Biotransformations of Imbricatolic Acid by Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus nigricans Cultures
Abstract
:Introduction
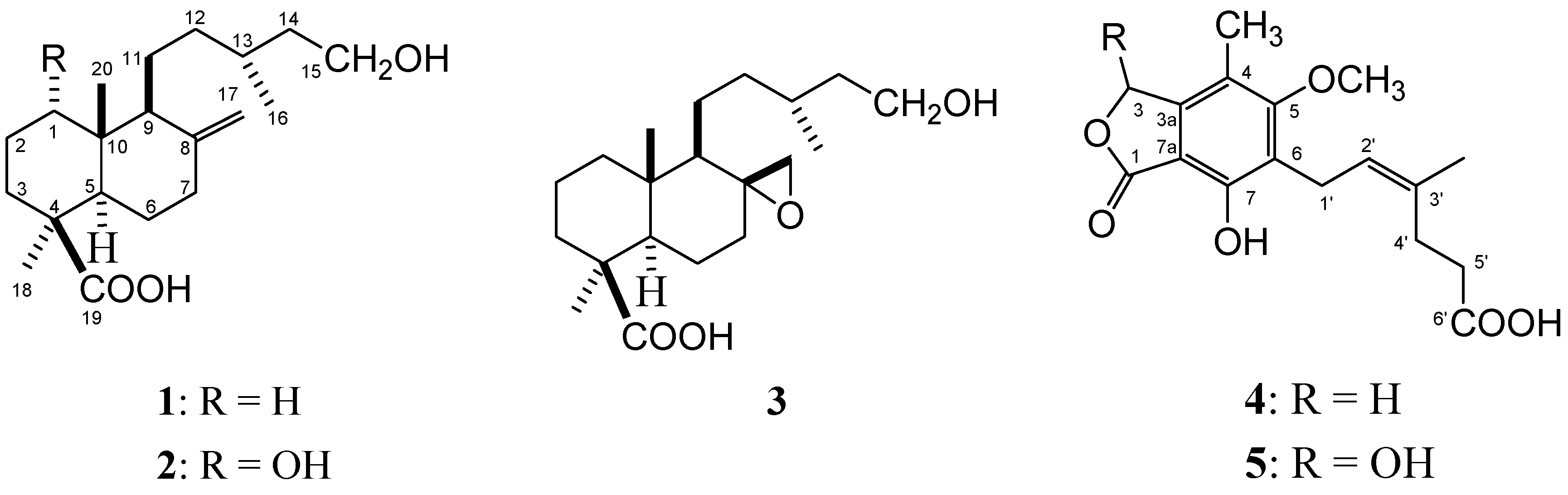
Results and Discussion
| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δC, mult. |
|---|---|---|
| H | C | |
| 1 | 3.85, br s | 71.20, CH |
| 2 | 1.60, 2.21, m | 27.50, CH2 |
| 3 | 1.94, 1.56, m | 30.70, CH2 |
| 4 | - | 44.00, qC |
| 5 | 1.82, m | 48.55, CH |
| 6 | 1.87-2.00, m | 25.81, CH2 |
| 7 | 1.89, 2.36, m | 38.39, CH2 |
| 8 | - | 148.62, qC |
| 9 | 2.21, m | 48.34, CH |
| 10 | - | 44.00, qC |
| 11 | 1.50, 1.31, m | 19.58, CH2 |
| 12 | 1.15, 1.37, m | 35.18, CH2 |
| 13 | 1.62, m | 29.14, CH |
| 14 | 1.70, 1.29, m | 38.81, CH2 |
| 15 | 3.66, 3.72, m | 61.13, CH2 |
| 16 | 0.88, d (6.6) | 20.55, CH3 |
| 17 | 4.53 s, 4.86 s | 106.96, CH2 |
| 18 | 1.25, s | 28.71, CH3 |
| 19 | - | 183.41, qC |
| 20 | 0.59, s | 13.24, CH3 |
Experimental
General
Microorganisms
Screening scale experiments
Preparative scale experiments and product isolation
Aspergillus niger ATCC 16404 culture.
Cunninghamella echinulata ATCC 8688a culture.
Rhizopus nigricans UBA6 culture.
MRC-5 cell culture
AGS cell culture
Cytotoxicity assay
Acknowledgements
References
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Astudillo, L.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Theoduloz, C.; Yáñez, T. Gastro-protective effect of the Mapuche crude drug Araucaria araucana resin and its main constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 101, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Astudillo, L.; Sepúlveda, B.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Theoduloz, C.; Yáñez, T.; Palenzuela, J.A. Gastroprotective effect and cytotoxicity of natural and semisynthetic labdane diterpenes from Araucaria araucana. Z. Naturforsch. C 2005, 60, 511–522. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.D.; Reynolds, W.F.; Reese, P.B. Stemodane skeletal rearrangement: chemistry and microbial transformation. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akihisa, T.; Hamasaki, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Ukiya, M.; Kimura, Y.; Nishino, H. Microbial transformation of isosteviol and inhibitory effects on Epstein-Barr virus activation of the transformation products. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.C.; Lo, K.L.; Lin, C.L.; Chakraborty, R. Microbial transformation of baccatin VI and 1beta-hydroxy baccatin I by Aspergillus niger. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 4493–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, B.M.; González, P.; Hernández, M.G.; Chamy, M.C.; Garbarino, J.A. Microbial transformation of 18-hydroxy-9,13-epi-ent-pimara-7,15-diene by Gibberella fujikuroi. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, B.M.; Hernández, M.G.; Artega, J.M.; Suárez, S. The microbiological transformation of the diterpenes dehydroabietanol and teideadiol by Mucor plumbeus. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.R.M.; Reese, P.B. Biotransformation of terpenes from Stemodia maritima by Aspergillus niger ATCC 9142. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.R.M.; Ruddock, P.L.D.; Lamm, A.S.; Reynolds, W.F.; Reese, P.B. Stemodane and stemarane diterpenoid hydroxylation by Mucor plumbeus and Whetzelinia sclerotiorum. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1898–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouiric, S.C.; Feresin, G.E.; Tapia, A.A.; Rossomando, P.C.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Bustos, D.A. 1β,7β-Dihydroxydehydroabietic acid, a new biotransformation product of dehydroabietic acid by Aspergillus niger. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 20, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Astudillo, L.; Palenzuela, J.A. Biotransformation of solidagenone by Alternaria alternata, Aspergillus niger and Curvularia lunata cultures. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 20, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Orden, A.A.; Cifuente, D.A.; Borkowski, E.J.; Tonn, C.E.; Kurina, M. Stereo- and regioselective hydroxylation of grindelic acid derivatives by Aspergillus niger. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, B.H.; dos Santos, M.C.; Leal, P.C. Biotransformation of the diperpenoid, isosteviol, by Aspergillus niger, Penicillium chrysogenum and Rhizopus arrhizus. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 737–741. [Google Scholar]
- San Feliciano, A.; Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Lopez, J.L.; de Pascual-Teresa, B. Labdane acids from polar extracts of Juniperus thurifera. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar]
- San Feliciano, A.; Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Lopez, J.L.; de Pascual-Teresa, B. Further diterpene acids from Juniperus thurifera. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Iwagawa, T.; Yaguchi, S.; Hase, T.; Okubo, T.; Kim, M. Diterpene glucosides from Viburnum suspensum. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdero, C.; Bohlmann, F.; Niemeyer, H. Friedolabdanes and other constituents from Chilean Haplopappus species. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakupovic, J.; Schuster, A.; Wasshausen, D.C. Acetylenes and labdanes from Baccharis pedunculata. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 2785–2787. [Google Scholar]
- González, G.A.; Bermejo, B.J.; Diaz, J.G.; Rodríguez Perez, E.M.; Yanes, A.C.; Rauter, P.; Pozo, J. Diterpenes and other constituents of Eupatorium salvia. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 321–323. [Google Scholar]
- Faini, F.; Labbe, F.; Torres, R.; Delle Monache, F.; Delle Monache, G. Diterpenes from Haplopappus chrysanthemifolius. Phytochemistry 1999, 52, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, G.O.; Reese, P.B. Biotransformation of diterpenes and diterpene derivatives by Beauveria bassiana ATCC 7159. Phytochemistry 2001, 56, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, A.S.; Reynolds, W.F.; Reese, P.B. Bioconversion of Stemodia maritima diterpenes and derivatives by Cunninghamella echinulata var. elegans and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.H.; Eugui, E.; Wang, C.C.; Allison, A.C. Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of some side-chain variants of mycophenolic acid. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Canton, A.; Amore, A.; Barbano, G.; Coppo, R.; Emma, F.; Grandaliano, G.; Klersy, C.; Perfumo, F.; Rizzoni, G.; Schena, F.P.; Sepe, V. One-year angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition plus mycophenolate mofetil immunosuppression in the course of early IgA nephropathy: a multicenter, randomised, controlled study. J. Nephrol. 2005, 18, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Casadio, F.; Croci, S.; D’Errico Grigioni, A.; Corti, B.; Grigioni, W.F.; Landuzzi, L.; Lollini, P.L. Renal transplantation toward the definition of immunosuppressive regimens with antitumor activity. Transplant. P. 2005, 37, 2144–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias-Zúñiga, A.; González-Lucas, A.; Domínguez, M.M. Total synthesis of mycophenolic acid. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Puel, O.; Tadrist, S.; Galtier, P.; Oswald, I.P.; Delaforge, M. Byssochlamys nivea as a source of mycophenolic acid. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 550–553. [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler, D.L.; Bartman, C.D.; Campbell, I.M. Mycophenolic acid production by Penicillium brevicompactum in two media. Can. J. Microbiol. 1979, 25, 940–943. [Google Scholar]
- Schneweis, I.; Meyer, K.; Hormansdorfer, S.; Bauer, J. Mycophenolic acid in silage. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3639–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, M.; Skouboe, P.; Frisvad, J.; Rossen, L. Reclassification of the Penicillium roqueforti group into three species on the basis of molecular genetic and biochemical profiles. Microbiology 1996, 142, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Smedsgaard, J.; Larsen, T.O.; Samson, R.A. Mycotoxins, drugs and other extrolites produced by species in Penicillium subgenus Penicillium. Stud. Mycol. 2004, 49, 201–241. [Google Scholar]
- Dictionary of Natural Products on CD-ROM. Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006.
- Jekkel, A.; Barta, I.; Kónya, A.; Süt, J.; Boros, S.; Horváth, G.; Ambrus, G. Microbiological transformation of mycophenolic acid. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2001, 11, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Jekkel, A.; Barta, I.; Boros, S.; Süt, J.; Horváth, G.; Szabó, Z.; Ambrus, G. Microbial transformation of mycophenolic acid Part II. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2002, 19–20, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Haun, M. Cytotoxicity of trans-dehydrocrotonin from Croton cajucara (Euphorbiaceae) on V79 cells and rat hepatocytes. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 1 and 3 are available from the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Aranda, C.; Kurina, M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Theoduloz, C. Biotransformations of Imbricatolic Acid by Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus nigricans Cultures. Molecules 2007, 12, 1092-1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051092
Schmeda-Hirschmann G, Aranda C, Kurina M, Rodríguez JA, Theoduloz C. Biotransformations of Imbricatolic Acid by Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus nigricans Cultures. Molecules. 2007; 12(5):1092-1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051092
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmeda-Hirschmann, Guillermo, Carlos Aranda, Marcela Kurina, Jaime A Rodríguez, and Cristina Theoduloz. 2007. "Biotransformations of Imbricatolic Acid by Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus nigricans Cultures" Molecules 12, no. 5: 1092-1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051092
APA StyleSchmeda-Hirschmann, G., Aranda, C., Kurina, M., Rodríguez, J. A., & Theoduloz, C. (2007). Biotransformations of Imbricatolic Acid by Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus nigricans Cultures. Molecules, 12(5), 1092-1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/12051092





