Reliability Modeling Method for Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation Based on the Generalized Wiener Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling of Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation
2.1. Generalized Wiener Process
2.2. Generalized Wiener Process Model with Accelerated Stress and Random Effects
3. Parameter Estimation
4. Case Studies
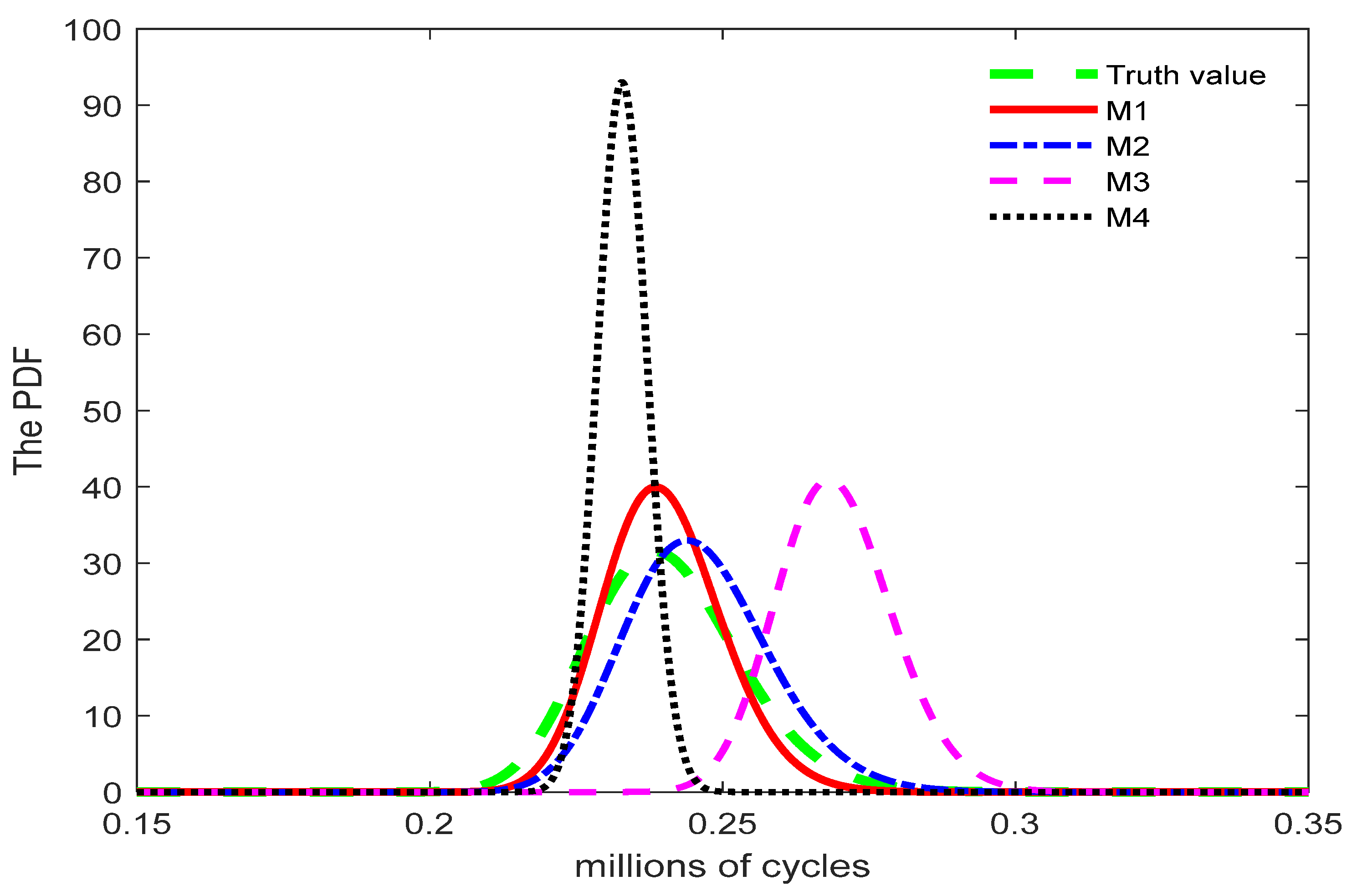
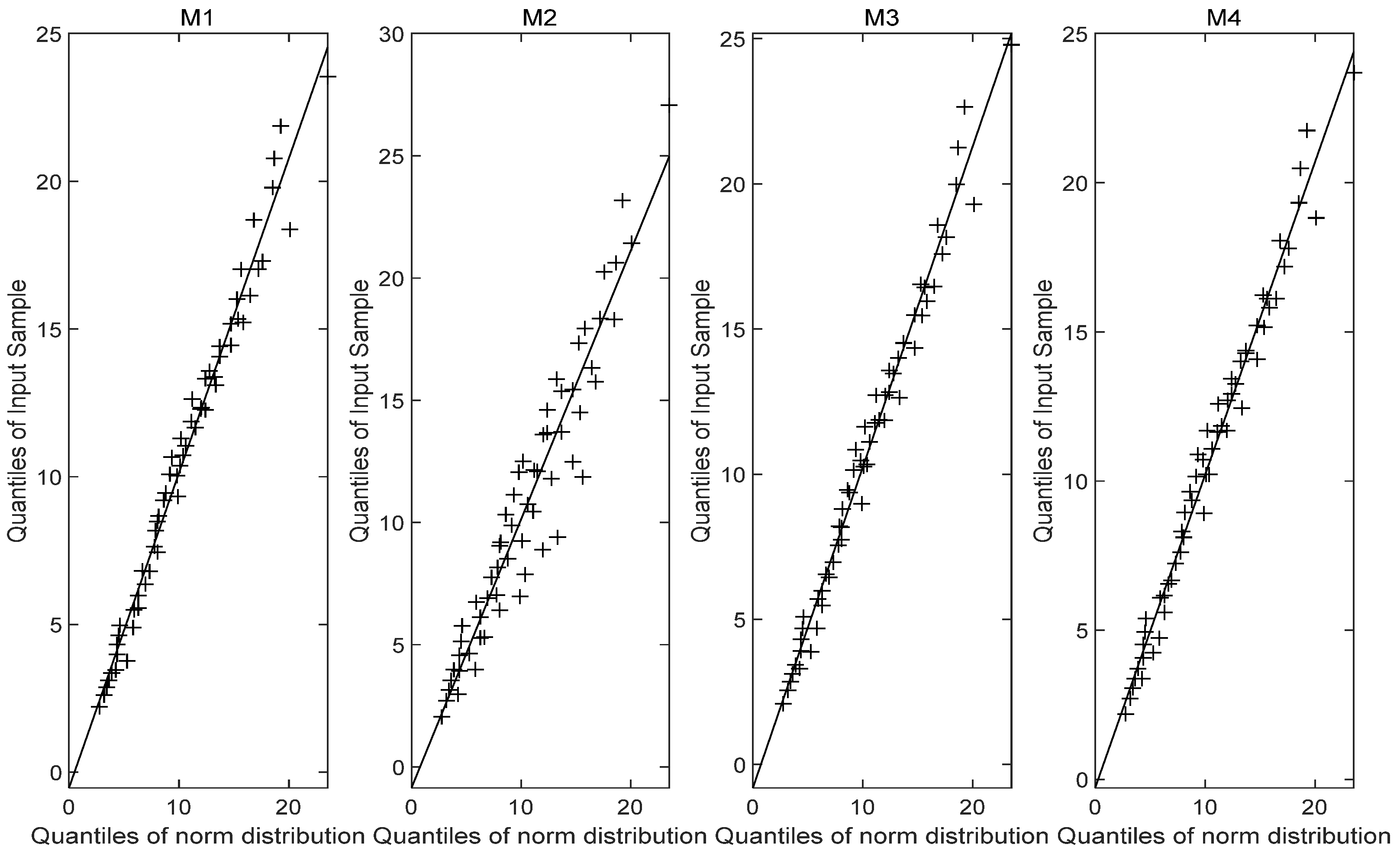
4.1. Simulation Study
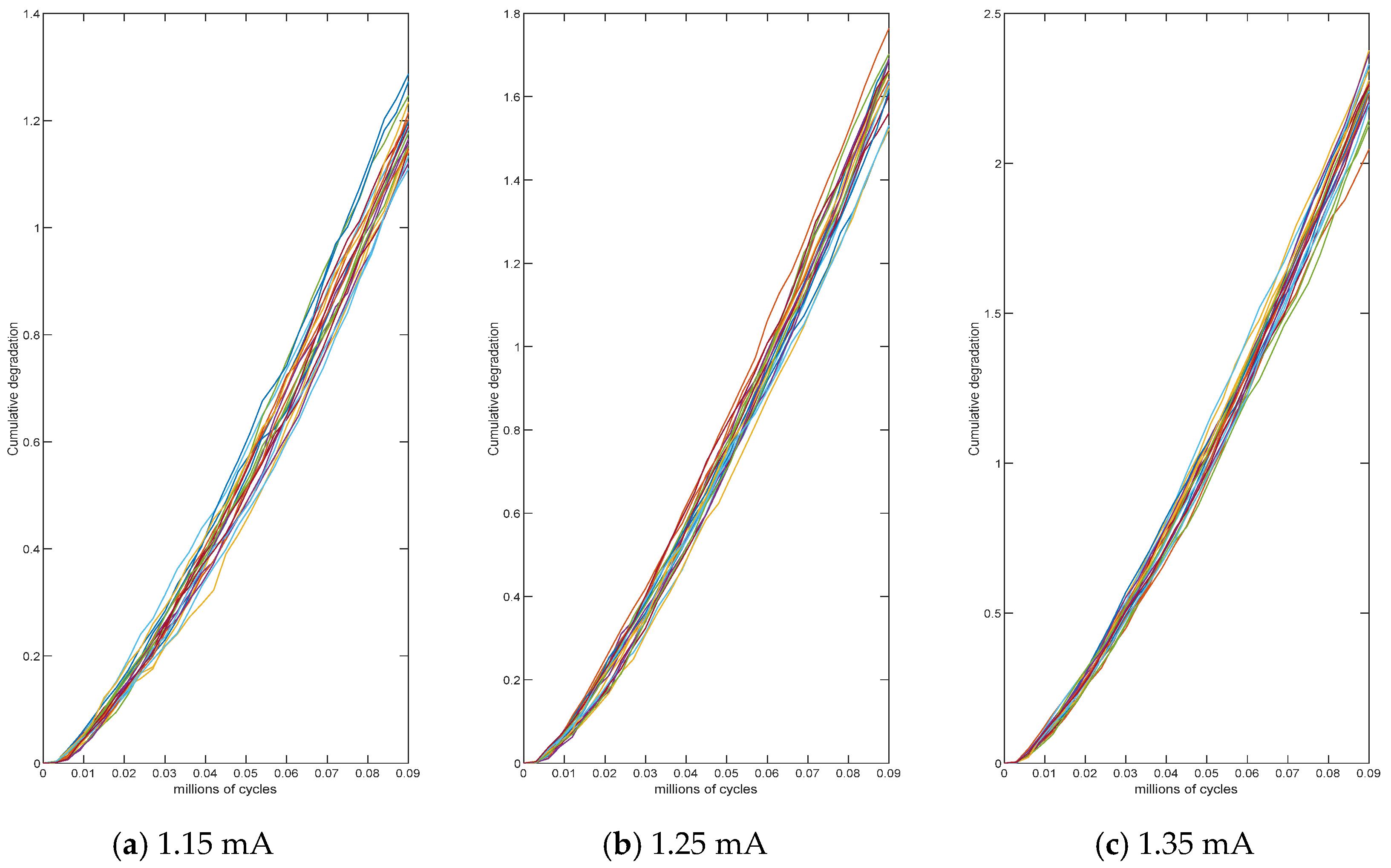
4.2. Application to the Stress Relaxation Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADT | Accelerated degradation test |
| CSADT | Constant-stress accelerated degradation test |
| MLE | Maximum likelihood estimation |
| EM | Expectation maximization |
| FHT | First hitting time |
| Probability density function | |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| MTTF | Mean time to failure |
| CI | Confidence interval |
Appendix A
| T | ID | Stress Relaxation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 °C | 1 | 2.12 | 2.70 | 3.52 | 4.25 | 5.55 | 6.12 | 6.75 | 7.22 | 7.68 | 8.46 | 9.46 |
| 2 | 2.29 | 3.24 | 4.16 | 4.86 | 5.74 | 6.85 | * | 7.40 | 8.14 | 9.25 | 10.55 | |
| 3 | 2.40 | 3.61 | 4.35 | 5.09 | 5.50 | 7.03 | 8.24 | 8.81 | 9.629 | 10.27 | 11.11 | |
| 4 | 2.31 | 3.48 | 5.51 | 6.20 | 7.31 | 7.96 | 8.57 | 9.07 | 10.46 | 11.48 | 12.31 | |
| 5 | 3.14 | 4.33 | 5.92 | 7.22 | 8.14 | 9.07 | 9.44 | 10.09 | 11.20 | 12.77 | 13.51 | |
| 6 | 3.59 | 5.55 | 5.92 | 7.68 | 8.61 | 10.37 | 11.11 | 12.22 | 13.51 | 14.16 | 15.00 | |
| 85 °C | 7 | 2.77 | 4.62 | 5.83 | 6.66 | 8.05 | 10.61 | 11.20 | 11.98 | 13.33 | 15.64 | |
| 8 | 3.88 | 4.37 | 6.29 | 7.77 | 9.16 | 9.90 | 10.37 | 12.77 | 14.72 | 16.80 | ||
| 9 | 3.18 | 4.53 | 6.94 | 8.14 | 8.79 | 10.09 | 11.11 | 14.72 | 16.47 | 18.66 | ||
| 10 | 3.61 | 4.37 | 6.29 | 7.87 | 9.35 | 11.48 | 12.40 | 13.70 | 15.37 | 18.51 | ||
| 11 | 3.42 | 4.25 | 7.31 | 8.61 | 10.18 | 12.03 | 13.70 | 15.27 | 17.22 | 19.25 | ||
| 12 | 5.27 | 5.92 | 8.05 | 9.81 | 12.40 | 13.24 | 15.83 | 17.59 | 20.09 | 23.51 | ||
| 100 °C | 13 | 4.25 | 5.18 | 8.33 | 9.53 | 11.48 | 13.14 | 15.55 | 16.94 | 18.05 | 19.44 | |
| 14 | 4.81 | 6.16 | 7.68 | 9.25 | 10.37 | 12.40 | 15.00 | 16.20 | 18.24 | 20.09 | ||
| 15 | 5.09 | 7.03 | 8.33 | 10.37 | 12.22 | 14.35 | 16.11 | 18.70 | 19.72 | 21.66 | ||
| 16 | 4.81 | 7.50 | 9.16 | 10.55 | 13.51 | 15.55 | 16.57 | 19.07 | 20.27 | 22.40 | ||
| 17 | 5.64 | 6.57 | 8.61 | 12.50 | 14.44 | 16.57 | 18.70 | 21.20 | 22.59 | 24.07 | ||
| 18 | 4.72 | 8.14 | 10.18 | 12.40 | 15.09 | 17.22 | 19.16 | 21.57 | 24.35 | 26.20 | ||
| T | Measurement Time Epochs (in Hours) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 °C | 108 | 241 | 534 | 839 | 1074 | 1350 | 1637 | 1890 | 2178 | 2513 | 2810 |
| 85 °C | 46 | 108 | 212 | 408 | 632 | 764 | 1011 | 1333 | 1517 | 2586 | |
| 100 °C | 46 | 108 | 212 | 344 | 446 | 626 | 729 | 927 | 1005 | 1218 | |
References
- Zheng, B.K.; Chen, C.; Lin, Y.G.; Hu, Y.F.; Ye, X.R.; Zhai, G.F.; Zio, E. Optimal design of step-stress accelerated degradation test oriented by nonlinear and distributed degradation process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2022, 217, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.R.; Hu, Y.F.; Zheng, B.K.; Chen, C.; Zhai, G.F. A new class of multi-stress acceleration models with interaction effects and its extension to accelerated degradation modelling. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2022, 228, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, Z.P.; Xu, M.H.; Li, Y.L. Novel reliability-based optimization method for thermal structure with hybrid random, interval and fuzzy parameters. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 47, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiang, X.; Xu, M.H.; Wu, T. Recent advances in surrogate modeling methods for uncertainty quantification and propagation. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Son, K.; Fouladirad, M.; Barros, A.; Levrat, E.; Iung, B. Remaining useful life estimation based on stochastic deterioration models: A comparative study. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2013, 112, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.Y.; Tseng, S.T. Mis-specification analysis of linear degradation models. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2009, 58, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, G.A.; Schenkelberg, F. Modelling accelerated degradation data using Wiener diffusion with a time scale transformation. Lifetime Data Anal. 1997, 3, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, X.S.; Wang, W.B.; Hu, C.H.; Zhou, D.H.; Pecht, M.G. Remaining useful life estimation based on a nonlinear diffusion degradation process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2012, 61, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Balakrishnan, N.; Guo, B. Residual life estimation based on a generalized Wiener degradation process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2014, 124, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.H.; Gu, D.W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Li, S.L.; Chen, B.K.; Chen, P.F. Multiple stresses optimization design of constant-stress accelerated degradation test based on Wiener process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2025, 239, 496–514. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.H.; Liao, H.T.; Ji, H.; Wang, S.P.; Yin, F.L.; Nie, S.L. Optimal design of hybrid accelerated test based on the Inverse Gaussian process model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2021, 210, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.J.; Wang, G.J.; Wei, W.M.; Jiang, M.Y. Remaining useful life evaluation for accelerated Wiener degradation process model with mixed random effects and measurement errors. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2023, 39, 1334–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Huang, H.Z.; Peng, W.W.; Zhou, J. Bayesian information fusion for degradation analysis of deteriorating products with individual heterogeneity. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2019, 233, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Su, X.B.; Wang, J.J. Nonlinear Doubly Wiener Constant-Stress Accelerated Degradation Model Based on Uncertainties and Acceleration Factor Constant Principle. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.J.; Guo, X.S.; Yu, C.Q.; Xue, H.J.; Zhou, Z.J. Accelerated degradation tests modeling based on the nonlinear wiener process with random effects. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 560726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.Y.; Sun, F.Q.; Wang, N. A general accelerated degradation model based on the Wiener process. Materials 2016, 9, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, H.F.; Chen, H.T.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zio, E. Accelerated degradation testing for lifetime analysis considering random effects and the influence of stress and measurement errors. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2024, 247, 110101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.H.; Liu, Z.G.; Tang, S.J.; Sun, X.Y.; Si, X.S. Remaining useful life prediction under imperfect prior degradation information. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 189262–189275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.S.; Chen, L.P.; Tang, L.C.; Xie, M. Accelerated degradation test planning using the inverse Gaussian process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2014, 63, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Xu, T.X.; Wang, W.Y. Remaining life prediction based on Wiener processes with ADT prior information. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2016, 32, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Research on the Theory and Method of Degradation Failure Modeling Based on Stochastic Process. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.B.; Fu, H.M.; Liu, C.R. A Wiener process model for accelerated degradation analysis considering measurement errors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 65, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Wang, B.X.; Wu, W.H.; Hong, Y.L. Reliability analysis for accelerated degradation data based on the Wiener process with random effects. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2020, 36, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.S.; Zhou, D.H. A generalized result for degradation model-based reliability estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 11, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noortwijk, J.M. A survey of the application of gamma processes in maintenance. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2009, 94, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingwood, B.R.; Mori, Y. Probabilistic methods for condition assessment and life prediction of concrete structures in nuclear power plants. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1993, 142, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Q.; Balakrishnan, N.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, J.L. Bivariate degradation analysis of products based on Wiener processes and copulas. J. Stat. Comput. Sim. 2013, 83, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.H.; Bae, S.J. A random-effect gamma process model with random initial degradation for accelerated destructive degradation testing data. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2024, 40, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A. Maximum likelihood estimation from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Life Cycle Reliability Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 351–354. [Google Scholar]






| Truth value | 16 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 0.04 |
| 17.7006 | 0.9677 | 1.0901 | 1.3695 | 1.0645 | 0.0086 | |
| 17.3076 | 1.0678 | 1.0643 | 1.3642 | 1 | 0.0085 | |
| 15.4473 | 0.6883 | 1.2732 | 1.3868 | 1.3868 | 0.0216 | |
| 18.4373 | − | 1.1944 | 1.3712 | 1.0821 | 0.0193 |
| Truth value | − | − | 0.2413 | [0.2172, 0.2677] |
| 7.3774 × 103 | −1.4743 × 104 | 0.2388 | [0.2214, 0.2611] | |
| 7.1753 × 103 | −1.4341 × 104 | 0.2449 | [0.2237, 0.2720] | |
| 7.4358 × 103 | −1.4474 × 104 | 0.2693 | [0.2510, 0.2896] | |
| 6.7516 × 103 | −1.3588 × 104 | 0.2329 | [0.2245, 0.2414] |
| 0.0999 | 0.0096 | 2.0150 | 0.4758 | 0.5006 | 0.0071 | |
| 0.3942 | 0.1091 | 0.5918 | 0.4374 | 1 | 3.0256 × 10−4 | |
| 0.0925 | 0.0121 | 2.1012 | 0.4791 | 0.4791 | 0.0083 | |
| 0.1179 | − | 2.0133 | 0.4525 | 0.6474 | 0.0096 |
| −60.1128 | 132.2256 | 1.6372 × 105 | [104,937.8751, 256,149.6332] | |
| −113.0995 | 236.1990 | 2.1228 × 104 | [7204.4619, 115,221.4058] | |
| −61.7570 | 133.5140 | 1.6794 × 105 | [102,645.0685, 278,910.1876] | |
| −181.5293 | 373.0586 | 1.6119 × 105 | [98,371.9130, 289,176.0514] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Yan, Z.; Jia, J. Reliability Modeling Method for Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation Based on the Generalized Wiener Process. Entropy 2025, 27, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121197
Li S, Yan Z, Jia J. Reliability Modeling Method for Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation Based on the Generalized Wiener Process. Entropy. 2025; 27(12):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121197
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shanshan, Zaizai Yan, and Junmei Jia. 2025. "Reliability Modeling Method for Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation Based on the Generalized Wiener Process" Entropy 27, no. 12: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121197
APA StyleLi, S., Yan, Z., & Jia, J. (2025). Reliability Modeling Method for Constant Stress Accelerated Degradation Based on the Generalized Wiener Process. Entropy, 27(12), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27121197






