ERLD-HC: Entropy-Regularized Latent Diffusion for Harmony-Constrained Symbolic Music Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a hierarchical generation architecture, ERLD-HC, which combines a VAE-based latent space representation with a denoising diffusion model, leveraging the strengths of both generative paradigms for symbolic music generation.
- We introduce an entropy-guided CRF module into the cross-attention of the diffusion model, enabling the incorporation of interpretable harmonic priors and the regulation of chord progression in a differentiable manner. This design enhances the harmonic coherence of generated sequences through internal inference, without requiring external chord labels or explicit chord conditioning.
2. Data Preprocessing
3. Methods
3.1. Model Network Structure
3.2. VAE-Encoder
3.3. Latent Diffusion
3.4. Chord Inference Based on Entropy-Regularized CRF
3.4.1. Pitch Class Entropy(PCE)
3.4.2. Chord Transition Entropy (CTE)
3.4.3. Key Matching Entropy (KME)
3.4.4. Tonal Entropy (TE)
3.4.5. CRF Training and Integration with Diffusion
3.5. VAE-Decoder
3.6. Loss Function Design
3.6.1. VAE Loss
3.6.2. Diffusion Model Loss
3.6.3. CRF Loss
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Dataset and Parameter Settings
4.2. Chord Confusion Analysis of CRF Strategy
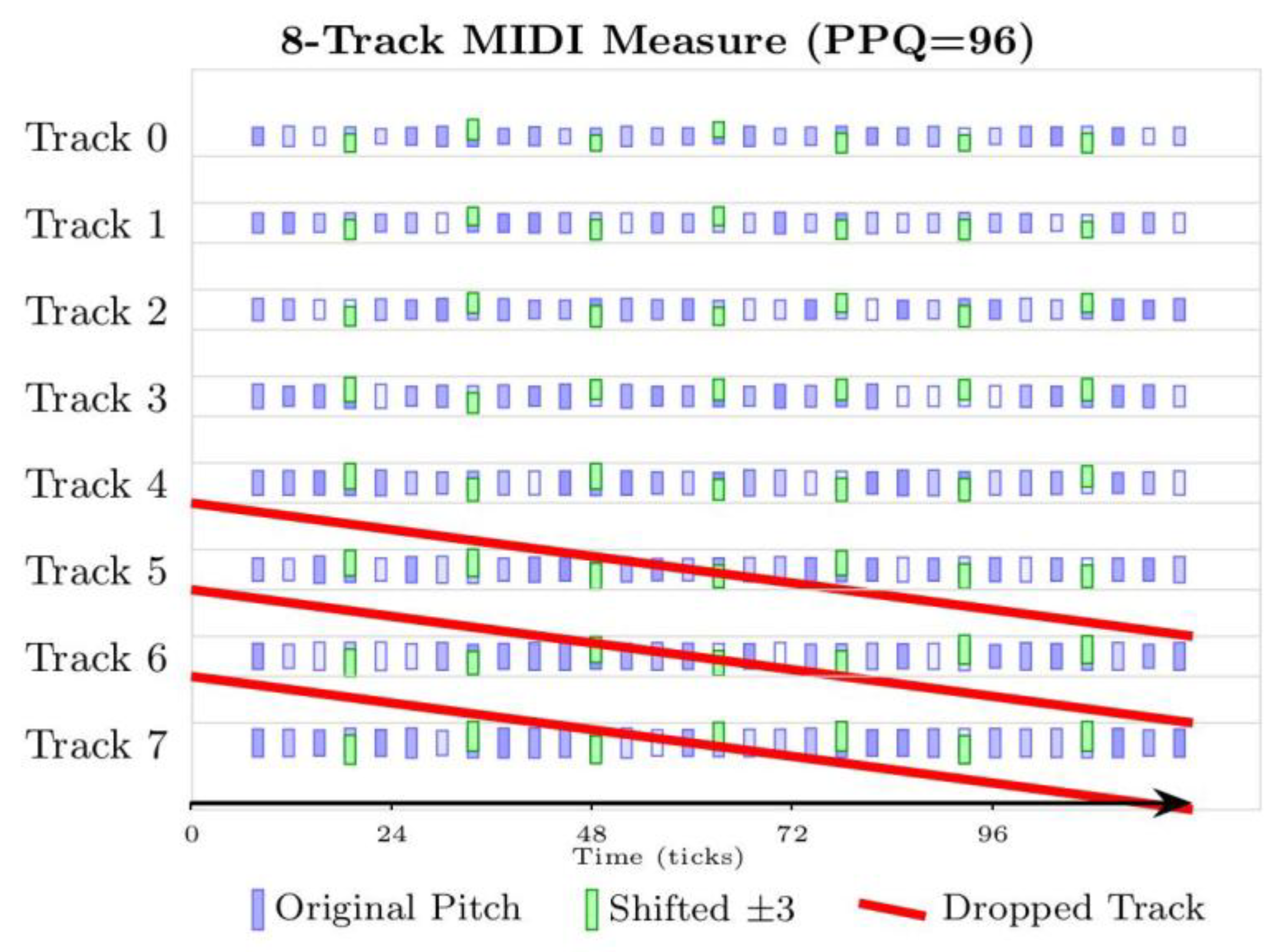
4.3. Visual Comparison of MIDI Generation Across Models
4.4. Design of Evaluation Indicators for Music Generation
4.4.1. Harmony Assessment
- Harmony Violation Rate (HVR)
- 2.
- Chord Transition Probability (CTP)
- 3.
- Chord Saturation (CS)
4.4.2. Melodic Assessment
- Pitch Contour Smoothness (PCS)
- 2.
- Contour Volatility (CV)
4.4.3. Overall Generation Quality
- Structural Index (SI)
- 2.
- Pitch Naturalness (PN)
4.4.4. Baselines for Comparison
4.4.5. Experimental Result
4.4.6. Subjective Listening Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, L. Using deep learning and genetic algorithms for melody generation and optimization in music. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 17419–17433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Su, Z.; Wu, Y. Hyperbolic Music Transformer for Structured Music Generation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 26893–26905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Engel, J.; Raffel, C.; Hawthorne, C.; Eck, D. A Hierarchical Latent Vector Model for Learning Long-Term Structure in Music. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 4364–4373. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-Z.A.; Vaswani, A.; Uszkoreit, J.; Simon, I.; Hawthorne, C.; Shazeer, N.; Dai, A.M.; Hoffman, M.D.; Dinculescu, M.; Eck, D. Music Transformer: Generating Music with Long-Term Structure. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tie, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Tie, J.; Qi, L.; Lu, Y. Hybrid Learning Module-Based Transformer for Multitrack Music Generation With Music Theory. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2025, 12, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Xiao, Z. Structured Music Transformer: Structured conditional music generation based on stylistic clustering using Transformer. In Proceedings of the 43rd Chinese Control Conference (CCC 2024), Kunming, China, 28–31 July 2024; pp. 8230–8235. [Google Scholar]
- Soua, R.; Livolant, E.; Minet, P. MUSIKA: A multichannel multi-sink data gathering algorithm in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Sardinia, Italy, 1–5 July 2013; pp. 1370–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, W.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Yang, Y.-H. Compound Word Transformer: Learning to Compose Full-Song Music over Dynamic Directed Hypergraphs. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Tan, X.; Wang, R.; Ju, Z.; Qin, T.; Liu, T.-Y. MusicBERT: Symbolic Music Understanding with Large-Scale Pre-Training. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 791–800. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, R.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wu, S.; Shen, T.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; et al. ChatMusician: Understanding and Generating Music Intrinsically with LLM. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 6252–6271. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fazekas, G.; Saitis, C. Composer Style-Specific Symbolic Music Generation using Vector Quantized Discrete Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 34th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), London, UK, 22–25 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, G.; Engel, J.; Hawthorne, C.; Simon, I. Symbolic Music Generation with Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Online, 7–12 November 2021; pp. 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Melechovsky, J.; Guo, Z.; Ghosal, D.; Majumder, N.; Herremans, D.; Poria, S. Mustango: Toward Controllable Text-to-Music Generation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 8293–8316. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Min, L.; Xia, G. Whole-Song Hierarchical Generation of Symbolic Music Using Cascaded Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2024), Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Nezhurina, M.; Berg-Kirkpatrick, T.; Dubnov, S. MusicLDM: Enhancing Novelty in text-to-music Generation Using Beat-Synchronous mixup Strategies. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024–2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 1206–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Ghatare, A.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sastry, C.S.; Gururani, S.; Oore, S.; Yue, Y. Symbolic music generation with non-differentiable rule guided diffusion. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zixun, G.; Makris, D.; Herremans, D. Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Networks for Conditional Melody Generation with Long-term Structure. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, M.; Wang, C.; Richard, G. Structure-Informed Positional Encoding for Music Generation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024–2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 951–955. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjeres, G.; Pachet, F.; Nielsen, F. DeepBach: A Steerable Model for Bach Chorales Generation. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1362–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.D.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F.C.N. Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2001), Williamstown, MA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2001; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. An Introduction to Feature Selection. In Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 487–519. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, P.; Ren, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Shang, S. Sequence Labeling With Meta-Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 3072–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Linear Methods for Regression. In The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 41–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-measure to ROC, Informedness, Markedness and Correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen, A.; SanMiguel, I.; Schröger, E. Representation of harmony rules in the human brain. Brain Res. 2007, 1155, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, C.; Brand, F.; Müller, M. Mid-level Chord Transition Features for Musical Style Analysis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 341–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y. Convergence properties of the K-means algorithms. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 28 November–3 December 1994; pp. 585–592. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Kappa | FCR | SRR |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAE | 0.076 | 0.250 | 0.066 |
| VAE+Diffusion | 0.41 | 0.523 | 0.000 |
| VAE+Diffusion+CRF | 0.61 | 0.681 | 0.140 |
| ERLD-HC | 0.83 | 0.863 | 0.333 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAE+Diffusion | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| VAE+Diffusion+CRF | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.68 |
| ERLD-HC | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.82 |
| Model | Harmony | Melodic | Overall Quality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVR | CTE | CS | PCS | CV | SI | PN | |
| VAE | 4.55% | 0.648 | 0.5 | 8.25 | 0.49 | 0.72 | 0.68 |
| VAE+Diffusion | 3.90% | 0.725 | 0.59 | 8.05 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.76 |
| VAE+Diffusion+CRF | 2.65% | 0.61 | 0.64 | 8.30 | 0.42 | 0.75 | 0.74 |
| ERLD-HC | 1.55% | 0.48 | 0.68 | 8.62 | 0.30 | 0.81 | 0.88 |
| Model | Harmony | Melodic | Overall Quality | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVR | CTE | CS | PCS | CV | SI | PN | |
| VAE | 3.13% | 0.316 | 0.56 | 1.97 | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.92 |
| VAE+Diffusion | 2.70% | 0.38 | 0.6 | 1.91 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.93 |
| VAE+Diffusion+CRF | 2.85% | 0.35 | 0.59 | 2.01 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.93 |
| ERLD-HC | 1.30% | 0.32 | 0.64 | 2.16 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.94 |
| Model | Melody (1–5) | Harmony (1–5) | Overall Quality (1–5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAE | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.9 |
| VAE+Diffusion | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.5 |
| VAE+Diffusion+CRF | 3.8 | 3.3 | 3.6 |
| ERLD-HC | 4.1 | 3.8 | 4.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y. ERLD-HC: Entropy-Regularized Latent Diffusion for Harmony-Constrained Symbolic Music Generation. Entropy 2025, 27, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090901
Li Y. ERLD-HC: Entropy-Regularized Latent Diffusion for Harmony-Constrained Symbolic Music Generation. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090901
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang. 2025. "ERLD-HC: Entropy-Regularized Latent Diffusion for Harmony-Constrained Symbolic Music Generation" Entropy 27, no. 9: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090901
APA StyleLi, Y. (2025). ERLD-HC: Entropy-Regularized Latent Diffusion for Harmony-Constrained Symbolic Music Generation. Entropy, 27(9), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090901





