Information Dynamics of the Mother–Fetus System Using Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Derived from Heart Sounds: A Longitudinal Study from Early Pregnancy to Postpartum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Measurement Environment
2.3. Heart-Sound Data Collection
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Lyapunov Exponent
2.6. KS Entropy Analysis
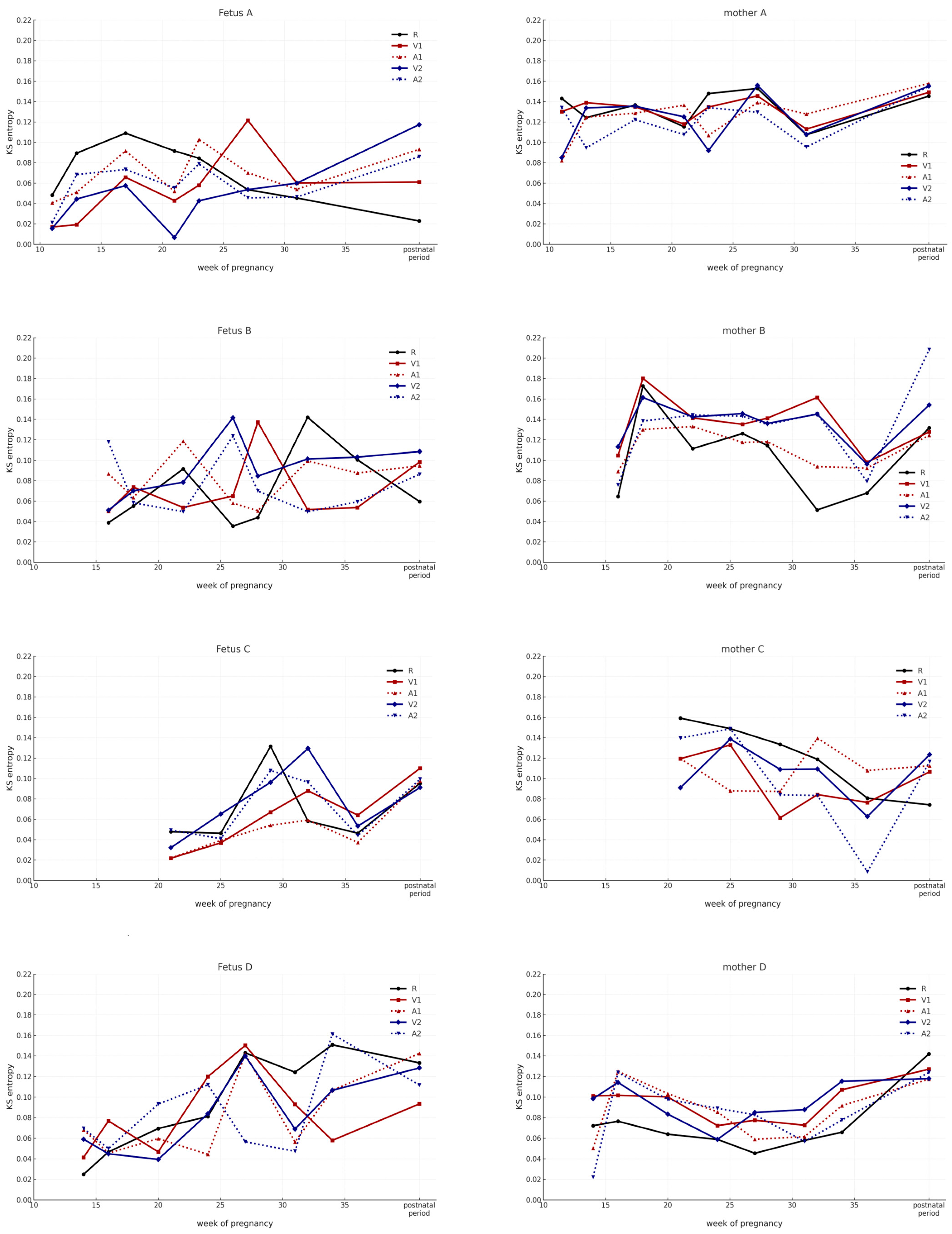
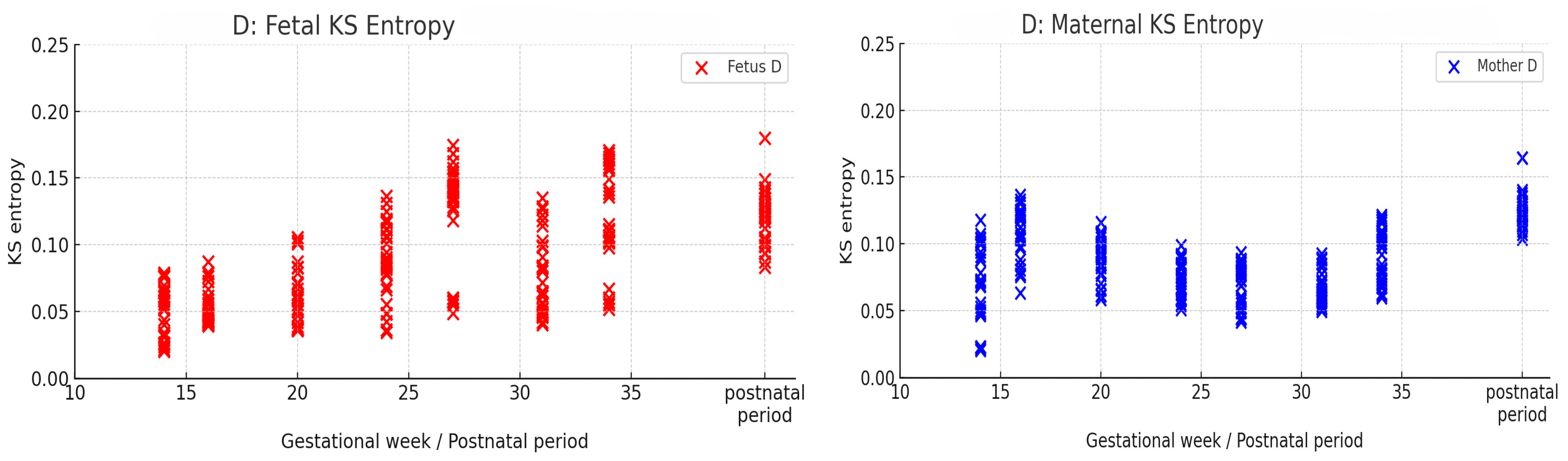
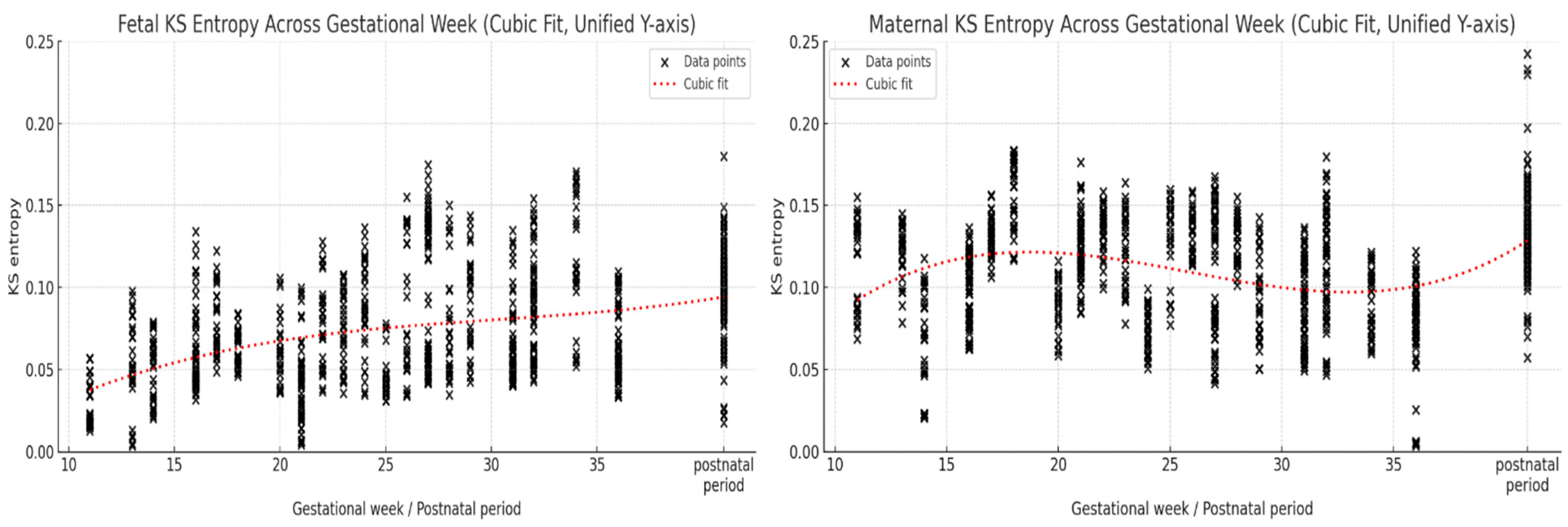
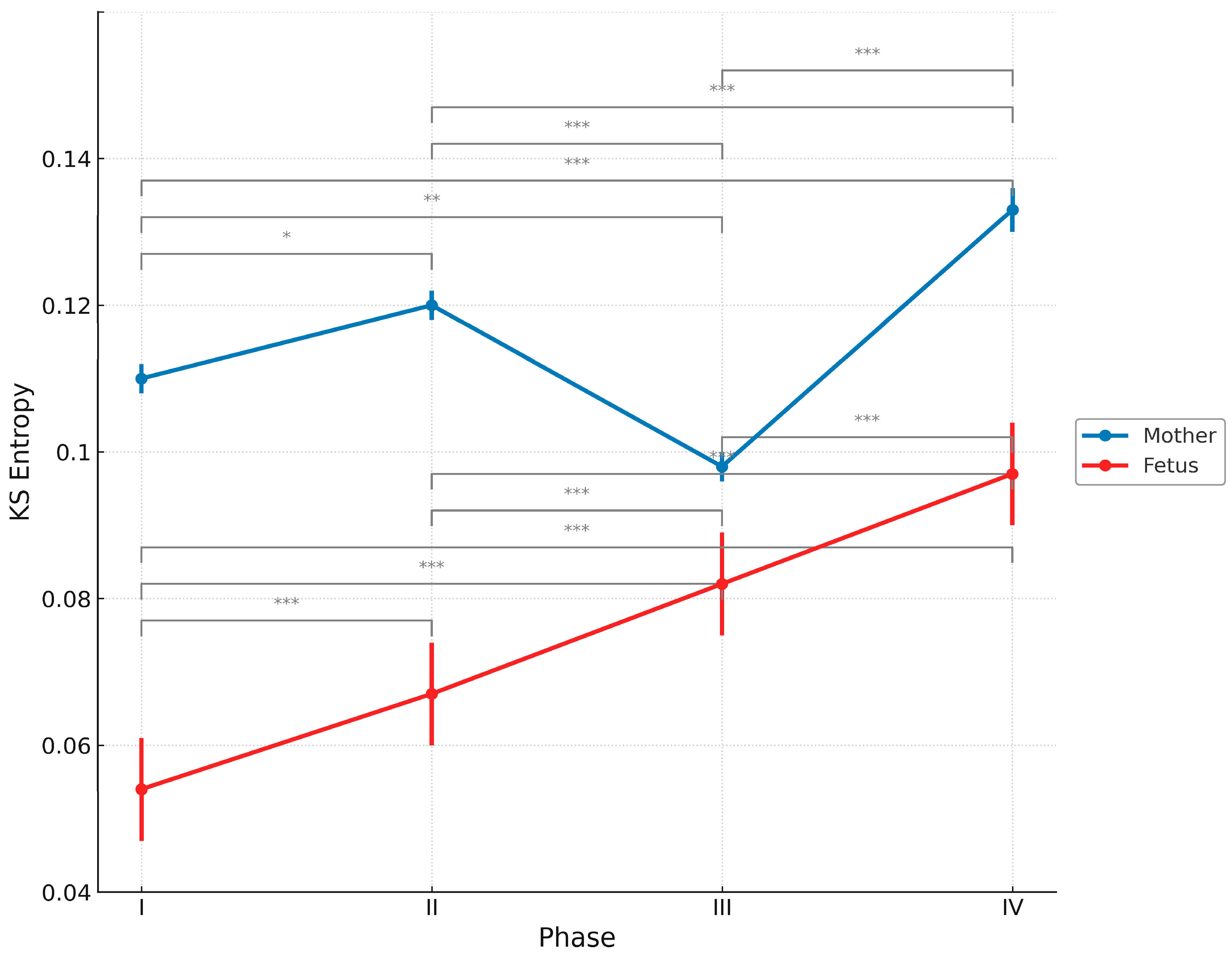
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of Heart-Sound Analysis
4.2. Importance of Aggregating Data
4.3. Temporal Changes in KS Entropy
4.4. Fetal and Maternal Dynamics from an Information-Theoretic Perspective
4.5. Clinical Significance and Application Potential
4.6. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KS entropy | Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy |
| λ | Lyapunov Exponent |
Appendix A

| Effect | df | F Value | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | 3, 890 | 5.35 | 0.0012 | ** |
| Year | 1, 890 | 0.45 | 0.5021 | n.s. |
| Sex | 1, 890 | 0.22 | 0.6403 | n.s. |
| Weeks | 1, 890 | 1.12 | 0.2914 | n.s. |
| Effect | df | F Value | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | 3, 892 | 47.79 | <0.0001 | *** |
| Year | 1, 892 | 1.69 | 0.4172 | n.s. |
| Sex | 1, 892 | 0.06 | 0.8447 | n.s. |
| Weeks | 1, 892 | 5.65 | 0.0177 | * |
References
- Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K.; Lipsitz, L.A. What is physiologic complexity, and how does it change with aging and disease? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, A.J.; Macklem, P.T. Complex systems and the technology of variability analysis. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R367–R384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csete, M.; Doyle, J.C. Reverse engineering of biological complexity. Science 2002, 295, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, W.C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, H. Systems biology: A brief overview. Science 2002, 295, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L. Network medicine—From obesity to the diseasome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, D. The Music of Life: Biology Beyond the Genome; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 1–20+46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, E. On Complexity; Hampton Press: Cresskill, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–21+49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Haken, H. Synergetics: An Introduction Nonequilibrium Phase Transitions and Self-Organization in Physics, Chemistry and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; Volume 191. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, K.; Tsuda, I. Complex Systems: Chaos and Beyond: A Constructive Approach with Applications in Life Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-Y.; Yorke, J. Period three implies chaos. Am. Math. Mon. 1975, 82, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, I.; Tahara, T.; Iwanaga, H. Chaos pulsation in human capillary vessels and its dependence on mental and physical conditions. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1992, 2, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babloyantz, A.; Salazar, J.M.; Nicolis, C. Evidence of chaotic dynamics of brain activity during the sleep cycle. Phys. Lett. A 1985, 111, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, T.; Tahara, T.; Iwanaga, H. Physiological significance of the Shil’nikov phenomenon in the focal accommodation system of the human eye. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1994, 4, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Lindenberg, A. The evolution of complexity in human brain development: An EEG study. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 99, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, G.; Allan, W.; Sobel, D.; Allan, K.D. Nonlinear control of heart rate variability in human infants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2608–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, S.; Iwanaga, H.; Tahara, T.; Kiyooka, Y.; Ohashi, K. Fetus and mother are a Deterministic chaos: Analysis of surrogate data method. J. Nurs. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, S.; Tahara, T.; Iwanaga, H.; Kiyooka, Y.; Ohashi, K. Emotional changes in Fetuses and mothers over the course of pregnancy: Chaos analysis of heart sounds. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2020, 13, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama, S.; Tahara, T.; Iwanaga, H.; Ohashi, K.; Endo, H. Changes in the heart sound–derived Lyapunov dimensions of mother-fetus pairs from early pregnancy to the postnatal period: A chaos theory-based analysis. J. Nurs. Sci. Eng. 2025, 12, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. A new metric invariant of transient dynamical systems and automorphisms in Lebesgue spaces. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1958, 119, 861–864. [Google Scholar]
- Sinai, Y.G. On the notion of entropy of a dynamical system. Dokl. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1959, 124, 768–771. [Google Scholar]
- Valenza, G.; Allegrini, P.; Lanata, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Dominant Lyapunov exponent and approximate entropy in heart rate variability during emotional visual elicitation. Front. Neuroeng. 2012, 5, 13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisilevsky, B.S.; Hains, S.M.J.; Lee, K.; King, X.; Huang, H.; Ye, H.H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z. Effects of experience on fetal voice recognition. Psychol. Sci. 2003, 14, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S. Multiscale distribution entropy analysis of short-term heart rate variability. Entropy 2008, 20, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, T.; Ribeiro, M.; Teixeira, A.; Castro, L.; Antunes, L.; Rocha, A.P. Nonlinear Methods Most Applied to Heart-Rate Time Series. Entropy 2020, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Baselli, G.; Liberati, D.; Montano, N.; Cogliati, C.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Measuring regularity by means of a corrected conditional entropy in sympathetic outflow. Biol. Cybern. 1998, 78, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.M.; Gladstone, I.M.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. A regularity statistic for medical data analysis. J. Clin. 1991, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisilevsky, B.S.; Hains, S.M.J.; Brown, C.A.; Lee, C.T.; Cowperthwaite, B.; Stutzman, S.S. Fetal sensitivity to properties of maternal speech and language. Infant Behav. Dev. 2000, 23, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Characterization of strange attractors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Sawada, Y. Measurement of the Lyapunov spectrum from a chaotic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 55, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S. What are SRB measures, and which dynamical systems have them? J. Stat. Phys. 2002, 108, 733–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Phys. D 1983, 9, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantz, H.; Schreiber, T. Nonlinear Time Series Analysis, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchfield, J.P.; Young, K. Inferring statistical complexity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L. Non-linear dynamics for clinicians: Chaos theory, fractals, and complexity at the bedside. Lancet 1996, 347, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, S.M.; Goldberger, A.L. Physiological time-series analysis: What does regularity quantify? Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, H1643–H1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesin, Y.B. Characteristic Lyapunov exponents and smooth ergodic theory. Russ. Math. Surv. 1977, 32, 55–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maršál, K. Ultrasound assessment of fetal circulation. Physiol. Rev. 1995, 75, 701–720. [Google Scholar]
- Kremkau, F.W. Sonography: Principles and Instruments, 9th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pretorius, D.H.; Nelson, T.R. Fetal heart: Examination and evaluation using ultrasound. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 1995, 16, 204–220. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L. Is the normal heartbeat chaotic or homeostatic? News Physiol. Sci. 1991, 6, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.; Leiter, J.C. Control of breathing and heart rate by the autonomic nervous system. Auton. Neurosci. 2012, 169, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes del Paso, G.A.; Langewitz, W.; Mulder, L.J.; van Roon, A.; Duschek, S. The utility of low frequency heart rate variability as an index of sympathetic cardiac tone: A review. Psychophysiology 2013, 50, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, A.; Schulz, S.; Schroeder, R.; Baumert, M.; Caminal, P. Methods derived from nonlinear dynamics for analysing heart rate variability. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronick, E.Z. The Neurobehavioral and Social-Emotional Development of Infants and Children; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, R. Parent–infant synchrony and the construction of shared timing. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, G.B.; Woodruff, W.H.; Brown, J.H. The fourth dimension of life: Fractal geometry and allometric scaling of organisms. Science 1999, 284, 1677–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.F.H.; Starr, T.B. Hierarchy: Perspectives for Ecological Complexity; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, S.A. The problem of pattern and scale in ecology. Ecology 1992, 73, 1943–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Berger, R.L. Statistical Inference, 2nd ed.; Duxbury Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.M. Introduction to Probability Models, 11th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, W. An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1968; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeberg, J.W. Eine neue Herleitung des Exponentialgesetzes in der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung. Math. Z. 1922, 15, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, P.; Geue, D.; Thiel, M.; Cysarz, D.; Lange, S.; Romano, M.C.; Wessel, N.; Kurths, J.; Grönemeyer, D.H. Influence of paced maternal breathing on fetal-maternal heart rate coordination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, M.; Magenes, G.; Cerutti, S.; Arduini, D. Linear and nonlinear parameters for the analysis of fetal heart rate signal from cardiotocographic recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozar, M.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Mestanik, M.; Matasova, K.; Zibolen, M.; Calkovska, A.; Javorka, K. Heart rate variability in healthy term newborns is related to delivery mode and postnatal adaptation. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Deem, M.W. Modularity, plasticity, and the development of the brain. In The Cognitive Neurosciences; Poeppel, D., Gazzaniga, M.S., Mangun, G.R., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Fagard, J.; Esseily, R.; Jacquey, L.; O’rEgan, K.; Somogyi, E. Fetal origin of sensorimotor behavior. Front. Neurorobot. 2018, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K. Life: An Introduction to Complex Systems Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, J.; Matsuoka, T.; Saito-Fujita, T.; Inaba, S.; Kunita, S.; Sugiyama, F.; Yagami, K.-I.; Fukamizu, A. Pregnancy associated homeostasis and dysregulation: Lessons from genetically modified animal models. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, T. The role of maternal hormones in regulating autonomic functions during pregnancy. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, C.J.; Moore, T.; Copel, J.A.; Silver, R.M.; Resnik, R. Creasy and Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice, 9th ed.; Elsevier-Health Sciences Division: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, S.P.; Lilly, C.L.; Claydon, E.A.; Wallace, J.; Merryman, K. Monitoring one heart to help two: Heartrate variability and resting heart rate using wearable technology in active women across the perinatal period. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, S.R.; Rowan, S.; Presby, D.M.; Claydon, E.A.; Capodilupo, E.R. Wearable-derived maternal heart rate variability as a novel digital biomarker of preterm birth. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPietro, J.A.; Hilton, S.C.; Hawkins, M.; Costigan, K.A.; Pressman, E.K. Maternal stress and fetal neurobehavioral development. Dev. Psychobiol. 2005, 47, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, U.; Bode, F.; Schmidt, A.; Nowack, S.; Rudolph, A.; Dölker, E.-M.; Schlattmann, P.; Götz, T.; Hoyer, D. Developmental milestones of the autonomic nervous system revealed via longitudinal monitoring of fetal heart rate variability. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Strathearn, L.; Swain, J.E. The maternal brain and its plasticity in humans. Horm. Behav. 2010, 77, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porges, S.W. The polyvagal theory: New insights into adaptive reactions of the autonomic nervous system. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2009, 76 (Suppl. 2), S86–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, P.J.; Russell, J.A. The expectant brain: Adapting for motherhood. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, R.; Wibral, M.; Lindner, M.; Pipa, G. Transfer entropy—Amodel-free measure of effective connectivity for the neurosciences. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Park, Y.-M.; Kim, D.-W.; Im, C.-H. Global synchronization index as a biological correlate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 66, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Haim, Y.; Marshall, P.J.; Fox, N.A. Developmental changes in heart period and high-frequency heart period variability from 4 months to 4 years of age. Dev. Psychobiol. 2000, 37, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massin, M.M.; Maeyns, K.; Withofs, N.; Ravet, F.; Gérard, P. Circadian variations of heart rate variability and spectral analysis of heart rate in healthy children. Cardiology 2000, 94, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Furlan, R.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Entropy, entropy rate, and pattern classification as tools to typify complexity in short heart period variability series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, M.K. Gender differences in the regulation of stress responses: An evolutionary perspective. Stress 2020, 23, 441–450. [Google Scholar]
| Case | Mother’s Age | Parity | Method of Delivery | Gestational Age at Birth | Birth Weight (g) | Sex | Apgar Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 27 | Primipara | Vaginal delivery | 38 w 5 d | 3038 | male | 9 |
| B | 29 | Primipara | Planned caesarean section | 38 w 4 d | 2982 | female | 9 |
| C | 28 | Multipara | Planned caesarean section | 38 w 2 d | 2874 | female | 8 |
| D | 37 | Multipara | Vaginal delivery | 41 w 1 d | 2640 | female | 9 |
| Phase | Fetus (Mean ± SD) | Mother (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|
| I | 0.054 ± 0.007 | 0.110 ± 0.002 |
| II | 0.067 ± 0.007 | 0.120 ± 0.002 |
| III | 0.082 ± 0.007 | 0.098 ± 0.002 |
| IV | 0.097 ± 0.007 | 0.133 ± 0.003 |
| Fetus | Mother | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Estimate | Standard Error | df | t Value | p-Value | Estimate | Standard Error | df | t Value | p-Value |
| I vs. II | −0.013 | 0.003 | 894 | −4.527 | <0.0001 | −0.007 | 0.003 | 895 | −2.641 | 0.0418 |
| I vs. III | −0.028 | 0.003 | 894 | −10.686 | <0.0001 | +0.009 | 0.002 | 895 | +3.975 | 0.0004 |
| I vs. IV | −0.042 | 0.003 | 893 | −12.425 | <0.0001 | −0.023 | 0.003 | 894 | −7.643 | <0.0001 |
| II vs. III | −0.015 | 0.003 | 892 | −5.620 | <0.0001 | +0.017 | 0.002 | 893 | +6.897 | <0.0001 |
| II vs. IV | −0.029 | 0.003 | 891 | −8.449 | <0.0001 | −0.017 | 0.003 | 893 | −5.335 | <0.0001 |
| III vs. IV | −0.014 | 0.003 | 891 | −4.401 | <0.0001 | −0.033 | 0.003 | 893 | −11.483 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishiyama, S.; Tahara, T.; Iwanaga, H.; Ohashi, K. Information Dynamics of the Mother–Fetus System Using Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Derived from Heart Sounds: A Longitudinal Study from Early Pregnancy to Postpartum. Entropy 2025, 27, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090969
Ishiyama S, Tahara T, Iwanaga H, Ohashi K. Information Dynamics of the Mother–Fetus System Using Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Derived from Heart Sounds: A Longitudinal Study from Early Pregnancy to Postpartum. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090969
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshiyama, Sayuri, Takashi Tahara, Hiroaki Iwanaga, and Kazutomo Ohashi. 2025. "Information Dynamics of the Mother–Fetus System Using Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Derived from Heart Sounds: A Longitudinal Study from Early Pregnancy to Postpartum" Entropy 27, no. 9: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090969
APA StyleIshiyama, S., Tahara, T., Iwanaga, H., & Ohashi, K. (2025). Information Dynamics of the Mother–Fetus System Using Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Derived from Heart Sounds: A Longitudinal Study from Early Pregnancy to Postpartum. Entropy, 27(9), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090969








