Abstract
We previously isolated a novel natural product, designated kohamaic acid A (KA-A, compound 1), as an inhibitor of the first cleavage of fertilized sea urchin eggs, and found that this compound could selectively inhibit the activities of mammalian DNA polymerases (pols). In this paper, we investigated the structure and bioactivity of KA-A and its chemically synthesized 11 derivatives (i.e., compounds 2–12), including KA-A - fatty acid conjugates. The pol inhibitory activity of compound 11 [(1S*,4aS*,8aS*)-17-(1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-2,5,5,8a-tetramethyl-naphthalen-1-yl)heptadecanoic acid] was the strongest among the synthesized compounds, and the range of IC50 values for mammalian pols was 3.22 to 8.76 μM; therefore, the length of the fatty acid side chain group of KA-A is important for pol inhibition. KA-A derivatives could prevent human cancer cell (promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60) growth with the same tendency as the inhibition of mammalian pols. Since pol β is the smallest molecule, we used it to analyze the biochemical relationship with KA-A derivatives. From computer modeling analysis (i.e., docking simulation analysis), these compounds bound selectively to four amino acid residues (Leu11, Lys35, His51 and Thr79) of the N-terminal 8-kDa domain of pol β, and the binding energy between compound 11 and pol β was largest in the synthesized compounds. The relationship between the three-dimensional molecular structures of KA-A-related compounds and these inhibitory activities is discussed.
Introduction
A novel sesterterpenic acid, kohamaic acid A (KA-A), was isolated from a marine sponge Ircinia sp. [1]. KA-A was first screened as an inhibitor of the first cleavage of fertilized sea urchin eggs [1], but we also found and reported that it inhibited the activities of DNA polymerases (pols) from the deuterostome branch in the phylogenetic tree, but not from plants, prokaryotes, or even protostomes such as insects and mollusks [2].
Pol is associated with genomic DNA replication, repair and recombination in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells reportedly contain three replicative types; pols α, δ, and ε, mitochondrial pol γ, and at least twelve repair types; pols β, δ, ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, λ, μ, and σ and REV1 [3]. The roles of the pols have not yet been fully established. Against this background, it is of interest that KA-A could only inhibit the activities of the deuterostome pols tested, including those of the sea urchin.
Pols α and β have been isolated and characterized from sea urchins [4, 5]. The possible role of cell multiplication in sea urchin gastrulation has been somewhat neglected and its importance is in general considered secondary [6]; however, it is well known that DNA synthesis continues during gastrulation [7, 8] and that the cell number increases about three times between the hatched blastula and the prism stage [7]. It has also been reported that primary mesenchyme cells undergo mitotic divisions after they have been shed into the blastocoel [9]. This indirect evidence suggests that KA-A is useful for investigating the relationship between sea urchin pols and the cleavage of fertilized sea urchin eggs, and that KA-A may induce inhibition of the first cleavage of fertilized sea urchin eggs by inhibiting DNA replication [2]; subsequently, we succeeded in chemically synthesizing KA-A (compound 1) and its eleven derivatives (compounds 2–12) (Figure 1) [10].
In this report, we investigated the inhibitory activities of mammalian pols and human cancer cell growth for the development of anticancer chemotherapy drugs, because the inhibition of pols will lead to cell death, especially under proliferation conditions such as in cancer cells; therefore, inhibitors of eukaryotic pols should be considered as potential agents for cancer chemotherapy. We also discuss the molecular inhibition mechanism of pol β activity by KA-A derivatives.
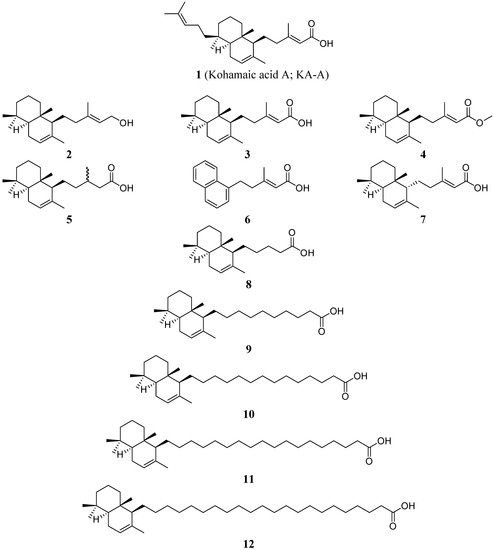
Figure 1.
Structures of kohamaic acid A and its derivatives.
Results and Discussion
Effects of KA-A derivatives on the activities of mammalian DNA polymerases α and β
As briefly described in the Introduction, we found and reported that KA-A (compound 1) is an inhibitor of pols only from the deuterostome branch in the phylogenetic tree, including mammals [2]. The purpose of this study was to investigate the inhibitory mechanism more precisely using eleven chemically synthesized derivatives of KA-A (compounds 2–12), which were prepared as described previously [10]. The chemical structures of KA-A and its analogs are shown in Figure 1.
First, the relative activities of calf pol α and rat pol β with two set concentrations (10 and 100 μM) of the test compounds are shown in Figure 2. Pol α and pol β were used as representative replicative pol and repair/recombination-related pol, respectively [11, 12]. As reported previously, KA-A dose-dependently inhibited the activities of pols α and β, and the IC50 values were 7.6 and 8.4 μM, respectively [2]. In the synthesized compounds (i.e., compounds 2–12), compounds 2 to 8 were weaker inhibitors of pols α and β than KA-A, and the inhibitory effect of compound 9 was as strong as that of KA-A, whereas, compounds 10–12 were stronger inhibitors than KA-A, and compound 11 had the strongest inhibitory effect on pols α and β of all the compounds tested. The inhibition of pol α activity by the compounds showed the same tendency as that of pol β activity. KA-A derivatives, such as compounds 8 to 12, have a conjugated fatty acid in the KA-A molecule, and we previously reported that longer chain fatty acids inhibit the activity of eukaryotic pols; therefore, the fatty acid region of compounds 10–12 must be important for inhibition.
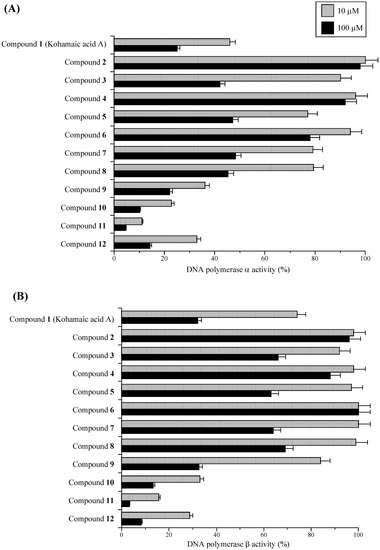
Figure 2.
Effects of kohamaic acid A derivatives (compounds 1–12) on the activities of mammalian DNA polymerases α and β.
Effects of KA-A derivatives on cultured human cancer cells
Interest also focused on developing agents for cancer chemotherapy using these inhibitors. Replicative pols, such as pol α, are regarded as potential targets of anticancer drugs, because they play central roles in DNA replication, which is indispensable for the proliferation of cancer cells. KA-A derivatives could therefore be useful in chemotherapy, and we investigated the cytotoxic effect of KA-A and its related compounds (i.e., compounds 1 to 12) against a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60.
As shown in Figure 3, 50 μM of compound 11 had the strongest growth inhibitory effect on HL-60 cells of the compounds tested, compounds 12 and 10 were the second and third strongest, respectively. Cell growth suppression had the same tendency as the inhibition of mammalian pols α and β among the compounds, suggesting that KA-A derivatives are able to penetrate cancer cells and reach the nucleus, inhibiting pol activity (Figure 2 and Figure 3). We therefore concentrated our efforts on (1S*,4aS*,8aS*)-17-(1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-2,5,5,8a-tetramethylnaphthalen-1-yl)heptadecanoic acid (11) in subsequent experiments.
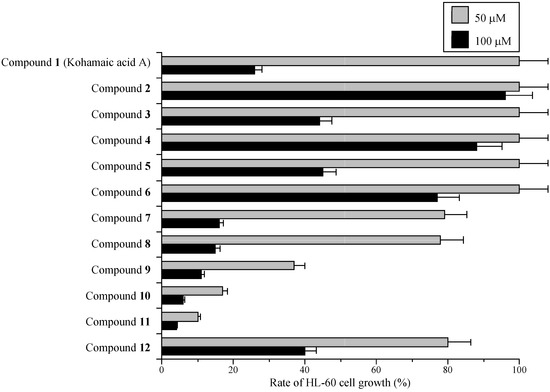
Figure 3.
Effects of kohamaic acid A derivatives (compounds 1–12) on proliferation of HL-60 cancer cells.
Inhibitory effect of compound 11 on the activities of DNA polymerases and other DNA metabolic enzymes
As shown in Table 1, compound 11 inhibited the activities of all the mammalian pols tested, and the range of the IC50 values was 3.22–8.76 μM. The inhibitory effect on human pol ε was the strongest of the mammalian pols tested. Given that the pol A family includes pol γ, the pol B family includes pols α, δ and ε, the pol X family includes pols β and λ, and the pol Y family includes pols η, ι and κ [13,14,15], compound 11 could inhibit the activities of all families of mammalian pols and fish pols such as cherry salmon pol δ. On the other hand, the activity of plant pols such as cauliflower pol α, prokaryotic pols such as the Klenow fragment of E. coli pol I, Taq pol and T4 pol, and DNA metabolic enzymes such as calf primase of pol α, T7 RNA polymerase, T4 polynucleotide kinase and bovine deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I), were not influenced by compound 11. When activated DNA was used as the DNA template-primer instead of poly(dA)/oligo(dT)12-18, the inhibition modes of these compounds did not change (data not shown). These results suggest that compound 11 should be classified as an inhibitor of mammalian pols.

Table 1.
IC50 values of compound 11 on the activities of various DNA polymerases and other DNA metabolic enzymes.
| Enzyme | IC50 values (μM) |
|---|---|
| Mammalian DNA polymerases | |
| Calf DNA polymerase α | 4.21 ± 0.21 |
| Rat DNA polymerase β | 5.50 ± 0.28 |
| Human DNA polymerase γ | 8.76 ± 0.44 |
| Human DNA polymerase δ | 4.89 ± 0.24 |
| Human DNA polymerase ε | 3.22 ± 0.16 |
| Human DNA polymerase η | 7.45 ± 0.37 |
| Human DNA polymerase ι | 7.84 ± 0.39 |
| Human DNA polymerase κ | 7.20 ± 0.36 |
| Human DNA polymerase λ | 4.67 ± 0.23 |
| Fish DNA polymerase | |
| Cherry salmon DNA polymerase δ | 4.30 ± 0.22 |
| Plant DNA polymerase | |
| Cauliflower DNA polymerase I (α-like) | >200 |
| Prokayotic DNA polymerases | |
| E. coli DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment) | >200 |
| Taq DNA polymerase | >200 |
| T4 DNA polymerase | >200 |
| Other DNA metabolic enzymes | |
| Calf Primase of DNA polymerase α | >200 |
| T4 Polynucleotide kinase | >200 |
| Bovine Deoxyribonuclease I | >200 |
Compound 11 was incubated with each pol (0.05 units) and other DNA metabolic enzymes. One unit of pol activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzed the incorporation of 1 nmol of dNTP (i.e., dTTP) into the synthetic DNA template-primers (i.e., poly(dA)/oligo(dT)12-18, A/T = 2/1) in 60 min at 37 °C under normal reaction conditions for each enzyme. Enzyme activity in the absence of the compounds was taken as 100%. Data are shown as the means ± SEM of four independent experiments.
Effect of interaction of nucleic acid, protein and compound 11
To determine whether the inhibition resulted in binding to DNA or enzymes, the interaction of compound 11 with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) was investigated based on the thermal transition of dsDNA with or without compound 11. The Tm of dsDNA with an excess amount of compound 11 (200 μM) was measured using a spectrophotometer equipped with a thermoelectric cell holder. In the concentration range used, no thermal transition of Tm was observed, whereas ethidium bromide used as a positive control, a typical intercalating compound, produced clear thermal transition (data not shown). These results indicate that compound 11 does not intercalate to DNA as a template-primer, and the compound may directly bind to the enzyme and inhibit its activity.

Table 2.
Effects of poly (rC), bovine serum albumin (BSA) or Nonidet P-40 (NP-40) on the inhibition of rat DNA polymerase β activity by compound 11.
| Compounds added to the reaction mixture | Relative activity of pol β (%) |
|---|---|
| Without compound 11 | |
| None (control) | 100 ± 5.0 |
| + 50 μM poly (rC) | 100 ± 4.6 |
| + 200 μg/ml BSA | 100 ± 8.9 |
| + 0.05 % NP-40 | 100 ± 5.9 |
| + 0.1 % NP-40 | 100 ± 8.5 |
| 10 μM compound 11 | |
| 10 μM compound 11 | 15.5 ± 0.78 |
| 10 μM compound 11 + 50 μM poly (rC) | 15.2 ± 0.74 |
| 10 μM compound 11 + 200 μg/ml BSA | 15.9 ± 1.1 |
| 10 μM compound 11 + 0.05 % NP-40 | 96.1 ± 7.6 |
| 10 μM compound 11 + 0.1 % NP-40 | 100 ± 8.8 |
| 100 μM compound 11 | |
| 100 μM compound 11 | 3.2 ± 0.16 |
| 100 μM compound 11 + 50 μM poly (rC) | 3.1 ± 0.15 |
| 100 μM compound 11 + 200 μg/ml BSA | 3.3 ± 0.19 |
| 100 μM compound 11 + 0.05 % NP-40 | 62.5 ± 4.1 |
| 100 μM compound 11 + 0.1 % NP-40 | 95.0 ± 7.6 |
50 μM poly (rC), 200 μg/ml BSA, 0.05% NP-40 or 0.1% NP-40 were added to the reaction mixture. In the absence of compound 11, DNA polymerase activity was taken as 100%. Data are shown as the means ± SEM of four independent experiments.
To determine the effects of a non-ionic detergent on the binding of compound 11 to rat pol β, Nonidet P-40 (NP-40) was added to the reaction mixture at a concentration of 0.05 or 0.1% (Table 2). In the absence of compound 11, the activity of pol β was not affected by the addition of NP-40, and we designated the activity in these cases as 100%. The inhibitory effect of compound 11 at 10 and 100 μM was completely reversed by the addition of 0.1% NP-40 to the reaction mixture. These results suggest that compound 11 can bind to and interact with the hydrophobic region of the enzyme protein. We also tested whether an excess amount of a substrate DNA analog, poly(rC) (50 μM), or a protein, BSA (200 μg/ml), could prevent the inhibitory effects of compound 11. If the compound binds to the enzymes by non-specific adhesion, the addition of the nucleic acid and/or protein will be expected to reduce inhibitory activity. Neither poly(rC) nor BSA influenced the inhibitory effects on compound 11, suggesting that the compound can interact selectively or bind to a specific site on pol β and not to the substrate (i.e., nucleic acid). These results for compound 11 were obtained using mammalian pols other than pol β (data not shown).
Pol β has the smallest molecular weight (i.e., 39-kDa) of all eukaryotic pols, and the three-dimensional structure of pol β was determined [16, 17]; therefore, we focused on analyzing the biochemical and molecular mechanism of pol β inhibition by compound 11 in the latter part of this study.
Mode of inhibition of DNA polymerase β by compound 11
Next, to elucidate the mechanism by which compound 11 inhibited pol β, the extent of inhibition as a function of substrate concentration was studied. In kinetic analysis of pol β, poly(dA)/oligo(dT)12-18 (molecular concentration of primer 3’-ends) and 2'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate (dTTP) were used as the DNA template-primer and 2’-deoxyribonucleotide 5’-triphosphate (dNTP) substrate, respectively. As shown in Table 3, double reciprocal plots (Lineweaver Burk plots) of the results showed that the compound 11-induced inhibition of rat pol β activity was competitive with respect to the DNA template-primer, because the apparent maximum velocity (Vmax) was unchanged at 111 pmol/h, whereas 22.0 pmol/h of the Michaelis constant (Km) increased in the presence of 9 μM of compound 11. The inhibition mode was also competitive with respect to the dNTP substrate, and the Vmax for the dNTP substrate was unchanged at 62.5 pmol/h, and the Km for the dNTP substrate increased from 3.05 to 10.8 μM in the presence of 9 μM of compound 11. The inhibition constant (Ki) values, obtained from Dixon plots, were found to be 1.96 μM and 2.36 μM for the DNA template-primer and dNTP substrate, respectively.

Table 3.
Kinetic analysis of the inhibitory effects of compound 11 on the activities of rat DNA polymerase β as a function of the DNA template-primer dose and the nucleotide substrate concentration.
| Enzyme | DNA Substrate | Compound 11 (μM) | Km a) (μM) | Vmax a) (pmol / h) | Ki b) (μM) | Inhibitory mode a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pol β | Template | 0 | 6.74 | 111 | 1.96 | Competitive |
| -primer c) | 3 | 8.77 | ||||
| 6 | 12.7 | |||||
| 9 | 22.0 | |||||
| Nucleotide d) | 0 | 3.05 | 62.5 | 2.36 | Competitive | |
| substrate | 3 | 4.03 | ||||
| 6 | 5.81 | |||||
| 9 | 10.8 |
a) These data were obtained from Lineweaver Burk plot. b) These data were obtained from Dixon plot. c) poly(dA)/oligo(dT)12-18. d) dTTP.
The inhibition of pol β by compound 11 had the same kinetic mode as that of other pol X family members, such as pol λ, i.e., competitive with respect to both the DNA template-primer and the dNTP substrate, suggesting that the compound can bind directly to both the DNA template-primer-binding site and the dNTP substrate-binding site, and may directly inhibit the DNA polymerization process. As the Ki values for nucleic acid were similar to those for the dNTP substrate, the affinity of compound 11 and the enzyme-nucleic acid may be the same as that of compound 11 and the enzyme-nucleotide substrate.
Three-dimensional modeling of the interaction of KA-A derivatives with DNA polymerase β
Further investigations of the three-dimensional structure of the binding site on pol β and the modes of binding of compound 11 are necessary. We previously reported the characteristics of binding between pol β and linear-long chain fatty acids (for example: C24-nervonic acid), which are components of KA-A derivative compounds 7–11, involved in the inhibition of pol β activity [18]. Pol β is the smallest known pol in animal cells with a molecular mass of 39-kDa, and its structure is highly conserved among mammals [19]. This protein has a modular two-domain structure, with apparent flexibility within a protease-sensitive region between residues 82–86, which separates the two domains, an N-terminal domain fragment (8-kDa), which retains binding affinity for single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), and a C-terminal domain fragment (31-kDa) with reduced pol activity (Figure 4A) [20, 21]. The linear-long chain fatty acids bound to pol β at the N-terminal 8-kDa domain, where they competed with the DNA template-primer [18, 22]. One molecule of each of the agents in the fatty acid region competed with one molecule of DNA template-primer, and subsequently interfered with the binding of a DNA template-primer to one 8-kDa domain, indicating that the 8-kDa domain fragment bound to the fatty acids as a 1:1 complex. Biochemical and surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore) demonstrated that KA-A derivatives, including compound 11, bound selectively to the N-terminal 8-kDa domain of pol β at a molecular ratio of 1 : 1, this compound inhibited ssDNA binding activity, and the binding of these compounds indirectly inhibited catalytic activity on the 31-kDa domain (data not shown).
The NMR structure of the N-terminal 8-kDa domain of pol β has been determined by Wilson, Mullen and their co-workers [22]. According to their results, the 8-kDa domain (residues 1–87) is formed by four α-helices, packed as two antiparallel pairs. The pairs of α-helices cross one another at 50°, giving them a V-like shape. The 8-kDa domain contains a motif termed the "Helix-hairpin-Helix" (HhH). The protein residues involved in template DNA-binding have been identified by NMR using chemical shift changes [23]. The Helix-3-hairpin-Helix-4 motif and residues in an adjacent W-type loop connecting helix-1 and helix-2 form the ssDNA interaction surface [24]. Furthermore, it was also found that several mutants of the 8-kDa domain (F25W, K35A, K60A and K68A) showed impaired template DNA-binding activity [25]. The structure of the 8-kDa domain fragment with linear-long chain fatty acids has been determined by multi-dimensional NMR in more detail [18]. The interactions with the fatty acids were mapped to one face of the fragment by characterizing backbone 1H and 15N chemical shift changes. In the 8-kDa domain fragment with linear-long chain fatty acids, the structure that forms the interface included helix-1, helix-2, helix-4, a turn (residues from 48 to 51) and residues adjacent to an Ω-type loop connecting helix-1 and helix-2. Since the alkyl chain group of the fatty acids appears to bind to Leu11, His51 and Thr79 of the interface on amino acid sheets of the 8-kDa domain fragment and the carboxyl group interacts with the Lys35 site, the distance between the alkyl chain end and the carboxyl end might be important for tight binding. Only the shifted cross-peaks of Leu11 and Thr79 were significantly changed by the length of the carbon chain. Longer fatty acids could bind to the fragment more tightly.
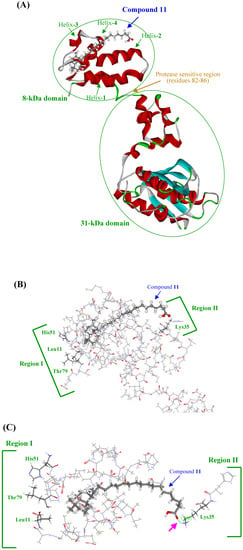
Figure 4.
Docking simulation of compound 11 with rat DNA polymerase β.
Based on these results, the binding of KA-A derivatives containing fatty acid (i.e., compounds 7–12) to the three-dimensional structure of rat pol β was simulated by utilizing the above information, and the interaction interface of these compounds on the amino acid sheets of the 8-kDa domain fragment was mostly the same as in linear-long chain fatty acids (for example: C24-nervonic acid). In the energy-minimized docking simulation, compound 11 was the strongest binding energy among the compounds tested, and the binding force (-106.53 kcal/mol) consisted of Coulomb force (-94.68 kcal/mol) and van der Waals force (-11.85 kcal/mol) (Table 4). In the order of binding energy, these KA-A-related compounds ranked as follows: compound 11 > compound 12 > compound 10 > compound 9 > compound 8 > compound 7. This energy of KA-A derivatives containing fatty acids showed the same tendency as the inhibitory activity of pol β (Figure 2B).

Table 4.
Binding energy of kohamaic acid A derivatives (compounds 7–12) and the 8-kDa domain of DNA polymerase β.
| Compound | Energy (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb | van der Waals | Total | |
| 7 | -12.81 | -6.89 | -19.70 |
| 8 | -4.48 | -7.79 | -12.27 |
| 9 | -56.61 | -9.44 | -66.05 |
| 10 | -65.42 | -10.20 | -75.62 |
| 11 | -94.68 | -11.85 | -106.53 |
| 12 | -66.14 | -17.23 | -83.37 |
The 8-kDa domain of rat DNA polymerase β (residues 2–88, PDB code; 1BPD) with each KA-A derivatives (compounds 7–12) is indicated. Binding energy was calculated by the flexible docking procedure in the affinity program within the Insight II modeling software (Accelrys Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
The molecular lengths of these compounds are shown in Table 5. Since compound 11 was the strongest inhibitor of pol β in compounds 7–12, the molecular length of compound 11 (i.e., 17.47 Å) might best fit the pocket of the 8-kDa domain.

Table 5.
The molecular length and wide of three-dimensional structure of kohamaic acid A derivatives (compounds 1–12).
| Compound | Length (Å) | Wide (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (kohamaic acid A) | 16.76 | 6.45 |
| 2 | 11.96 | 6.45 |
| 3 | 12.08 | 6.45 |
| 4 | 13.92 | 6.45 |
| 5 | 11.42 | 6.45 |
| 6 | 11.28 | 5.10 |
| 7 | 11.51 | 6.45 |
| 8 | 11.57 | 6.45 |
| 9 | 17.47 | 6.45 |
| 10 | 22.31 | 6.45 |
| 11 | 26.69 | 6.45 |
| 12 | 31.61 | 6.45 |
The energy-minimized three-dimensional molecular structures of KA-A and its derivatives (compounds 1–12) were prepared using Insight II (Accelrys, San Diego, CA, USA), and the maximum length and width of the compounds were measured.
Therefore, docking simulation of compound 11 and the 8-kDa domain of pol β is shown in Figure 4, and the compound 11 binding interface of the 8-kDa domain having the same pocket (i.e., the crevice between helix-1 and helix-2) as linear-long chain fatty acids (Figure 4A). This result suggested that Lys35, which is a hydrophilic amino acid in "region II", bound to the carboxyl group of compound 11, and Leu11 and His51, which are hydrophobic amino acids in "region I", bound to the bicyclic core part of compound 11 (Figure 4B). Prasad et al. reported that DNA template [i.e., p(dT)8] binding activity was impaired in site-directed mutants of Phe25, Lys35, Lys60 or Lys68 [25]. Region II containing Lys35, shown in Figure 4B, appears to have an important role in the effect of compound 11. This compound probably competes with the DNA template-primer at residue Lys35 and binds to the site, which subsequently inhibits ssDNA-binding activity in the 8-kDa domain. In region I shown in Figure 4B, Leu11, His51 and Thr79 are different from other DNA-binding sites (i.e., Phe25, Lys60 and Lys68), suggesting that the hydrophobic moieties of the alkyl chain and bicyclic core part in compound 11 do not disturb the binding of the DNA template-primer, and these hydrophobic amino acids in region I must be important for binding to the compound by hydrophobic force. In this docking simulation, the carboxyl group of compound 11 and the residue of Lys35 made a hydrogen bond (pink arrow in Figure 4C). The carboxyl group in compound 11 is thought to be important for the inhibition of pol β, because the compound modified from the carboxyl group to a methyl ester could not inhibit activity (data not shown). The distance between the Lys35 hydrophilic region and Leu11 and His51 hydrophobic regions fits the length of the U-shaped compound 11, and intercalated smoothly into the pocket between helix-1, 2 and helix-3, 4; therefore, both the three-dimensional molecular length and the carboxyl end of KA-A derivatives are important for both fitting to bind the pocket and the inhibitory activity of DNA polymerization and ssDNA binding on the 8-kDa domain of pol β. The three-dimensional structural binding analysis between the 8-kDa domain fragment of pol β and compound 11 will be measured using the multi-dimensional (1H-15N HMQC) NMR for further study.
Although the polymerase active site of pol β is homologous to other pols, it structure is unique to family X pols [3]. These results suggested that other pols from alternate families (e.g., families A, B and Y) might have similar binding sites even though they do not have an equivalent domain.
Drug design will be possible by investigating the tightness of the binding between the KA-A derivatives and pol β. Based on information available from NMR analysis, computer simulation of the conformational changes in pol β with or without newly designed KA-A related compounds will be useful for this purpose.
We have been screening for new pol inhibitors to use for analyzing the structure and function of mammalian pols to understand their precise roles in vivo, and to develop drug design strategies for the development of cancer chemotherapy agents. These inhibitors are not only molecular tools for analyzing pols, but are also potentially useful for cancer chemotherapy. Subsequently, we found that KA-A (compound 1) was a potentially useful agent [2], and synthesized KA-A derivatives (compounds 2 – 12) [10]. The inhibitory effect of compound 11 on both mammalian pol activity and human cancer cell growth was strongest of all compounds tested (Figure 2 and Figure 3), and this compound inhibited enzyme activity at an IC50 of 4.21 μM for pol α and 5.50 μM for pol β (Table 1). This compound showed markedly stronger inhibitory effects on pol α than aphidicolin (IC50 = 40 μM) (data not shown). We should also emphasize that compound 11 is a 4-fold stronger pol β inhibitor than dideoxyTTP, a potent inhibitor of pol β [26]. Due to their strong inhibitory effects, these KA-A derivatives could be useful as pol inhibitors.
In this report, we explained the structure-function relationship in the inhibition of pols by synthetic derivatives of KA-A, and elucidated the molecular mechanism of the inhibitory action of these compounds on pol activity and mammalian cell proliferation. In compound 11, not only the fatty acid region but the bicyclic core part might have an important role in the inhibition of pol activity. The molecular mechanism of the inhibition seemed to be dependent on the fatty acid chain length.
In this study, we discussed the pharmaceutical potential of KA-A derivatives such as compound 11 as inhibitors of mammalian pol and human cancer cell growth. This will be a useful approach to finding and developing future therapeutic drugs.
Experimental
General
Except for natural KA-A (compound 1), all derivatives (compounds 2–12) were synthesized in a non-enantioselective manner [10]. The chemical structures of the compounds are shown in Figure 1. Nucleotides and chemically synthesized DNA template-primers, such as poly(dA) and oligo(dT)12-18, and radioisotope reagents such as [3H]-dTTP (43 Ci/mmol) were purchased from GE Healthcare Bio-Science Corp. (Buckinghamshire, UK). All other reagents were of analytical grade and were purchased from Nacalai Tesque, Ltd. (Kyoto, Japan).
Enzymes
Pol α was purified from calf thymus by immuno-affinity column chromatography as described by Tamai et al. [27]. Recombinant rat pol β was purified from E. coli JMpβ5 as described by Date et al. [28]. The human pol γ catalytic gene was cloned into pFastBac. Histidine-tagged enzyme was expressed using the BAC-TO-BAC HT Baculovirus Expression System according to the supplier's manual (LIFE TECHNOLOGIES, MD, USA) and purified using ProBoundresin (Invitrogen Japan, Tokyo, Japan) [29]. Human pols δ and ε were purified by the nuclear fractionation of human peripheral blood cancer cells (Molt-4) using the second subunit of pols δ and ε-conjugated affinity column chromatography, respectively [30]. Recombinant human pols η and ι tagged with His6 at their C-terminal were expressed in SF9 insect cells using the baculovirus expression system, and were purified as described previously [31, 32]. A truncated form of pol κ (i.e., hDINB1DC) with 6 x His-tags attached at the C-terminal was overproduced using the BAC-to-BAC Baculovirus Expression System kit (GIBCO BRL, MD, USA) and purified as described previously [33]. Recombinant human His-pol λ was overexpressed and purified according to a method described previously [34]. Fish pol δ was purified from the testis of cherry salmon (Oncorhynchus masou) [35]. Pol I (α-like) from a higher plant, cauliflower inflorescence, was purified according to the methods outlined by Sakaguchi et al. [36]. The Klenow fragment of pol I from E. coli was purchased from Worthington Biochemical Corp. (Freehold, NJ, USA). Taq pol, T4 pol, T7 RNA polymerase and T4 polynucleotide kinase were purchased from Takara (Kyoto, Japan). Bovine pancreas deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) was obtained from Stratagene Cloning Systems (La Jolla, CA, USA).
DNA polymerase assays
The reaction mixtures for pol α, pol β, fish pol δ, plant pol I (α-like) and prokaryotic pols were described previously [37, 38], and those for pol γ, and pols δ and ε were as described by Umeda et al. [29] and Ogawa et al. [39], respectively. The reaction mixtures for pols η, ι and κ were the same as for pol α, and the reaction mixture for pol λ was the same as that for pol β.
For pols, poly(dA)/oligo(dT)12-18 (A/T = 2/1) and dTTP were used as the DNA template-primer and nucleotide (i.e., dNTP) substrate, respectively. KA-A analogues (i.e., compounds 1–12) were dissolved in distilled dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at various concentrations and sonicated for 30 sec. Aliquots of 4 μL of sonicated samples were mixed with 16 μL of each enzyme (final amount 0.05 units) in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) containing 1 mM dithiothreitol, 50% glycerol and 0.1 mM EDTA, and kept at 0 °C for 10 min. These inhibitor-enzyme mixtures (8 μl) were added to 16 μL of each of the enzyme standard reaction mixtures, and incubation was carried out at 37 °C for 60 min, except for Taq pol, which was incubated at 74 °C for 60 min. Activity without the inhibitor was considered 100%, and the remaining activity at each concentration of the inhibitor was determined relative to this value. One unit of pol activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzed the incorporation of 1 nmol of dNTP (i.e., dTTP) into synthetic DNA template-primers in 60 min at 37 °C under the normal reaction conditions for each enzyme [37, 38].
Investigation of growth rate on cultured human cancer cells
To investigate the effects of KA-A derivatives in cultured cells, we used a human cancer cell line, HL-60, human promyelocytic leukemia cells (IFO 050022), supplied by the Health Science Research Resources Bank (Osaka, Japan). The cells were routinely cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, 100 unit/mL penicillin, and 1.6 mg/mL NaHCO3. The cells were cultured at 37 °C in standard medium in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2-95% air. The rate of the cancer cell growth of the compound was investigated as follows: high concentrations (10 mM) of the compounds were dissolved in DMSO and stocked. Approximately 1 x 104 cells per well were inoculated in 96-well micro plates, and then the compound stock solution was diluted to various concentrations, and applied to each well. After incubation for 24 hr, the survival rate was determined by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay [40].
Other enzyme assays
The primase activity of calf pol α, the activities of T7 RNA polymerase, T4 polynucleotide kinase and bovine DNase I were measured in standard assays according to the manufacturer's specifications as described by Tamiya-Koizumi et al. [41], Nakayama et al. [42], Soltis et al. [43], and Lu and Sakaguchi [44], respectively.
KA-A derivatives docking modeling
The molecular docking of KA-A derivatives and the 8-kDa domain of pol β (Protein Data Bank (PDB) code: 1BNO and 1BPD) was performed using a fixed docking procedure in the Affinity program of Insight II modeling software (Accerlys Inc., San Diego, CA, USA, 1999). The calculations used a CVFF force-field in the Discovery program and a Monte Carlo strategy in the Affinity program [45]. Each energy-minimized final docking position of KA-A derivatives was evaluated using the interactive score function in the Ludi module. The Ludi score includes the contribution of the loss of translational and rotational entropy of the fragment, the number and quality of hydrogen bonds, and contributions from ionic and lipophilic interactions to the binding energy.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid for Kobe-Gakuin University Joint Research (A), and “Academic Frontier” Project for Private Universities: matching fund subsidy from MEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology), 2006–2010 (Y. M. and H. Y.). Y. M. acknowledges a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A) (No. 19680031) from MEXT, Grants-in-Aid from the Nakashima Foundation (Japan), Foundation of Oil & Fat Industry Kaikan (Japan), The Salt Science Research Foundation, No. 08S3 (Japan), and a Grant from the Industrial Technology Research Program from NEDO (Japan). We thank Takasago International Corporation for the generous gift of farnesol, the starting material for analogue synthesis. We also thank Ms. Akiyo Inoue for helpful support.
References and Notes
- Kokubo, S.; Yogi, K.; Uddin, M. J.; Inuzuka, T.; Suenaga, K.; Ueda, K.; Uemura, D. Kohamaic acids A and B, novel cytotoxic sesterterpenic acids, from the marine sponge Ircinia sp. Chem. Lett. 2001, 30, 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushina, Y.; Murakami, C.; Yogi, K.; Ueda, K.; Ishidoh, T.; Takemura, M.; Perpelescu, M.; Suzuki, M.; Oshige, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Saneyoshi, M.; Yoshida, H.; Sakaguchi, K. Kohamaic acid A, a novel sesterterpenic acid, inhibits activities of DNA polymerases from deuterostomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1648, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher, U.; Maga, G.; Spadari, S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L. M. S. Phylogeny of DNA polymerase-β. Science 1976, 191, 1183–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Hobart, P. M.; Infante, A. A. A low molecular weight DNA polymerase β in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpurantus. Partial purification, properties, and changes in development. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 8229–8238. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, T.; Wolpert, L. Cellular movement and contact in sea urchin morphogenesis. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1967, 42, 442–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Petrocellis, B.; Filosa-Parisi, S.; Monroy, A.; Parisi, E. Cell and tissue interactions. Lash, J.W., Burger, M., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, E.; Filosa, S.; De Petrocellis, B.; Monroy, A. The pattern of cell division in the early development of the sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. Dev. Biol. 1978, 65, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katow, H.; Solursh, M. Ultrastructure of blastocoel material in blastulae and gastrulae of the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus. J. Exp. Zool. 1980, 213, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, H.; Kamatani, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Tashiro, T.; Sasaki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y. Synthetic studies on kohamaic acids: Synthesis of structurally simplified analogs of kohamaic acid A. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 3071–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebenek, K.; Kunkel, T. A. DNA Repair and Replication. In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Yang, W., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, USA, 2004; Volume 69, pp. 137–165. [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg, E. C.; Feaver, W. J.; Gerlach, V. L. The many faces of DNA polymerases: strategies for mutagenesis and for mutational avoidance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5681–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgers, P. M.; Koonin, E. V.; Bruford, E.; Blanco, L.; Burtis, K. C.; Christman, M. F.; Copeland, W. C.; Friedberg, E. C.; Hanaoka, F.; Hinkle, D. C.; Lawrence, C. W.; Nakanishi, M.; Ohmori, H.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S.; Reynaud, C. A.; Sugino, A.; Todo, T.; Wang, Z.; Weill, J. C.; Woodgate, R. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases: proposal for a revised nomenclature. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43487–43490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, H.; Friedberg, E. C.; Fuchs, R. P.; Goodman, M. F.; Hanaoka, F.; Hinkle, D.; Kunkel, T. A.; Lawrence, C. W.; Livneh, Z.; Nohmi, T.; Prakash, L.; Prakash, S.; Todo, T.; Walker, G. C.; Wang, Z.; Woodgate, R. The Y-family of DNA polymerases. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E. V. DNA polymerase β-like nucleotidyltransferase superfamily: identification of three new families, classification and evolutionary history. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, M. R.; Pelletier, H.; Kumar, A.; Wilson, S. H.; Kraut, J. Crystal structure of rat DNA polymerase β: evidence for a common polymerase mechanism. Science 1994, 264, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, H.; Sawaya, M. R.; Kumar, A.; Wilson, S. H.; Kraut, J. Structures of ternary complexes of rat DNA polymerase β, a DNA template-primer, and ddCTP. Science 1994, 264, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushina, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Date, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Saneyoshi, M.; Sugawara, F.; Sakaguchi, K. Mode analysis of a fatty acid molecule binding to the N-terminal 8-kDa domain of DNA polymerase β. A 1:1 complex and binding surface. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25599–25607. [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg, A.; Baker, T. A. DNA replication, 2nd Ed.; Freeman W., H., Co., N.Y., Eds.; Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 6, pp. 197–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Abbotts, J.; Karawya, E. M.; Wilson, S. H. Identification and properties of the catalytic domain of mammalian DNA polymerase β. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7156–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Widen, S. G.; Williams, K. R.; Kedar, P.; Karpel, R. L.; Wilson, S. H. Studies of the domain structure of mammalian DNA polymerase β. Identification of a discrete template binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; DeRose, E. F.; Prasad, R.; Wilson, S. H.; Mullen, G. P. Assignments of 1H, 15N, and 13C resonances for the backbone and side chains of the N-terminal domain of DNA polymerase β Determination of the secondary structure and tertiary contacts. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 9537–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, M. R.; Prasad, R.; Wilson, S. H.; Kraut, J.; Pelletier, H. Crystal structures of human DNA polymerase β complexed with gapped and nicked DNA: evidence for an induced fit mechanism. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 11205–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Prasad, R.; Wilson, S. H.; DeRose, E. F.; Mullen, G. P. Three-dimensional solution structure of the N-terminal domain of DNA polymerase β and mapping of the ssDNA interaction interface. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 6188–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Beard, W. A.; Chyan, J. Y.; Maciejewski, M. W.; Mullen, G. P.; Wilson, S. H. Functional analysis of the amino-terminal 8-kDa domain of DNA polymerase β as revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. DNA binding and 5'-deoxyribose phosphate lyase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 11121–11126. [Google Scholar]
- Izuta, S.; Saneyoshi, M.; Sakurai, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kojima, K.; Yoshida, S. The 5'-triphosphates of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and 2', 3'-dideoxynucleosides inhibit DNA polymerase γ by different mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 179, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, K.; Kojima, K.; Hanaichi, T.; Masaki, S.; Suzuki, M.; Umekawa, H.; Yoshida, S. Structural study of immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase α-DNA primase complex from calf thymus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 950, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hirose, F.; Nishimoto, Y.; Tanihara, K.; Matsukage, A. Expression of active rat DNA polymerase β in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, S.; Muta, T.; Ohsato, T.; Takamatsu, C.; Hamasaki, N.; Kang, D. The D-loop structure of human mtDNA is destabilized directly by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+), a parkinsonism-causing toxin. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshige, M.; Takeuchi, R.; Ruike, R.; Kuroda, K.; Sakaguchi, K. Subunit protein-affinity isolation of Drosophila DNA polymerase catalytic subunit. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 35, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, C.; Kusumoto, R.; Iwai, S.; Hanaoka, F. Mechanisms of accurate translesion synthesis by human DNA polymerase η. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3100–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissier, A.; Frank, E. G.; McDonald, J. P.; Iwai, S.; Hanaoka, F.; Woodgate, R. Misinsertion and bypass of thymine-thymine dimers by human DNA polymerase ι. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5259–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, E.; Ogi, T.; Kusumoto, R.; Iwai, S.; Masutani, C.; Hanaoka, F.; Ohmori, H. Error-prone bypass of certain DNA lesions by the human DNA polymerase κ. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki, N.; Yoshida, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Toji, S.; Tamai, T.; Koiwai, O. Over-expression of human DNA polymerase λ in E. coli and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Genes Cells 2000, 7, 639–651. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Saneyoshi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Hirokawa, S.; Amano, R.; Liu, X.; Inomata, M.; Maruyama, T. Synthetic Nucleoside and Nucleotides. 43. Inhibition of vertebrate telomerases by carbocyclic oxetanocin G (C.OXT-G) triphosphate analogues and influence of C.OXT-G treatment on telomere length in human HL60 cells. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2006, 25, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, K.; Hotta, Y.; Stern, H. Chromatin-associated DNA polymerase activity in meiotic cells of lily and mouse. Cell Struct. Funct. 1980, 5, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushina, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Yagi, H.; Kurosawa, T.; Onoue, M.; Seto, H.; Horie, T.; Aoyagi, N.; Yamaoka, M.; Matsukage, A.; Yoshida, S.; Sakaguchi, K. Fatty acids selectively inhibit eukaryotic DNA polymerase activities in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1308, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushina, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Matsukage, A.; Sakaguchi, K. The inhibitory action of fatty acids on DNA polymerase β. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1336, 509–521. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, A.; Murate, T.; Suzuki, M.; Nimura, Y.; Yoshida, S. Lithocholic acid, a putative tumor promoter, inhibits mammalian DNA polymerase β. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiya-Koizumi, K.; Murate, T.; Suzuki, M.; Simbulan, C. G.; Nakagawa, M.; Takamura, M.; Furuta, K.; Izuta, S.; Yoshida, S. Inhibition of DNA primase by sphingosine and its analogues parallels with their growth suppression of cultured human leukemic cells. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1997, 41, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, C.; Saneyoshi, M. Inhibitory effects of 9-α-D-xylofuranosyladenine 5'-triphosphate on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase I and II from cherry salmon (Oncorhynchus masou). J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 1985, 97, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Soltis, D. A.; Uhlenbeck, O. C. Isolation and characterization of two mutant forms of T4 polynucleotide kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 11332–11339. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B. C.; Sakaguchi, K. An endo-exonuclease from meiotic tissues of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus: Its purification and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21060–21066. [Google Scholar]
- Kurinov, I. V.; Myers, D. E.; Irvin, J. D.; Uckun, F. M. X-ray crystallographic analysis of the structural basis for the interactions of pokeweed antiviral protein with its active site inhibitor and ribosomal RNA substrate analogs. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the synthesized KA-A compounds 2–12 are available from Dr. H. Takikawa (Kobe University).
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).