Abstract
A non-endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle is analyzed by introducing a factor of non-endoreversibility. The form of power output and ecological function, and the role of this factor is discussed. The Gutkowics-Krusin, Procaccia and Ross method to build a general expression for both the power output and the ecological function for this cycle is used. A numerical analysis of these expresions is made and the results are compared with other kind of approaches found in the literature of finite time thermodynamics.
PACS:
44.6.+k; 44.90.+c
1. Introduction
As it is known the Curzon and Ahlborn cycle [1] is a model of an endoreversible engine, shown in Figure 1. The efficiency of this cycle is a bound of real engines and it is written as
where
is the cold reservoir temperature and
is the hot reservoir temperature. This endoreversible cycle is an engine in which entropy production during the exchange of heat between the system and its reservoirs of heat is only taken into account.
Equation (1) has been recovered by some procedures [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Particularly in reference [3] the optimal configuration of heat engines was studied. More recently this subject had been also studied by other authors [10,11,12,13,14]. On other hand, Gutkowics-Krusin, et al [9] introduced a procedure in which the power output of this cycle is took as a function of the compression ratio by using the parameter
~, where
and
are the maximun and the minimum volumes spanned in the cycle, respectively. Recently, with this method Ladino-Luna and de la Selva [15] by using Newton heat transfer law for ideal gas as working substance, and Ladino-Luna [16,17] for a van der Waals gas as working substance and by using Dulong and Petit heat transfer law, found the form of the function introduced by Angulo-Brown, named ecological function,
where P is the power output,
is the temperature of cold reservoir and
is the total entropy production. They shown that ecological function has a similar property as power output when the compression ratio is taking into account, e. g. ecological efficiency obtained at maximum ecological function, with the definition
,
is a bound for efficiencies when the Curzon and Ahlborn model is performing at maximum ecological function, and when it is taking into account the time of all the processes in the cycle.
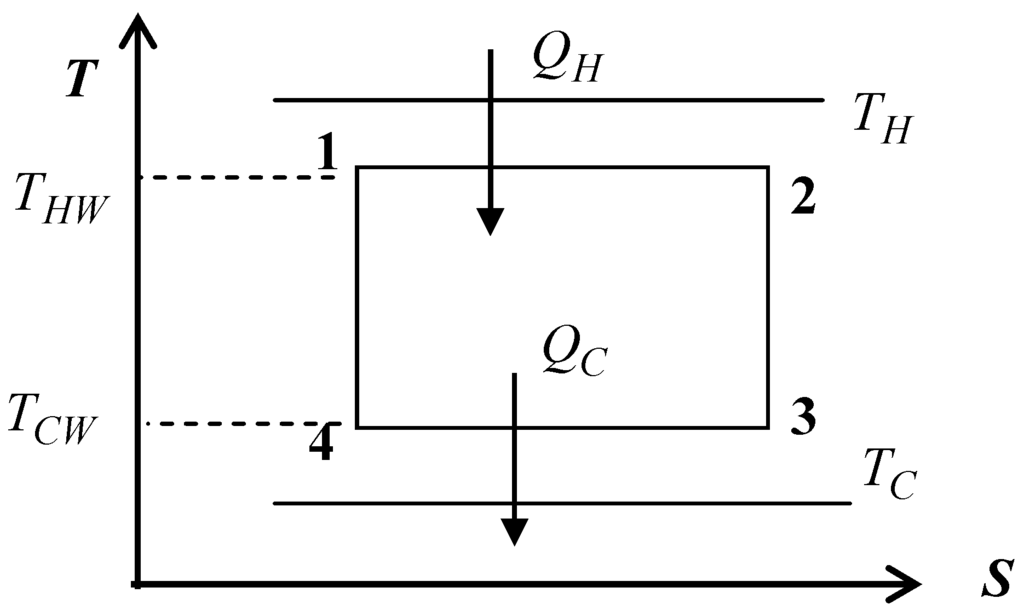
Figure 1.
Curzon and Ahlborn cycle in the entropy, S, vs temperature, T, plane.
and
are the hot and cool temperatures of the isothermic processes of the cycle.
Angulo-Brown proposed an ecological criterion for finite-time Carnot heat engines, Equation (3), that represents a compromise between the high power output P and a loss power
. However Yan [18] showed that it might be more reasonable to use
if the cold reservoir temperature
is not equal to the enviroment temperature
because in the definition of E two diferent quantities, exergy output a non-exergy
, were compared together. The criterion function
could be more reasonable than Angulo-Brown criterion. Nevertheless, since
when
for the goal of this paper it can be used the optimization of E.
It is important to remark that Curzon and Ahlborn efficiency is an adequate approximation for conventional power plants, and ecological efficiency is the adequate approximation for modern power plants (nuclear and others) [19].
On other hand, except in reference [19], all of above authors consider an endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle; but in nature there is not any endoreversible engine. Thus other authors had analized the non-endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle [20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
Firstly Wu and Kiang [20] introduced a non-endoreversibility parameter, later Chen [21] analyzed the effect of thermal resistances, heat leakage and internal irreversibility by this non-endoreversibility parameter,
where
is the change of entropy obtained during the exchange of heat from the engine to cold reservoir, and
is the change of entropy obtained during the exchange of heat from the hot reservoir to engine. Chen et al [22,23] carried out the ecological optimization for generalized irreversible Carnot engine with heat resistance, heat leakage and internal irreversibility for Newton heat transfer law, and linear phenomenological heat transfer law. Zhu et al [24,25] generalized convective heat transfer law
, and generalized radiative heat transfer law
. More recently the ecological optimization for generalized irreversible universal heat engine, including Diesel, Otto, Bryton Atkinson, Dual and Miller cycles, with heat resistance, heat leakage and internal irreversibility was carried out for newton heat transfer law [26]. The efficiency obtained by introducing this parameter, Equation (4), at maximum power output is [21],
Angulo-Brown et al [19] shown that a general property of endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle previously demostrated [27] can be extended for a non-endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle. Velasco et al [28] follow the idea in references [21], and they found expressions to measure possible reductions of undesired effects in heat engines operation. They pointed out that IS is not depending of
and rewrote equation (5) as,
Even more, Angulo-Brown et al [29] applied variational calcuclus to show that both the saving function [28] and a modified ecological criteria are equivalent.
In present work it is shown that the internal irreversibilities can be taken into account by replacing the ratio in the square root for ecological efficiency, Equation (3), by
in case of a non endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle and with instantaneous adiabats. More general expressions for non-instantaneous adiabats are presented also by using compression ratio. The Gutkowics-Krusin, Procaccia and Ross method [9] is combined with the Chen cyclic model [21] by taking into account the parameter of non-endoreversibility
to obtain the form of power output function and of ecological function. Results are compared with others found in the literature of finite time thermodynamics.
2. Power output and ecological function for instantaneous adiabats
Consider the non-endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle model shown in Figure 2.
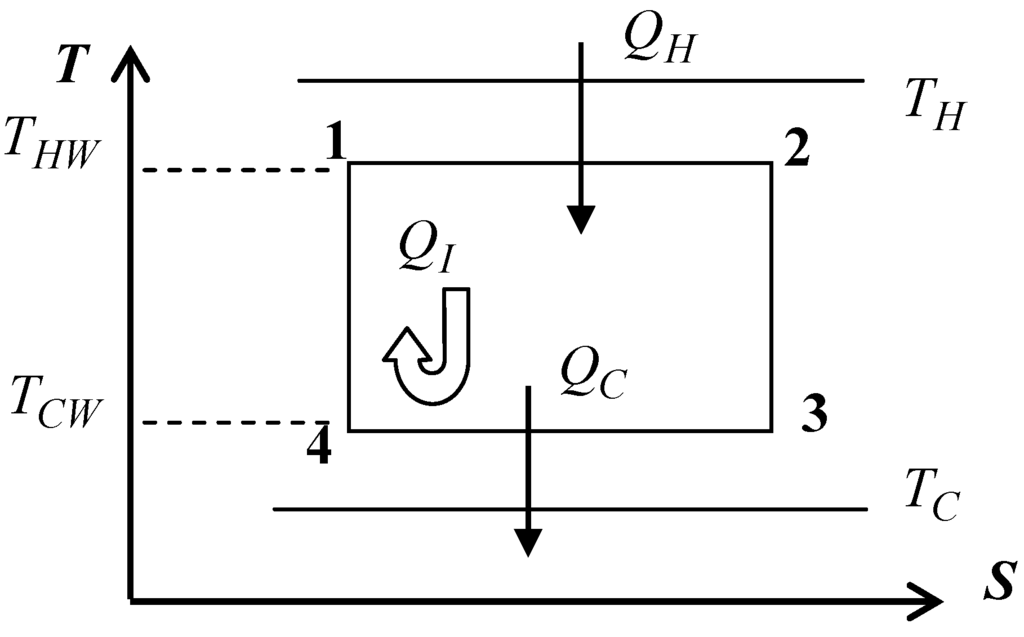
Figure 2.
Curzon and Ahlborn cycle in the S-T plane. is a heat generated by internal phenomena.
From the second law of thermodynamics the Clausius inequality can be written as,
and by introducing the non-endoreversibility parameter
, Equation (7) becomes,
so that it is possible to write,
Let it suppose one mol of ideal gas as working substance in the engine. Thus heat exchange can be written for each one of the isothermic branches in Figure 2 as,
where
are the volumes obtained on the first isothermic process in the Curzon and Ahlborn cycle shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, and R is the universal constant of ideal gases. It is obtained the work from the engine by using Equation (9) as,
On other hand, there are some possibilities to write the total time of cycle. The simplest of them is considering this time like in references [9,15,16] with instantaneous adiabats. Assuming the exchange of heat obtained by Newton heat transfer law between two environments at temperatures,
and
,
, with rapidity of heat exchange
, and with
the heat conductance, one has
Each of processes in the cycle occur with a different heat conductance. So, for simplicity let assume the same heat conductance in the processes of heat transfer in the Curzon and Ahlborn cycle. By ussing Equation (9) the total time of performing of cycle can be written now as,
and as a consequence the power output is now,
Equation (14) can be simplified with the definitions,
and by using the parameter
definite since Equation (5). One has the new simplified expression for power output as,
As well as it is made for the work obtained from the engine, the change of entropy in the cycle is,
and the corresponding ecological function is now written as,
or with the changes of variables taken previously in power output, one has,
Notice the similar algebraic structure of both power output and ecological function compared with these obtained in references [9,15,16]. Function
depends on the parameters
and
, as a consequence the efficiency will be a function of the same variables. Now, it has to obtain the efficiencies at maximum power output and at maximum ecological function from a general expression in a similar form as in references [9,15,16],
3. Curzon and Ahlborn efficiency and ecological efficiency
Function
could be obtained for both maximization of power output and maximization of ecological function. Taking the derivative of both power output and ecological function for u at
constant,
and
, it is obtain
as,
Now, from the derivative of power output at
,
, it is obtain,
which relate the variables u and
; and by substituting (20) into (21) it follows that,
and it is obtain the efficiency at maximum power output, namely,
whose is the result obtained in references [21].
Similarly, in case of ecological function, by taking the derivative
, one can find a relation between the variables
and u, that is the following one,
and by substituting Equation (20) into (23) it is obtain the expression of
,
and the efficiency at maximum ecological function, Equation (18), is,
As in the paper of Velasco et al [28], it is introduced the change
where
, for case of ideal gas as working substance, and because it is found that the parameter
has values into the range [0.8,0.9] for real engines, Table 1 shows a comparison between values of efficiencies from reference [28] and efficiencies calculated by Equation (25) in the range [0.8,0.9] of parameter I. Furthermore, Figure 3 shows that Equation (25) improve the values of theoretical efficiencies respect to the values calculated in reference [28]. The parameter
appears into (1.11,1.25).
The parameter I permits a more realistic evaluation of performance of power plants as it could be appreciate in Figure 4, in wich is compared the endoreversible ecological efficiency, Equation (3), vs the non-endoreversible ecological efficiency, Equation (25). For power output one obtains the same comparison. Also the parameter I is not depend of working substance, only it is necesary to take a fluid as it. In addition to, as it can be verified, in the limit
it is recovered the endorreversible behavior of Curzon and Ahlborn cycle, so that
and
. Figure 4 also shows this assumption.

Table 1.
Comparison of efficiencies obtained by Velasco et. al. [28] with efficiencies from Equation (25).
| Power Plant | (K) | (K) | , | , | |
| Doel 4 (Belgium), 1985. | 283 | 566 | 0.297 to 0.357 | 0.35000 | 0.31535 to 0.3545 |
| Almaraz II (nuclear pressurized water reactor) Spain | 290 | 600 | 0.315 to 0.373 | 0.34500 | 0.3306 to 0.36889 |
| Sizewell B (nuclear pressurized water reactor) U. K. | 288 | 581 | 0.302 to 0.361 | 0.36300 | 0.3198 to 0.35821 |
| Cofrentes (nuclear boiling water reactor) Spain | 289 | 562 | 0.282 to 0.343 | 0.34000 | 0.30238 to 0.34228 |
| Heysham (nuclear advanced gas cooled reactor) U. K. | 288 | 727 | 0.410 to 0.460 | 0.40000 | 0.41206 to 0.44568 |
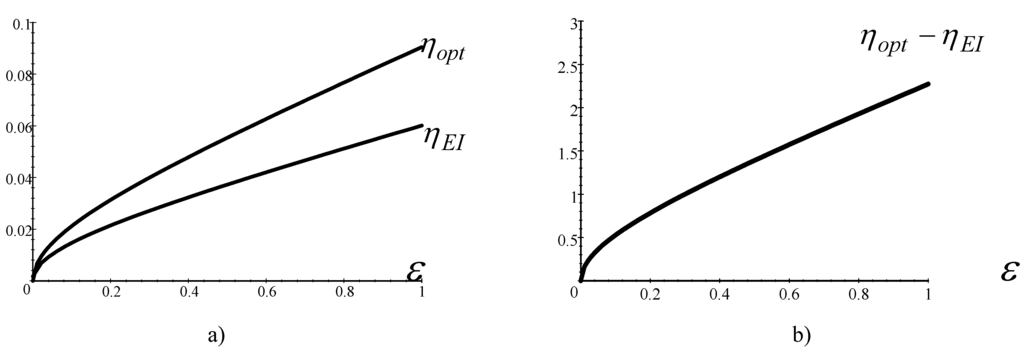
Figure 3.
Comparative graphics between efficiencies
and
. a) Difference of extreme values one by one for
. b) Difference
, in the extreme of range of values for I.
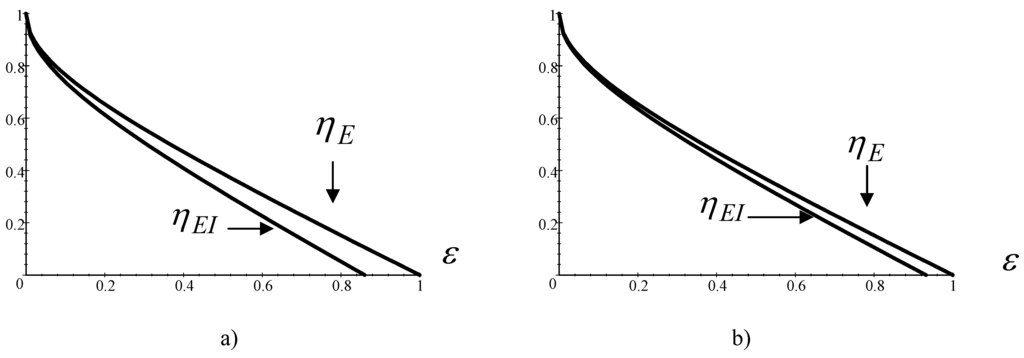
Figure 4.
Comparison graphics between efficiencies
and
. a) For
. b) For
.
4. More general expressions for power output and for ecological function
To introduce the compression ratio it is neccesary to take into account the time of the adiabatic processes in the cycle. There is not a direct procedure to calculate this time, so that it is assume a similar procedure used in references [9,15,16]. Suppousing the adiabatic processes as multiple of the time of isothermic processes, the time of the first and the second adiabatic processes respectively are,
The negative sign in
is introduced because the time has to be positive. Suppousing one mol of working substansce, now the total time of the cycle is,
The relation for volumes in adiabatic processes,
, is used. So the power output of the cycle could be written by taking into account the changes of variables shown in Equation (15) as,
and it could be verified that Equation (28) reduces to Equation (16) when
. Similarly ecological function can be written as,
Similar results found in references [9,15] could be obtained now. On other hand, it is interesting to point out that power output and ecological function can be obtained for instantaneous adiabats and a non-linear heat transfer law, like
, as
5. Concluding remarks
A first interesting feature of the above results is that from the procedure to build power output and ecological function used in references [9,15,16], one can obtain similar expressions of the corresponding power output and ecological function for case of a non endoreversible Curzon and Ahlborn cycle. One has to introduce appropiate changes to obtain Equation (16) and Equation (18) in case of instantaneous adiabats. Numerical results obtained by other authors could be improve as it is shown in Table 1. Even more one has to hope a more improve if it is taking into account compression ratio by using a linear approximation of efficiencies obtained from maximization of Equation (28) and Equation (29). In case of a non ideal gas as working substance is important to point out that parameter
appears by equation of state as was enphazised in reference [16] when the total heat is calculated. Also for case of non linear heat transfer law this parameter appears in a similar way. Notice that the Gutkowics-Krusin et al procedure [9] could be took as a methodology to take into account internal irreversibilities of the cycle. The relation of non-endoreversibilty parameter with physical quantities of power plants exceeds this paper, in which it is shown the plausibility of the propoused optimization method, and it deserves a special treatment in a further paper.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Dr. F. Angulo-Brown for valuble comments and suggestions. Also tanks to the reviwers for important suggestions to improve this paper.
References
- Curzon, F. L.; Ahlborn, B. Efficiency of a Carnot Engine at Maximum Power Output. Am. J. Phys. 1975, 43, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, P.; Andresen, B.; Berry, R.S. Thermodynamics in Finite Time. I. Potencials for Finite-time processes. Phys. Rev. A 1976, 15, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M. Optimal Configuration of a Class of Irreversible Heat Engines. I. Phys. Rev. A 1979, 19, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar]Optimal Configuration of a Class of Irreversible Heat Engines. II. Phys. Rev. A 1979, 19, 1277–1288.Optimal Configuration of an Irreversible Heat Engine with Fixed Compression Ratio. Phys. Rev. A 1980, 22, 1741–1752.
- De Vos, A. Efficiency of some Heat Engines at Maximum-power Conditions. Am. J. Phys. 1985, 53, 570–573. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yan, Z. Unified Description of Endoreversible Cycles. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 39, 4140–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, J. A Class of Irreversible Carnot Refrigeration Cycles with a General heat Transfer Law. J. Phys D: Appl. Phys. 1990, 23, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhan, E. Efficiency of Nonideal Carnot Engines with Friction and Heat Losses. Am. J. Phys. 2002, 70, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Entropy Generation Minimization: The New Thermodynamics of Finite-size Devices and Finite-time processes. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 1191–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkowics-Krusin, D.; Procaccia, I.; Ross, J. On the Efficiency of Rate Processes. Power and Effiency of Heat Engines. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 3898–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badescu, V. Optimal paths for minimizing lost avilable work during usual heat transferprocess. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2004, 29, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelkin, S.A.; Andresen, B.; Burzler, J.M.; Hoffman, K.H.; Tsirlin, A.M. Maximum power processfor multi-source endoreversible heat engines. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelkin, S.A.; Andresen, B.; Burzler, J.M.; Hoffman, K.H.; Tsirlin, A.M. Thermo-mechanical systems with several heat reservoirs: maximum power processes. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2005, 30, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Optimal configuraction of a clas of endoreversibleheat engines with linear phenomenological heat transfer law [q ∝ ∆(T−1)]. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 124907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, F. Endoreversible heat engines for maximum power output with fixed duration and radiative heat transfer law. Applied Energy 2007, 84, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladino-Luna, D.; de la Selva, S.M.T. The Ecological Efficiency of a Thermal Finite Time Engine. Rev. Mex. Fís. 2000, 46, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ladino-Luna, D. Van der Waals gas as working substance in a Curzon and Ahlborn-Novikov engine. Entropy 2005, 7, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]Ladino-Luna, D. Efficiency of a Curzon and Ahlborn engine with Dulong-Petit heat transfer law. Rev. Mex. Fís. 2003, 49, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Brown, F. An Ecological Optimization Criterion for Finite-time Heat Engines. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 7465–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z. Commente on “Ecological optimization criterion for finite time engines”. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Brown, F.; Árias-Hernández, F.A.; Páez-Hernández, R.T. A General Property of Non-endoreversible Thermal Cycles. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Kiang, R.L. Finite-time thermodynamic analisys of a Carnot engine with internal irreversibility. Int. J. Energy 1992, 17, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The Maximum Power Output and Maximum Efficiency of an Irreversible Carnot Heat Engine. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1994, 27, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar]The Efficiency of an Irreversible Combined Cycle at Maximum Specific Power Output. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 2818–2822.
- Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Ecological optimization of generalized irreversible Carnot engines. Applied Energy 2004, 77, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, X.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Exergy-based ecological optimization of linear phenomenological heat transfer law irreversible Carnot engines. Applied Energy 2006, 83, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. The ecological optimization of generalized irreversible Carnot engine with generalized heat transfer law. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2003, 24, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; .Sun, F.; Wu, C. Effect of heat transfer law on the ecological optimization of a generalized irreversible Carnot engine. Open System & Information Dynamics 2005, 12, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, F. Power, efficiency, entropy generation rate and ecological optimization for a class of generalized universal heat engine cycles. Applied Energy 2007, 84, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Árias-Hernández, L.A.; Angulo-Brown, F. A General Property of Endoreversible Termal Engines. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, S.; Roco, J.M.M.; Medina, A.; White, J.A.; Calvo-Hernández, A. Optimization of Heat Engines Including the Saving of Natural Resources and the Reduction of Termal Pollution. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Angulo-Brown, F.; Ares de Parga, G.; Arias-Hernández, L.A. A Variational Approach to Ecological-type Optimization Criteria for Finite-time Termal Engine Models. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2002, 35, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar]
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
