Mixed Control Strategy for a Class of Sector-Bounded Nonlinear Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Problem Formulation
4. Weighted Gain Characterization
5. Mixed Strategy Control
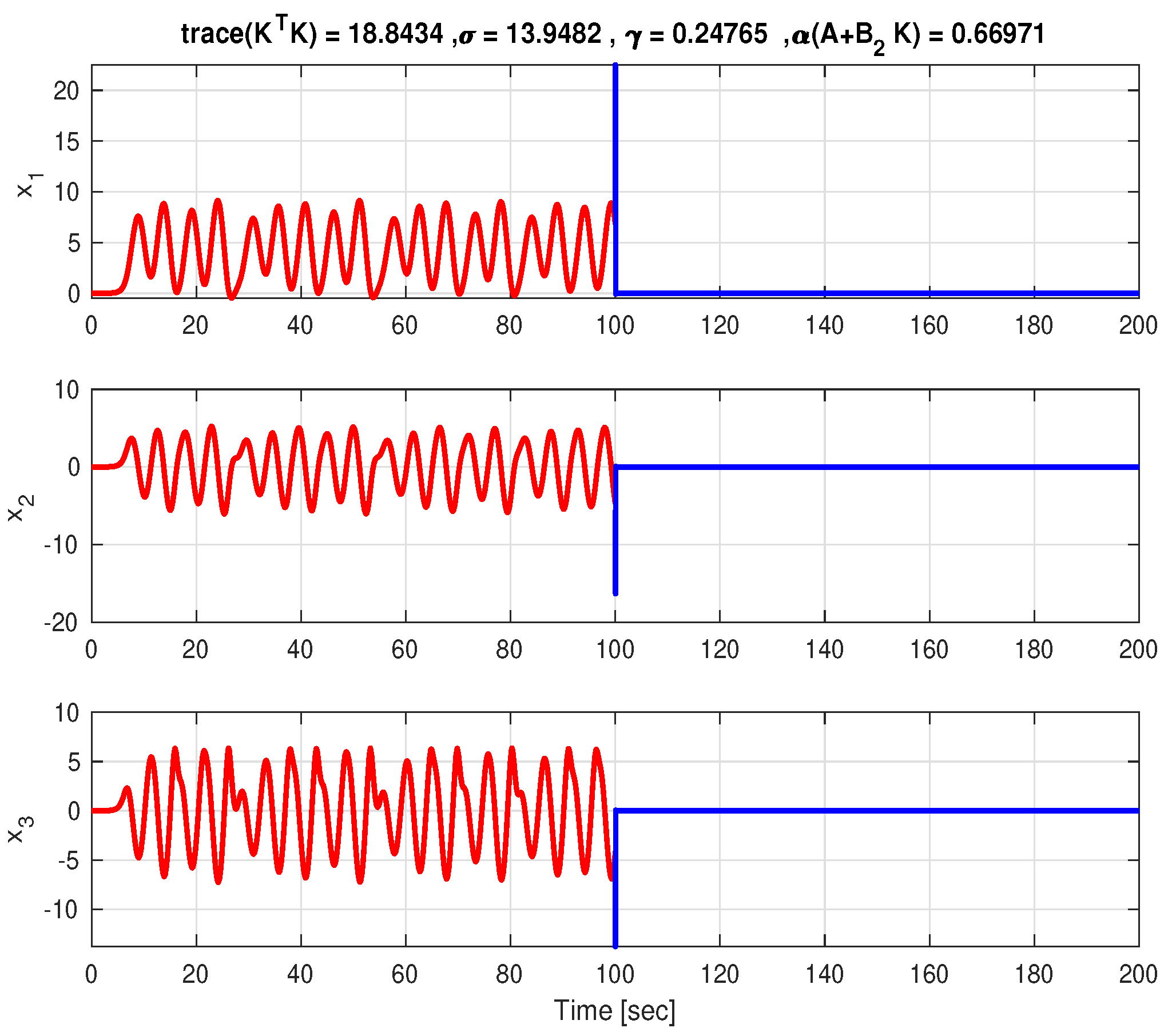
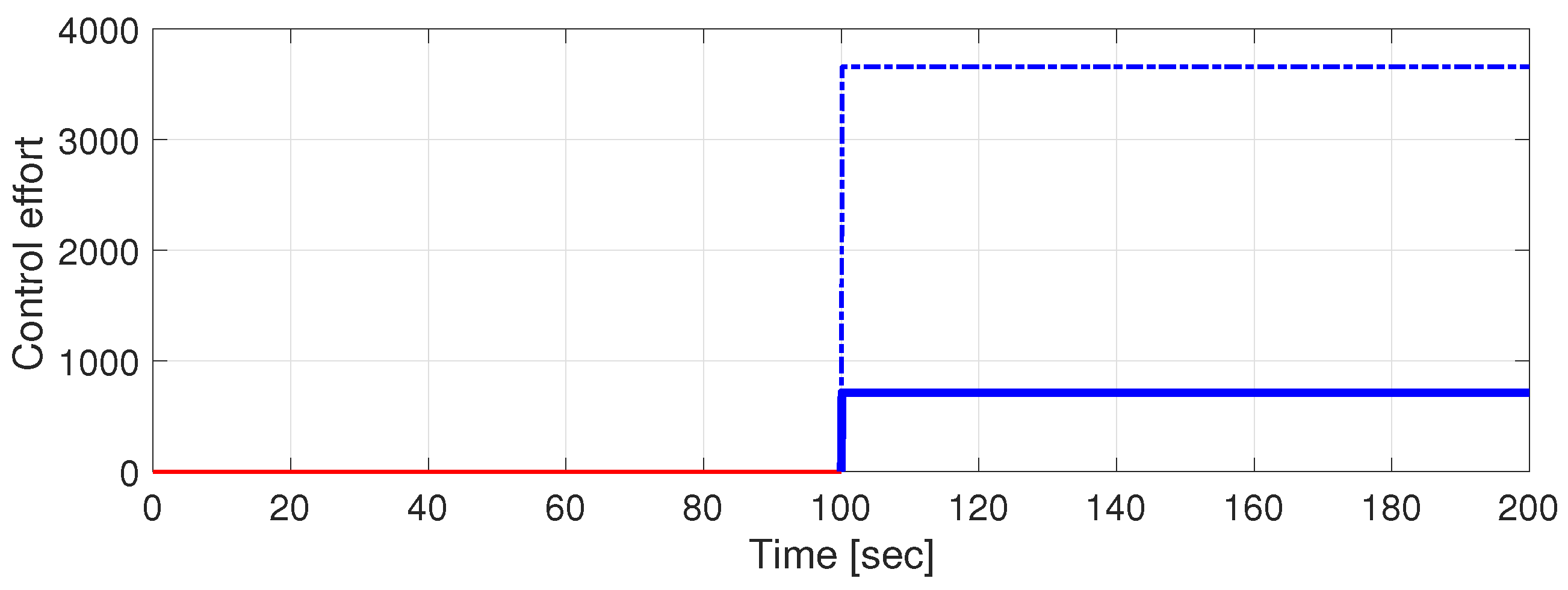
6. A Numerical Example
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wellens, T.; Vyacheslav, S.; Buchleitner, B. Stochastic resonance. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2004, 67, 45–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, V.L. Chaotic, Stochastic Resonance, and Anti-Resonance Phenomena in Optics. Resonance 2017, 4, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Borkowski, L.S. Multimodal transition and stochastic antiresonance in squid giant axons. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1006.1069v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundeep, S.; Wang, J.B.; Griffo, A.; Alvarez-Gonzales, F. Anti-resonance phenomenon and peak voltage stress within PWM inverter fed stator winding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11826–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.B.; Yoo, W.S.; Kim, J.Y. Sensitivity analysis of anti-resonance frequency for vibration test control of a fixture. KSME Int. J. 2003, 17, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, E. Stochastic Resonances and Antiresonances in Rotating Mechanisms. In Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics: Proceedings of the Second International Nonlinear Dynamics Conference (NODYCON 2021); Lacarbonara, W., Balachandran, B., Leamy, M.J., Ma, J., Tenreiro Machado, J.A., Stepan, G., Eds.; NODYCON Conference Proceedings Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, A.-M.; Yaesh, I. Stochastic Antiresonance for Systems with Multiplicative Noise and Sector-Type Nonlinearities. Entropy 2024, 26, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, J.L.; Bormann, R.; Eurich, C.; Ohira, T.; Milton, J. State-dependent noise and human balance control. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2001, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.L.; Milton, J.G. On-Off Intermitency in a Human Balancing Task. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 158702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondo, A.E.; Mazzarino, L.; Pluchino, A. Yaesh, Noise and Financial Stylized Facts: A Stick Balancing Approach. Entropy 2023, 25, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgonnikov, A.; Lubashevsky, I.; Mozgovoy, M. Computer Simulation of Stick Balancing. Action Point Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 Joint International Conference on Human-Centered Computer Environments, HCCE ’12, Aizu-Wakamatsu, Japan, 8–13 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.C.; Glover, K.; Khargonekar, K.; Francis, B.A. State-space solutions to standard H2 and H∞ control problems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1989, 34, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X. Stability of Stochastic Differential Equations with Respect to Semimartingales; Longman Scientific & Technical: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Oksendal, B. Stochastic Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Khasminskii, R. Stochastic Stability of Differential Equations, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, A.M.; Yaesh, I. Markovian Jump-delayed Hopfield Networks with Multiplicative Noise. Automatica 2008, 44, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjerdpongchai, D.; Kimura, H. Robust Analysis of Discrete-Time Lur’e Systems with Slope Restrictions using Convex Optimization. Asian J. Control 2002, 4, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lure, A.I.; Postnikov, V.N. On the theory of stability of control systems. Appl. Math. Mech. 1944, 8, 246–248. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; El Ghaoui, L.; Feron, E.; Balakrishnan, V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinski, A.H. Stochastic Processes and Filtering Theory; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, H.S.; Zhong, G.Q.; Tang, W.K.S. Use of Neurons in Chaos Generation. In Proceedings of the ICONS 2003, Faro, Portugal, 26–27 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Löfberg, J.L. YALMIP: A Toolbox for Modeling and Optimization in MATLAB. In Proceedings of the CACSD Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–4 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by Superpositions of a Sygmoidal Function. Math. Control Signals Syst. 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris Lecar Model. Available online: https://github.com/jonmarty/Morris-Lecar/blob/master/MorrisLecar.ipynb (accessed on 18 June 2018).
| R | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoica, A.-M.; Yaesh, I. Mixed Control Strategy for a Class of Sector-Bounded Nonlinear Systems. Entropy 2025, 27, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030261
Stoica A-M, Yaesh I. Mixed Control Strategy for a Class of Sector-Bounded Nonlinear Systems. Entropy. 2025; 27(3):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030261
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoica, Adrian-Mihail, and Isaac Yaesh. 2025. "Mixed Control Strategy for a Class of Sector-Bounded Nonlinear Systems" Entropy 27, no. 3: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030261
APA StyleStoica, A.-M., & Yaesh, I. (2025). Mixed Control Strategy for a Class of Sector-Bounded Nonlinear Systems. Entropy, 27(3), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030261






