A DREM-Based Approach for the Identification of Chaotic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
Preamble
- Consider a smooth nonlinear system, described by the state vector and by the output vector , of the formwhere is a smooth vector function and is a constant parameter vector. Let be the time derivative of the vector Y. We say that the vector state X is algebraically observable if it can be uniquely expressed asfor some integer j and for some smooth function .
- Moreover, if the vector of parameters, P, satisfies the linear relationwhere and are, respectively, and smooth matrices, then P is said to be algebraically linearly identifiable with respect to the output vector Y.
2. Problem Formulation
- Regarding the parametric convergence, even when it is not possible to mathematically prove it, there exists strong evidence that allows us to claim that we can almost always accomplish convergence to the actual parameter values. The latter also holds for non-chaotic behavior.
- The parameter estimation convergence time can be as small as needed if we choose a suitable identification parameter, as we show in the following sections.
- This parameter identification problem has been previously tackled using the gradient descent and the least-squares methods. However, these methods only ensure parameter estimation convergence as time approaches infinity, provided the system exhibits chaotic behavior.
3. The Identification Procedure
4. Output Identification of Some Oscillatory Systems
4.1. Duffing System
4.2. Genecio System
4.3. The Van der Pol oscillator
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luviano-Juarez, A.; Cortes-Romero, J.; Sira-Ramirez, H. Synchronization of chaotic oscillators by means of generalized proportional integral observers. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2010, 20, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijberts, H.; Nijmeijer, H. Nonlinear chaos control and synchronization. In Handbook of Chaos Control; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 719–749. [Google Scholar]
- Alligood, K.T.; Sauer, T.D.; Yorke, J.A.; Chillingworth, D. Chaos: An introduction to dynamical systems. SIAM Rev. 1998, 40, 732. [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel, A.; Weiss, J.N.; Ditto, W.L.; Spano, M.L. Chaos control of cardiac arrhythmias. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1995, 5, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Escobar, M.A.; Meranza-Castillón, M.O.; López-Gutiérrez, R.M.; Cruz-Hernández, C. Suggested integral analysis for chaos-based image cryptosystems. Entropy 2019, 21, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidouche, B.; Guesmi, K.; Essounbouli, N. Mastering chaos: A review. Annu. Rev. Control 2024, 58, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijberts, H.; Nijmeijer, H.; Willems, R. System identification in communication with chaotic systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, U.; Hasler, M.; Schwarz, W. Communication by chaotic signals: The inverse system approach. In Proceedings of the ISCAS’95-International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 April–3 May 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 680–683. [Google Scholar]
- Poznyak, A.S.; Yu, W.; Sanchez, E.N.; Sira-Ramirez, H. Robust identification by dynamic neural networks using sliding mode learning. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1998, 38, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, R.M.; Luviano-Juárez, A.; Rincón-Pasaye, J.J. On nonlinear observers: A differential algebraic approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 American Control Conference, New York, NY, USA, 11–13 July 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1682–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Femat, R.; Alvarez-Ramírez, J.; Fernández-Anaya, G. Adaptive synchronization of high-order chaotic systems: A feedback with low-order parametrization. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2000, 139, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Guerra, R.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Cruz-Hernández, C.; SÁNCHEZ-LÓPEZ, C. Chaotic communication system using Chua’s oscillators realized with CCII+ s. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2009, 19, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, H.; Renson, L. Noninvasive adaptive control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown parameters. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2025, 24, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X. Generalized synchronization and parameters identification of different-dimensional chaotic systems in the complex field. Fractals 2021, 29, 2150081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliess, M.; Sira-Ramirez, H. Control via state estimations of some nonlinear systems. In Proceedings of the Ifac Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systtems (Nolcos 2004), Stuttgart, Germany, 1–3 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fliess, M.; Sira-Ramírez, H. An algebraic framework for linear identification. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 2003, 9, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar Ibanez, C.; Sira-Ramírez, H.; Jorge Sanchez, H. An algebraic approach for the reconstruction of Chua’s system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2008, 18, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimassi, H.; Loría, A. Adaptive unknown-input observers-based synchronization of chaotic systems for telecommunication. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2010, 58, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ibáñez, C.; Herrera, J.S.; Garrido-Moctezuma, R. Parametric estimation of the Duffing system by using a modified gradient algorithm. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 372, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ibáñez, C.; Suarez-Castanon, M.; Sira-Ramírez, H. Control of the Chua’s System based on a Differential Flatness Approach. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2004, 14, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-López, R.; Femat, R.; Martínez-Guerra, R. Importance of chaos synchronization on technology and science. In Chaos Synchronization and Cryptography for Secure Communications: Applications for Encryption; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 210–246. [Google Scholar]
- Modares, H.; Alfi, A.; Fateh, M.M. Parameter identification of chaotic dynamic systems through an improved particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3714–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfi, A. Particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamic inertia weight for online parameter identification applied to Lorenz chaotic system. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2012, 8, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, B. Parameter estimation for chaotic systems by particle swarm optimization. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2007, 34, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnur, R. Synchronization-based approach for estimating all model parameters of chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 027204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.; Nichols, J.; Virgin, L. Parameter estimation for chaotic systems using a geometric approach: Theory and experiment. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 70, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, M. Parameter estimation for chaotic systems by hybrid differential evolution algorithm and artificial bee colony algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 77, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Cao, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhangzhong, L.; Zheng, W.; Wang, L. Parameter estimation of Lorenz chaotic system based on a hybrid Jaya-Powell algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 20514–20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ibañez, C.; García-Canseco, E.; Martínez-García, R.; Martínez-García, J.C.; Suarez-Castañon, M.S. An I&I-based observer to solve the output-feedback synchronization problem for a class of chaotic systems. Asian J. Control 2018, 20, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannis, D.; Astolfi, A.; Ortega, R.; Hilairet, M. A nonlinear tracking controller for voltage-fed induction motors with uncertain load torque. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2009, 17, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, A.; Ortega, R. Immersion and invariance: A new tool for stabilization and adaptive control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2003, 48, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylev, D.N.; Doria-Cerezo, A.; Pyrkin, A.A.; Bobtsov, A.A.; Ortega, R. A new approach for flux and rotor resistance estimation of induction motors. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobtsov, A.; Nikolaev, N.; Ortega, R.; Efimov, D. State observation of affine-in-the-states time-varying systems with unknown parameters and delayed measurements. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.; Bobtsov, A.; Pyrkin, A.; Aranovskiy, S. A parameter estimation approach to state observation of nonlinear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 2015, 85, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranovskiy, S.; Bobtsov, A.; Ortega, R.; Pyrkin, A. Parameters estimation via dynamic regressor extension and mixing. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 6971–6976. [Google Scholar]
- Astolfi, A.; Karagiannis, D.; Ortega, R. Nonlinear and Adaptive Control with Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 187. [Google Scholar]
- Sira-Ramirez, H.; Fliess, M. An algebraic state estimation approach for the recovery of chaotically encrypted messages. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2006, 16, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guerra, R.; Yu, W. Chaotic synchronization and secure communication via sliding-mode observer. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2008, 18, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.; Aranovskiy, S.; Pyrkin, A.A.; Astolfi, A.; Bobtsov, A.A. New results on parameter estimation via dynamic regressor extension and mixing: Continuous and discrete-time cases. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 66, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, I.D.; Lozano, R.; M’Saad, M.; Karimi, A. Adaptive Control: Algorithms, Analysis and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear output-feedback tracking using high-gain observer and variable structure control. Automatica 1997, 33, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K.; Praly, L. High-gain observers in nonlinear feedback control. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2014, 24, 993–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genesio, R.; Tesi, A. Harmonic balance methods for the analysis of chaotic dynamics in nonlinear systems. Automatica 1992, 28, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Robust exact differentiation via sliding mode technique. Automatica 1998, 34, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Second-order sliding-mode observer for mechanical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
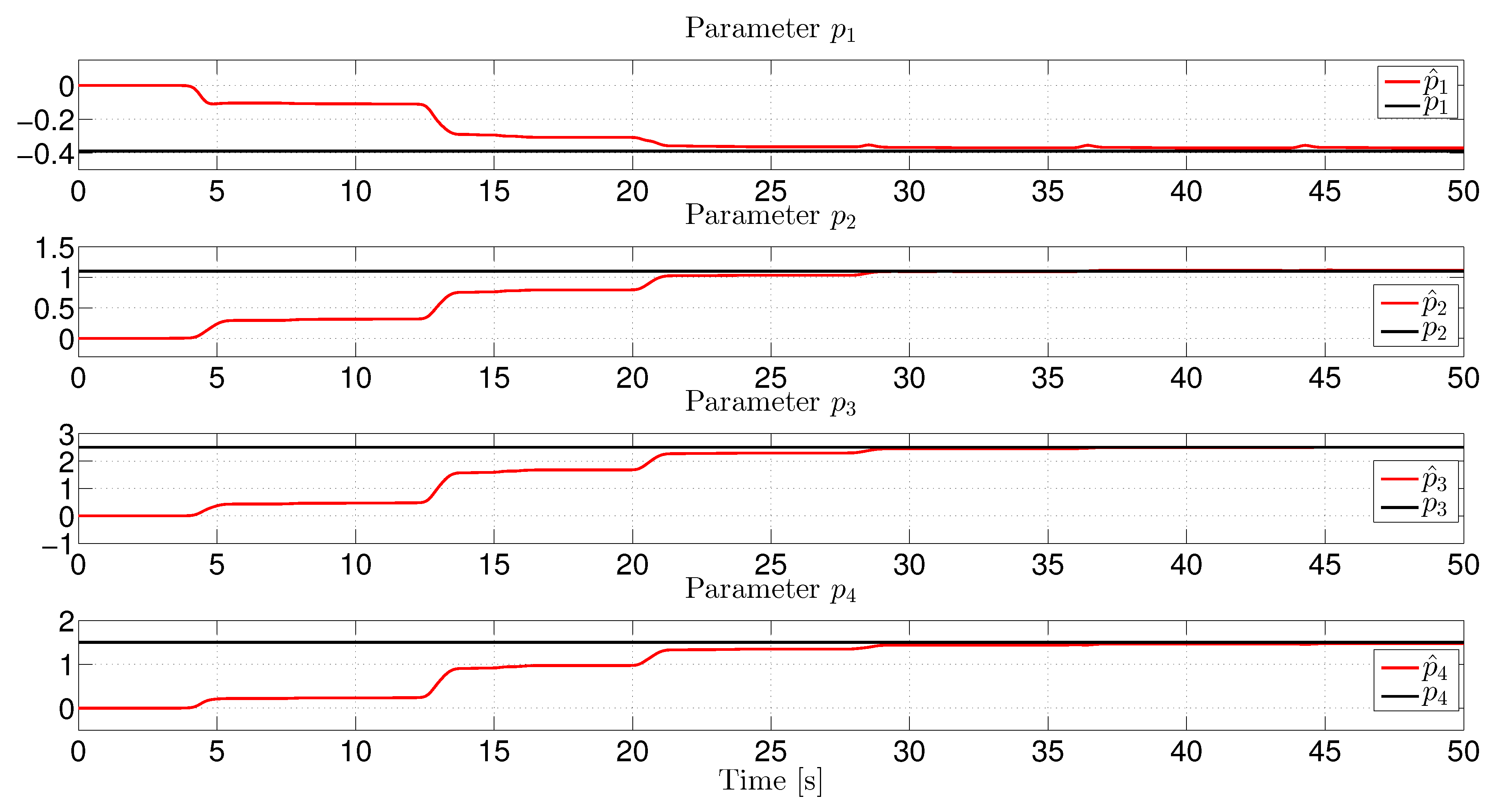
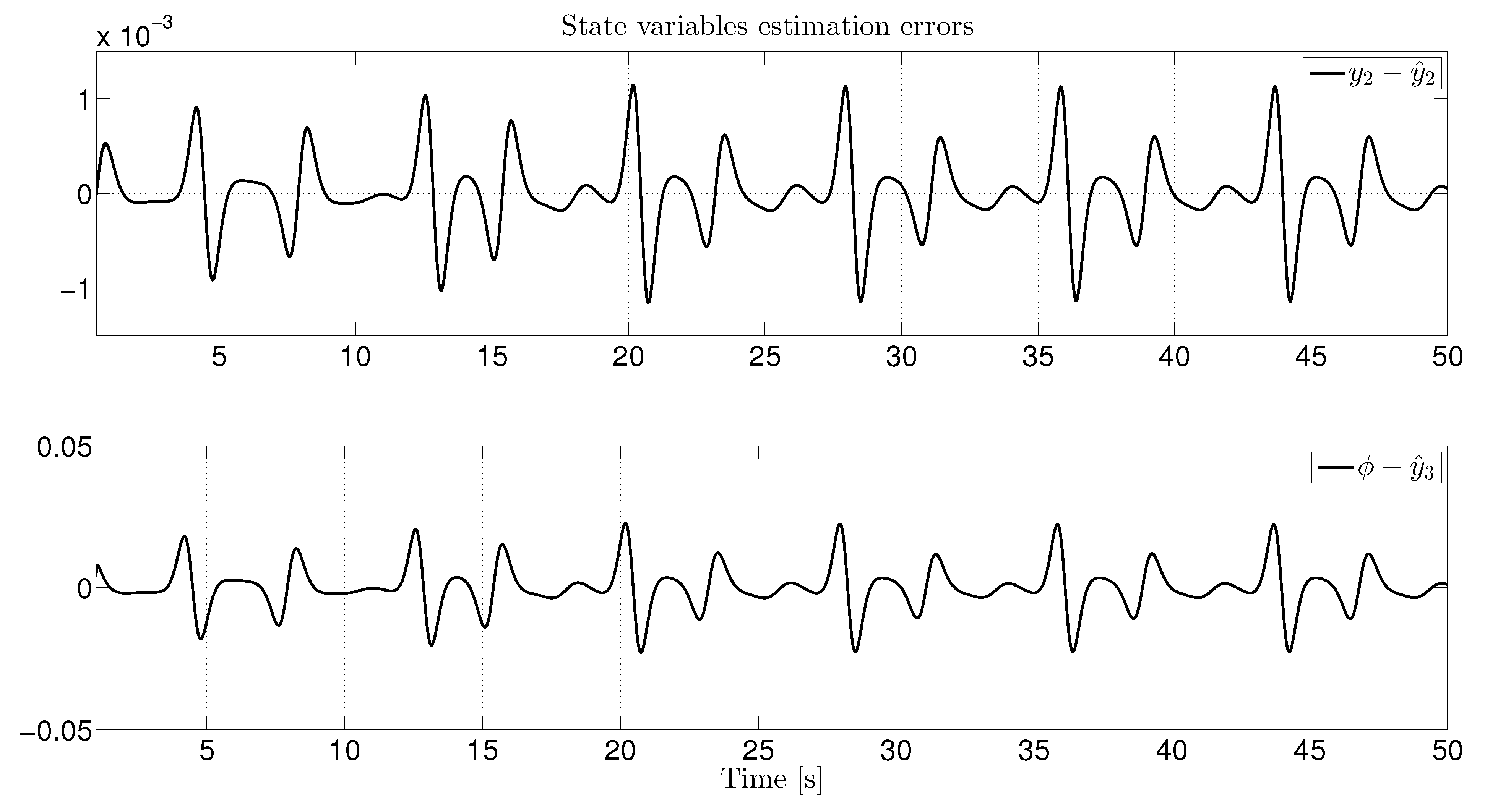
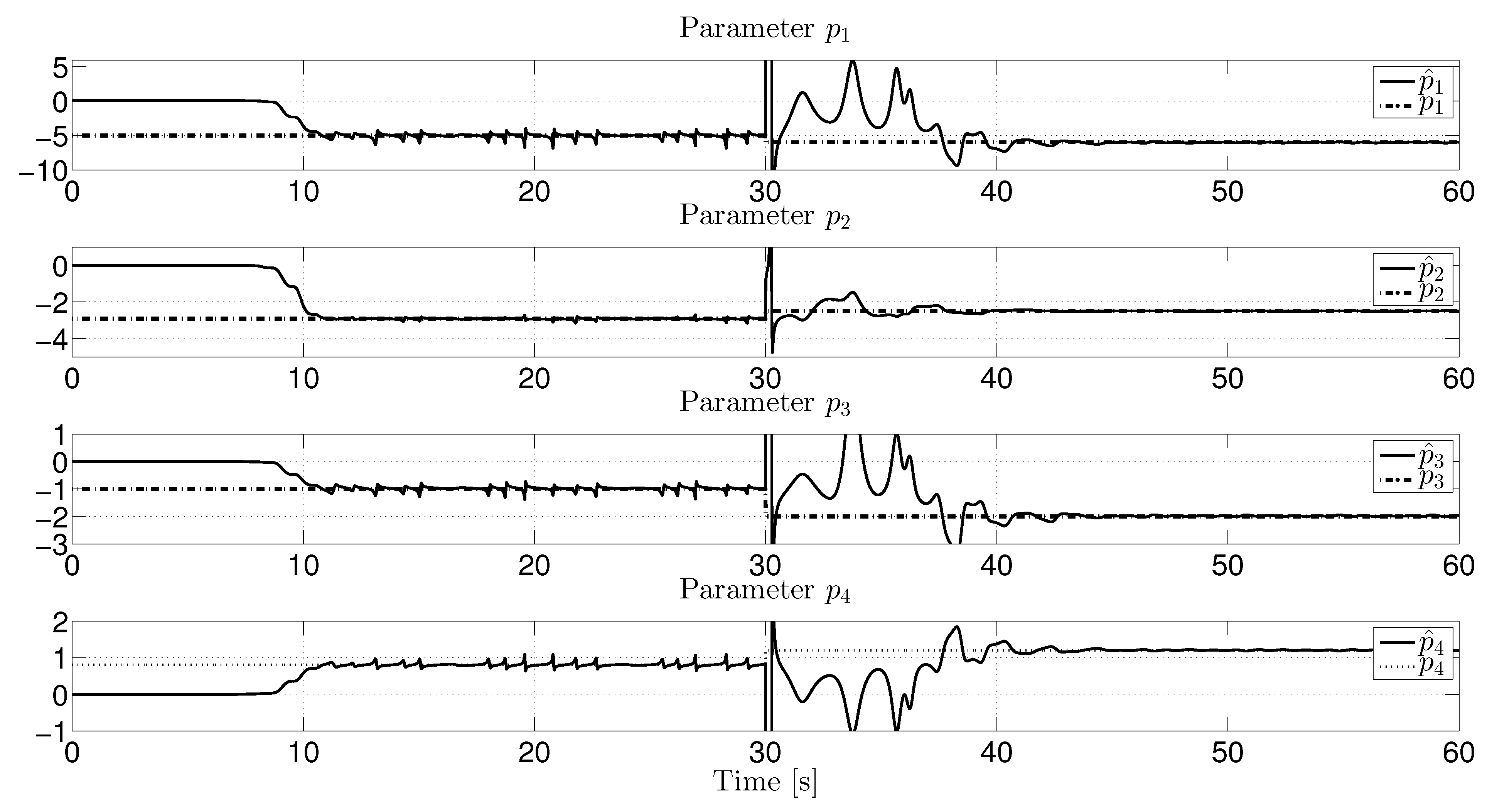
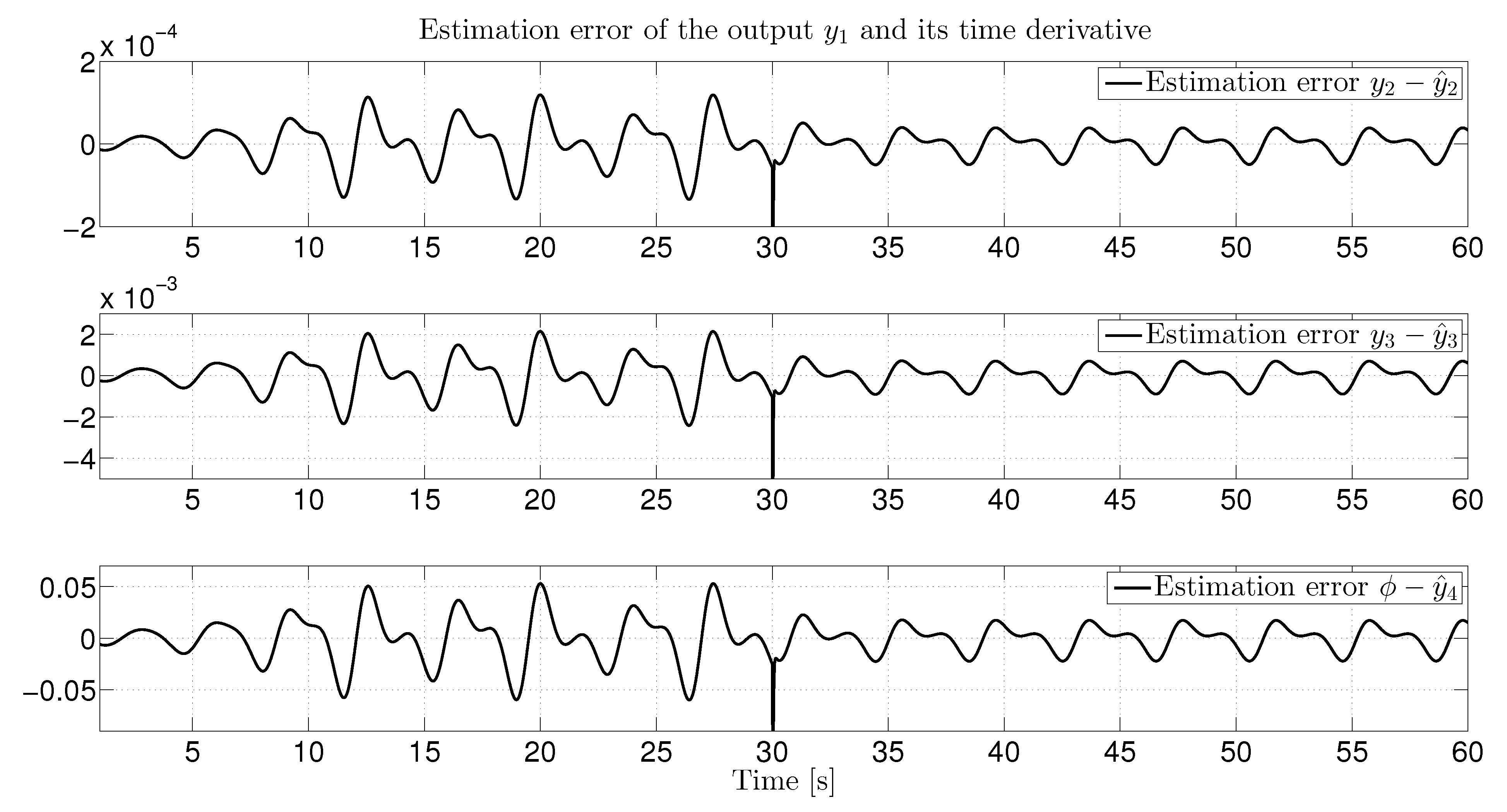
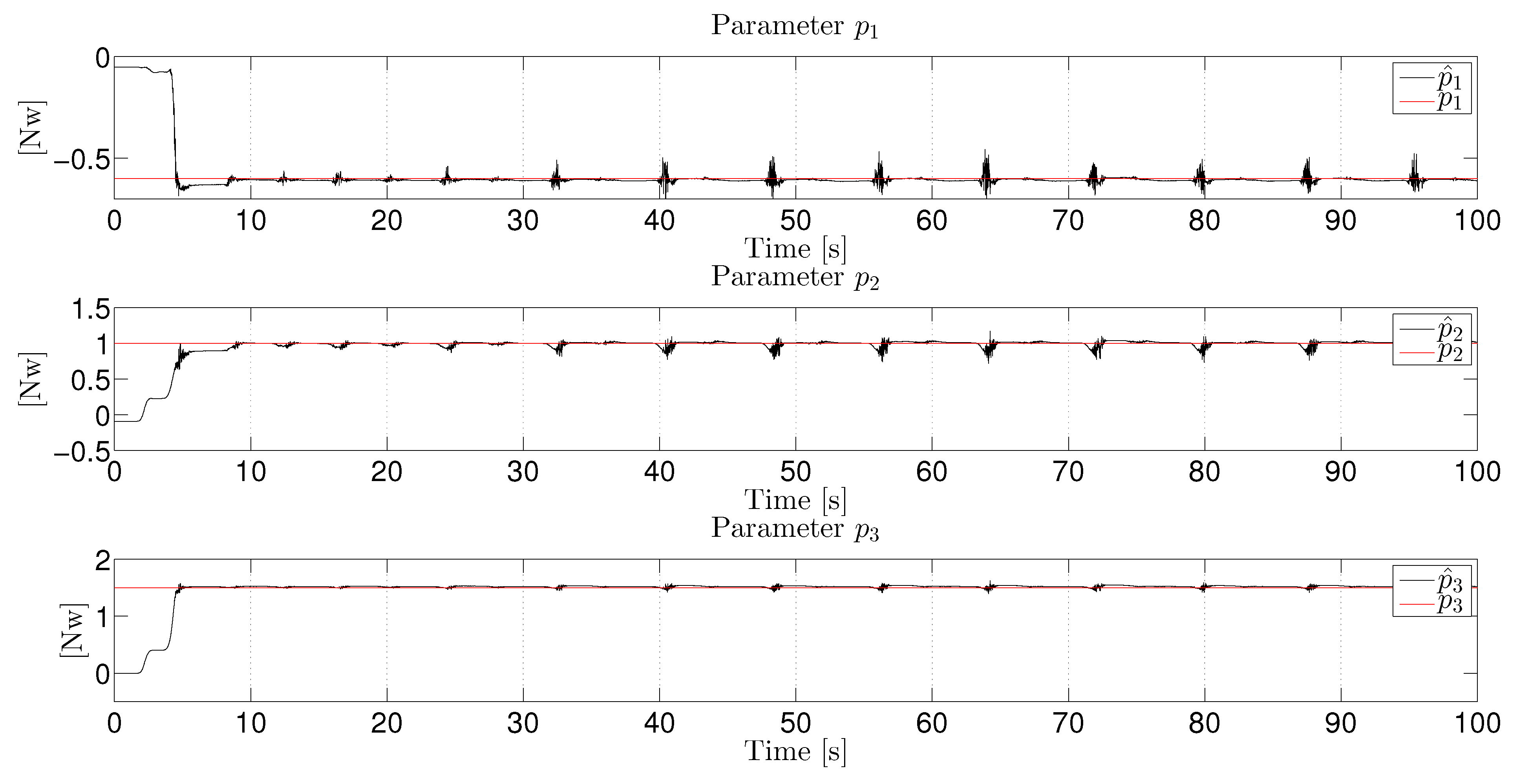
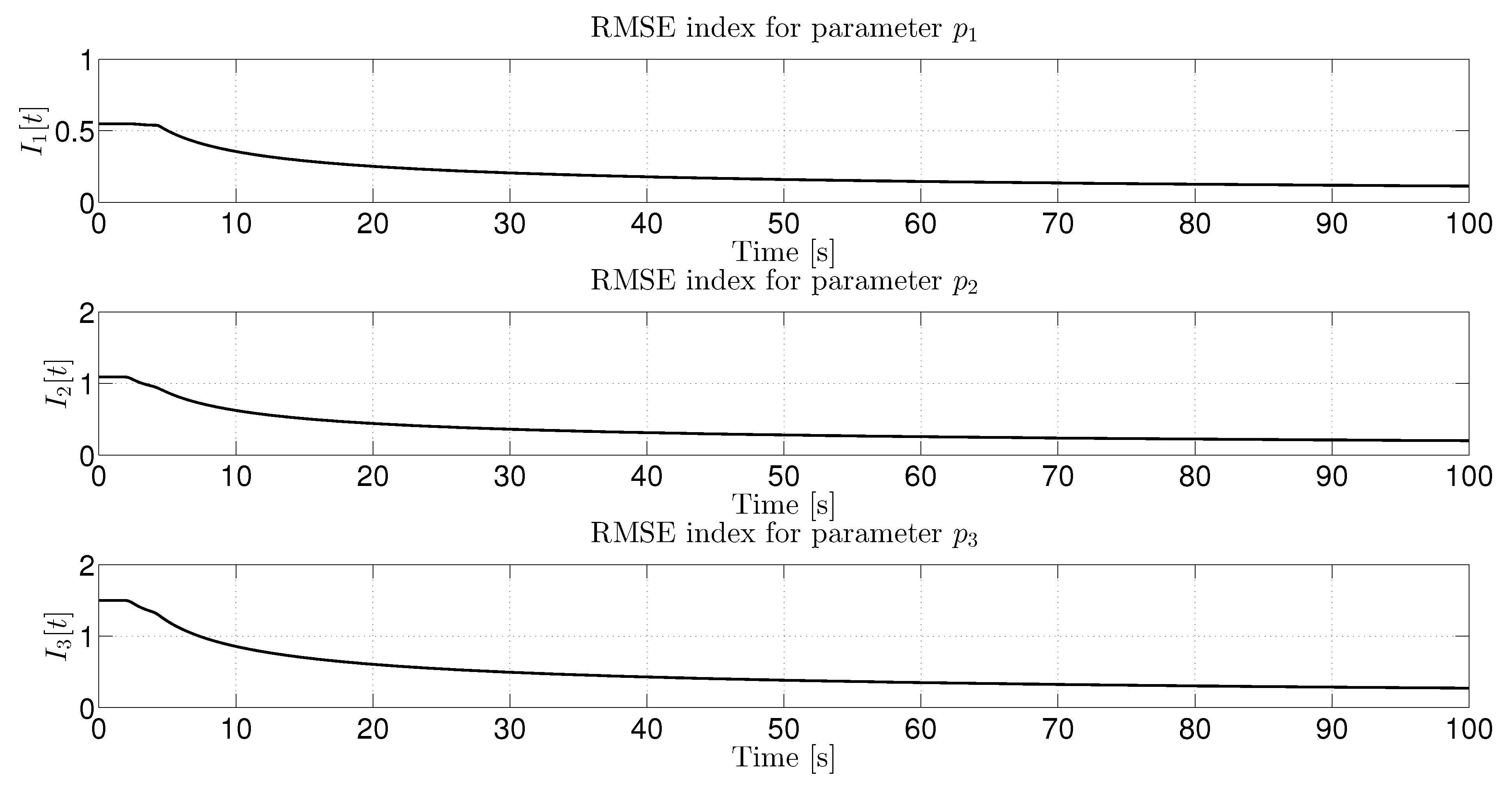
| Parameter Estimation Errors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oscillatory System | ||||
| Duffing | ||||
| Genesio | ||||
| Van der Pol | N/A | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar-Ibanez, C.; Suarez-Castanon, M.S.; Saldivar, B.; Valdez-Rodríguez, J.E.; García-Canseco, E. A DREM-Based Approach for the Identification of Chaotic Systems. Entropy 2025, 27, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090971
Aguilar-Ibanez C, Suarez-Castanon MS, Saldivar B, Valdez-Rodríguez JE, García-Canseco E. A DREM-Based Approach for the Identification of Chaotic Systems. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090971
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar-Ibanez, Carlos, Miguel S. Suarez-Castanon, Belem Saldivar, José E. Valdez-Rodríguez, and Eloísa García-Canseco. 2025. "A DREM-Based Approach for the Identification of Chaotic Systems" Entropy 27, no. 9: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090971
APA StyleAguilar-Ibanez, C., Suarez-Castanon, M. S., Saldivar, B., Valdez-Rodríguez, J. E., & García-Canseco, E. (2025). A DREM-Based Approach for the Identification of Chaotic Systems. Entropy, 27(9), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090971






