A New 3-Benzylchroman Derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan)
Abstract
:Introduction
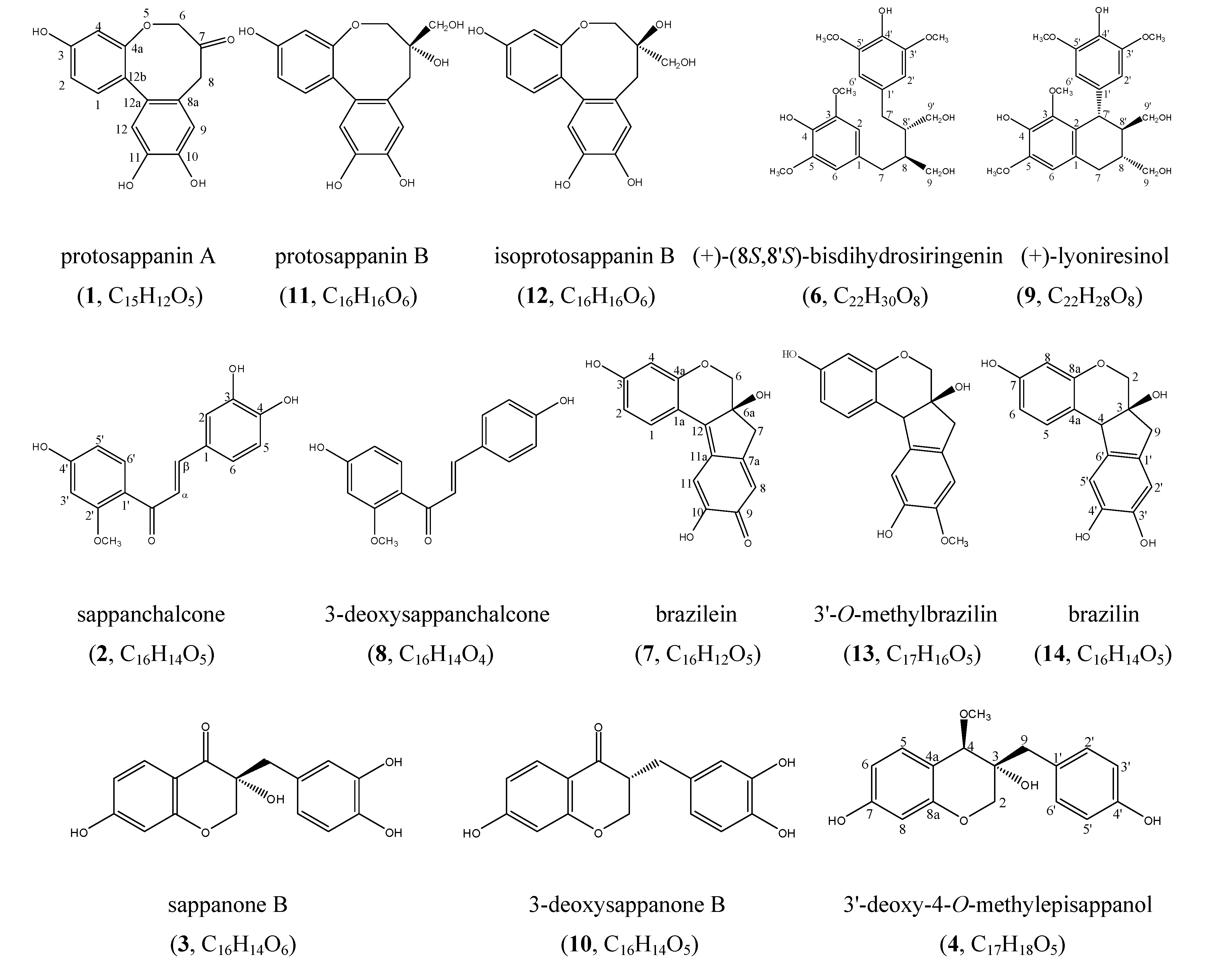
Results and Discussion
| No. | δ H | δ C | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3.82 (1H, d, J = 11.0 Hz), 4.10 (1H, d, J = 11.0 Hz) | 71.2 | 71.1, 78.8, 157.2 |
| 3 | 71.7 | ||
| 4 | 3.60 (1H, s) | 78.8 | 56.9, 71.7, 134.3, 157.2 |
| 4a | 113.6 | ||
| 5 | 6.96 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz) | 134.3 | 78.8, 157.2, 160.5 |
| 6 | 6.34 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz) | 108.9 | 104.5, 113.6 |
| 7 | 160.5 | ||
| 8 | 6.28 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz) | 104.5 | 157.2, 160.5 |
| 8a | 157.2 | ||
| 9 | 2.70 (1H, d, J = 13.5 Hz), 2.91 (1H, d, J = 13.5 Hz) | 40.5 | 71.7, 78.8, 128.9, 133.8 |
| 1′ | 128.9 | ||
| 2′,6′ | 7.16 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz) | 133.8 | 40.5, 133.8, 158.1 |
| 3′,5′ | 6.77 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz) | 116.6 | 116.6, 128.9, 158.1 |
| 4′ | 158.1 | ||
| 4-OCH3 | 3.30 (3H, s) | 56.9 | 78.8 |
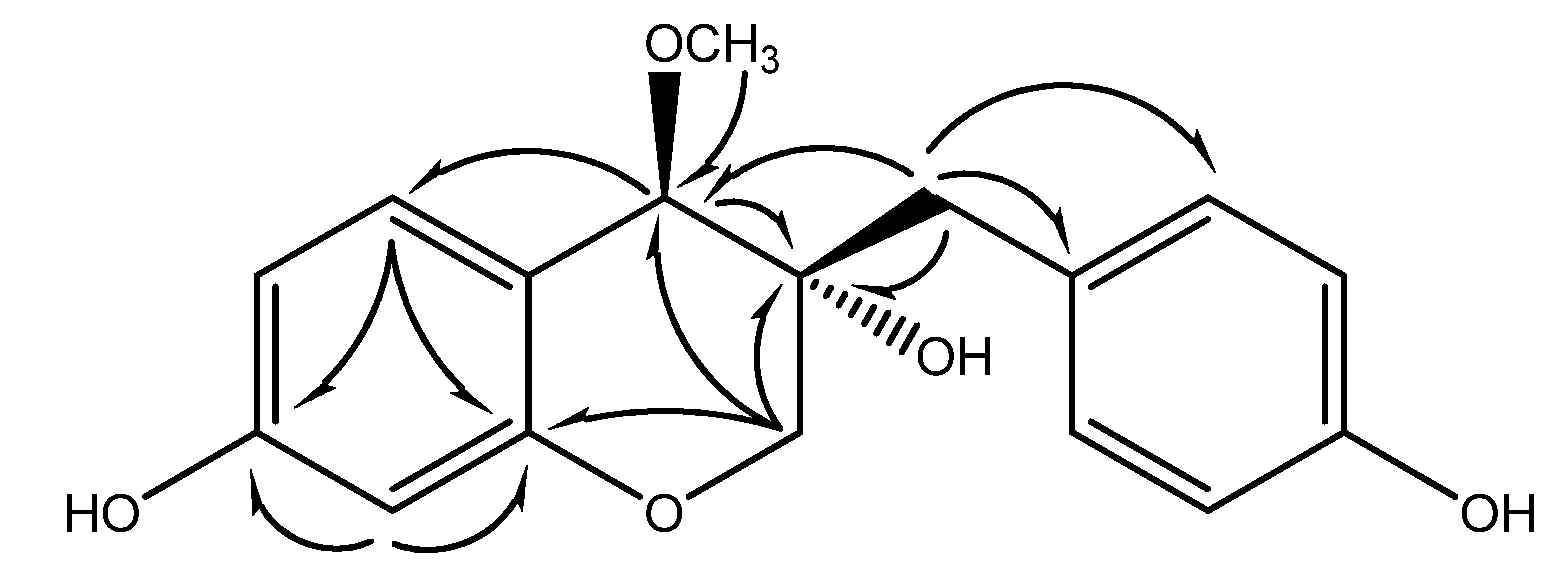
Conclusions
Experimental
General
Plant Material
Extraction and Isolation
Compound characterization
 = -21.0 (c 0.15, MeOH), UV (MeOH) λmax nm (log ε): 284 (3.54), 277 (3.58), 224 (4.04) nm; IR
= -21.0 (c 0.15, MeOH), UV (MeOH) λmax nm (log ε): 284 (3.54), 277 (3.58), 224 (4.04) nm; IR 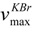 cm-1: 3450 (OH), 3927, 1621 and 1511 (Ar), 1382, 1162 cm-1; 1H and 13C-NMR spectral data were listed in Table1; EIMS m/z (rel. int.): [M]+ 302 (3), 272 (4), 153 (100), 123 (40), 107 (47), 77 (18); HREIMS m/z: 302.1147 [M]+ (calcd for C17H18O5, 302.1149).
cm-1: 3450 (OH), 3927, 1621 and 1511 (Ar), 1382, 1162 cm-1; 1H and 13C-NMR spectral data were listed in Table1; EIMS m/z (rel. int.): [M]+ 302 (3), 272 (4), 153 (100), 123 (40), 107 (47), 77 (18); HREIMS m/z: 302.1147 [M]+ (calcd for C17H18O5, 302.1149). = + 10.0 (c 0.21, MeOH); 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 2.51 (2H, m, H-8 and 8′), 3.11 (2H, dd, J = 13, 7 Hz, H-7a and 7a′), 3.15 (2H, dd, J = 13, 7 Hz, H-7b and 7b′), 3.73 (12H, s, 3, 3′, 5 and 5′-OCH3), 4.12 (2H, dd, J = 11, 5 Hz, H-9a and 9a′), 4.19 (2H, dd, J = 11, 5 Hz, H-9b and 9b′), 6.76 (4H, s, H-2, 2′, 6 and 6′); 13C-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 132.1 (C-1 and 1′), 107.5 (C-2 and 2′), 149.0 (C-3 and 3′), 135.4 (C-4 and 4′), 149.0 (C-5 and 5′), 107.5 (C-6 and 6′), 36.4 (C-7 and 7′), 44.3 (C-8 and 8′), 61.3 (C-9 and 9′), 56.3 (3, 3′, 5 and 5′-OCH3). The NMR spectral data were in accordance with those reported [26, 27].
= + 10.0 (c 0.21, MeOH); 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 2.51 (2H, m, H-8 and 8′), 3.11 (2H, dd, J = 13, 7 Hz, H-7a and 7a′), 3.15 (2H, dd, J = 13, 7 Hz, H-7b and 7b′), 3.73 (12H, s, 3, 3′, 5 and 5′-OCH3), 4.12 (2H, dd, J = 11, 5 Hz, H-9a and 9a′), 4.19 (2H, dd, J = 11, 5 Hz, H-9b and 9b′), 6.76 (4H, s, H-2, 2′, 6 and 6′); 13C-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 132.1 (C-1 and 1′), 107.5 (C-2 and 2′), 149.0 (C-3 and 3′), 135.4 (C-4 and 4′), 149.0 (C-5 and 5′), 107.5 (C-6 and 6′), 36.4 (C-7 and 7′), 44.3 (C-8 and 8′), 61.3 (C-9 and 9′), 56.3 (3, 3′, 5 and 5′-OCH3). The NMR spectral data were in accordance with those reported [26, 27]. = + 2.08 (c 0.24, MeOH); 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 2.24 (1H, m, H-8), 2.65 (1H, m, H-8′), 3.07 (1H, m, H-7a), 3.12 (1H, m, H-7b), 3.64 (6H, s, 3′ and 5′-OCH3), 3.76 (3H, s, 3-OCH3), 3.77 (3H, s, 5-OCH3), 4.09 (2H, m, H-9), 4.17 (2H, m, H-9′), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 5.5 Hz, H-7′), 6.78 (1H, s, H-6), 6.93 (1H, s, H-6′); 13C-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 129.5 (C-1), 126.6 (C-2), 147.9 (C-3), 139.4 (C-4), 148.2 (C-5), 107.4 (C-6), 33.8 (C-7), 41.6 (C-8), 66.4 (C-9), 138.4 (C-1′), 107.3 (C-2′), 148.9 (C-3′ and 5′), 135.8 (C-4′), 107.3 (C-6′), 42.3 (C-7′), 49.3 (C-8′), 64.1 (C-9′), 59.6 (3-OCH3), 56.0 (5-OCH3), 56.4 (3′ and 5′-OCH3) was identified based on analysis of the literature data [27,28,29].
= + 2.08 (c 0.24, MeOH); 1H-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 2.24 (1H, m, H-8), 2.65 (1H, m, H-8′), 3.07 (1H, m, H-7a), 3.12 (1H, m, H-7b), 3.64 (6H, s, 3′ and 5′-OCH3), 3.76 (3H, s, 3-OCH3), 3.77 (3H, s, 5-OCH3), 4.09 (2H, m, H-9), 4.17 (2H, m, H-9′), 5.06 (1H, d, J = 5.5 Hz, H-7′), 6.78 (1H, s, H-6), 6.93 (1H, s, H-6′); 13C-NMR (pyridine-d5) δ: 129.5 (C-1), 126.6 (C-2), 147.9 (C-3), 139.4 (C-4), 148.2 (C-5), 107.4 (C-6), 33.8 (C-7), 41.6 (C-8), 66.4 (C-9), 138.4 (C-1′), 107.3 (C-2′), 148.9 (C-3′ and 5′), 135.8 (C-4′), 107.3 (C-6′), 42.3 (C-7′), 49.3 (C-8′), 64.1 (C-9′), 59.6 (3-OCH3), 56.0 (5-OCH3), 56.4 (3′ and 5′-OCH3) was identified based on analysis of the literature data [27,28,29]. = - 10.0 (c 0.81, MeOH), 1H-NMR (acetone-d6) δ: 2.55 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 10.0 Hz, H-9a), 2.81 (1H, m, H-3), 3.07 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 10.0 Hz, H-9b), 4.15 (1H, dd, J = 11.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2a), 4.35 (1H, dd, J = 11.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2b), 6.37 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-8), 6.56 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, H-6′), 6.60 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, H-6), 6.76 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-2′), 6.77 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5′), 7.73 (1H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-5); 13C-NMR (acetone-d6) δ: 71.7 (C-2), 49.1 (C-3), 193.3 (C-4), 115.9 (C-4a), 130.9 (C-5), 112.3 (C-6), 166.0 (C-7), 104.4 (C-8), 165.5 (C-8a), 33.4 (C-9), 132.2 (C-1′), 117.2 (C-2′), 146.9 (C-3′), 145.5 (C-4′), 117.9 (C-5′), 122.3 (C-6′) was identified by comparison of its 1H-NMR data with the reported for this compound [9].
= - 10.0 (c 0.81, MeOH), 1H-NMR (acetone-d6) δ: 2.55 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 10.0 Hz, H-9a), 2.81 (1H, m, H-3), 3.07 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 10.0 Hz, H-9b), 4.15 (1H, dd, J = 11.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2a), 4.35 (1H, dd, J = 11.0, 9.0 Hz, H-2b), 6.37 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-8), 6.56 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, H-6′), 6.60 (1H, dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, H-6), 6.76 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz, H-2′), 6.77 (1H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, H-5′), 7.73 (1H, d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-5); 13C-NMR (acetone-d6) δ: 71.7 (C-2), 49.1 (C-3), 193.3 (C-4), 115.9 (C-4a), 130.9 (C-5), 112.3 (C-6), 166.0 (C-7), 104.4 (C-8), 165.5 (C-8a), 33.4 (C-9), 132.2 (C-1′), 117.2 (C-2′), 146.9 (C-3′), 145.5 (C-4′), 117.9 (C-5′), 122.3 (C-6′) was identified by comparison of its 1H-NMR data with the reported for this compound [9].Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Karapanagiotis, I.; Lakka, A.; Valianou, L.; Chryssoulakis, Y. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of colouring matters in historical garments from the Holy Mountain of Athos. Microchim. Acta 2008, 160, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, R. Status of natural dyes and dye-yielding plants in India. Curr. Sci. 2007, 92, 916–925. [Google Scholar]
- The Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, 2005 ed.; (Part I); Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, I.S.; Jung, K.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, H.K. Anticomplementary activity of constituents from heartwood of Caesalpina sappan. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 456–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Xie, W.D.; Lei, F.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, Y.N.; Su, H.; Du, L.J. Brazilein, an important immunosuppressive component from Caesalpinia sappan L. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Nagumo, S.; Eguchi, I.; Lee, S.M.; Suzuki, T. Sappanchalcone from Caesalpinia sappan L., the proposed biosynthetic precursor of brazilin. Yakugaku Zasshi 1984, 104, 935–938. [Google Scholar]
- Fuke, C.; Yamahara, J.; Shimokawa, T.; Kinjo, J.; Tomimatsu, T.; Nohara, T. Two aromatic compounds related to brazilin from Caesalpinia sappan. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimokawa, T.; Kinjo, J.; Yamahara, J.; Yamasaki, M.; Nohara, T. Two novel aromatic compounds from Caesalpinia sappan. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 3545–3547. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, T.; Sakashita, S.; Nakata, H.; Shimokawa, T.; Kinjo, J.E.; Yamahara, J.; Yamasaki, M.; Nohara, T. 3-Benzylchroman derivatives related to brazilin from Sappan Lignum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Nagumo, S.; Lee, S.M.; Eguchi, I.; Kawai, K.I. Protosappanin A, a novel biphenyl compound from Sappan Lignum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, M.; Nagumo, S. Protosappanin B, a new dibenzoxocin derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan). Heterocycles 1986, 24, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Nakata, H.; Saitoh, T. Homoisoflavonoids and related compounds: V. A novel dibenzoxocin derivative from Caesalpinia sappan L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3615–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Nakata, H.; Yamada, H.; Nagai, M.; Saitoh, T. Homoisoflavonoids and related compounds: II. Isolation and absolute configurations of 3,4-dihydroxy lated homoisoflavans and brazilins from Caesalpinia sappan L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Nagumo, S. Protosappanin C from Sappan Lignum and absolute configuration of protosappanins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3002–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Nakata, H.; Saitoh, T. Homoisoflavonoids from Caesalpinia sappan. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Saitoh, T. Homoisoflavonoids and related compounds: IV. Absolute configurations of homoisoflavonoids from Caesalpinia sappan L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3597–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Nagumo, S. Protosappanins E-1 and E-2, stereoisomeric dibenzoxocins combined with brazilin from Sappan Lignum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Baek, N.I.; Oh, S.R.; Jung, K.Y.; Lee, I.S.; Lee, H.K. NMR assignment of brazilein. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- OuYang, B.; Ke, C.Q.; He, Z.S.; Yang, Y.P.; Ye, Y. Brazilide A, a novel lactone with an unprecedented keleton from Caesalpinia sappan. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1731–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan Reddy, V.L.; Ravikanth, V.; Jansi Lakshmi, V.V.N.S.; Suryanarayan Murty, U.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Inhibitory activity of homoisoflavonoids from Caesalpinia sappan against Beauveria bassiana. Fitoterapia 2003, 74, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.T.; Awale, S.; Tezuka, Y.; Tran, Q.L.; Kadota, S. Neosappanone A, a xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory dimeric methanodibenzoxocinone with a new carbon skeleton from Caesalpinia sappan. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 8519–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.T.; Awale, S.; Tezuka, Y.; Tran, Q.L.; Kadota, S. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors from the heartwood of vietnamese Caesalpinia sappan. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Nakata, H.; Nuno, M.; Ozawa, T.; Saitoh, T. Homoisoflavonoid and related compounds. III: Phenolic constituents of Caesalpinia japonica Sieb. et Zucc. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.H.; Zhang, L.; Du, G.H.; Qin, H.L. Study on the chemical constituents of Caesalpinia sappan. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2007, 19, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.A.; Yang, R.Z. A new hydroquinone diglucoside from Lysimachia fordiana. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2004, 40, 457–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.; Yamauchi, T. Lignans from Trachelospermum asiaticum (Tracheolospermum. II). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 4340–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, H.; Takeda, Y.; Zhang, R.S.; Tanitame, A.; Tsai, Y.L.; Kitagawa, I. Indonesian medicinal plants. IV. On the constituents of the bark of Fagara rhetza (Rutaceae). (2). Lignan glycosides and two apioglucosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Guo, D.A.; Li, C.L.; Zheng, J.H.; Kazuo, K.; Jia, Z.H.; Tamotsu, N. Studies on the lignan glycosides from Gaultheria Yunnanensis. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1999, 34, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.L.; Mu, Q.; Hu, C.Q. Studies on the phenylpropanoids from Caragana rosea. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2003, 15, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2008 by the authors. Licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, L.-c.; Huang, X.-a.; Lai, Z.-y.; Hu, Y.-j.; Liu, H.-j.; Cai, X.-l. A New 3-Benzylchroman Derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan). Molecules 2008, 13, 1923-1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081923
Fu L-c, Huang X-a, Lai Z-y, Hu Y-j, Liu H-j, Cai X-l. A New 3-Benzylchroman Derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan). Molecules. 2008; 13(8):1923-1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081923
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Lin-chun, Xin-an Huang, Zhen-yuan Lai, Ying-jie Hu, Hong-jiao Liu, and Xiao-ling Cai. 2008. "A New 3-Benzylchroman Derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan)" Molecules 13, no. 8: 1923-1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081923
APA StyleFu, L.-c., Huang, X.-a., Lai, Z.-y., Hu, Y.-j., Liu, H.-j., & Cai, X.-l. (2008). A New 3-Benzylchroman Derivative from Sappan Lignum (Caesalpinia sappan). Molecules, 13(8), 1923-1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081923




