Electrochemical Behavior and Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Natural Phenolics
Abstract
:Introduction
Results and Discussion
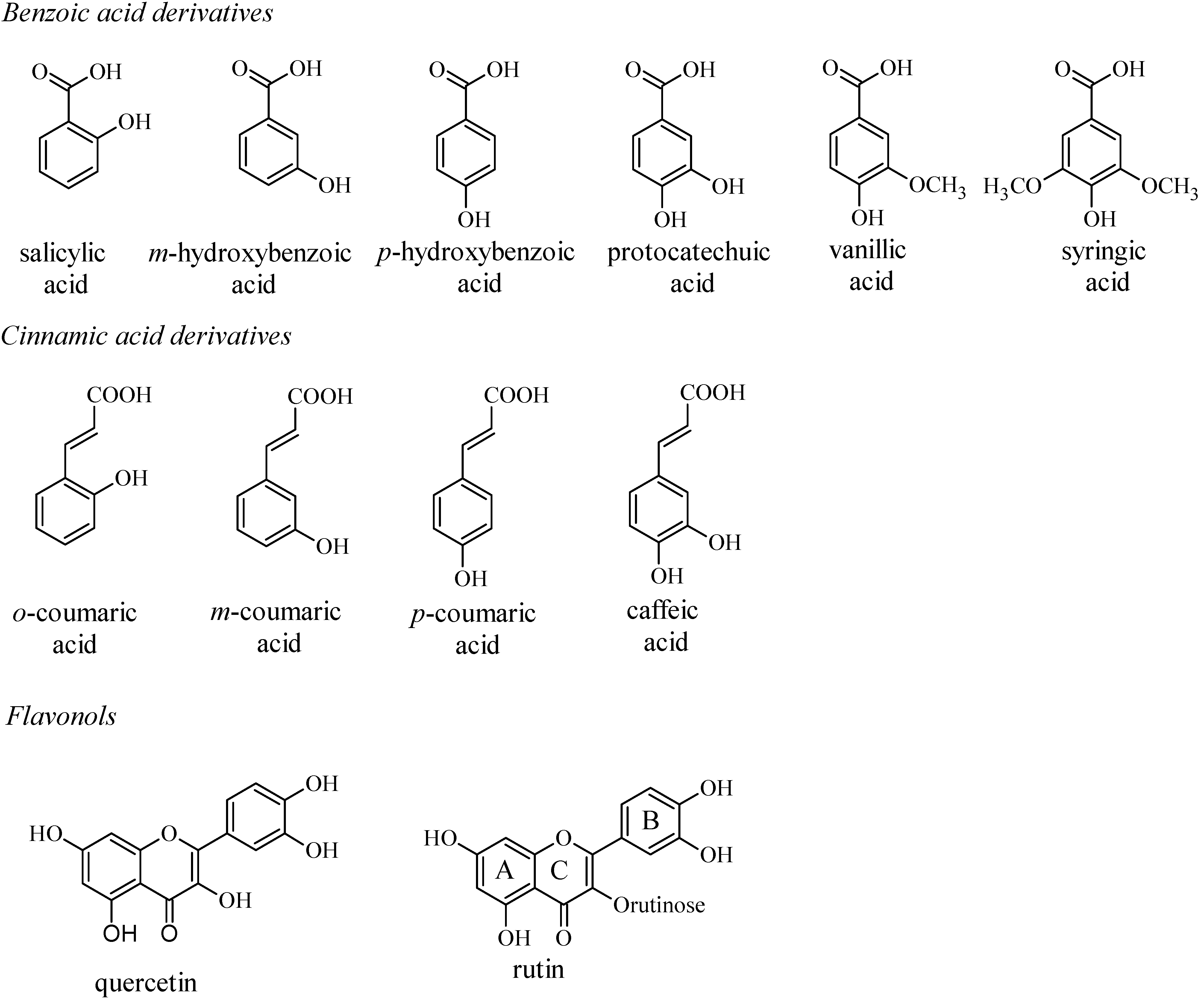
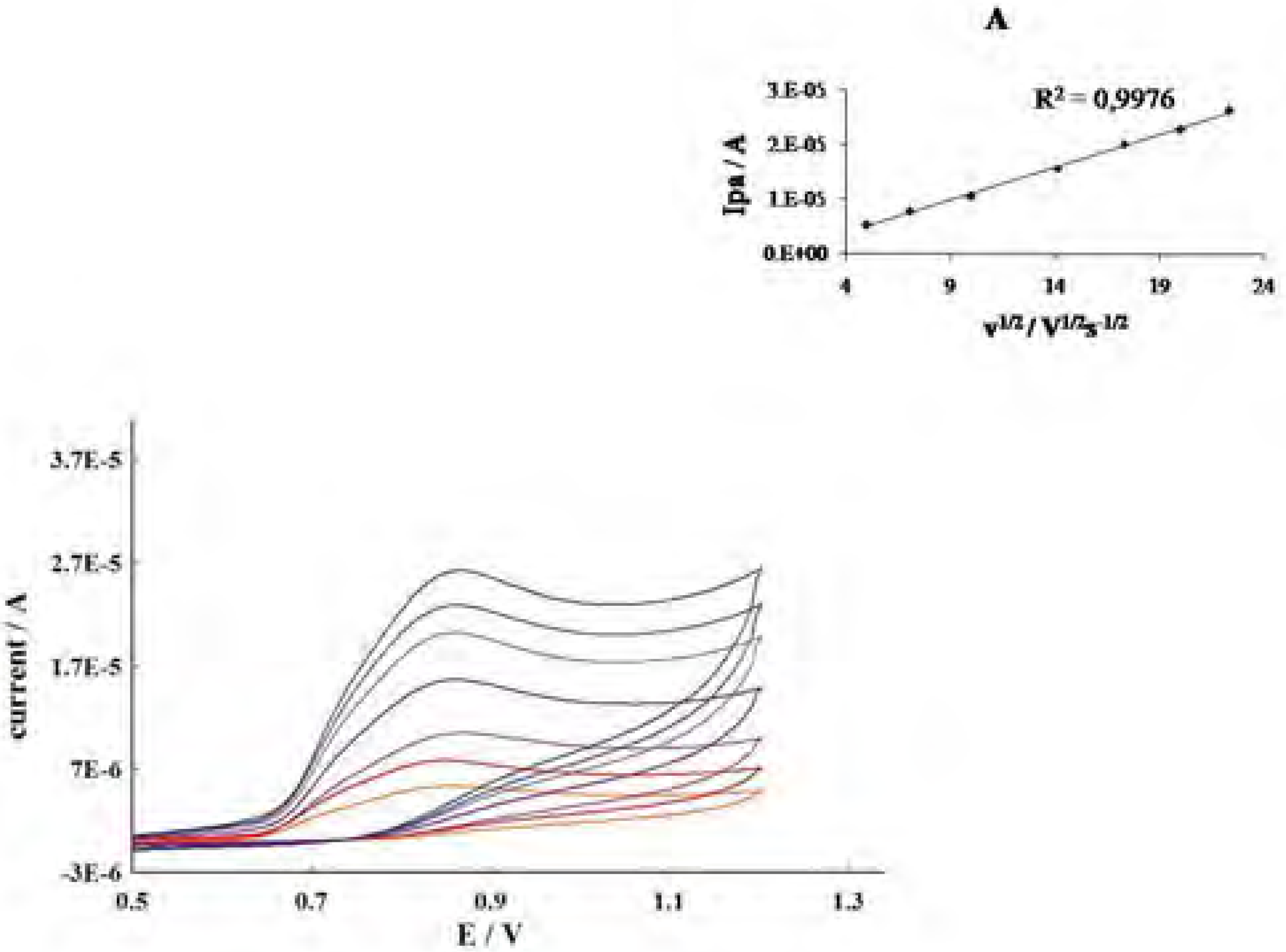
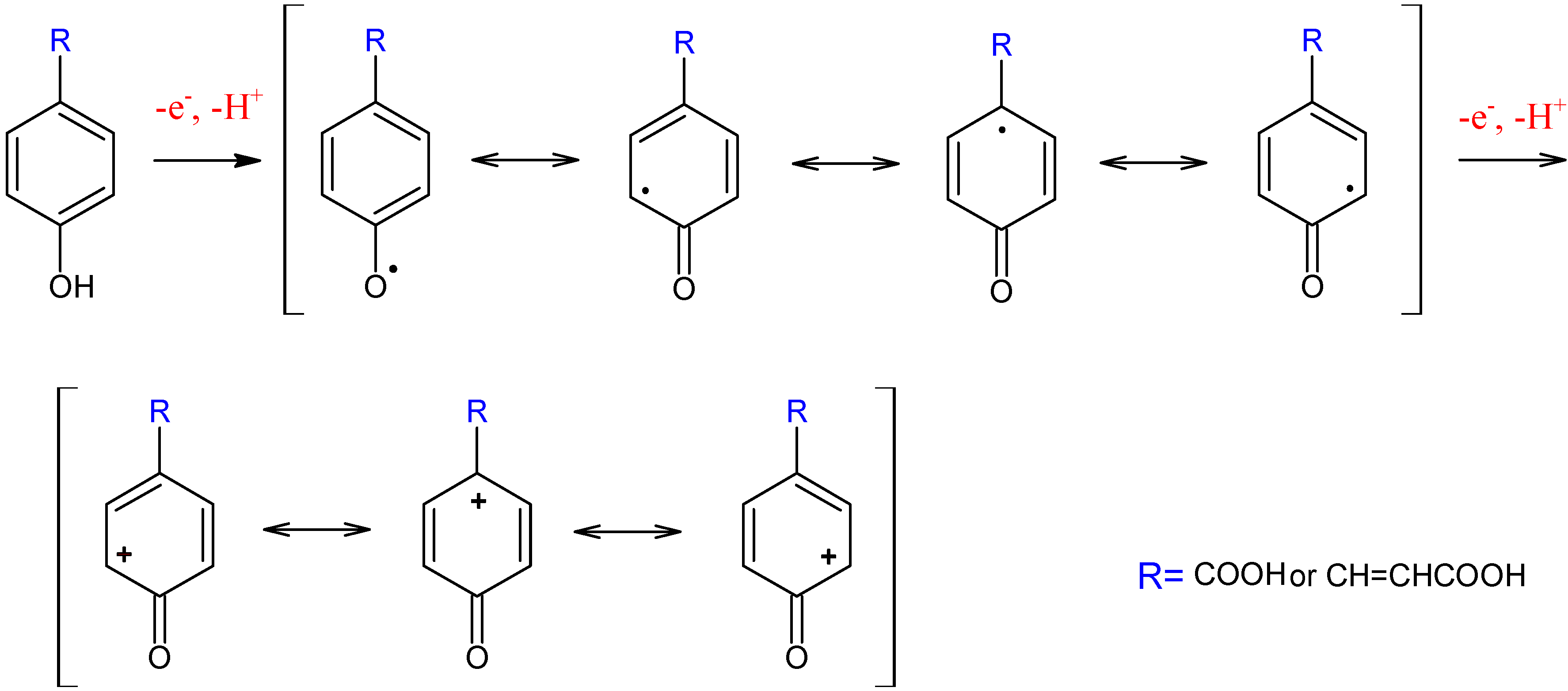
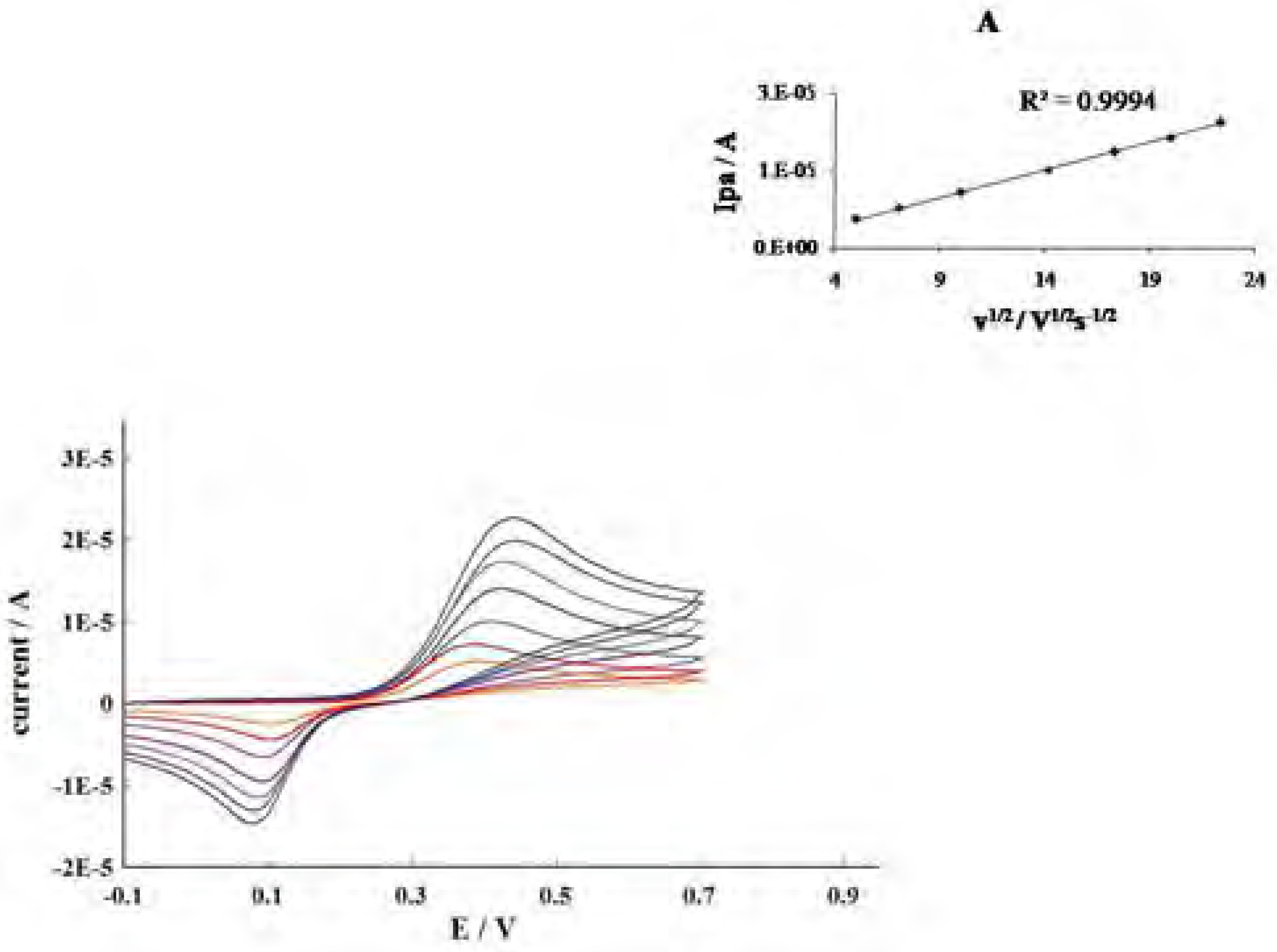
| Phenolics | Epa (V)a | Lipid peroxidation(percent inhibition)b |
|---|---|---|
| salicylic acid | 0.94 | -12.1 ± 1.8 |
| m-hydroxy-benzoic acid | 0.83 | -10.1 ± 3.0 |
| p-hydroxy-benzoic acid | 0.87 | -11.4 ± 2.0 |
| protocatechuic acid | 0.41 | +15.5 ± 0.3 |
| vanillic acid | 0.73 | -12.5 ± 1.1 |
| syringic acid | 0.49 | -5.4 ± 1.1 |
| o-coumaric acid | 0.75 | -13.0 ± 1.0 |
| m-coumaric acid | 0.78 | -10.6 ± 1.1 |
| p-coumaric acid | 0.67 | -23.3 ± 3.1 |
| caffeic acid | 0.45 | +11.2 ± 2.2 |
| quercetin | 0.10 | +67.8 ± 2.0 |
| rutin | 0.23 | +10.0 ± 3.6 |
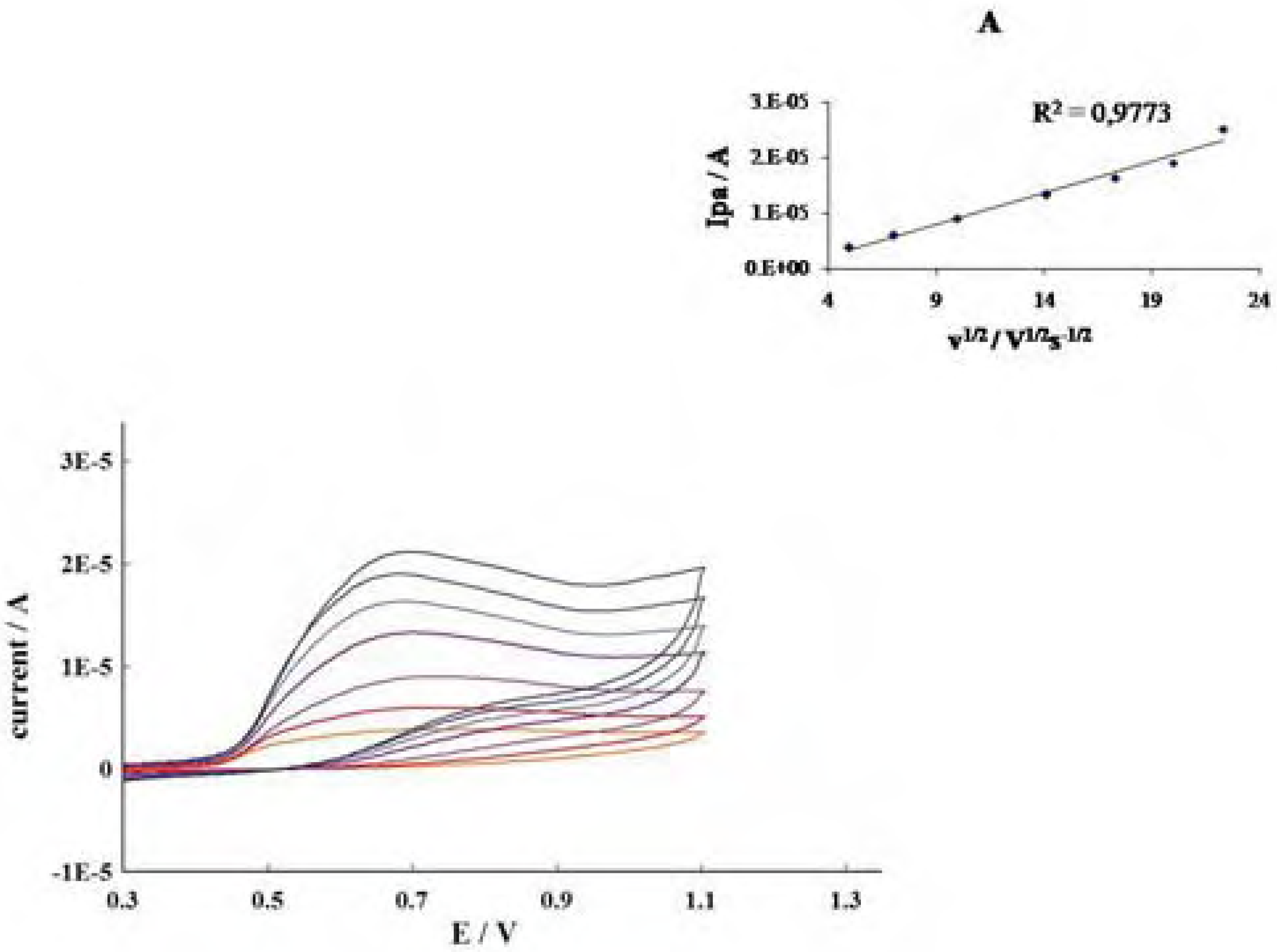
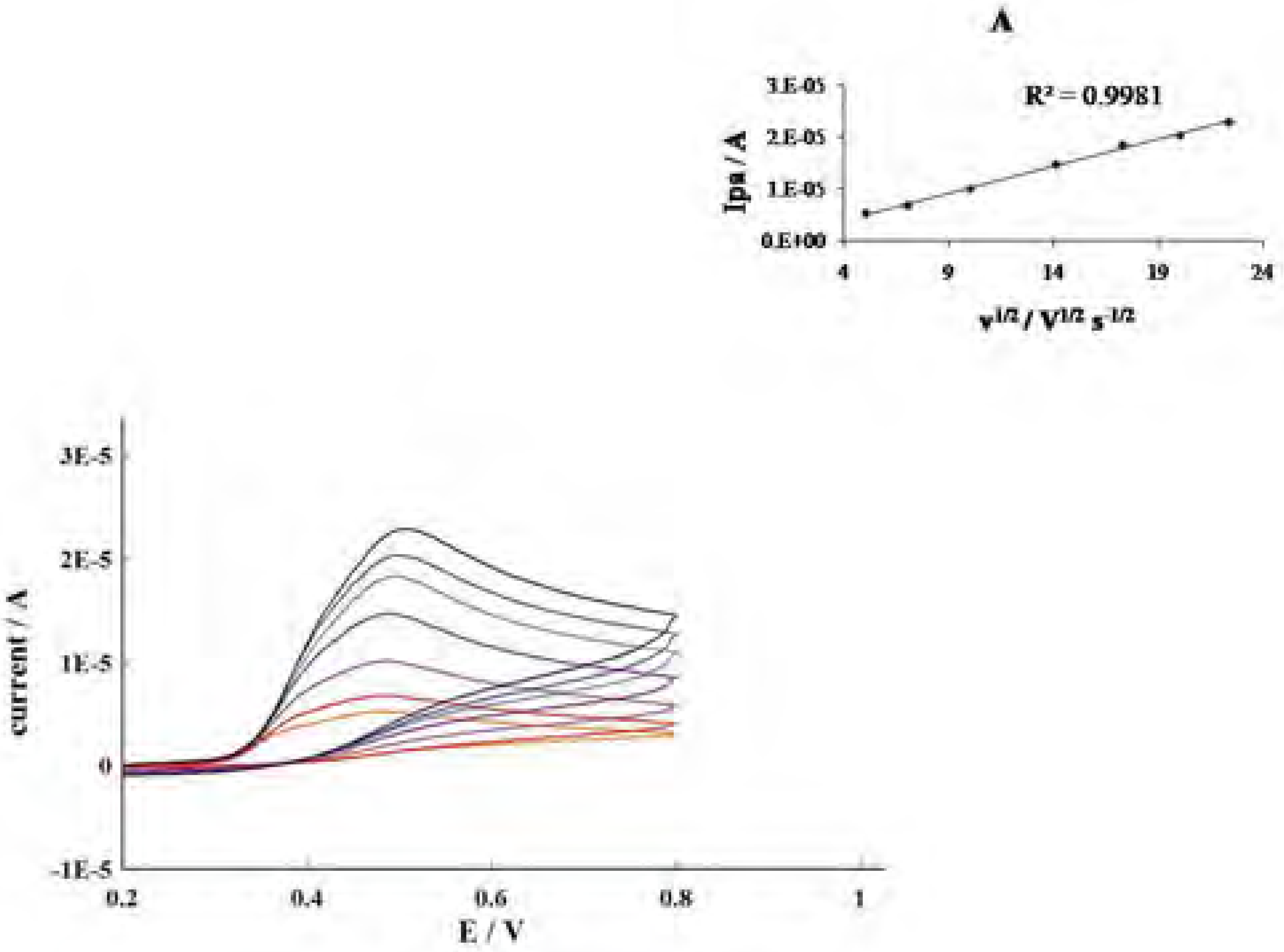
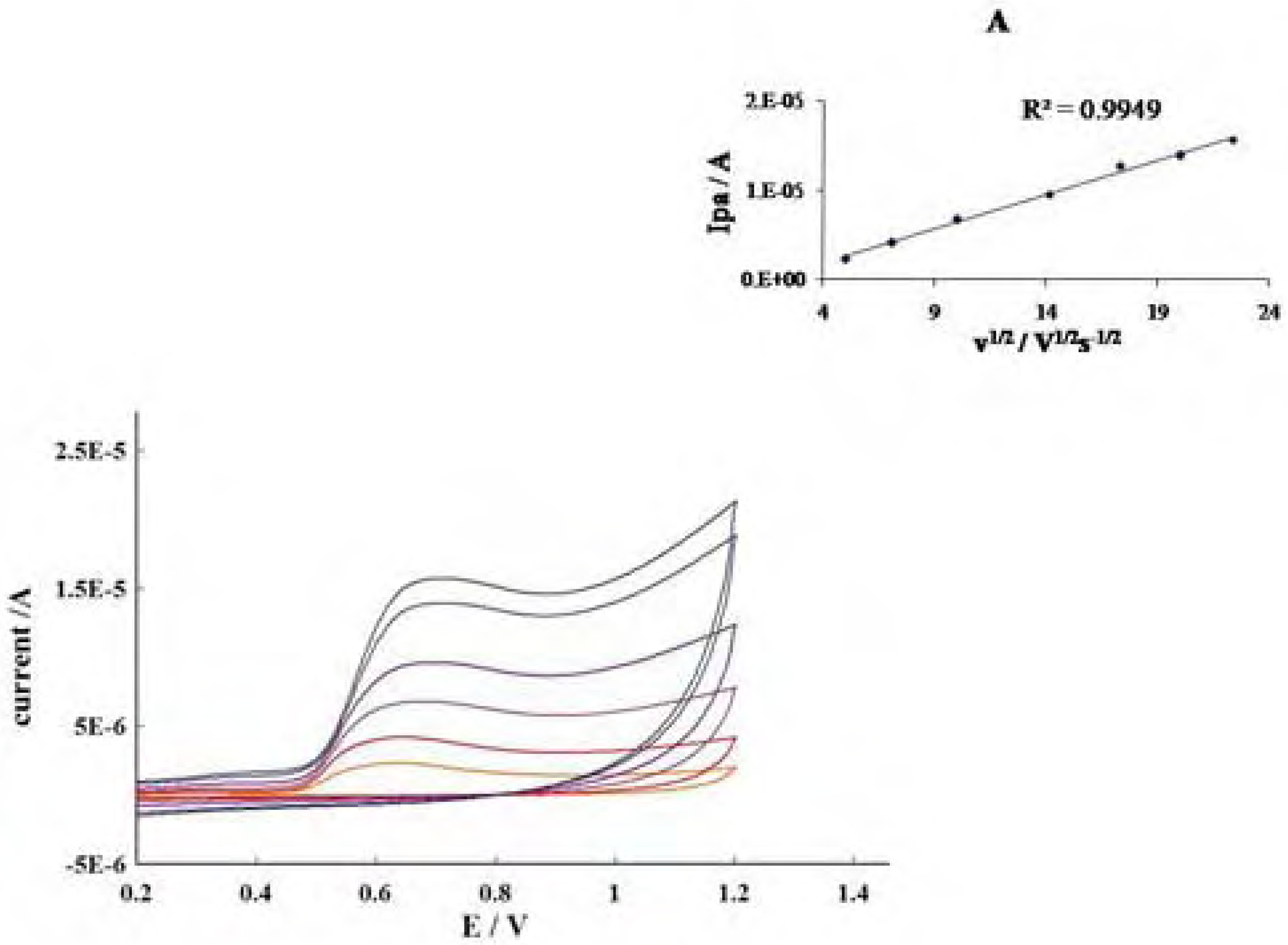
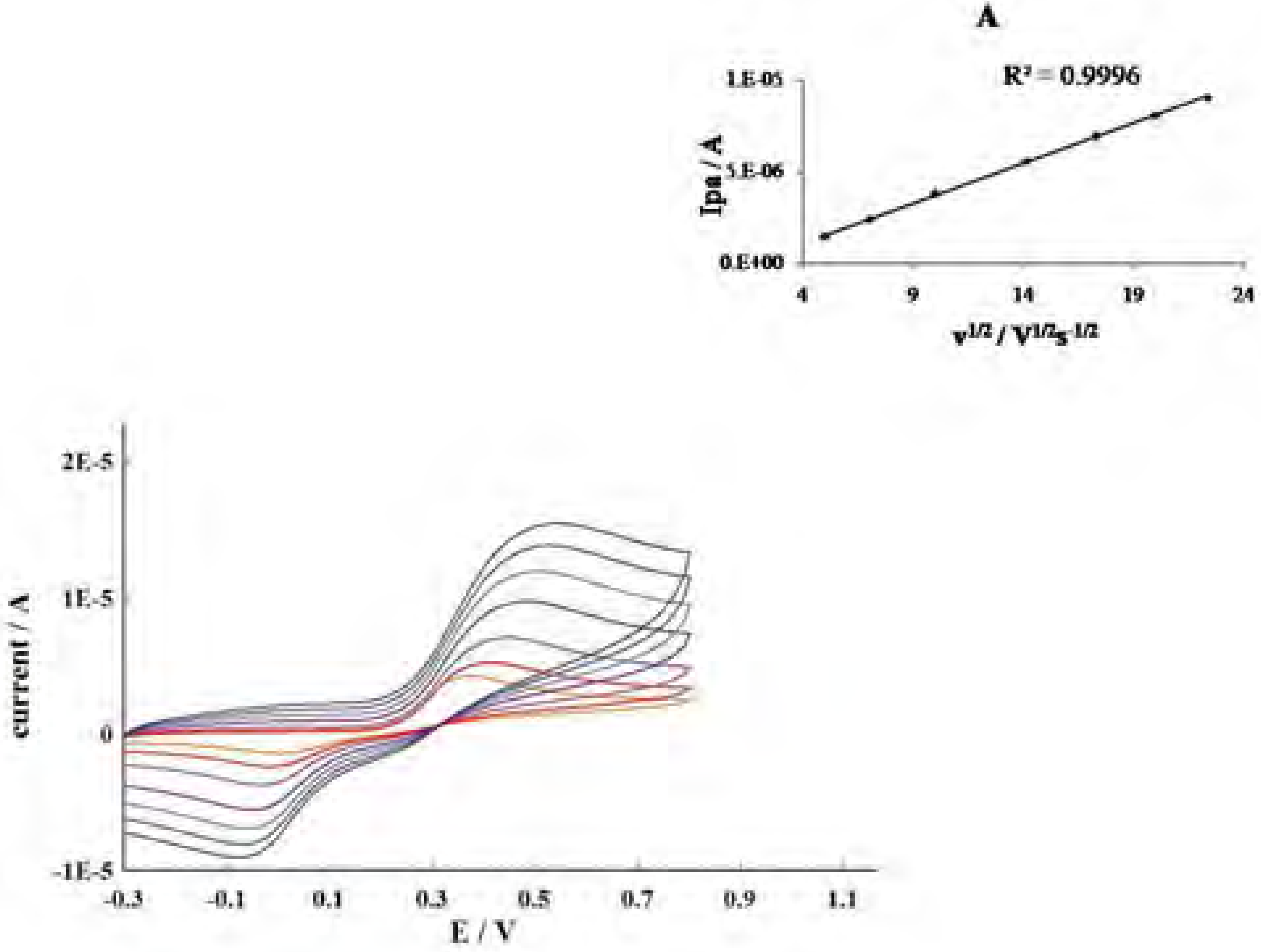
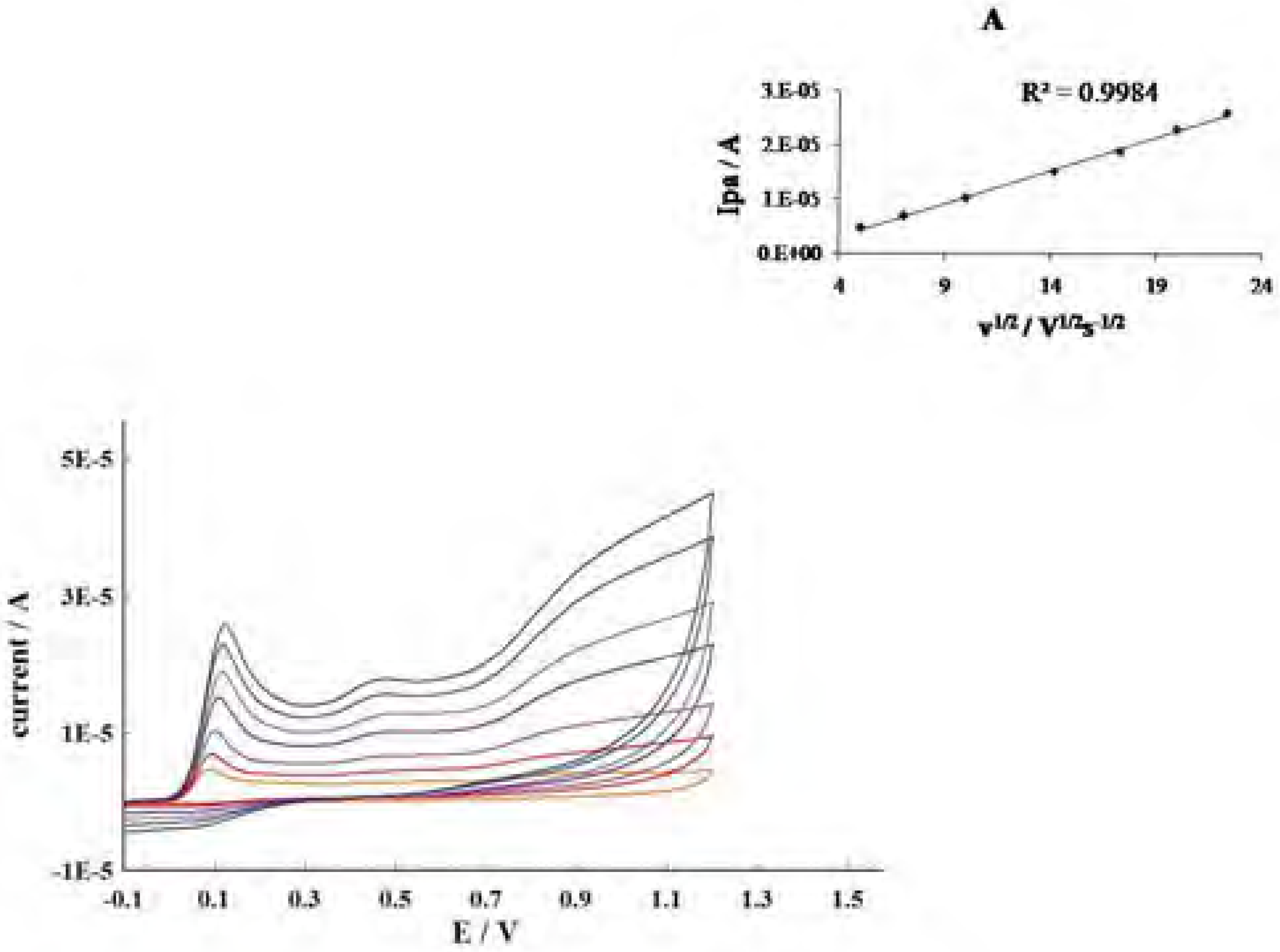
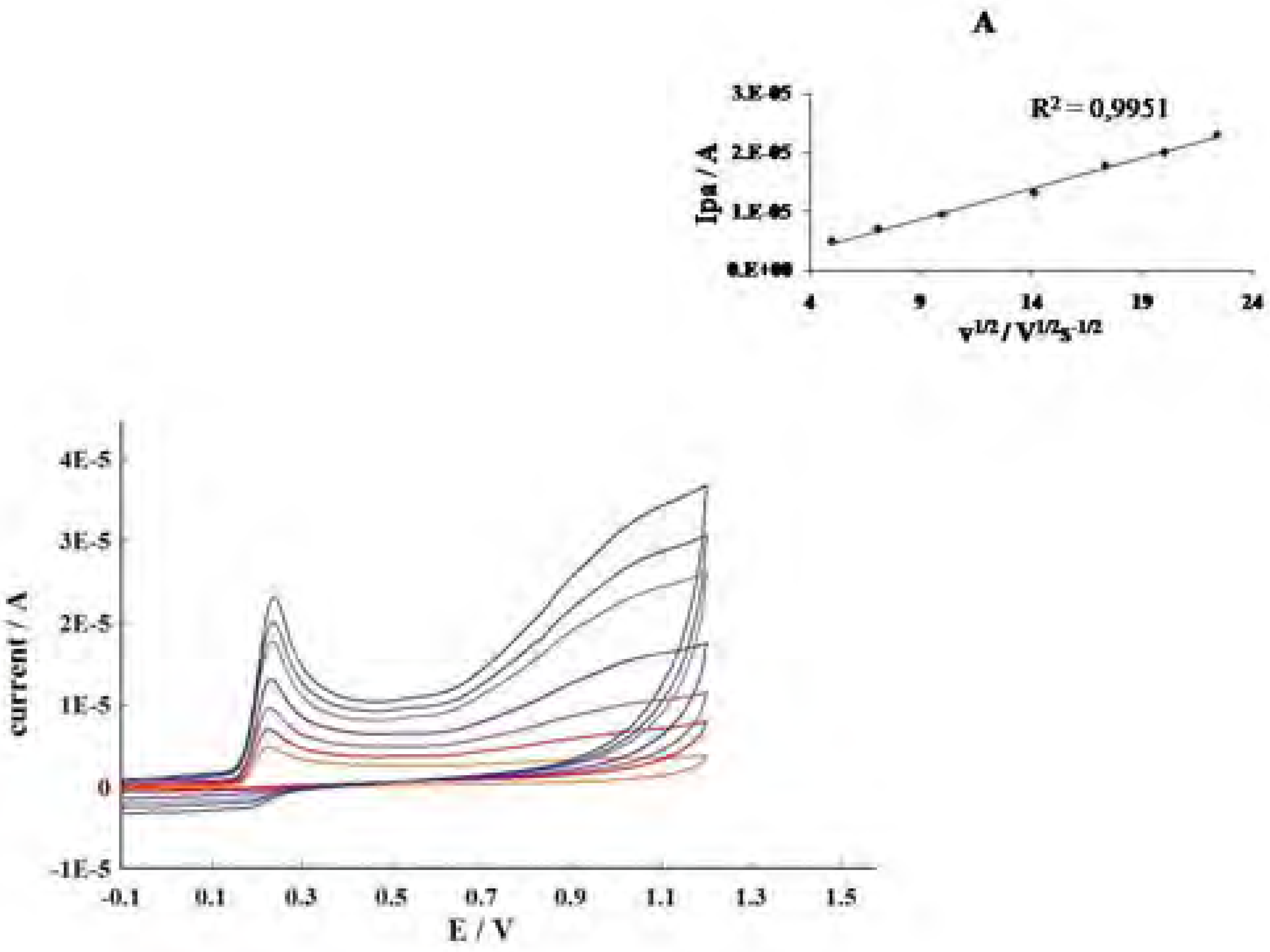
Conclusions
Experimental
General
Cyclic Voltammetry
Lipid peroxidation
References
- Visioli, F.; Galli, C. Olive oil phenols and their potential effects on human health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4292–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanos, A.G.; Wrolstad, E.R. Phenolics of apple, pear, and white grape juices and their changes with processing and storage-a review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, D.; Sanders, K.; Kolybaba, M.; Lopez, D. Case-control study of phytoestrogens and breast cancer. Lancet 1997, 9083, 990–994. [Google Scholar]
- Vinson, A.J.; Hao, Y.; Su, X.; Zubik, L. Phenol antioxidant quantity and quality in foods: vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 46, 3630–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Nakao, M.; Akaike, T.; Ono, K.; Maeda, H. Alkylperoxyl radical-scavenging activity of various flavonoids and other phenolic compounds: implications for the anti-tumor-promoter effect of vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faylkner, L.R. Electrochemical methods, fundamentals and applications, Second Ed. ed; Wiley: New York, 2001; pp. 496–505. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.; Varela, H.; Torresi, R.M.; Tremiliosi-Filho, G. Electrode passivation caused by polymerization of different phenolic compounds. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Hammerich, O. Organic electrochemistry, Fourth Ed. ed; Marcel Dekker: New York, 2001; pp. 590–611. [Google Scholar]
- Hotta, H.; Ueda, M.; Nagano, S.; Tsvjino, Y.; Koyama, J. Mechanistic study of the oxidation of caffeic acid by digital simulation of cyclic voltammograms. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 303, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, S.R.; Shain, I. Theory of stationary electrode polarography for a chemical reaction coupled between two charge transfers. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 178–190. [Google Scholar]
- Trabelsi, S.K.; Tahar, N.B.; Abdelhedi, R. Electrochemical behavior of caffeic acid. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.W.; da Rocha, C.; Cardoso, C.L.; Silva, S.D.H.; Zanoni, B.M.V. Determination of the relative contribution of phenolic antioxidants in orange juce by voltammetric methods. J. Food Com. Anal. 2004, 17, 619–633. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Carrupt, P.A.; Zini, R.; Bree, F.; Tillement, J.P.; Hostettmann, K.; Testa, B. Electrochemical behaviour and antioxidant activity of some natural polyphenols. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson, P.H.; Kaufman, D.A.; Lunte, E.C. Electrochemistry of catehol-containing flavonoids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Ghica, M.E.; Brett, A.M.O. Electrochemical oxidation of rutin. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, A.M.O.; Ghica, M.E. Electrochemical oxidation of quercetin. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem. J. 1984, 219, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sakihama, Y.; Cohen, M.F.; Grace, S.C.; Yamasaki, H. Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology 2002, 177, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Chang, W. Kinetic deoxyribose degradation assay and its application in assessing the antioxidant activities of phenolic compounds in a Fenton- type reaction system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 478, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Kinetic analysis and mechanistic aspects of autoxidation of catehins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1569, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labieniec, M.; Gabryelak, T. Study of interactions between phenolic compounds and H2O2 or Cu (II) ions in B14 Chinese hamster cells. Cell Boil. Intr. 2006, 30, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labieniec, M.; Gabryelak, T. Antioxidative and oxidative changes in the digestive gland cells of freshwater mussels Unio tumidus caused by selected phenolic compounds in the presence of H2O2 or Cu2+ ions. Toxicol. In Vitro 21, 146–156. [CrossRef]
- Rodtjer, A.; Skibsted, L.H.; Andersen, M.L. Antioxidative and prooxidative effects of extracts made from cherry liqueur pomace. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto, M.; Sonda, T.; Nagayama, K.; Tabata, M. Effects of pH and metal ions on antioxidative activities of catechins. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briante, R.; Febbraio, F.; Nucci, R. Antioxidant properties of low molecular weight phenols present in the Mediterranean diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6975–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, D.; Fernandez-Pachon, M.S.; Troncoso, M.A.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. Comparison of antioxidant activity of wine phenolic compounds and metabolites in vitro. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, L.R.; Mazza, G. Assessing antioxidant and prooxidant activities of phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3597–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Lan, W.Z.; Quin, W.M.; Xu, H.B. Effects of salicylic acid on fungal elicitor-induced membrane-lipid peroxidation and taxol production in cell suspension cultures of Taxus chinensis. Proc. Biochem. 2001, 37, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Natella, F.; Nardini, M.; di Felice, M.; Scaccini, C. Benzoic and cinnamic acid derivates as antioxidants: structure-activity relation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bors, W.; Heller, W.; Michel, C.; Saran, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants: determination of radical-scavenging efficiencies. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kotani, A.; Arai, K.; Kusu, F. Estimation of the antioxidant activities of flavonoids from their oxidation potentials. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmartin, A.P.; Zou, H.; Waterhouse, L.A. A cyclic voltammetry method suitable for characterizing antioxidant properties of wine and wine phenolics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Galato, D.; Ckless, K.; Susin, F.M..; Giacomelli, C.; Robeiro-do-Valle, M.R.; Spinelli, A. Antioxidaant capacity of phenolics and related compounds: correlation among electrochemical, visible spectroscopy methods and structure-antioxidant activity. Redox Report 2001, 6, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Firuzi, O.; Lacanna, A.; Petrucci, R.; Marrosu, G.; Saso, L. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of flavonoids by " ferric reducing antioxidant power" assay and cyclic voltammetry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1721, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, M. L.; Lauridsen, R.K.; Skibsted, L.H. Optimizing the use of phenolic compounds in foods. In Phytochemical Functional Foods; Johnson, I., Williamson, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, 2003; pp. 315–346. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Sofic, E.; Prior, R.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant behavior of flavonoids: structure-activity relationships. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkowski, A; Piotrowska, M. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of some medicinal plants from the Lamiaceae. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.C.; Kim, C.S.; Hwang, S.S.; Choi, K.B.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, H.S.; Kim, K.S. Antioxidant activity and free radical scavenging capacity between Korean medicinal plants and flavonoids by assay-guided comparison. Plant Sci. 2002, 163, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample availability: Contact the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Simić, A.; Manojlović, D.; Šegan, D.; Todorović, M. Electrochemical Behavior and Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Natural Phenolics. Molecules 2007, 12, 2327-2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102327
Simić A, Manojlović D, Šegan D, Todorović M. Electrochemical Behavior and Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Natural Phenolics. Molecules. 2007; 12(10):2327-2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102327
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimić, Aleksandra, Dragan Manojlović, Dejan Šegan, and Marija Todorović. 2007. "Electrochemical Behavior and Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Natural Phenolics" Molecules 12, no. 10: 2327-2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102327
APA StyleSimić, A., Manojlović, D., Šegan, D., & Todorović, M. (2007). Electrochemical Behavior and Antioxidant and Prooxidant Activity of Natural Phenolics. Molecules, 12(10), 2327-2340. https://doi.org/10.3390/12102327




