Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition Using SSA-EMS Algorithm for Feature Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Methods
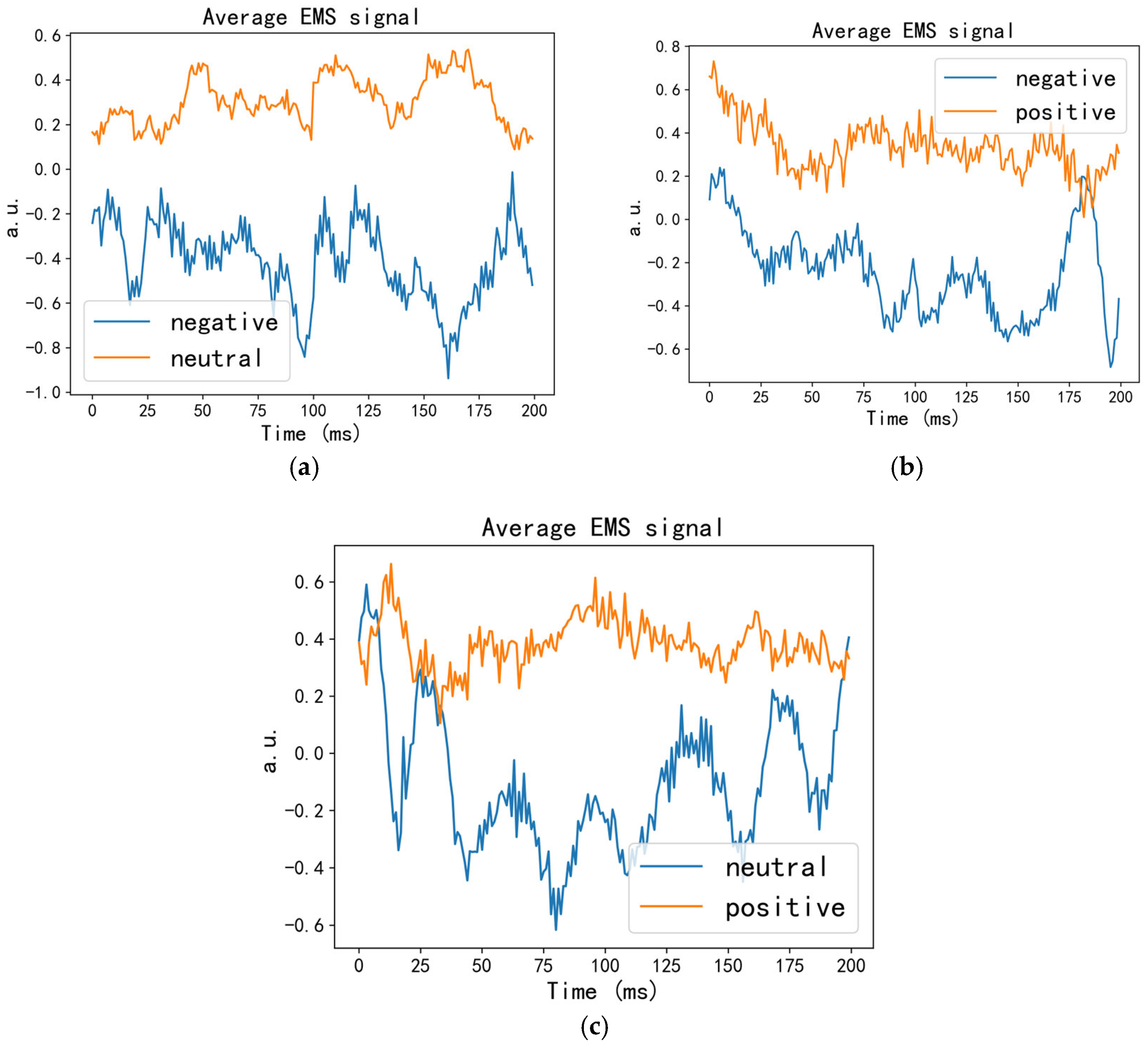
2.2.1. EMS Algorithm
2.2.2. SSA Algorithm
2.2.3. Feature Extraction Process Based on SSA-EMS Algorithm
- 1.
- Spatial Filter Learning
- 2.
- Data Projection—mutual information optimization
- 3.
- Construction of Stable Representations—Entropy rate convergence
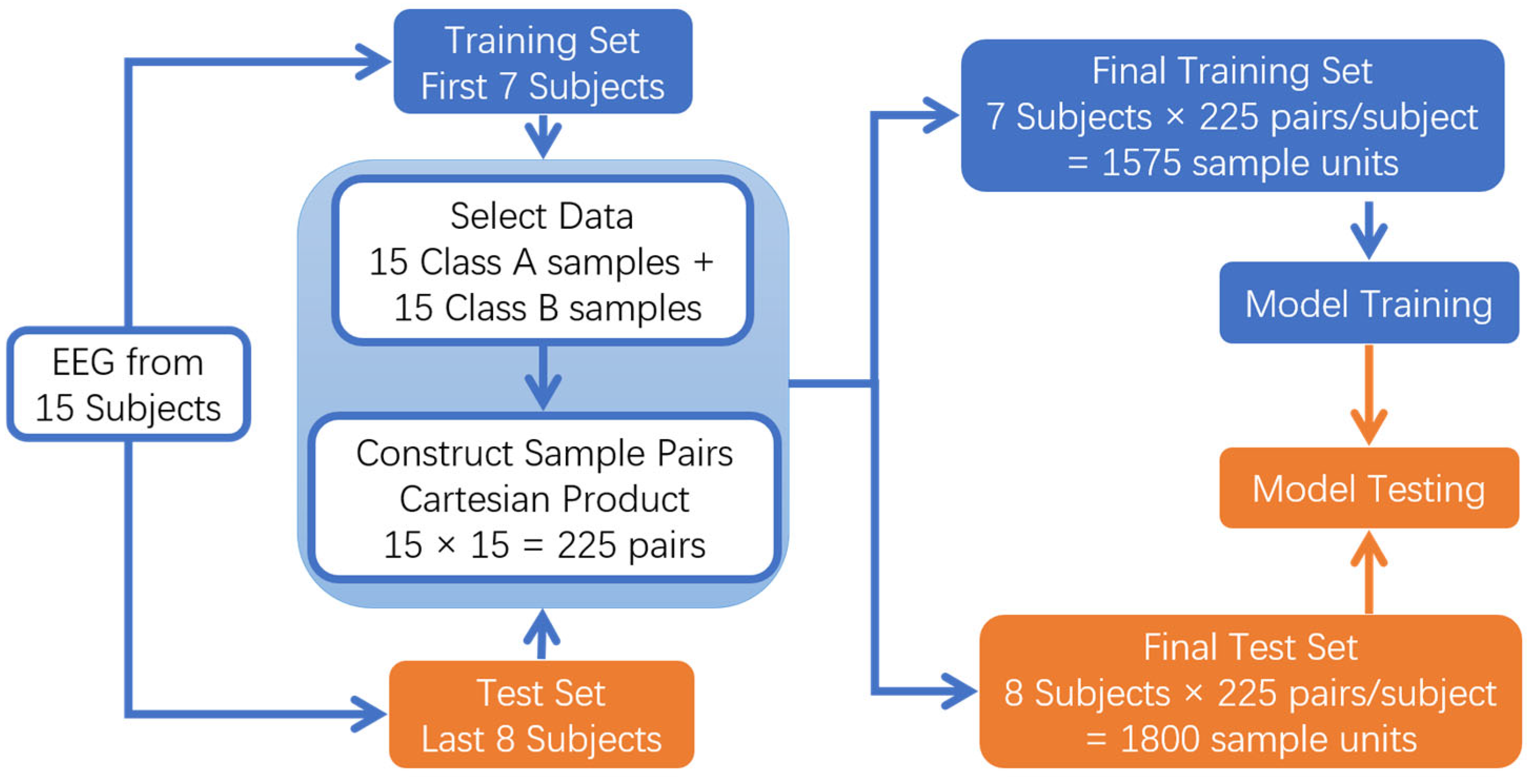
2.2.4. Cross-Subject Data Processing in Seed Emotional EEG
- 1.
- Cross-subject sample combination data processing
- 2.
- Subject-Independent Evaluation Method
3. Results
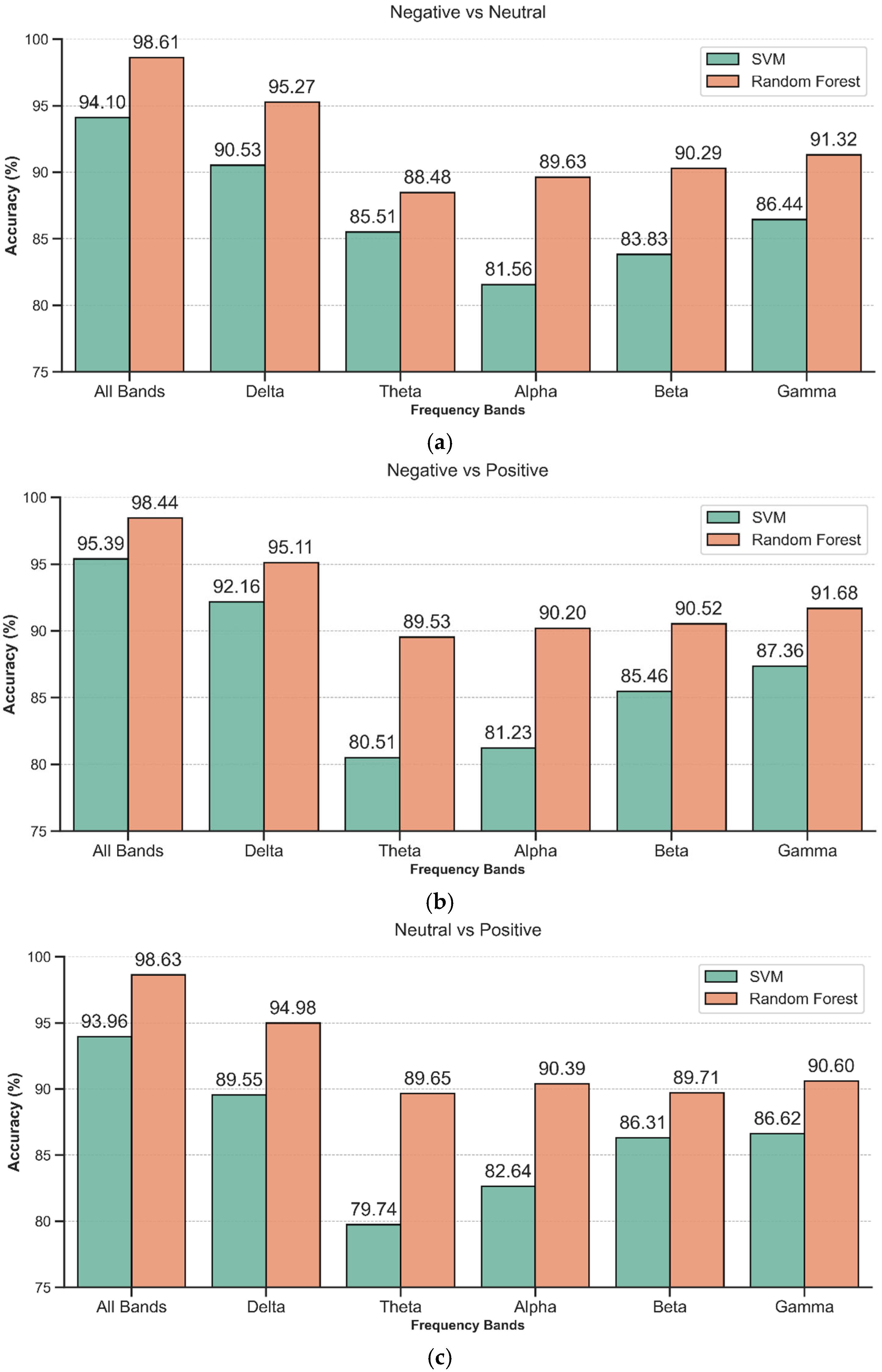
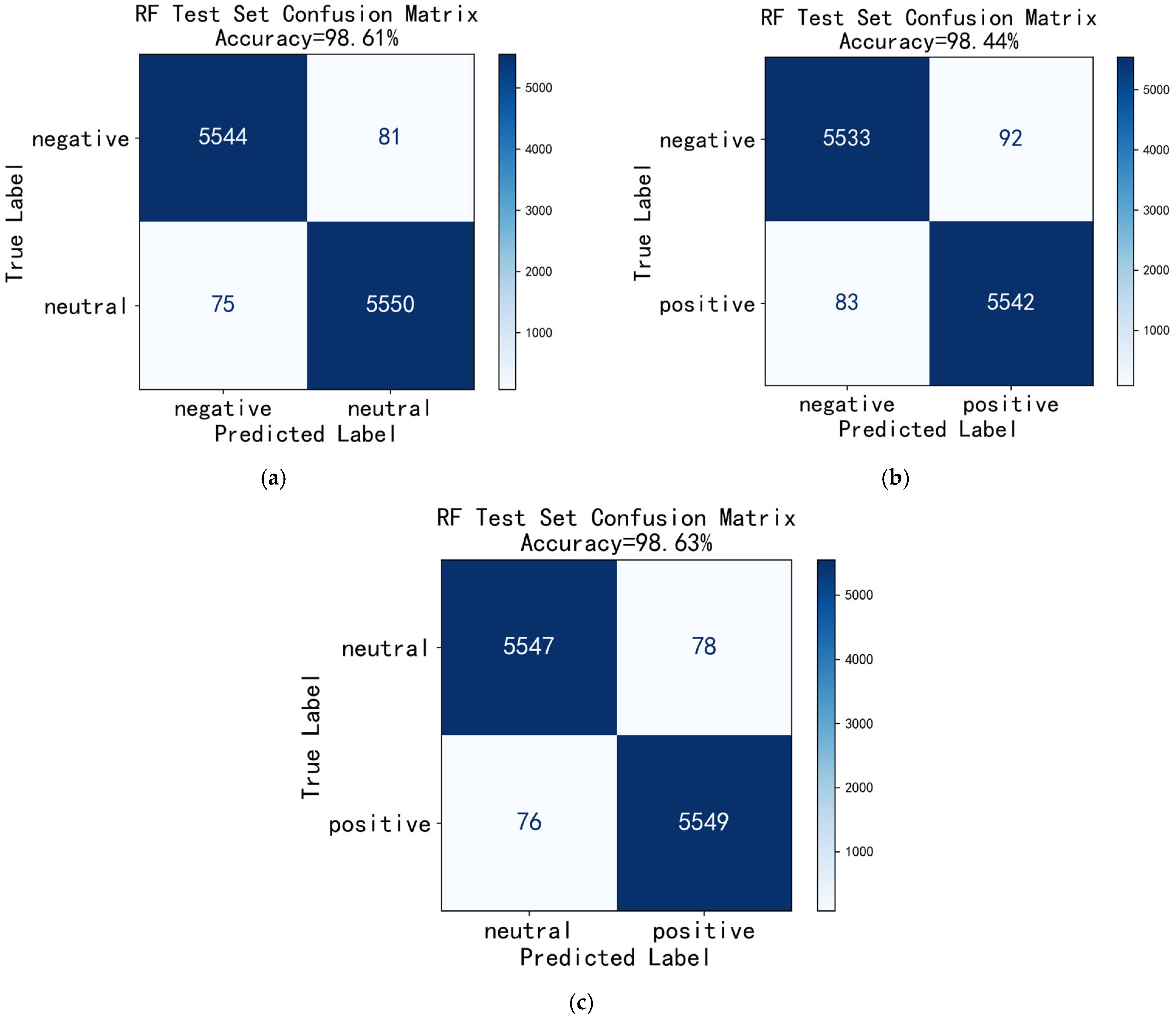
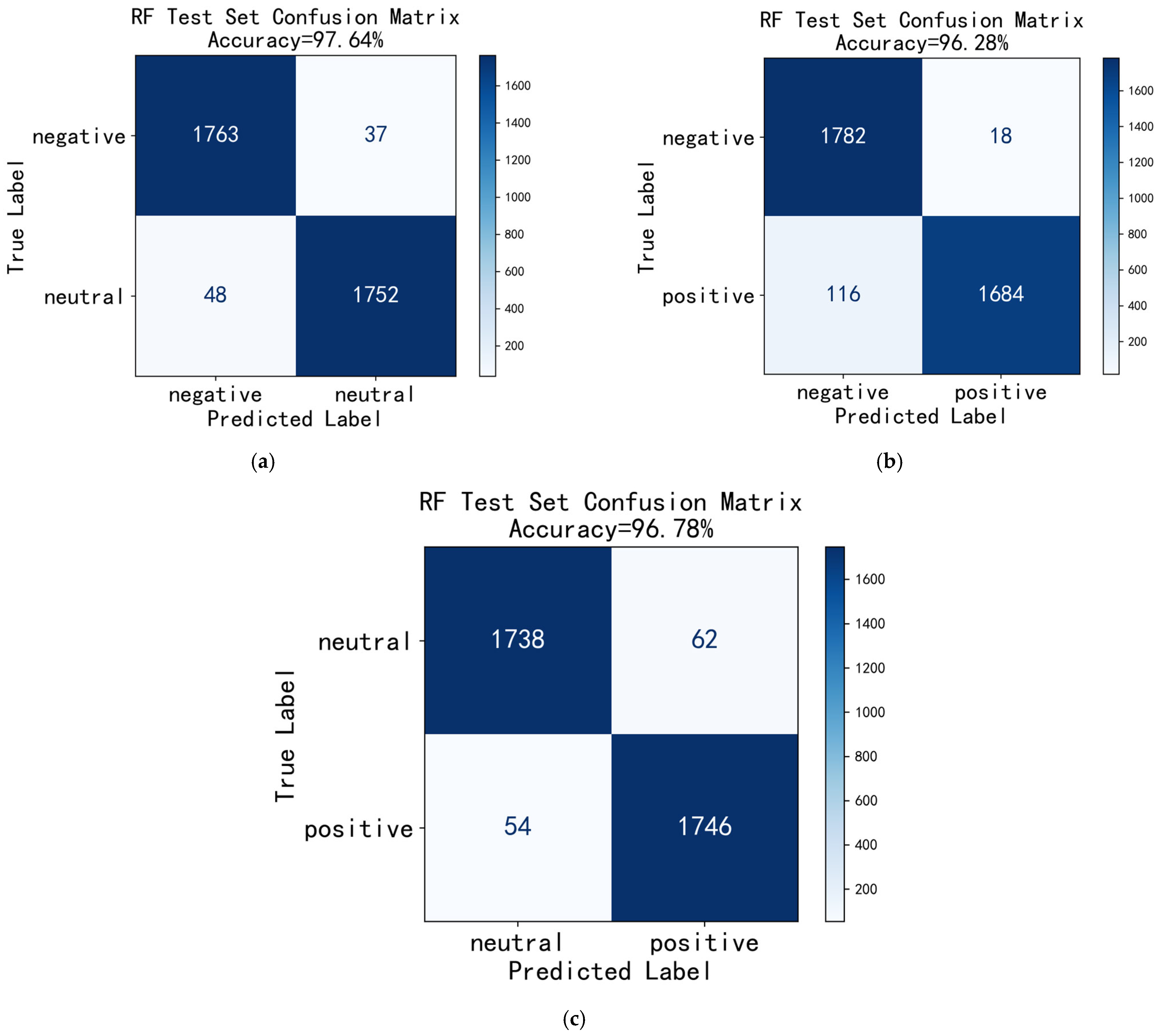
3.1. Cross-Subject Sample Combination Classification
3.2. Classification Results of “Subject-Independent” Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthunayagom, P.; Subhajini, A.C. Deciphering Feelings: Exploring EEG Data for Human Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Sustainable Communication Networks and Application (ICSCNA), Theni, India, 11–13 December 2024; pp. 1181–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, J. Enhancing Emotion Recognition in EEG Signals using Fractional Fourier Transform. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 17th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Suzhou, China, 28–31 October 2024; pp. 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Gkintoni, E.; Aroutzidis, A.; Antonopoulou, H.; Halkiopoulos, C. From Neural Networks to Emotional Networks: A Systematic Review of EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Cognitive Neuroscience and Real-World Applications. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.-E.-N.; Sarkar, A.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, M.B.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Moni, M.A. Recognition of human emotions using EEG signals: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hbibi, B.; Khiari, C.; Wirsing, K.; Mili, L.; Baccar, K.; Mami, A. Identifying and Removing Interference and Artifacts in Multifractal Signals With Application to EEG Signals. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 119090–119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiya, S.; Alhanai, T.; Ghassemi, M.M. Artifact Detection and Correction in EEG data: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Virtual Event, 4–6 May 2021; pp. 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Jmail, N.; Gavaret, M.; Wendling, F.; Kachouri, A.; Hamadi, G.; Badier, J.M.; Bénar, C.G. A comparison of methods for separation of transient and oscillatory signals in EEG. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 199, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, X.; Xia, L.; Ma, H.; Tan, T.-P. Domain adaptation spatial feature perception neural network for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1471634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; An, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. DA-CapsNet: A multi-branch capsule network based on adversarial domain adaption for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. Knowl. Based Syst. 2023, 283, 111137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; Yang, K.; Sang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B. A Random Forest Weights and 4-Dimensional Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network for EEG Based Emotion Recognition. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 39549–39563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Shoeibi, A.; Khodatars, M.; Bagherzadeh, S.; Shalbaf, A.; López-García, D.; Górriz, J.M.; Acharya, U.R. Emotion recognition in EEG signals using deep learning methods: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 165, 107450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, C.L.P.; Zhang, T. GDDN: Graph Domain Disentanglement Network for Generalizable EEG Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 15, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Y. DMMR: Cross-Subject Domain Generalization for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition via Denoising Mixed Mutual Reconstruction. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, A.; Li, X.; Lv, Z. Cross-Subject Emotion Recognition with CT-ELCAN: Leveraging Cross-Modal Transformer and Enhanced Learning-Classify Adversarial Network. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, L.; Zu, W.; Feng, W.; Hang, W. Adaptive deep feature representation learning for cross-subject EEG decoding. BMC Bioinform. 2024, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuragi, A.; Sisodia, D.S.; Pachori, R.B. EEG-based cross-subject emotion recognition using Fourier-Bessel series expansion based empirical wavelet transform and NCA feature selection method. Inf. Sci. 2022, 610, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Ma, R.; Wang, Y. Functional connectivity-enhanced feature-grouped attention network for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 283, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, H.; Kong, W.; Nie, F.; Lu, B.-L.; Cichocki, A. Joint EEG Feature Transfer and Semisupervised Cross-Subject Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 8104–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurger, A.; Marti, S.; Dehaene, S. Reducing multi-sensor data to a single time course that reveals experimental effects. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.-L.; Lu, B.-L. Investigating Critical Frequency Bands and Channels for EEG-based Emotion Recognition with Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. (IEEE TAMD) 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.N.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Differential Entropy Feature for EEG-based Emotion Classification. In Proceedings of the 6th International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2013; pp. 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H. Singular Spectrum Analysis: Methodology and Comparison. J. Data Sci. 2007, 5, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.C.; Tuy, P.G.S.E.; Mahmoudvand, R. Randomized singular spectrum analysis for long time series. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2018, 88, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, K.; Nose-Togawa, N. An Adaptive Orthogonal SSA Decomposition Algorithm for a Time Series. Adv. Data Sci. Adapt. Anal. 2018, 10, 1850002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, A.; Dahleh, M.A.; Mann, S.; Shah, D. SAMoSSA: Multivariate Singular Spectrum Analysis with Stochastic Autoregressive Noise. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.16491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanseverino, C.M.R. Singular spectrum analysis and forecasting of failure time series. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 114, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golyandina, N.; Zhigljavsky, A.A. SSA for Forecasting, Interpolation, Filtering and Estimation; Singular Spectrum Analysis for Time Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbarzadeh, M.; Aminghafari, M. A New Hybrid-Multiscale SSA Prediction of Non-Stationary Time Series. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2016, 15, 1650005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmouche, J.; Fourer, D.; Auger, F.; Borgnat, P.; Flandrin, P. The Sliding Singular Spectrum Analysis: A Data-Driven Nonstationary Signal Decomposition Tool. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leles, M.C.R.; Sansão, J.P.H.; Mozelli, L.A.; Guimarães, H.N. Improving reconstruction of time-series based in Singular Spectrum Analysis: A segmentation approach. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 77, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenberger, C.M.A.; Ertel, W.; Schwenker, F.; Schneider, M. Singular Spectrum Analysis and Circulant Maximum Variance Frames. Adv. Data Sci. Adapt. Anal. 2022, 14, 2250008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudvand, R.; Najari, N.; Zokaei, M. On the Optimal Parameters for Reconstruction and Forecasting in Singular Spectrum Analysis. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 2013, 42, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golyandina, N.; Nekrutkin, V.; Zhigljavsky, A.A. Analysis of Time Series Structure—SSA and Related Techniques. In Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Xie, H.-B. Denoising Nonlinear Time Series Using Singular Spectrum Analysis and Fuzzy Entropy. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2016, 33, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzi, P.; Karel, J.M.H.; Meste, O.; Peeters, R.L.M. Singular Spectrum Decomposition: A New Method for Time Series Decomposition. Adv. Data Sci. Adapt. Anal. 2014, 6, 1450011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramfort, A.; Luessi, M.; Larson, E.; Engemann, D.A.; Strohmeier, D.; Brodbeck, C.; Goj, R.; Jas, M.; Brooks, T.; Parkkonen, L.; et al. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Ki, M.; Hong, K.; Byun, H. Subject-Independent EEG-based Emotion Recognition using Adversarial Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hamel, L. Model Assessment with ROC Curves. In Encyclopedia of Data Warehousing and Mining; 2009; Available online: https://homepage.cs.uri.edu/faculty/hamel/pubs/hamel-roc.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Fahmy Amin, M. Confusion Matrix in Binary Classification Problems: A Step-by-Step Tutorial. J. Eng. Res. 2022, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; He, R.; Yang, S.; Guo, L. EEG-based cross-subject emotion recognition using multi-source domain transfer learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 84, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Ng, M.K.-P.; Qian, T.; Wang, S. Multi-modal Mood Reader: Pre-trained Model Empowers Cross-Subject Emotion Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.19373. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Kim, E.Y. Interpretable Cross-Subject EEG-Based Emotion Recognition Using Channel-Wise Features. Sensors 2020, 20, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonacci, Y.; Toppi, J.; Pietrabissa, A.; Anzolin, A.; Astolfi, L. Measuring Connectivity in Linear Multivariate Processes with Penalized Regression Techniques. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 30638–30652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Chen, J. Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition Using SSA-EMS Algorithm for Feature Extraction. Entropy 2025, 27, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090986
Lu Y, Chen J. Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition Using SSA-EMS Algorithm for Feature Extraction. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090986
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yuan, and Jingying Chen. 2025. "Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition Using SSA-EMS Algorithm for Feature Extraction" Entropy 27, no. 9: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090986
APA StyleLu, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Cross-Subject EEG Emotion Recognition Using SSA-EMS Algorithm for Feature Extraction. Entropy, 27(9), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090986





