Bioreversible Derivatives of Phenol. 1. The Role of Human Serum Albumin as Related to the Stability and Binding Properties of Carbonate Esters with Fatty Acid-like Structures in Aqueous Solution and Biological Media
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion
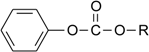
| Compound | R | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -C2H5 | Ethyl phenyl carbonate |
| 2 | -C(CH3)3 | t-Butyl phenyl carbonate |
| 3 | -C6H5 | Diphenyl carbonate |
| 4 | -CH2COOH | 2-(Phenoxycarbonyloxy)-acetic acid |
| 5 | -(CH2)5COOH | 6-(Phenoxycarbonyloxy)-hexanoic acid |
| 6 | -(CH2)7COOH | 8-(Phenoxycarbonyloxy)-octanoic acid |
| 7 | -(CH2)11COOH | 12-(Phenoxycarbonyloxy)-dodecanoic acid |
| 8 | -(CH2)15COOH | 16-(Phenoxycarbonyloxy)-hexadecanoic acid |
| 9 | - | Phenyl acetate |
Hydrolysis in biological media
| Compound | Half-life ± SD (min) | log P d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer, pH 7.40 | 4.3% HSA | 4.3% HSAc) | 80% Human plasma | 20% rat liver homogenate | ||
| 1 | 7.9 (± 1.0) × 103 | 77 ± 3.2 | 82 ± 2.5 | 1.13 ± 0.10 | b) | 2.17 |
| 2 | 31 ± 0.6 | 268 ± 14 | 248 ± 24 | 82 ± 7.4 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 3.02 |
| 3 | 4.6 (± 0.03) × 102 | 14 ± 2.3 | 16.9 ± 1.3 | 0.18 ± 0.002 | b) | 3.21 |
| 4 | 31 ± 0.2 | 148 ± 1.3 | 147 ± 5.0 | 74 ± 1.0 | 0.90 ± 0.16f) | 1.72 |
| 5 | 1.7 (± 0.02) × 104 | 421 ± 20 | 422 ± 4.7 | 38 ± 2.8 | b) | 2.56 |
| 6 | 1.7 (± 0.15) × 104 | 72 ± 1.6 | 70 ± 1.3 | 7.5 ± 1.1 | b) | 3.39 |
| 7 | 1.4 (± 0.07) × 104 | 1.0 (± 0.2) × 104 | 7.0 (± 2.2) × 103 | 661 ± 86 | b) | 4.26 |
| 8 | n.d.g) | 142 ± 3.9 | 146 ± 2.2 | 40 ± 2.0 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 4.67 |
| 9 | 3.0 (± 0.36) × 103 | 11.9 ± 0.3 | 12.6 ± 0.3 | b) | b) | 1.49e) |
- a)
- Experiments performed in triplicate.
- b)
- Degraded within 15 s.
- c)
- 1 × 10-4 M physostigmine added to HSA solution.
- d)
- Logarithm to the octanol-water partition coefficient (log P) taken from [45].
- e)
- From [51].
- f)
- Mixed kinetics observed. Half-life calculated from t½ = ln2/(Vmax/Km). Vmax and Km obtained by nonlinear regression analysis using an integrated form of the Michaelis-Menten equation [52].
- g)
- n.d., not determined due to solubility limitations.
Hydrolysis in HSA solution
Hydrolysis in rat liver homogenate
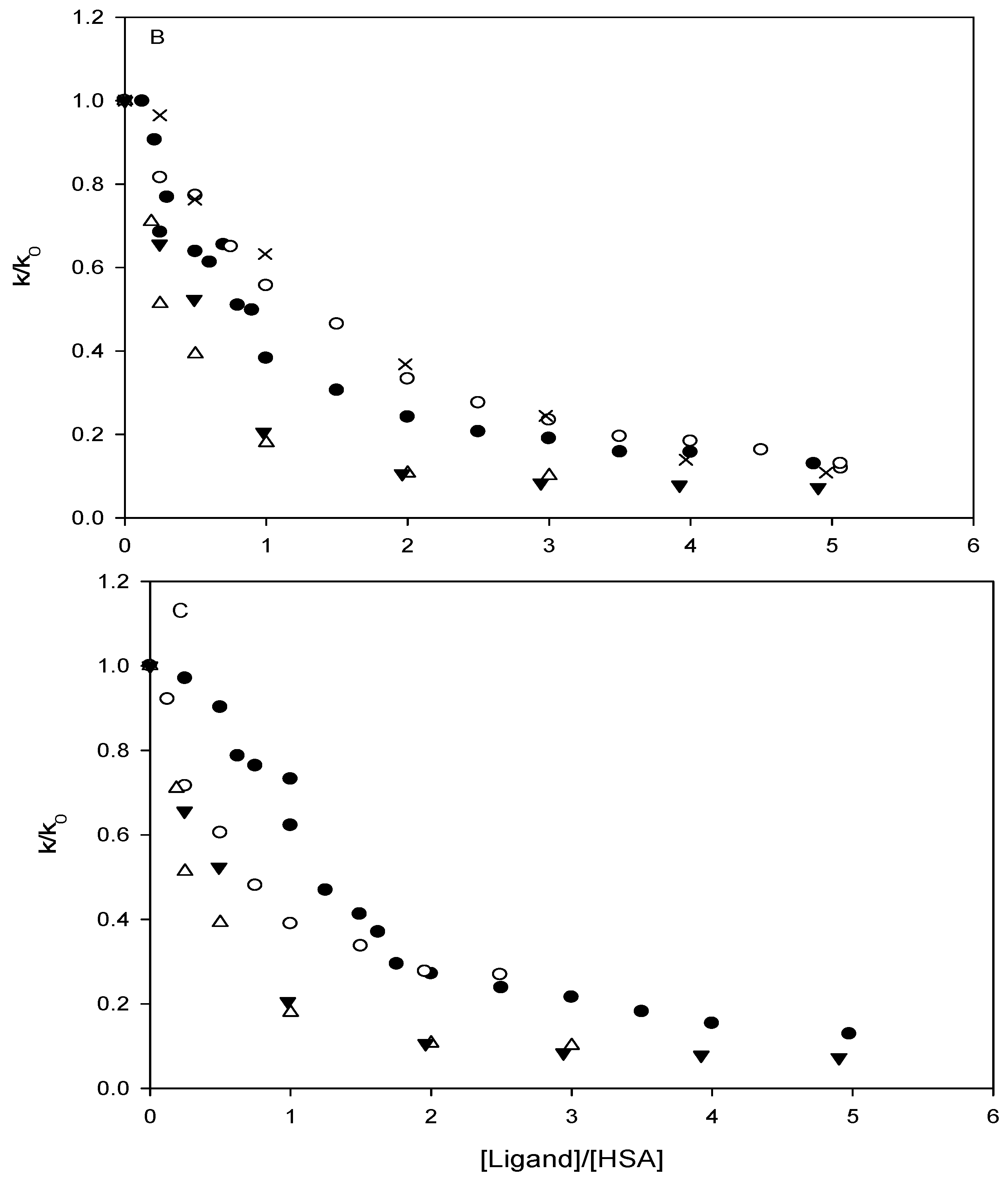
Affinity of carbonate esters for human serum albumin as studied by a spectrophotometric assay
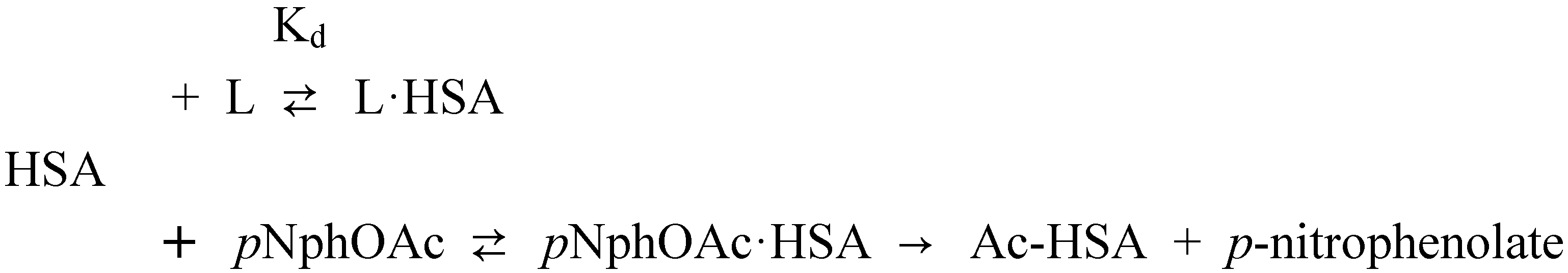
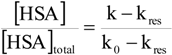
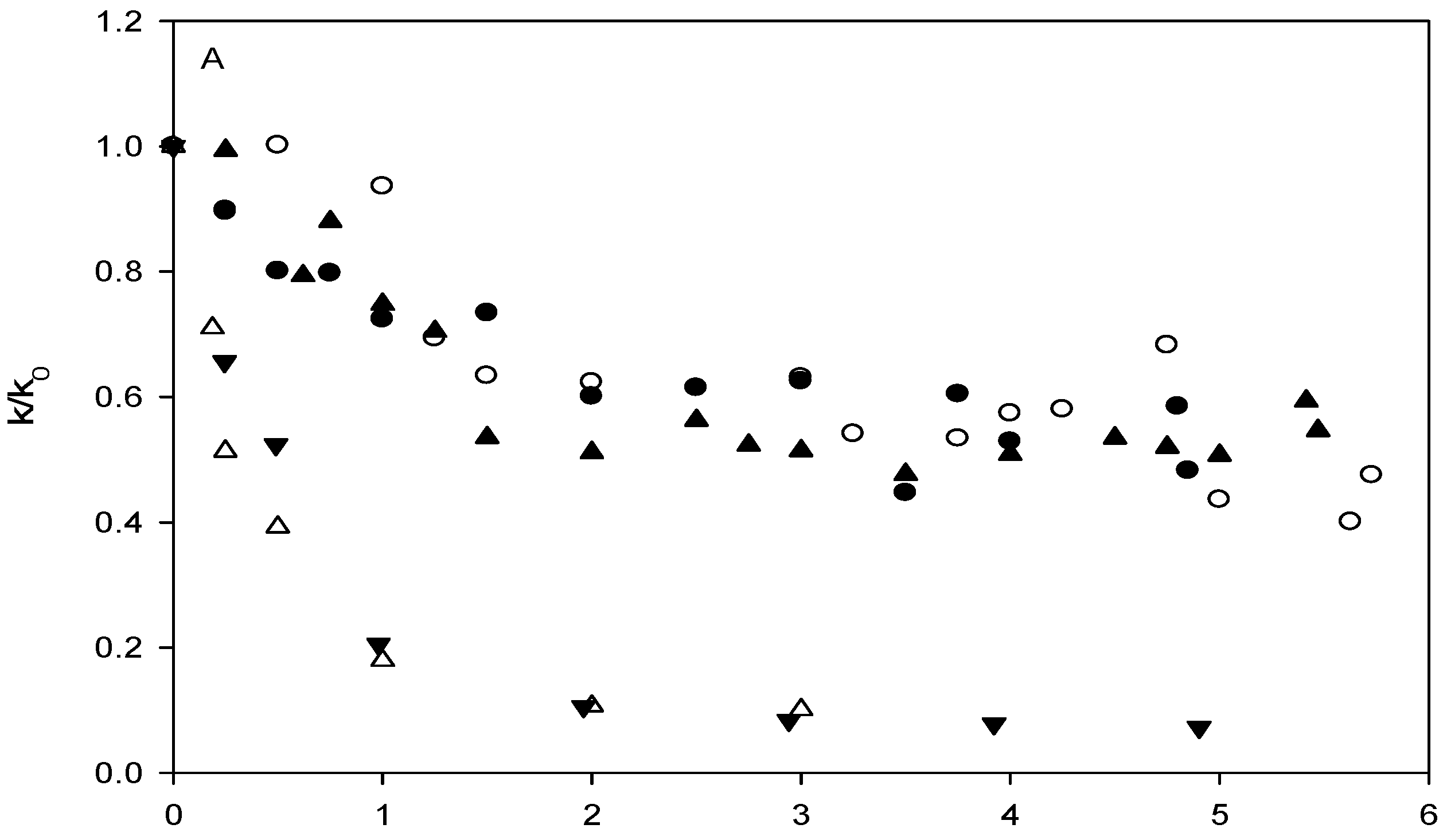
Conclusions
Experimental
Chemicals
Apparatus
Kinetic measurements
p-Nitrophenyl acetate – human serum albumin affinity assay
References
- Lipinski, C. A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B. W.; Feeney, P. J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeef, A. Physicochemical profiling (Solubility, permeability and charge state). Curr. Topics Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 277–351. [Google Scholar]
- Muegge, I. Selection criteria for drug-like compounds. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Waterbeemd, H.; Smith, D. A.; Beumont, K.; Walker, D. K. Property-based design: optimization of drug absorption and pharmacokinetics. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1313–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W. P.; Murcko, A.; Murcko, M. A. Recognizing molecules with drug-like properties. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundgaard, H. Design of prodrugs: Bioreversible derivatives for various functional groups and chemical entities. In Design of prodrugs; Bundgaard, H., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 1985; pp. 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, C. S.; Østergaard, J. Design and application of prodrugs. In Textbook of drug design and discovery, 3 ed.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P., Liljefors, T., Madsen, U., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, 2002; pp. 410–458. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, B.; Mayer, J. M. Concepts in prodrug design to overcome pharmacokinetic problems. In Pharmacokinetic optimization in drug research; Testa, B., van de Waterbeemd, H., Folkers, G., Guy, R., Eds.; Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta/Wiley-VCH: Zürich, 2001; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, B.; Mayer, J. M. Hydrolysis in drug and prodrug metabolism. Chemistry, biochemistry, and enzymology; Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta: Zürich, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Prodrugs: challenges and rewards. Part 1; Stella, V. J.; Borchardt, R. T.; Hageman, M. J.; Oliyai, R.; Maag, H.; Tilley, J. W. (Eds.) Springer-AAPS Press: New York, 2007.
- Jusko, W. J.; Gretch, M. Plasma and tissue protein binding of drugs in pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab. Rev. 1976, 5, 43–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, T. C. Free drug measurements: methodology and clinical significance. Clin. Chim. Acta 1985, 151, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallner, J. J. Binding of drugs by albumin and plasma protein. J. Pharm. Sci. 1977, 66, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. C.; Guttmann, D. E. The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 1968, 57, 895–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T., Jr. All about albumin. Biochemistry, genetics, and medical applications; Academic Press: San Diego, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen, U.; Chuang, V. T. G.; Otagiri, M. Practical aspects of the ligand-binding and enzymatic properties of human serum albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzhals, P.; Havelund, S.; Jonassen, I.; Kiehr, B.; Larsen, U. D.; Ribel, U.; Markussen, J. Albumin binding of insulins acylated with fatty acids: characterization of the ligand-protein interaction and correlation between binding affinity and timing of the insulin effect in vivo. Biochem. J. 1995, 312, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzhals, P.; Havelund, S.; Jonassen, I.; Markussen, J. Effect of fatty acids and selected drugs on the albumin binding of a long-acting, acylated insulin analogue. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markussen, J.; Havelund, S.; Kurtzhals, P.; Andersen, A. S.; Halstrøm, J.; Hasselager, E.; Larsen, U. D.; Ribel, U.; Schäffer, L.; Vad, K.; Jonassen, I. Soluble, fatty acid acylated insulins bind to albumin and show protracted action in pigs. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L. B.; Nielsen, P. F.; Huusfeldt, P. O.; Johansen, N. L.; Madsen, K.; Pedersen, F. Z.; Thøgersen, H.; Wilken, M.; Agersø, H. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, N.; Yamashita, S.; Sakuragi, n.; Doi, K.; Okada, S.; Shimidzu, K.; Sumi, M.; Nadai, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Suda, Y. Therapeutic efficacy of 5-fluorouracil prodrugs using endogenous serum proteins as drug carriers: A new strategy in drug delivery system. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Suda, Y.; Shimidzu, K.; Sumi, M.; Oku, N.; Kusumoto, S.; Nadai, T.; Yamashita, S. The synthesis and in vitro and in vivo stability of 5-fluorouracil prodrugs which possess serum albumin binding potency. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 16, 876–878. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, S.; Suda, Y.; Masada, M.; Nadai, T.; Sumi, M. 5-Fluorouracil derivatives with serum protein binding potencies. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2861–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tove, S. B. The esterolytic activity of serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1962, 57, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. P. Enzyme-like activities associated with albumin. In Albumin structure, function and uses, 1 ed.; Rosenoer, V. M., Oratz, M., Rotschild, M. A., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1977; pp. 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Means, G. E.; Bender, M. L. Acetylation of human serum albumin by p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 4989–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S. M.; Tozer, T. N. First-pass elimination. Basic concepts and clinical consequenses. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1984, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, J.; Larsen, C. Bioreversible derivatives of phenol. II. Reactivity of carbonate esters with fatty-acid like structure towards hydrolysis in aqueous solutions. Molecules 2007, 12, 2396–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballinger, L. N.; Cross, S. E.; Roberts, M. S. Availability and mean transit times of phenol and its metabolites in the isolated perfused rat liver: Normal and retrograde studies using tracer concentrations of phenol. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. O.; Lunte, C. E. In vivo microdialysis sampling in the bile, blood, and liver of rats to study the disposition of phenol. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M. K.; Houston, J. B. In vivo assessment of extrahepatic conjugative metabolism in first pass effects using the model compound phenol. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1980, 32, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M. K.; Houston, J. B. In vivo capacity of hepatic and extrahepatic enzymes to conjugate phenol. Drug Metab. Disp. 1984, 12, 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- stergaard, J.; Schou, C.; Larsen, C.; Heegaard, N. H. H. Evaluation of capillary electrophoresis frontal analysis for the study of low molecular weight drug-human serum albumin interactions. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 2842–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judis, J. Binding of selected phenol derivatives to human serum proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Shibata, T. Binding of alkyl- and alkoxy-substituted simple phenolic compounds to human serum proteins. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2000, 107, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Mørk, N.; Bundgaard, H. Phenyl carbamates of amino acids as prodrug forms for protecting phenols against first-pass metabolism. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 81, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholt, K.; Mørk, N.; Begtrup, M. Hemiesters of aliphatic dicarboxylic acids as cyclization-activated prodrug forms for protecting phenols against first-pass metabolism. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 123, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, K. F.; Bundgaard, H. Cyclization-activated phenyl carbamate prodrug forms for protecting phenols against first-pass metabolism. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 91, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, K. F.; Strøm, F.; Sforzini, B. V.; Begtrup, M.; Mørk, N. Evaluation of phenyl carbamates of ethyl diamines as cyclization-activated prodrug forms for protecting phenols against first-pass metabolism. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 112, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard, H.; Buur, A.; Chang, S.-C.; Lee, V. H. L. Timolol prodrugs: synthesis, stability and lipophilicity of various alkyl, cycloalkyl and aromatic esters of timolol. Int. J. Pharm. 1988, 46, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard, H.; Buur, A.; Chang, S.-C.; Lee, V. H. L. Prodrugs of timolol for improved ocular delivery: synthesis, hydrolysis kinetics and lipophilicity of various timolol esters. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 33, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner-Guenat, M.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Lisa, G.; Testa, B.; Rose, S.; Thomas, K.; Jenner, P.; Ventura, P. Esters of L-dopa: Structure-hydrolysis relationships and ability to induce circling behaviour in an experimental model of hemiparkinsonism. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, W. S.; Schwering, J. E.; Lyle, P. A.; Smith, S. J.; Engelhardt, E. L. Cyclization-activated prodrugs. Basic carbamates of 4-hydroxyanisole. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, K.; Miyazaki, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Oh-E, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Enzymatic hydrolysis of haloperidol decanoate and its inhibition by proteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar]
- stergaard, J.; Hansen, S. H.; Larsen, C.; Schou, C.; Heegaard, N. H. H. Determination of octanol-water partition coefficients for carbonate esters and other small organic molecules by microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Krisch, K. Carboxylic ester hydrolases. In The enzymes, 3 ed.; Boyer, P. D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, 1971; pp. 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B. D.; Conradi, R. A.; Spilman, C. H.; Forbes, A. D. Strategies in the design of solution-stable, water-soluble prodrugs III: Influence of the pro-moiety on the bioconversion of 21-esters of corticosteroids. J. Pharm. Sci. 1985, 74, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, N. M.; Bundgaard, H. Prodrug as drug delivery systems. 68. Chemical and plasma-catalyzed hydrolysis of various esters of benzoic acid: a reference system for designing prodrug esters of carboxylic acid agents. Int. J. Pharm. 1987, 39, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, C.; Kurtzhals, P.; Johansen, M. Kinetics of regeneration of metronidazole from hemiesters of maleic acid, succinic acid and glutaric acid in aqueous buffer, human plasma and pig liver homogenate. Int. J. Pharm. 1988, 41, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, M.; Larsen, C. Stability and kinetics of hydrolysis of metronidazole monosuccinate in aqueous solution and in plasma. Int. J. Pharm. 1984, 21, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Hoekman, D. Exploring QSAR. Hydrophobic, electronic, and steric constants, 1 ed.; ACS: Washington, 1995; Vol. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, N. M.; Bundgaard, H. Glycolamide esters as biolabile prodrugs of carboxylic acid agents: Synthesis, stability, bioconversion, and physicochemical properties. J. Pharm. Sci. 1988, 77, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, D. C.; Ho, J. X. Structure of serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 153–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Molecular aspects of ligand binding to serum albumin. Pharmacol. Rev. 1981, 33, 17–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Structure and ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. Dan. Med. Bull. 1990, 37, 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Vorum, H. Reversible ligand binding to human serum albumin. Theoretical and clinical aspects. Dan. Med. Bull. 1999, 46, 379–399. [Google Scholar]
- Charbon, V.; Latour, I.; Lambert, D. M.; Buc-Calderon, P.; Neuvens, L.; De Keyser, J.-L.; Gallez, B. Targeting of drug to the hepatocytes by fatty Acids. Influence of the carrier (albumin or galactosylated albumin) on the fate of the fatty acids and their analogs. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gallez, B.; Debuyst, R.; Demeure, R.; Dejehet, F.; Grandin, C.; Van Beers, B.; Taper, H.; Pringot, J.; Dumont, P. Evaluation of a Nitroxyl Fatty Acid as Liver Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993, 30, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D. M. Rationale and applications of lipids as prodrug carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11 (Suppl. 2), S15–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, D. Y.; Mellick, G. D.; Prankerd, R. J.; Roberts, M. S. Synthesis, identification, characterization, stability, solubility, and protein binding of ester derivatives of salicylic acid and diflunisal. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 153, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Aarons, L.; Clifton, P.; Fleming, G.; Rowland, M. Aspirin binding and the effect of albumin on spontaneous and enzyme-catalysed hydrolysis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1980, 32, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfbeis, O. S.; Gürakar, A. The effect of fatty acid chain length on the rate of arylester hydrolysis by various albumins. Clin. Chim. Acta 1987, 164, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.-W. M.; Means, G. E. Characterization of a small apolar anion binding site of human Serum albumin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1979, 192, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Ma, S.-F.; Watanabe, H.; Yamaotsu, N.; Hirono, S.; Kurono, Y.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Esterase-like activity of serum albumin: characterization of its structural chemistry using p-nitrophenyl esters as substrates. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, A.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Mayer, J. M.; Testa, B. Esterase-like activity of human serum albumin toward prodrug esters of nicotinic acid. Drug Metabol. Dispos. 1997, 25, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, A.; Mayer, J. M.; Testa, B. Nicotinate esters: Their binding to and hydrolysis by human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1992, 44, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelpton, R.; Hurst, P. R. The binding of physostigmine to human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 804–805. [Google Scholar]
- Chapuis, N.; Brühlmann, C.; Reist, M.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Mayer, J. M.; Testa, B. The esterase-like activity of serum albumin may be due to cholinesterase contamination. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, V. J.; Charman, W. N.; Naringrekar, V. H. Prodrugs. Do they have advantages in clinical practice? Drugs 1985, 29, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D. J.; Wade, D. N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D. J.; Wade, D. N. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1976, 12, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Fehske, K. J.; Müller, W. E.; Wollert, U. The location of drug binding sites in human serum albmin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Evidence for a large and flexible region of human serum albumin possessing high affinity binding sites for salicylate, warfarin, and other ligands. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 160–171. [Google Scholar]
- Wanwimolruk, S.; Birkett, D. J.; Brooks, P. M. Structural requirements for drug binding to site II on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1983, 24, 458–463. [Google Scholar]
- Irikura, M.; Takadate, A.; Goya, S.; Otagiri, M. 7-Alkylaminocoumarin-4-acetic acids as fluorescent probe for studies of drug-binding sites on human serum albumin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollenne, N. P.; Means, G. E. Characterization of a specific drug binding site of human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1979, 15, 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Kurono, Y.; Ohta, N.; Yotsuynagi, T.; Ikeda, K. Effect of drug binding on the esterase-like activity of human serum albumin. III. Evaluation of reactivities of the two active sites by using clofibric acid as an inhibitor. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Tanase, S.; Nakajou, K.; Maruyama, T.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Role of Arg-410 and Tyr-411 in human serum albumin for ligand binding and esterase-like activity. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 813–819. [Google Scholar]
- Kurono, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Yamada, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Ikeda, K. Effects of drug binding on the esterase-like activity of human serum albumin. VII. Subdivision of R-type drugs inhibiting the activity towards p-nitrophenyl acetate. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, Y.; Kurono, Y.; Yotsuynagi, T.; Ikeda, K. Effects of drug binding on the esterase activity of human serum albumin: Inhibition modes and binding sites of anionic drugs. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurono, Y.; Ikeda, K. Effect of drug binding on the esterase-like activity of human serum albumin. IV. Application of an analog computer to determination of the multiple dissociation constants. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisiger, R. A. Dissociation from albumin: A potentially rate-limiting step in the clearance of substances by the liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K. A. Chemical kinetics. The study of reaction rates in solution; VCH Publishers: New York, 1990. [Google Scholar]
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Ostergaard, J.; Larsen, C. Bioreversible Derivatives of Phenol. 1. The Role of Human Serum Albumin as Related to the Stability and Binding Properties of Carbonate Esters with Fatty Acid-like Structures in Aqueous Solution and Biological Media. Molecules 2007, 12, 2380-2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102380
Ostergaard J, Larsen C. Bioreversible Derivatives of Phenol. 1. The Role of Human Serum Albumin as Related to the Stability and Binding Properties of Carbonate Esters with Fatty Acid-like Structures in Aqueous Solution and Biological Media. Molecules. 2007; 12(10):2380-2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102380
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstergaard, Jesper, and Claus Larsen. 2007. "Bioreversible Derivatives of Phenol. 1. The Role of Human Serum Albumin as Related to the Stability and Binding Properties of Carbonate Esters with Fatty Acid-like Structures in Aqueous Solution and Biological Media" Molecules 12, no. 10: 2380-2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102380
APA StyleOstergaard, J., & Larsen, C. (2007). Bioreversible Derivatives of Phenol. 1. The Role of Human Serum Albumin as Related to the Stability and Binding Properties of Carbonate Esters with Fatty Acid-like Structures in Aqueous Solution and Biological Media. Molecules, 12(10), 2380-2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102380




