Research on Joint Game-Theoretic Modeling of Network Attack and Defense Under Incomplete Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Modeling of Incomplete Information in Network Environments
2.2. Applications of Graph Neural Networks in Network Environments
2.3. Current Research on Multi-Agent Network Games
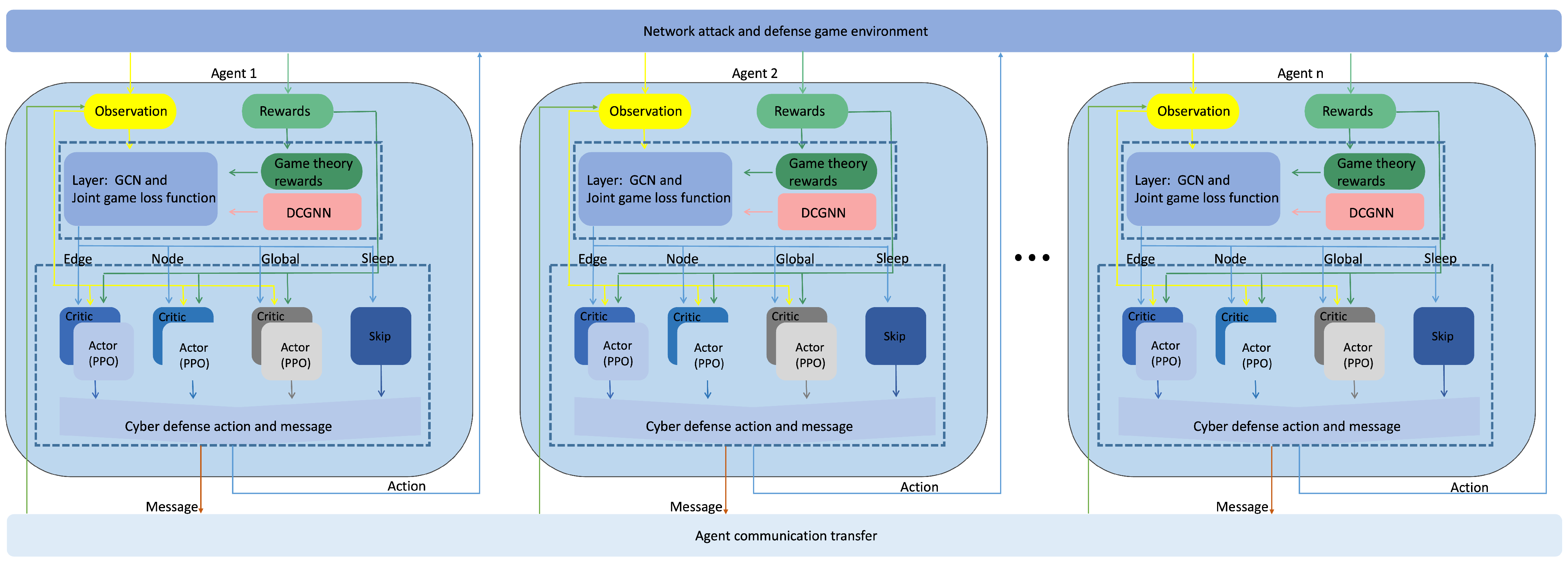
3. Technical Architecture and Overall Framework Design
4. Dynamic Strategy Coordination and Optimization in Network Attack and Defense
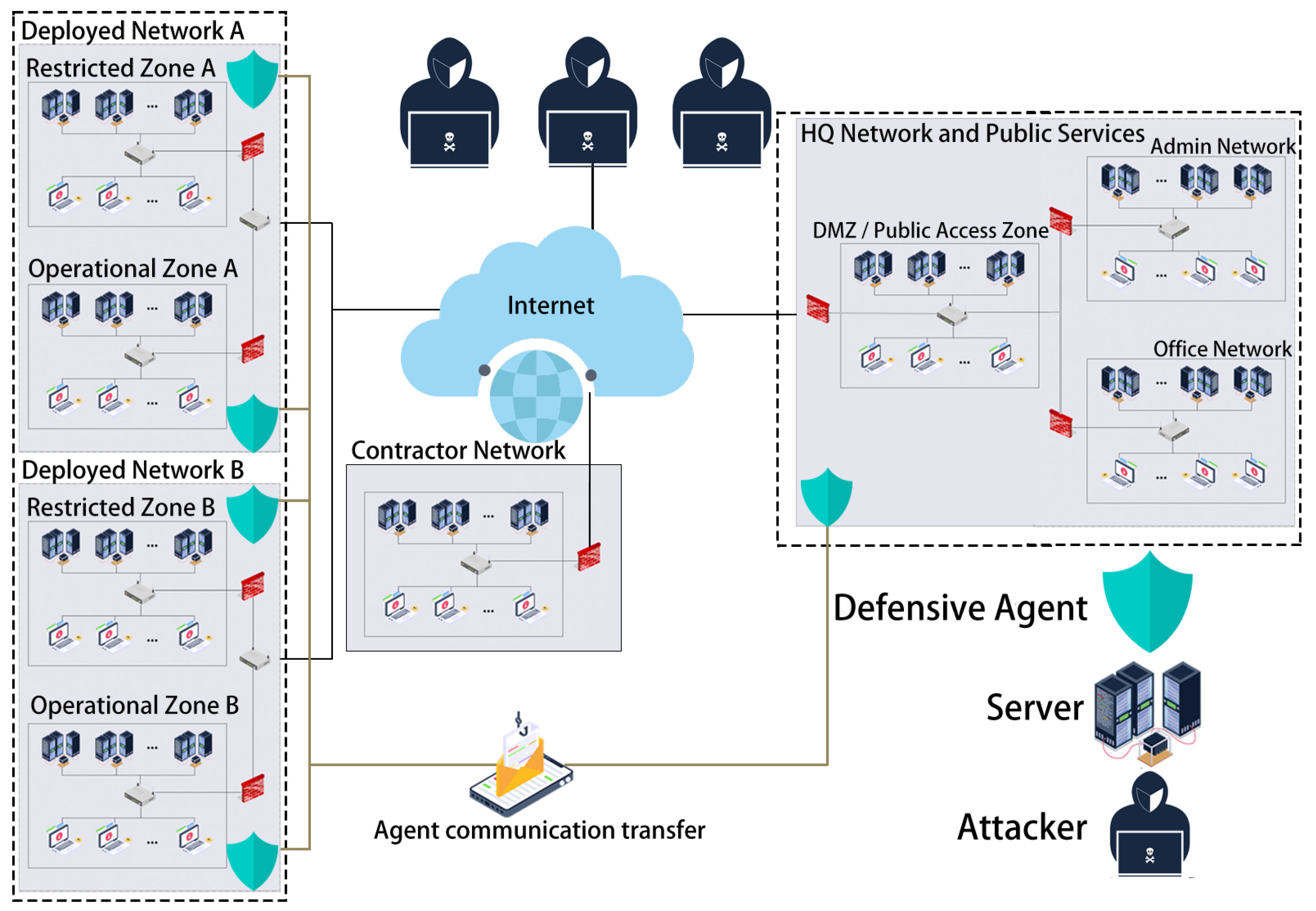
4.1. Modeling Attack and Defense Environment Based on Incomplete Information
4.2. Modeling Incomplete Information Based on Game Theory
4.2.1. Derivation of the Defender’s Utility Function
- : the probability that the user agent takes action in state .
- : the probability that the attacker agent takes action in state .
- : the probability that the user agent g fails due to the defensive action of agent given that the user and attacker take actions and , respectively, in state .
4.2.2. Nash Equilibrium Existence Proof
- Boundedness: The strategy set forms a probability simplex, strictly confined within the closed interval , making the strategy space evidently bounded.
- Closedness: The simplex is a closed set, as every point on its boundary is included in the set itself, thereby ensuring closedness.
- Convexity: The simplex is inherently a convex set, as any linear combination of points within the set remains in the set.
4.2.3. Bayesian Nash Equilibrium Modeling
- : policy ratio.
- : advantage estimation.
- : loss of the value network, typically mean squared error.
- : entropy of the policy, to encourage exploration.
- , : weight coefficients.
- : weight of the game-theoretic loss in total loss.
- : number of defender agents.
4.3. Bayesian Belief Update Modeling
- : the conditional probability of receiving new observation given that the attacker took action and the previous observation was .
- : the marginal probability of observing , which can be computed via the law of total probability:
5. Multi-Agent Joint Game-Theoretic Decision Making
5.1. Multi-Agent Cooperative Optimization
5.2. DCGNN: A Multi-Agent Joint Communication Game-Theoretic Decision Network Based on Graph Neural Networks
6. Experiments
6.1. Experimental Scenario and Design
- RQ1: Can the proposed JG-Defense method, by introducing a joint game-theoretic loss function, comprehensively optimize multi-agent strategic utility in incomplete information games, thereby achieving higher strategy coordination and system robustness in dynamic network defense environments?
- RQ2: Does the proposed DCGNN effectively extract critical topological structures and evolving attack patterns in dynamic network environments? Can its multi-layer graph convolutional architecture enhance the defense agents’ perception and response to complex environmental changes?
- RQ3: Does the multi-agent communication mechanism introduced in the DCGNN enable efficient information sharing and contextual reasoning? Can it strengthen strategy coordination among agents, thereby enhancing the effectiveness and robustness of the joint game-theoretic model in practical attack–defense scenarios?
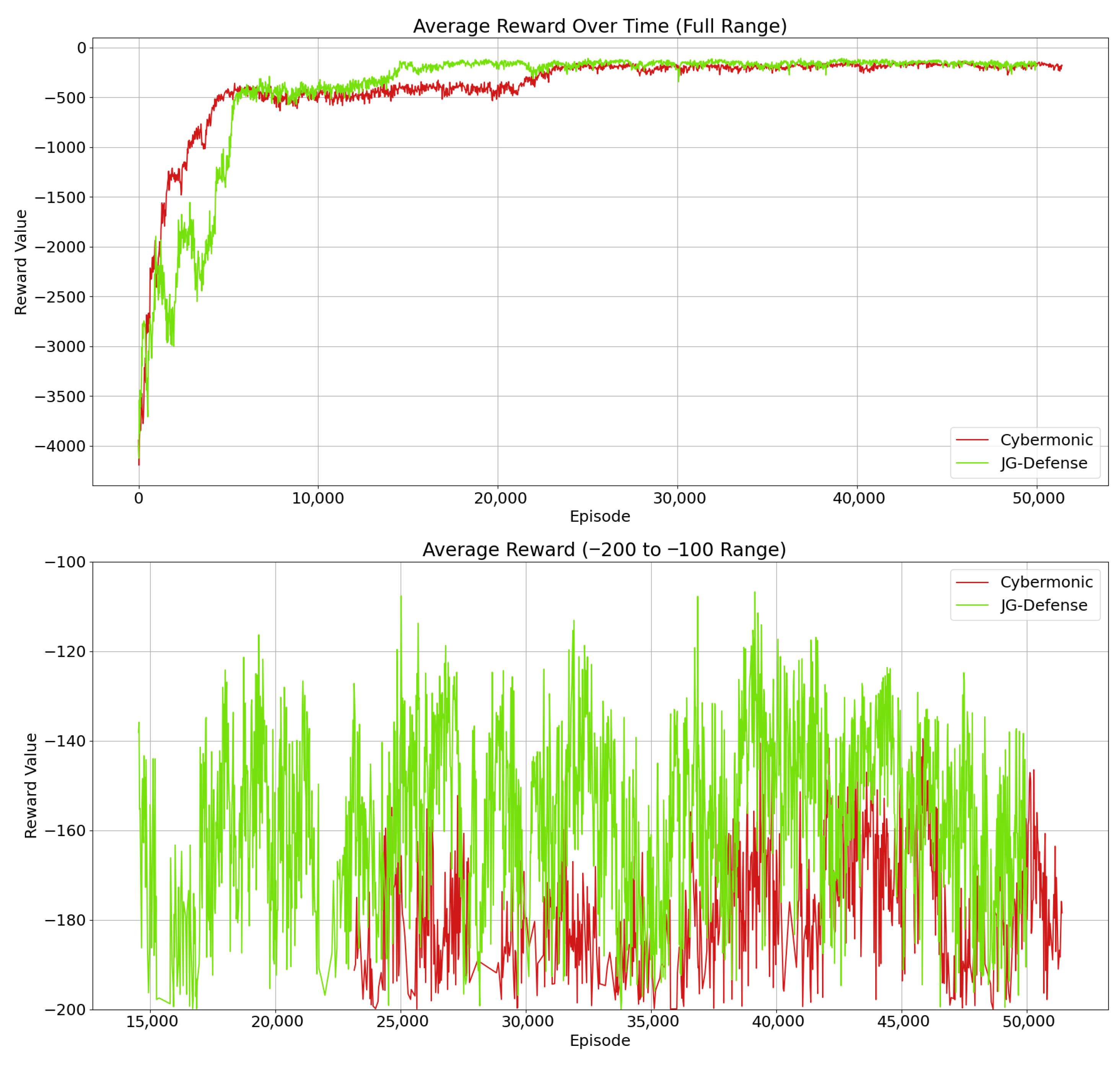
6.2. The Role of the JG-Defense Method in Optimizing Defense Strategies Through Joint Game Theory
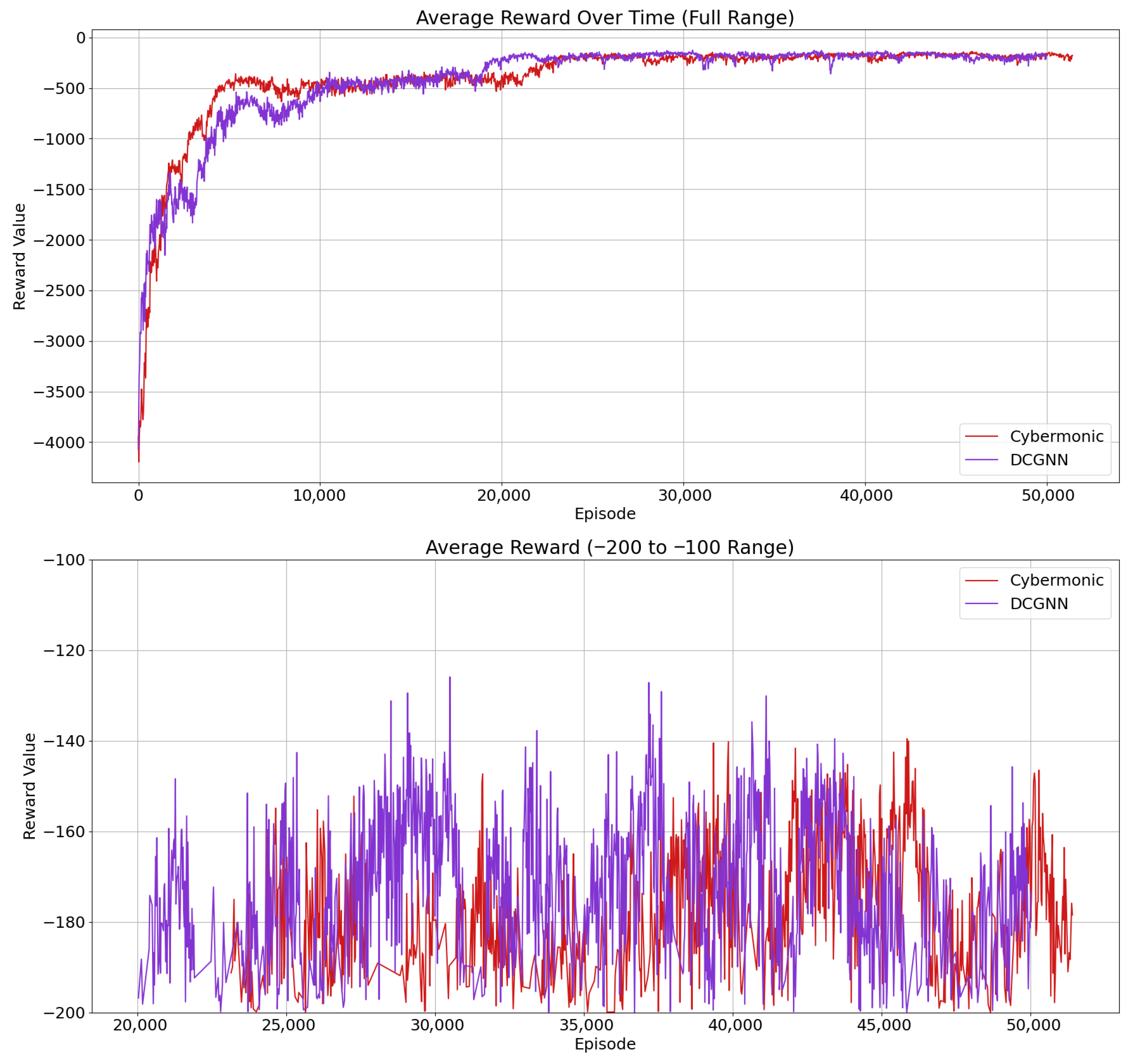
6.3. Feature Extraction Capability of DCGNN in Dynamic Network Environments
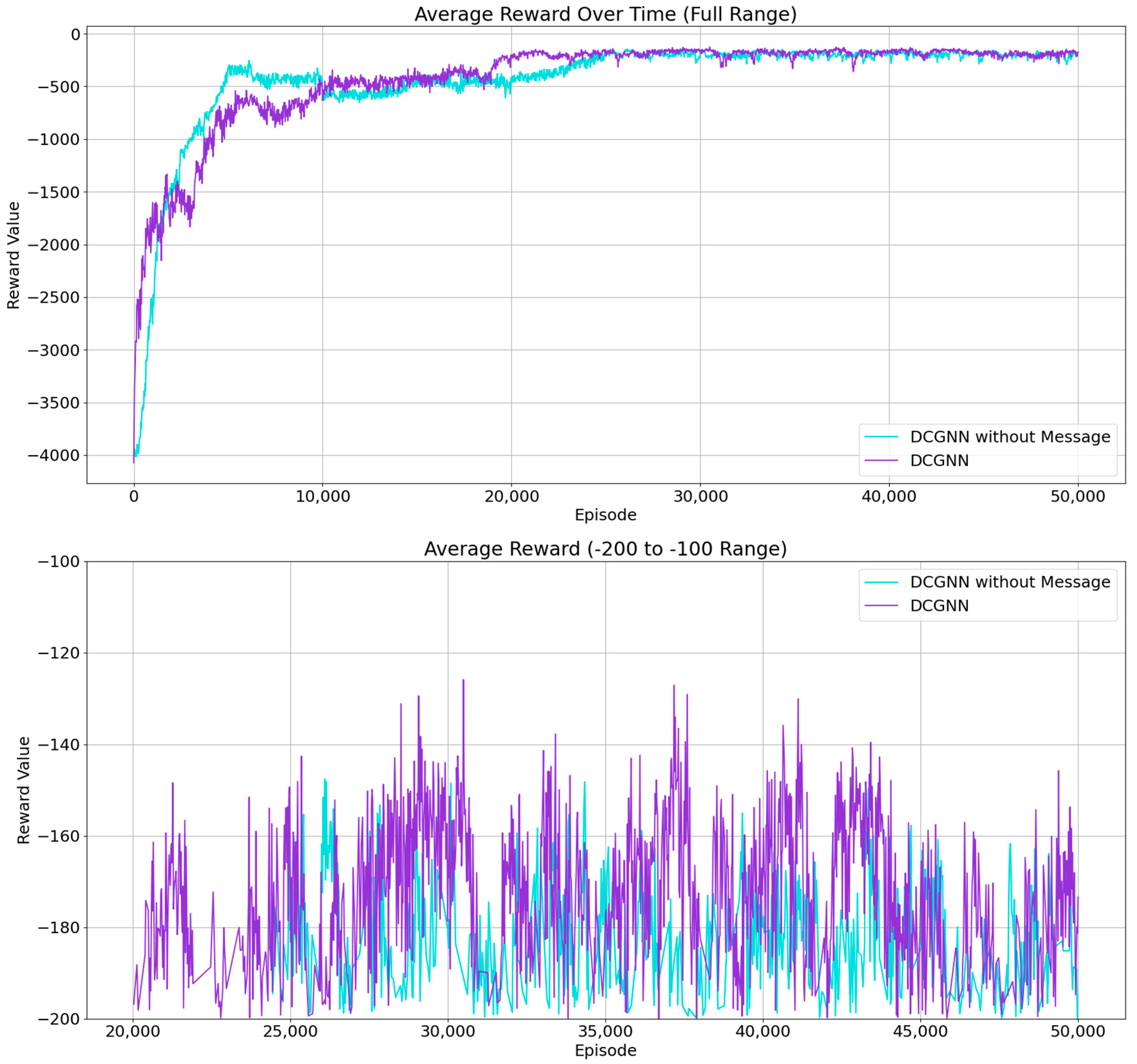
6.4. Impact of Inter-Agent Communication in DCGNN on Defense Performance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, H.; Yu, X.; Sui, Y.; Shao, F.; Sun, R. Topological Graph Convolutional Network Based on Complex Network Characteristics. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 64465–64472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albreiki, B.; Habuza, T.; Zaki, N. Extracting topological features to identify at-risk students using machine learning and graph convolutional network models. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehling, E.; Rasouli, M.; Teneketzis, D. Optimal Defense Policies for Partially Observable Spreading Processes on Bayesian Attack Graphs. In Proceedings of the Second ACM Workshop on Moving Target Defense, MTD ’15, Denver, CO, USA, 12 October 2015; pp. 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q. Dynamic defenses in cyber security: Techniques, methods and challenges. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mi, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, J. A differential game approach for real-time security defense decision in scale-free networks. Comput. Netw. 2023, 224, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Gunn, L.J.; Guo, M.; Ali Babar, M.; Abbott, D. Game Theoretical Modelling of Network/Cybersecurity. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 154167–154179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, C.; Cui, G.; Li, B.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, Y. A Game-Theoretical Approach for Mitigating Edge DDoS Attack. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.T.; Borkotokey, S.; Lahcen, R.A.M.; Mohapatra, R.N. A generic scheme for cyber security in resource constraint network using incomplete information game. Evol. Intell. 2023, 16, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. Network Situation Awareness Model Based on Incomplete Information Game. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Privacy in New Computing Environments, Xi’an, China, 30–31 December 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, M.R.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Pacheco, J.; Chen, H. An Adversarial Reinforcement Learning Framework for Robust Machine Learning-based Malware Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Orlando, FL, USA, 28 November–1 December 2022; pp. 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ma, X. Double DQN Method for Botnet Traffic Detection System. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 79, 509–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, M.; Dong, A.; Yang, Y. An active learning framework using deep Q-network for zero-day attack detection. Comput. Secur. 2024, 139, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Alsmadi, I.; Alhamdani, W.; Tawalbeh, L. Zero-day attack detection: A systematic literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10733–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munikoti, S.; Agarwal, D.; Das, L.; Halappanavar, M.; Natarajan, B. Challenges and Opportunities in Deep Reinforcement Learning With Graph Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Review of Algorithms and Applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 15051–15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.A.; Gokulnath, B. Design of an Improved Method for Task Scheduling Using Proximal Policy Optimization and Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 174472–174490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Lin, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z. A Survey on Graph Neural Networks for Intrusion Detection Systems: Methods, Trends and Challenges. Comput. Secur. 2024, 141, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhu, T.; Ren, W.; Hong, Y. Defense against membership inference attack in graph neural networks through graph perturbation. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2023, 22, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiddin, A.; Atat, R.; Ismail, M.; Boyaci, O.; Davis, K.R.; Serpedin, E. Generalized graph neural network-based detection of false data injection attacks in smart grids. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2023, 7, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Lv, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, G. Application of a dynamic line graph neural network for intrusion detection with semisupervised learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 18, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Huang, M.; Meng, L.; Zhu, X. SSP: Semantic space projection for knowledge graph embedding with text descriptions. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Pan, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks: A Survey Toward Private and Secure Applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Deng, J.; Tong, L.; Xu, W. A method of network attack-defense game and collaborative defense decision-making based on hierarchical multi-agent reinforcement learning. Comput. Secur. 2024, 142, 103871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Du, W.; Ding, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; An, B. Multiagent Reinforcement Learning With Graphical Mutual Information Maximization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; Yi, M.; Liu, A. GPDS: A multi-agent deep reinforcement learning game for anti-jamming secure computing in MEC network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Q. The role of information structures in game-theoretic multi-agent learning. Annu. Rev. Control 2022, 53, 296–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.F., Jr. Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1950, 36, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, J.F. Non-cooperative Games. Ann. Math. 1951, 54, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksberg, I.L. A Further Generalization of the Kakutani Fixed Point Theorem, with Application to Nash Equilibrium. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1952, 3, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Created by Maxwell Standen, David Bowman, Son Hoang, Toby Richer, Martin Lucas, Richard Van Tassel, Phillip Vu, Mitchell Kiely, KC C., Natalie Konschnik, Joshua Collyer. Cyber Operations Research Gym. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/cage-challenge/CybORG (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Kiely, M.; Ahiskali, M.; Borde, E.; Bowman, B.; Bowman, D.; van Bruggen, D.; Cowan, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Devendorf, E.; Edwards, B.; et al. Exploring the Efficacy of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Cyber Defence: A CAGE Challenge 4 Perspective. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 28907–28913. [Google Scholar]

| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| Set of agents: defenders (), attackers (), and users () | |
| Strategy set of defender agent k at time t | |
| Strategy set of attacker agent k at time t | |
| Network state (scenario) at round t | |
| Network transition function | |
| Observation space of agent i at time t | |
| Weight for service continuity | |
| Weight for defense cost | |
| Penalty weight for user failure due to defense | |
| Cost of executing defense action a | |
| L | Loss from failed user operation due to defense |
| Mixed defense strategy of at node v | |
| Utility of defense strategy at node v | |
| Probability that defense of causes user g to fail | |
| Probability user agent takes action in state | |
| Probability attacker takes action in state | |
| Conditional probability of user g failure under actions | |
| PPO loss function | |
| Value network loss | |
| Policy entropy for exploration | |
| Policy ratio | |
| Advantage estimate | |
| Game-theoretic loss (negative utility sum) | |
| Attacker coalition | |
| Joint action space | |
| Joint attacker action at t | |
| Total loss with game-theoretic term | |
| Strategy parameter of defender agent | |
| Set of critical nodes | |
| Strategy space of defender at node v | |
| Belief over attacker actions based on observation | |
| Observation of defender at time t | |
| Weight of game-theoretic loss in total loss |
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| CPU | 16 vCPU Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8474C |
| RAM | 80 GB |
| GPU | A4000 |
| Anaconda | 4.10.3 |
| Keras | 2.6 |
| Python | 3.8 |
| Action | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HQ Network Local Work Fails | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| HQ Network Access Service Fails | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| HQ Network Red Impact/Access | −3 | −3 | −3 |
| Contractor Network Local Work Fails | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Contractor Network Access Service Fails | −5 | 0 | 0 |
| Contractor Network Red Impact/Access | −5 | 0 | 0 |
| Restricted Zone A Local Work Fails | −1 | −2 | −1 |
| Restricted Zone A Access Service Fails | −3 | −1 | −3 |
| Restricted Zone A Red Impact/Access | −1 | −3 | −3 |
| Operational Zone A Local Work Fails | −1 | −10 | −1 |
| Operational Zone A Access Service Fails | −1 | 0 | −1 |
| Operational Zone A Red Impact/Access | −1 | −10 | −1 |
| Restricted Zone B Local Work Fails | −1 | −1 | −2 |
| Restricted Zone B Access Service Fails | −3 | −1 | −1 |
| Restricted Zone B Red Impact/Access | −1 | −1 | −3 |
| Operational Zone B Local Work Fails | −1 | −1 | −10 |
| Operational Zone B Access Service Fails | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| Operational Zone B Red Impact/Access | −1 | −1 | −10 |
| Internet Local Work Fails | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Internet Access Service Fails | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Internet Red Impact/Access | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, X. Research on Joint Game-Theoretic Modeling of Network Attack and Defense Under Incomplete Information. Entropy 2025, 27, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090892
Wang Y, Liu X, Yu X. Research on Joint Game-Theoretic Modeling of Network Attack and Defense Under Incomplete Information. Entropy. 2025; 27(9):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090892
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yifan, Xiaojian Liu, and Xuejun Yu. 2025. "Research on Joint Game-Theoretic Modeling of Network Attack and Defense Under Incomplete Information" Entropy 27, no. 9: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090892
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, X., & Yu, X. (2025). Research on Joint Game-Theoretic Modeling of Network Attack and Defense Under Incomplete Information. Entropy, 27(9), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27090892






