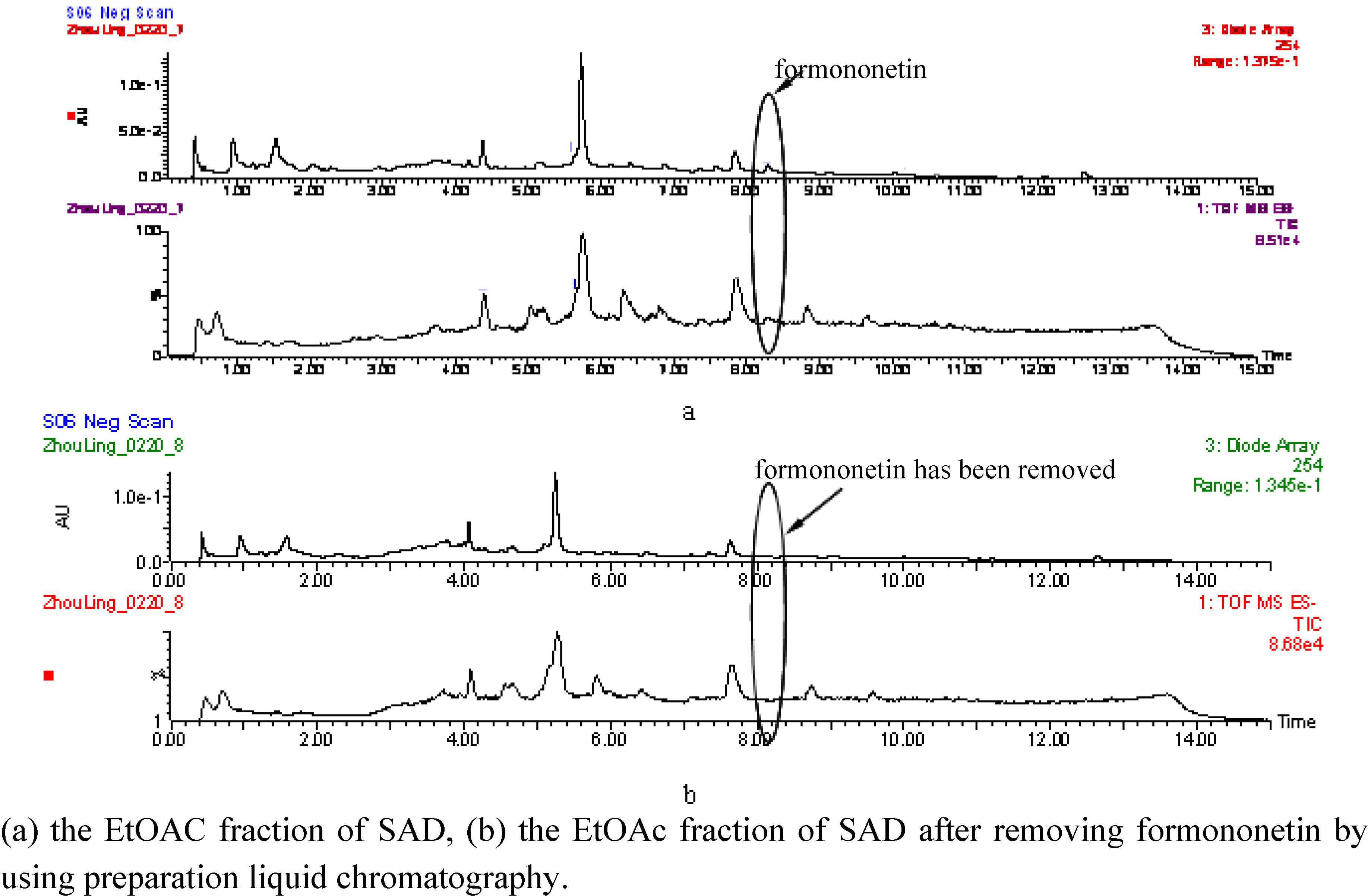
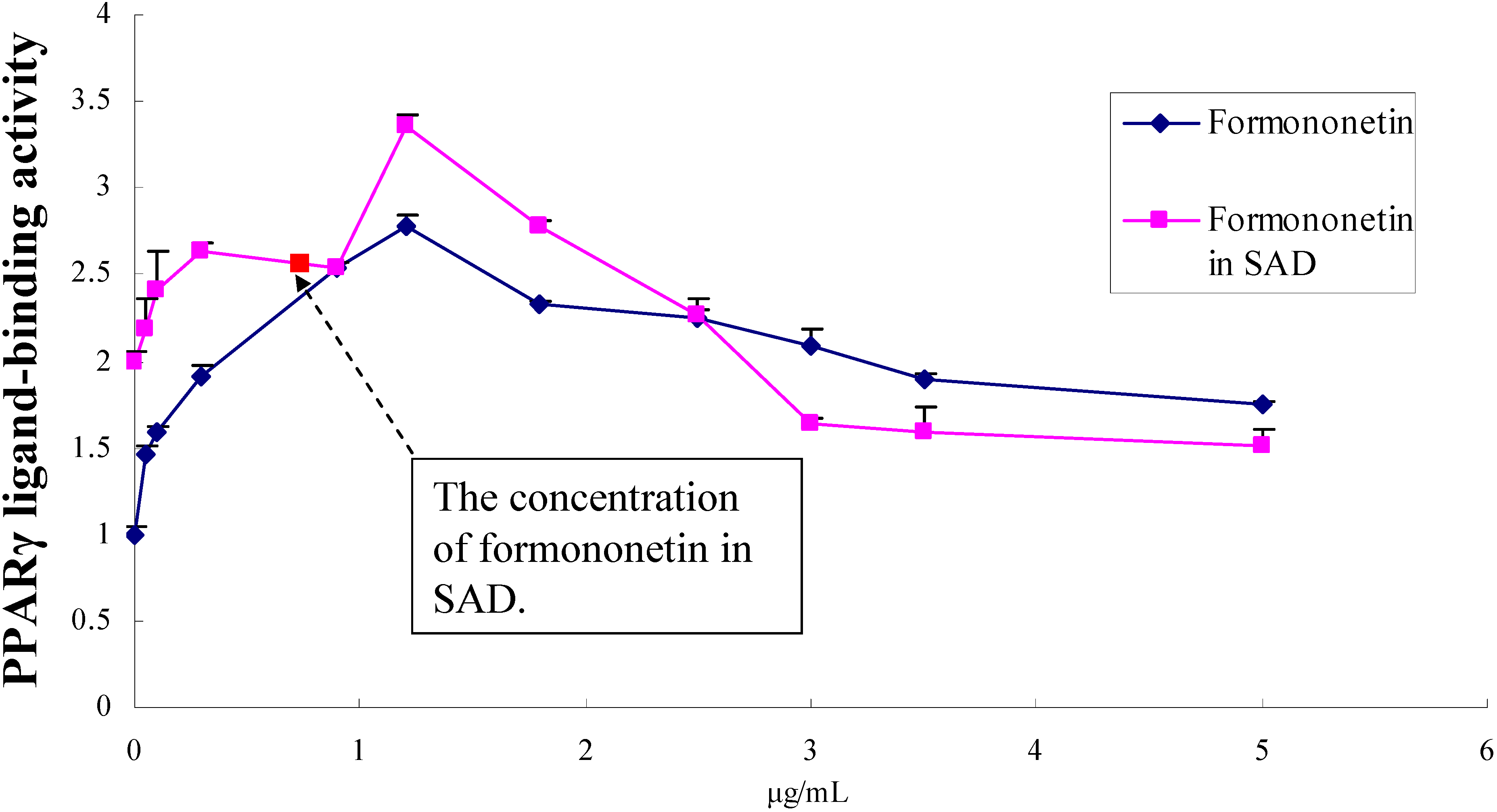
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and reagents
3.2. Plant material
3.3. Sample preparation
3.4. Equipment and chromatographic conditions
3.5. Mass spectrometric conditions
3.6. Equipment and conditions of preparative liquid chromatography
3.7. Cell culture and full-length reporter-gene bioassays
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 1-10 are available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Xue, T.; Roy, R. Studying traditional Chinese medicine. Science 2003, 300, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Pharmacopoeia Commission of P.R. China, The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 59, 140, 223.
- Wang, Z.J.; Wo, S.K.; Wang, L.; Lau, C.B.S.; Lee, V.H.L.; Chow, M.S.S.; Zuo, Z. Simultaneous quantification of active components in the herbs and products of Si-Wu-Tang by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.W.; Cao, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.X. Rapid, sensitive quantitation of major constituents in Danggui Buxue Tang by ultrafast HPLC-TOF/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 49, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Q.W.; Tu, P.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Guo, B.L.; Li, S.P. A rapid method for simultaneous determination of 15 flavonoids in Epimedium using pressurized liquid extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Z.; Ying, X.; Cui, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, F. A rapid ultra-performance liquid chromatography-eletrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric method for the qualitative and the quantitative analysis of the constituents of the flower of Trollius ledibouri Reichb. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 580, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Majors, R.E. High speed analyses using rapid resolution liquid chromatography on 1.8-μm porous particles. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Q.; Liang, X. High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of protoberberine alkaloids in medicine herb. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 2000, 405, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Schoonjans, K.; Staels, B.; Auwerx, J. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARs) and their effects on lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1302, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Chan, T.A.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. PPARδ is an APC-regulated target of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cell 1999, 99, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.B.; Zhang, H.; Rasmussen, T.H.; Petersen, R.K.; Flindt, E.N.; Kristiansen, K. Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor δ (PPARδ) –mediated regulation of preadipocyte proliferation and gene expression is dependent on cAMP signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar]
- Rangwala, S.M.; Lazar, M.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in diabetes and metabolism. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2004, 25, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.J.; Holder, J.C. PPAR-γ agonists: therapeutic role in diabetes, in inflammation and cancer. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2000, 21, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.B. The role of PPARs in inflammation and immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 388–400. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, N.; Mach, F.; Sauty, A.; Leung, J.H.; Sarafi, M.N.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Libby, P.; Plutzky, J.; Luster, A.D. PPARg activators inhibit Interferon-gamma-induced expression of the T cell-active CXC chemokines IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC in human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6503–6508. [Google Scholar]
- Ricote, M.; Li, A.C.; Willson, T.M.; Kelly, C.J.; Glass, C.K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 1998, 391, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.M.; Liu, H.T.; Ng, Y.; Chan, Y.H.; Yong, E.L. Differential effects of isoflavones, from Astragalus membranaceus and Pueraria thomsonii, on the activation of PPARa, PPARg, and adipocyte differentiation in vitro. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 899–905. [Google Scholar]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Tang, Y.-P.; Gao, L.; Fan, X.-S.; Liu, C.-M.; Wu, D.-K. Separation, Characterization and Dose-Effect Relationship of the PPARγ-Activating Bio-Active Constituents in the Chinese Herb Formulation ‘San-Ao Decoction’. Molecules 2009, 14, 3942-3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14103942
Zhou L, Tang Y-P, Gao L, Fan X-S, Liu C-M, Wu D-K. Separation, Characterization and Dose-Effect Relationship of the PPARγ-Activating Bio-Active Constituents in the Chinese Herb Formulation ‘San-Ao Decoction’. Molecules. 2009; 14(10):3942-3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14103942
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ling, Yu-Ping Tang, Lu Gao, Xin-Sheng Fan, Chun-Mei Liu, and De-Kang Wu. 2009. "Separation, Characterization and Dose-Effect Relationship of the PPARγ-Activating Bio-Active Constituents in the Chinese Herb Formulation ‘San-Ao Decoction’" Molecules 14, no. 10: 3942-3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14103942
APA StyleZhou, L., Tang, Y.-P., Gao, L., Fan, X.-S., Liu, C.-M., & Wu, D.-K. (2009). Separation, Characterization and Dose-Effect Relationship of the PPARγ-Activating Bio-Active Constituents in the Chinese Herb Formulation ‘San-Ao Decoction’. Molecules, 14(10), 3942-3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14103942




