Coupled Dynamics of Information–Epidemic Spreading with Resource Allocation and Transmission on Multi-Layer Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
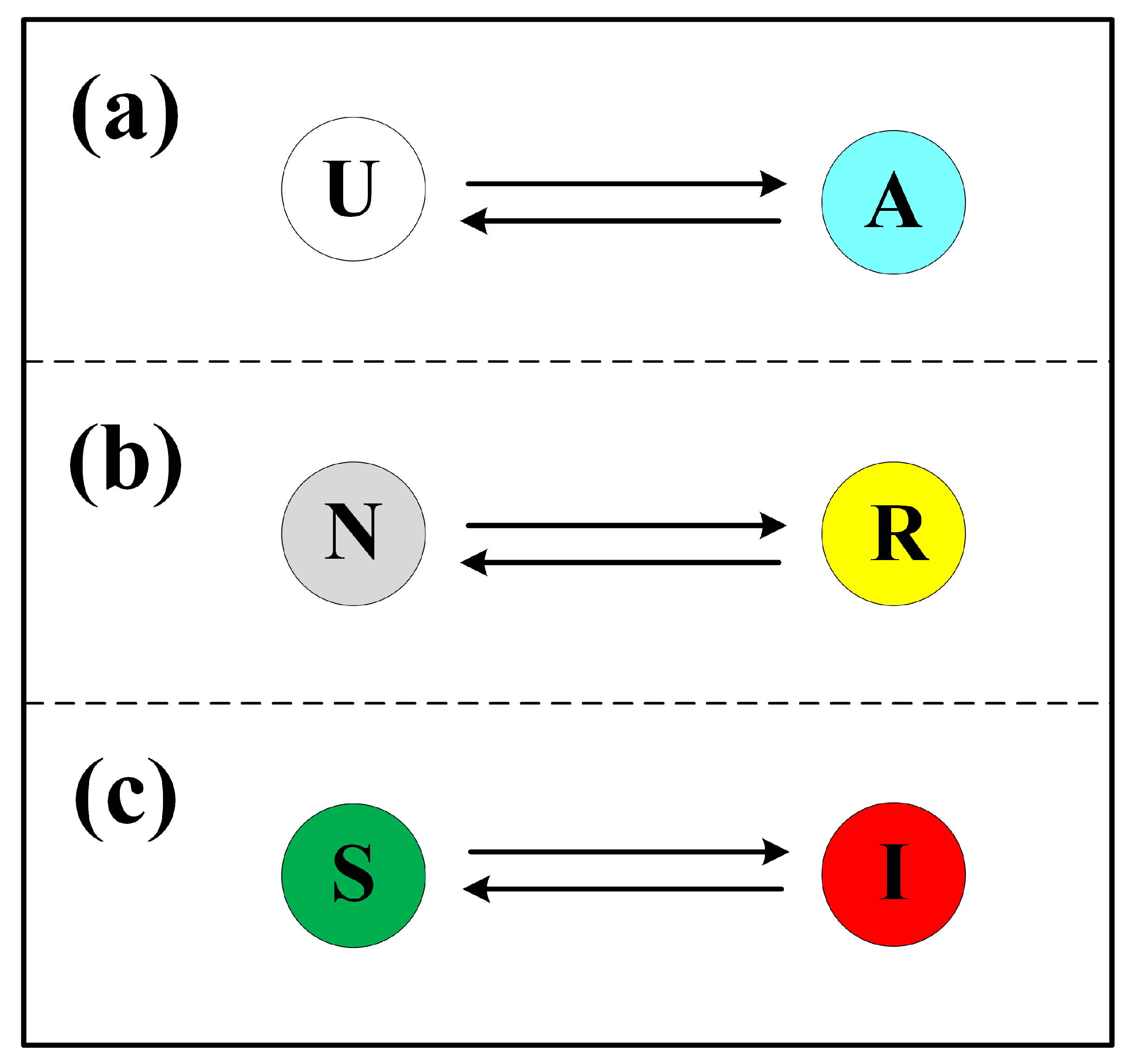
2. Co-Evolutionary Spreading Model
2.1. Information Diffusion
2.2. Resource Transmission
2.3. Disease Propagation
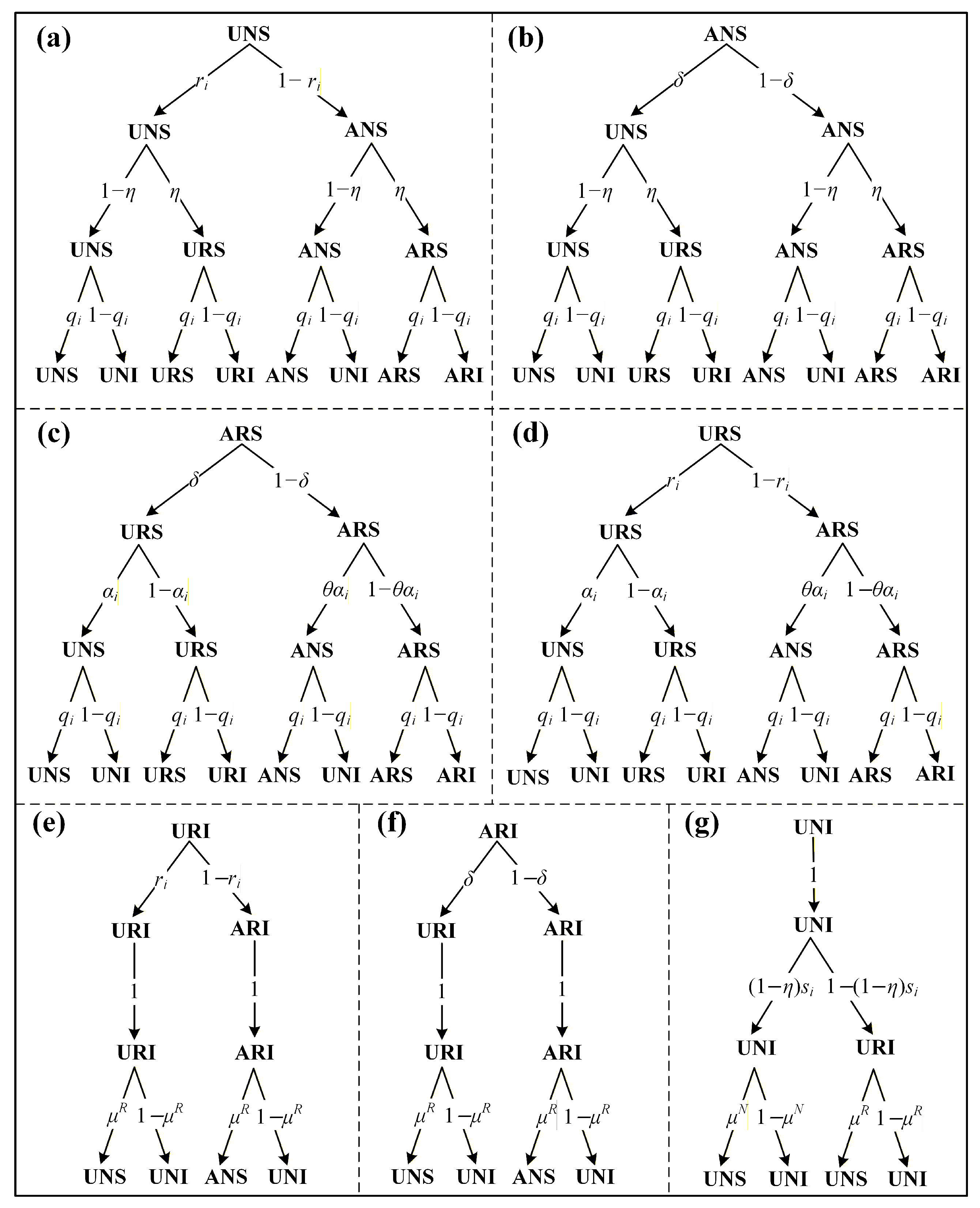
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Dynamical Equations
3.2. Epidemic Threshold
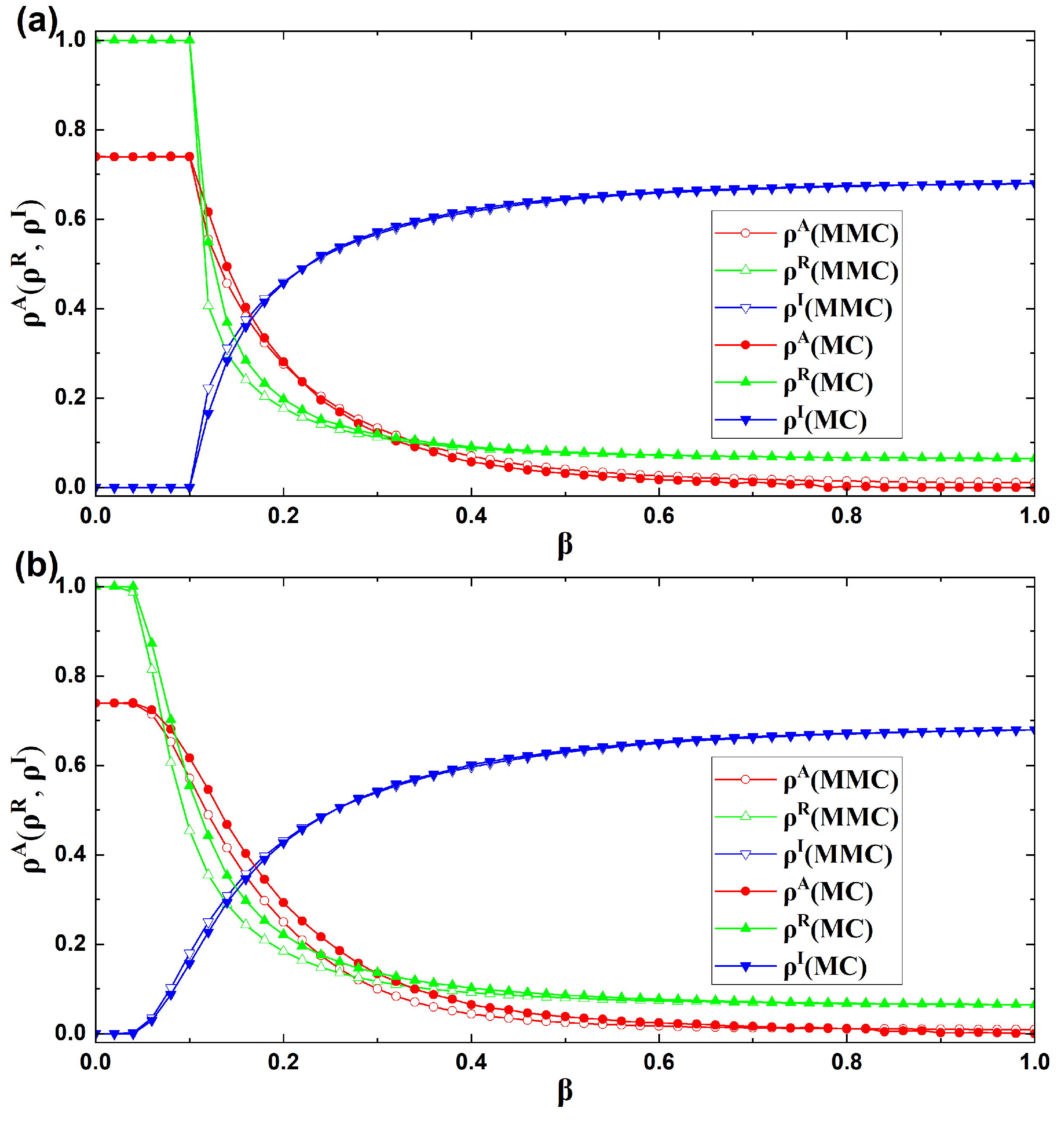
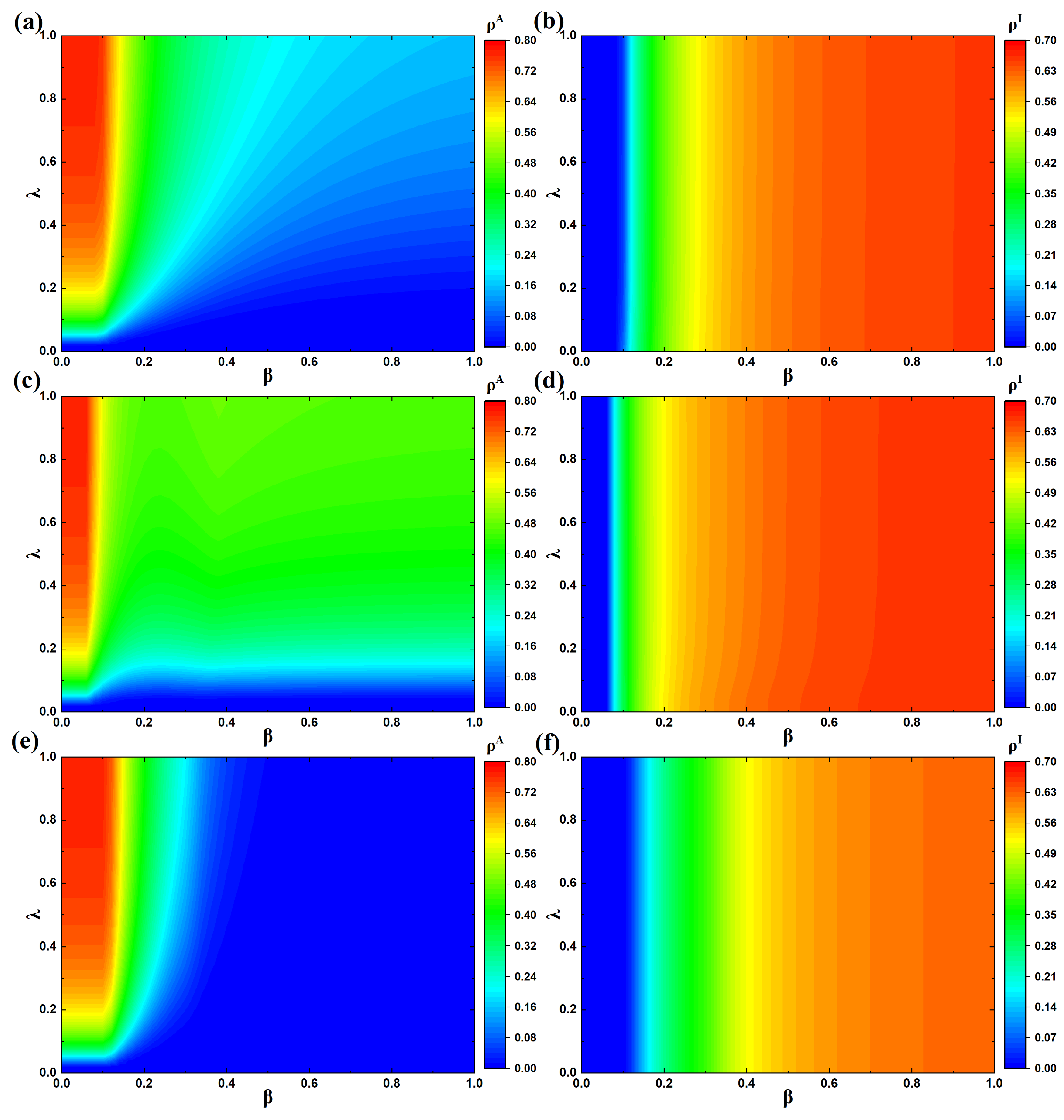
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Accuracy Analysis of the Dynamical Equations
4.2. Analysis of Epidemic Prevalence
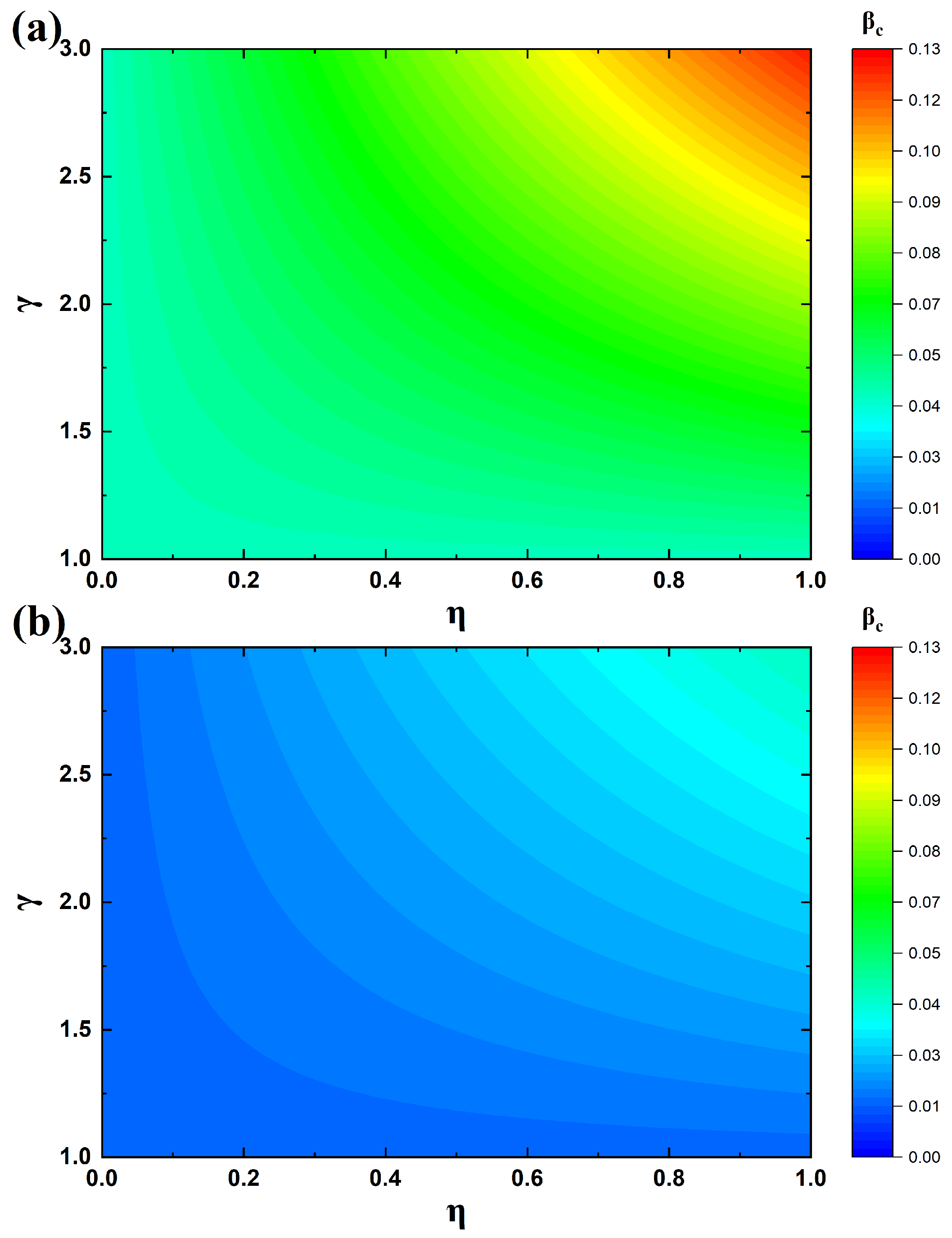
4.3. Analysis of the Epidemic Threshold
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckee, C.; Noor, A.; Sattenspiel, L. Thinking clearly about social aspects of infectious disease transmission. Nature 2021, 595, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.; Fraser, C.; Donnelly, C.A.; Ghani, A.C.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Hedley, A.J.; Leung, G.M.; Ho, L.-M.; Lam, T.H.; Thach, T.Q.; et al. Transmission dynamics of the etiological agent of SARS in Hong Kong: Impact of public health interventions. Science 2003, 300, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaxman, S.; Mishra, S.; Gandy, A.; Unwin, H.J.T.; Mellan, T.A.; Coupland, H.; Whittaker, C.; Zhu, H.; Berah, T.; Eaton, J.W.; et al. Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe. Nature 2020, 584, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassly, N.C.; Fraser, C. Mathematical models of infectious disease transmission. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Yang, M.; Xie, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Yang, D.; Sun, G.-Q.; et al. Modelling multiscale infectious disease in complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2025, 1113, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, C.J.E.; Lessler, J. Opportunities and challenges in modeling emerging infectious diseases. Science 2017, 357, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, S.; Salathé, M.; Jansen, V.A.A. Modelling the influence of human behaviour on the spread of infectious diseases: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perra, N. Non-pharmaceutical interventions during the COVID-19 pandemic: A review. Phys. Rep. 2021, 913, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowzari, C.; Preciado, V.M.; Pappas, G.J. Optimal resource allocation for control of networked epidemic models. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2017, 4, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Xia, C.; Perc, M. Diffusion of resources and their impact on epidemic spreading in multilayer networks with simplicial complexes. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 164, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar]
- Hethcote, H.W. The mathematics of infectious diseases. SIAM Rev. 2000, 42, 599–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, A.; Katriel, G. Mathematical modelling and prediction in infectious disease epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleta, A.; Ferraz de Arruda, G.; Moreno, Y. Data-driven contact structures: From homogeneous mixing to multilayer networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.J.; Huang, P.; Yin, F.; Luo, X.I.; Almquist, Z.W.; Hipp, J.R.; Butts, C.T. Spatial heterogeneity can lead to substantial local variations in COVID-19 timing and severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24180–24187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic spreading in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3200–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Latora, V.; Moreno, Y.; Chavez, M.; Hwang, D.-U. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2006, 424, 175–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C.; Van Mieghem, P.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 925–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Q.; He, R.; Hou, L.-F.; Luo, X.; Gao, S.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-K. Optimal control of spatial diseases spreading in networked reaction–diffusion systems. Phys. Rep. 2025, 1111, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Q.-H.; Liang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, T. Coevolution spreading in complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2019, 820, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad-Roy, C.M.; Traulsen, A. Dynamics in a behavioral–epidemiological model for individual adherence to a nonpharmaceutical intervention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2311584120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Hong, Z.; Yin, Q.; Xia, C. Coupled propagation dynamics on complex networks: A brief review. Europhys. Lett. 2024, 145, 11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, S.; Gilad, E.; Watkins, C.; Jansen, V.A.A. The spread of awareness and its impact on epidemic outbreaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6872–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-K.; Liu, C.; Zhan, X.-X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.-X.; Zhang, Y.-C. Dynamics of information diffusion and its applications on complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2016, 651, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, C. Co-evolution spreading of multiple information and epidemics on two-layered networks under the influence of mass media. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 102, 3039–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauch, C.T.; Galvani, A.P. Social factors in epidemiology. Science 2013, 342, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelä, M.; Arenas, A.; Barthelemy, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Moreno, Y.; Porter, M.A. Multilayer networks. J. Complex Netw. 2014, 2, 203–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Bianconi, G.; Criado, R.; del Genio, C.I.; Gómez-Gardeñes, J.; Romance, M.; Sendiña-Nadal, I.; Wang, Z.; Zanin, M. The structure and dynamics of multilayer networks. Phys. Rep. 2014, 544, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Domenico, M.; Granell, C.; Porter, M.A.; Arenas, A. The physics of spreading processes in multilayer networks. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, G.F.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Moreno, Y. Fundamentals of spreading processes in single and multilayer complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2018, 756, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, M. More is different in real-world multilayer networks. Nat. Phys. 2023, 19, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, F.; Liò, P.; Sguanci, L. Risk perception in epidemic modeling. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 061904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moinet, A.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Barrat, A. Effect of risk perception on epidemic spreading in temporal networks. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 012313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Diestra, J.L.; Meyers, L.A. Local risk perception enhances epidemic control. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granell, C.; Gómez, S.; Arenas, A. Dynamical interplay between awareness and epidemic spreading in multiplex networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 128701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Epidemic propagation with positive and negative preventive information in multiplex networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C. Information–epidemic co–evolution propagation under policy intervention in multiplex networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 14583–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, J.; Han, Z.; Zhu, P. Coupled epidemic dynamics with awareness heterogeneity in multiplex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 187, 115335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. Effects of isolation and information dissemination on epidemic dynamics in multiplex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2025, 199, 116889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wesemael, T.; Rocha, L.E.C.; Baetens, J.M. Epidemic risk perception and social interactions lead to awareness cascades on multiplex networks. J. Phys. Complex. 2025, 6, 015011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, E.; Bagnoli, F. Epidemic spreading and risk perception in multiplex networks: A self-organized percolation method. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 052817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dai, X.; Wang, L.; Perra, N.; Wang, Z. Epidemic spreading in metapopulation networks coupled with awareness propagation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 7686–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Xia, C. Heterogeneous propagation processes between awareness and epidemic on signed multiplex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 183, 114858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhang, C.; Hou, L.; Wang, K. Coupled epidemic-information propagation with stranding mechanism on multiplex metapopulation networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2024, 11, 6727–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ruan, Z.; Cao, Z.; Xuan, Q.; Zeng, D.D. Effect of heterogeneous risk perception on information diffusion, behavior change, and disease transmission. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 042314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, J. The effect of information-driven resource allocation on the propagation of epidemic with incubation period. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 110, 2913–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Yu, Y. The impact of the self-recognition ability and physical quality on coupled negative information-behavior-epidemic dynamics in multiplex networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 169, 113229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wang, X. Impact of positive and negative information on epidemic spread in a three-layer network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 186, 115264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Hong, Z. Coupled Dynamics of Information–Epidemic Spreading with Resource Allocation and Transmission on Multi-Layer Networks. Entropy 2025, 27, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101080
Yin Q, Wang Z, Wang K, Hong Z. Coupled Dynamics of Information–Epidemic Spreading with Resource Allocation and Transmission on Multi-Layer Networks. Entropy. 2025; 27(10):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101080
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Qian, Zhishuang Wang, Kaiyao Wang, and Zhiyong Hong. 2025. "Coupled Dynamics of Information–Epidemic Spreading with Resource Allocation and Transmission on Multi-Layer Networks" Entropy 27, no. 10: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101080
APA StyleYin, Q., Wang, Z., Wang, K., & Hong, Z. (2025). Coupled Dynamics of Information–Epidemic Spreading with Resource Allocation and Transmission on Multi-Layer Networks. Entropy, 27(10), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101080





