Preparation of 6-Substituted Quinoxaline JSP-1 Inhibitors by Microwave Accelerated Nucleophilic Substitution
Abstract
:Introduction
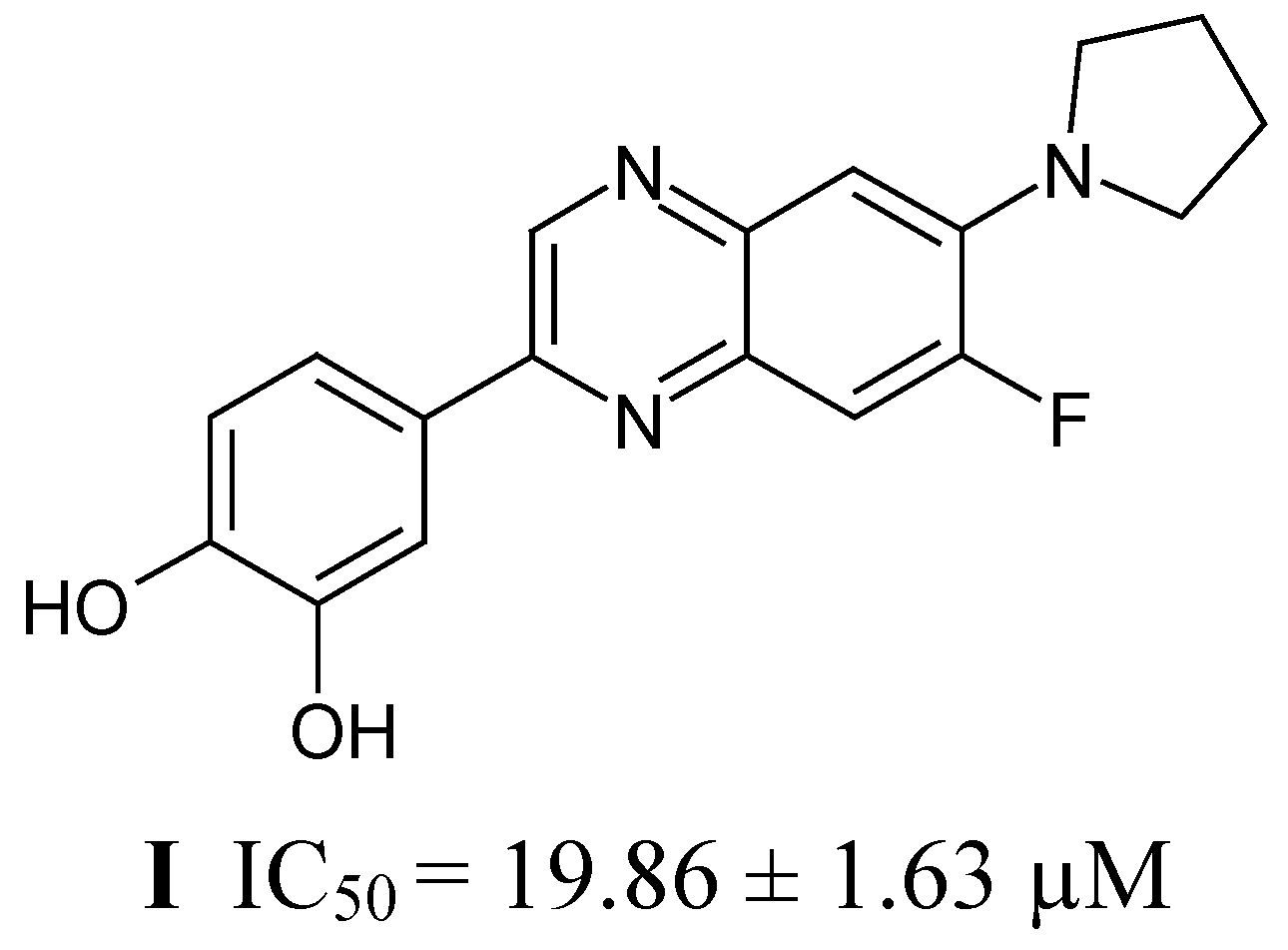
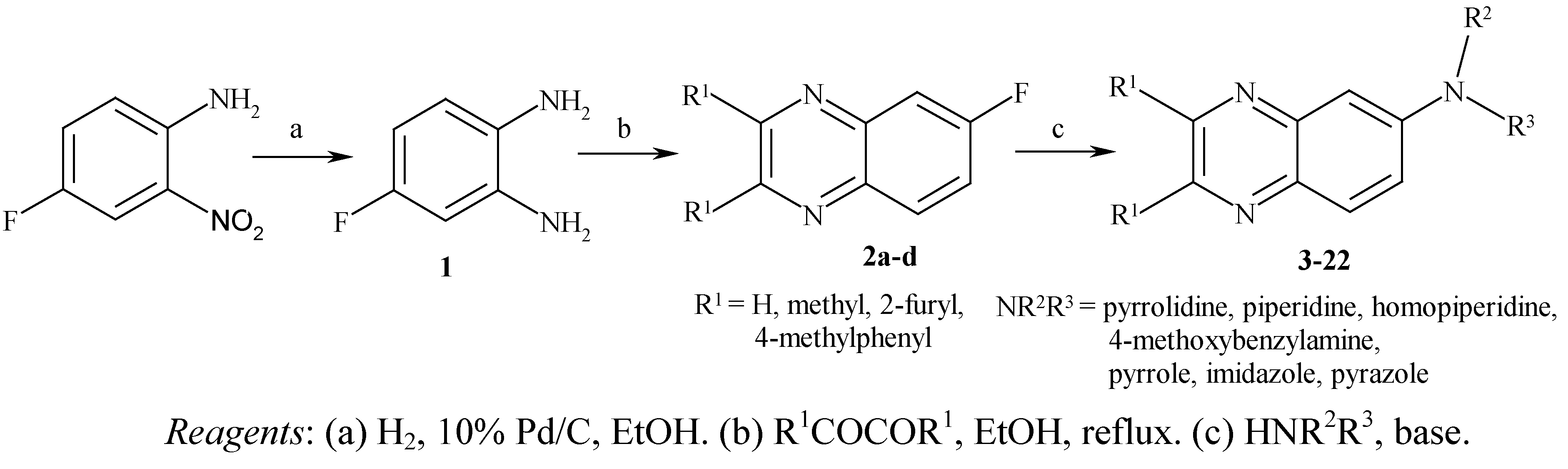
Results and Discussion
Chemistry
| Entry | 2a (equiv.) | Pyrrolidine (equiv.) | Base | Solvent | T (°C) | t (min) | Yield of 3a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 189 | 30 | 16b |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 189 | 180 | 22b |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMF | 120 | 30 | 22c |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | NMP | 200 | 30 | 55c |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 200 | 30 | 93c |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | DBU | DMSO | 200 | 30 | 30c |
| 7 | 1 | 2 | NaOH | DMSO | 200 | 30 | 80c |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 200 | 30 | 30c |
| 9 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 180 | 30 | 71c |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 220 | 30 | 83c |
| 11 | 1 | 2 | K2CO3 | DMSO | 200 | 20 | 70c |
| Entry | Compound | R1 | NR2R3 | Yield (%)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | H | Pyrrolidine | 93 |
| 2 | 4 | H | Piperidine | 85 |
| 3 | 5 | H | 4-Methoxybenzylamine | 45 |
| 4 | 6 | H | Imidazole | 92b |
| 5 | 7 | H | Pyrazole | 88b |
| 6 | 8 | Methyl | Pyrrolidine | 88c |
| 7 | 9 | Methyl | Piperidine | 50c |
| 8 | 10 | Methyl | Imidazole | 88 |
| 9 | 11 | Methyl | Pyrazole | 88 |
| 10 | 12 | 2-Furyl | Pyrrolidine | 93 |
| 11 | 13 | 2-Furyl | Piperidine | 90 |
| 12 | 14 | 2-Furyl | Homopiperidine | 73 |
| 13 | 15 | 2-Furyl | 4-Methoxybenzylamine | 80 |
| 14 | 16 | 2-Furyl | Pyrrole | 94 |
| 15 | 17 | 2-Furyl | Imidazole | 97 |
| 16 | 18 | 2-Furyl | Pyrazole | 97 |
| 17 | 19 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrrolidine | 90c |
| 18 | 20 | 4-Methylphenyl | Homopiperidine | 50c |
| 19 | 21 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrrole | 96 |
| 20 | 22 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrazole | 96 |
Biological activity
| Entry | Compound | R1 | NR2R3 | JSP-1 IC50 (μM)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | 2-Furyl | Pyrrolidine | 7.51±0.81 |
| 2 | 13 | 2-Furyl | Piperidine | 4.18±0.03 |
| 3 | 14 | 2-Furyl | Homopiperidine | 5.37±0.53 |
| 4 | 15 | 2-Furyl | 4-Methoxybenzylamine | 6.44±1.02 |
| 5 | 16 | 2-Furyl | Pyrrole | 2.61±0.34 |
| 6 | 17 | 2-Furyl | Imidazole | 4.77±0.32 |
| 7 | 18 | 2-Furyl | Pyrazole | 8.03±0.99 |
| 8 | 19 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrrolidine | 31.62±1.84 |
| 9 | 20 | 4-Methylphenyl | Homopiperidine | 9.20±0.65 |
| 10 | 21 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrrole | 9.23±0.90 |
| 11 | 22 | 4-Methylphenyl | Pyrazole | 42.44±4.80 |
| 12 | Reference | 3-((5-((4-fluorophenyl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxo)-3-thiazolidinyl)-benzoic acid [35] | 15.37±0.13 | |
Conclusions
Experimental Section
General
General procedure for the preparation of 6-fluoroquinoxalines 2a-d: Preparation of 6-fluoro-quinoxaline (2a)
General procedure for the preparation of 6-aminoquinoxalines 3-22 under microwave irradiation: Synthesis of 6-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-quinoxaline (3).
JSP-1 Inhibition Activities Assay
Acknowledgements
References
- Nikam, S. S.; Cordon, J. J.; Ortwine, D. F.; Heimbach, T. H.; Blackburn, A. C.; Vartanian, M. G.; Nelson, C. B.; Schwarz, R. D.; Boxer, P. A.; Rafferty, M. F. Design and synthesis of novel quinoxaline-2,3-dione AMPA/GlyN receptor antagonists: Amino acid derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 2266–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auberson, Y. P.; Bischoff, S.; Moretti, R.; Schmutz, M.; Veenstra, S. J. 5-Aminomethyl-quinoxaline-2, 3-diones. Part I: A novel class of AMPA receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Auberson, Y. P.; Acklin, P.; Allgeier, H.; Biollaz, M.; Bischoff, S.; Ofner, S.; Veenstra, S. J. 5-Aminomethylquinoxaline-2,3-diones. Part II: N-aryl derivatives as novel NMDA/glycine and AMPA antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K. S.; Qian, L. G.; Dickinson, K. E. J.; Delaney, C. L.; Bird, J. E.; Waldron, T. L.; Moreland, S. Synthesis, biological properties, and structure-activity-relationships of quinoxaline angiotensin-II receptor antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1993, 3, 2667–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. S.; Qian, L. G.; Bird, J. E.; Dickinson, K. E. J.; Moreland, S.; Schaeffer, T. R.; Waldron, T. L.; Delaney, C. L.; Weller, H. N.; Miller, A. V. Quinoxaline N-Oxide containing potent angiotensin-II receptor antagonists - synthesis, biological properties, and structure-activity-relationships. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Melero, C.; Maya, A. B. S.; del Rey, B.; Pelaez, R.; Caballero, E.; Medarde, M. A new family of quinoline and quinoxaline analogues of combretastatins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, S.; Loriga, M.; Paglietti, G. Quinoxaline chemistry. Part XVII. Methyl [4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetates and ethyl N-{[4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetyl} glutamates analogs of methotrexate: synthesis and evaluation of in vitro anticancer activity. Il Farmaco 2004, 59, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, P.; Vitale, G.; Loriga, M.; Paglietti, G. Quinoxaline chemistry. Part 13: 3-carboxy-2-benzylamino-substituted quinoxalines and N-[4-[(3-carboxyquinoxalin-2-yl) aminomethyl]benzoyl]-L-glutamates: synthesis and evaluation of in vitro anticancer activity. Il Farmaco 2000, 55, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Monge, A.; Palop, J. A.; de Cerain, A. L.; Senador, V.; Martinez-Crespo, F. J.; Sainz, Y.; Narro, S.; Garcia, E.; de Miguel, C.; Gonzalez, M.; Hamilton, E.; Barker, A. J.; Clarke, E. D.; Greenhow, D. T. Hypoxia-selective agents derived from quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, A.; Loriga, M.; Zanetti, S.; Sechi, L. A. Quinoxalin-2-ones: Part 5. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of 3-alkyl-, 3-halomethyl- and 3-carboxyethylquinoxaline-2-ones variously substituted on the benzo-moiety. Il Farmaco 2003, 58, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Desrivot, J.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P. M.; Franck, X.; Hocquemiller, R.; Figadere, B. Synthesis and antiprotozoal activity of some new synthetic substituted quinoxalines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamino, R. J. Thiocyanatoquinoxaline compounds with immunomodulating activity. U.S. Patent 4,540,693, 1985. [Chem. Abstr. 1986, 104, 88601]. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Gui, C.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H.; Nan, F.; Shen, J.; Bai, D.; Chen, K.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H. One novel quinoxaline derivative as a potent human cyclophilin A inhibitor shows highly inhibitory activity against mouse spleen cell proliferation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5527–5534. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Luche, R.; Wei, B.; Gordon, M. L.; Diltz, C. D.; Tonks, N. K. Activation of the Jnk signaling pathway by a dual-specificity phosphatase, JSP-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2001, 98, 13613–13618. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, A.; Merlo, J. J.; Na, S. Q.; Kholod, N.; Jaroszewski, L.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Williams, S.; Godzik, A.; Posada, J. D.; Mustelin, T. Inhibition of T Cell Antigen Receptor Signaling by VHR-related MKPX (VHX), a New Dual Specificity Phosphatase Related to VH1 Related (VHR). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5524–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A. J.; Zhou, G. S.; Juan, T.; Colicos, S. M.; Cannon, J. P.; Cabriera-Hansen, M.; Meyer, C. F.; Jurecic, R.; Copeland, N. G.; Gilbert, D. J.; Jenkins, N. A.; Fletcher, F.; Tan, T. H.; Belmont, J. W. The dual specificity JKAP specifically activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36592–36601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Rojas, A.; Godzik, A.; Mustelin, T. The dual-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase family. Top. Curr. Genetics 2004, 5, 333–358. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R. J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, A. M.; Davis, R. J. Targeting JNK for Therapeutic Benefit: from JUNK to gold? Nat. Rev. Drug Disc. 2003, 2, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. J.; Wisnoski, D. D.; Wolkenberg, S. E.; Leister, W. H.; Wang, Y.; Lindsley, C. W. General microwave-assisted protocols for the expedient synthesis of quinoxalines and heterocyclic pyrazines. Tetrahderon Lett. 2004, 45, 4873–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Jalil, R. J.; Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; Voelter, W.; Heeg, P.; El-Abadelah, M. M.; Sabri, S. S. Synthesis and properties of some 2,3-disubstituted 6-fluoro-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)quinoxalines. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2000, 37, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Charushin, V. N.; Mokrushina, G. A.; Tkachev, A. V. Nucleophilic substitutions in 6,7-difluoroquinoxalines. J. Fluorine Chem. 2001, 107, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotovskaya, S. K.; Romanova, S. A.; Charushin, V. N.; Chupakhin, O. N. Fluorine-containing heterocycles: VII. Nucleophilic substitution in 6,7-difluoroquinoxalines. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 38, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, Y.; Shiga, F.; Asano, J.; Ando, N.; Uchiki, H.; Anraku, T. Synthesis and AMPA receptor antagonistic activity of a novel class of quinoxalinecarboxylic acid with a substituted phenyl group at the C-7 position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, Y.; Shiga, F.; Asano, J.; Ando, N.; Uchiki, H.; Fukuchi, K.; Anraku, T. Design, synthesis, and AMPA receptor antagonistic activity of a novel 6-nitro-3-oxoquinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid with a substituted phenyl group at the 7 position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5841–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, K.; Grivas, S. New synthetic routes to the potent mutagen 3,7,8-Trimethyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-f]quinoxalin-2-amine. Acta Chem. Scand. Ser.B. 1986, 40, 486–492. [Google Scholar] Grivas, S.; Olsson, K. An improved synthesis of 3,8-Dimethyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-f]quinoxalin-2-amine(“MeIQx”) and its 2-14C-labelled analogue. Acta Chem. Scand. Ser.B. 1985, 39, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kappe, C. O. Controlled microwave heating in modern organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. 2004, 43, 6250–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersmark, K.; Larhed, M.; Wannberg, J. Microwave-enhanced medicinal chemistry: A high-speed opportunity for convenient preparation of protease inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2004, 7, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Mavandadi, F.; Lidstrom, P. Microwave - Assisted chemistry in drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidstrom, P.; Tierney, J.; Wathey, B.; Westman, J. Microwave assisted organic synthesis–a review. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9225–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, Q. X. Syntheses of heterocyclic compounds under microwave irradiation. Heterocycles. 2004, 63, 903–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N. S.; Roth, G. P. Recent trends in microwave-assisted synthesis. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2002, 5, 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D. R.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Du, Y. L.; Shen, J. K. Microwave-assisted rapid and straight-forward synthesis of 2-aryl-4-quinolones from acylated 2'-aminoacetopheinones. Tetrahderon Lett. 2006, 47, 6997–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Dunbar, L. J.; Green, I. G.; Harvey, I. W.; Shepherd, T.; Smith, D. M.; Wong, R. K. C. Polyaza heterocycles. Part 2. Nucleophilic substitution of halogens in halogenoquinoxalino[2,3-c]cinnolines. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 1994, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar]
- Cutshall, N. S.; O’Day, C.; Prezhdo, M. Rhodanine derivatives as inhibitors of JSP-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3374–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2006 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Qiu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Shen, J. Preparation of 6-Substituted Quinoxaline JSP-1 Inhibitors by Microwave Accelerated Nucleophilic Substitution. Molecules 2006, 11, 988-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/11120988
Zhang L, Qiu B, Li X, Wang X, Li J, Zhang Y, Liu J, Li J, Shen J. Preparation of 6-Substituted Quinoxaline JSP-1 Inhibitors by Microwave Accelerated Nucleophilic Substitution. Molecules. 2006; 11(12):988-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/11120988
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Li, Beiying Qiu, Xin Li, Xin Wang, Jingya Li, Yongliang Zhang, Jian Liu, Jia Li, and Jingkang Shen. 2006. "Preparation of 6-Substituted Quinoxaline JSP-1 Inhibitors by Microwave Accelerated Nucleophilic Substitution" Molecules 11, no. 12: 988-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/11120988
APA StyleZhang, L., Qiu, B., Li, X., Wang, X., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Li, J., & Shen, J. (2006). Preparation of 6-Substituted Quinoxaline JSP-1 Inhibitors by Microwave Accelerated Nucleophilic Substitution. Molecules, 11(12), 988-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/11120988




