Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility Analysis of MEG in Patients with Schizophrenia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Collection of MEGs
2.3. Preprocessing of MEGs
2.4. Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility
2.5. Statistical Methods
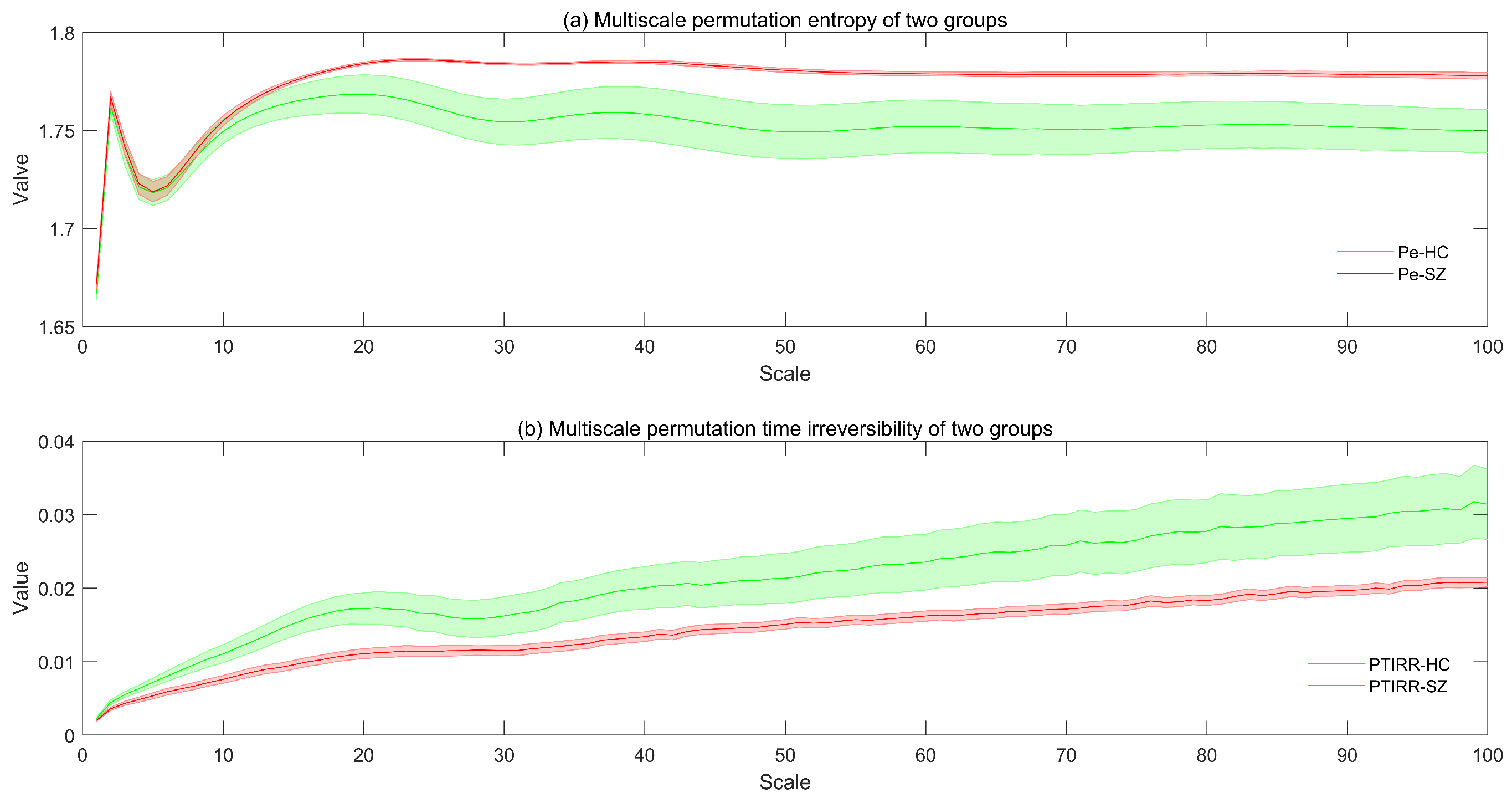
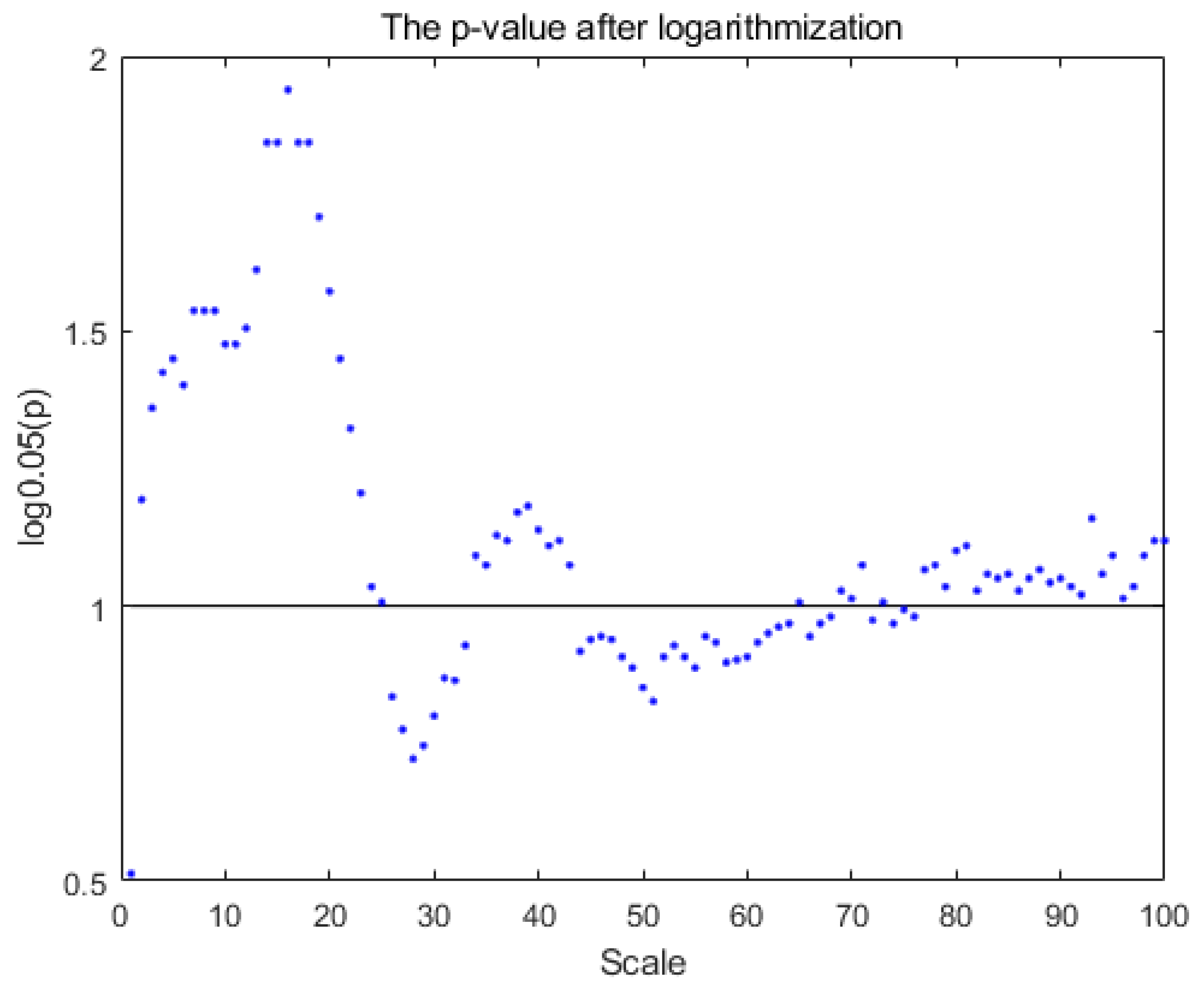
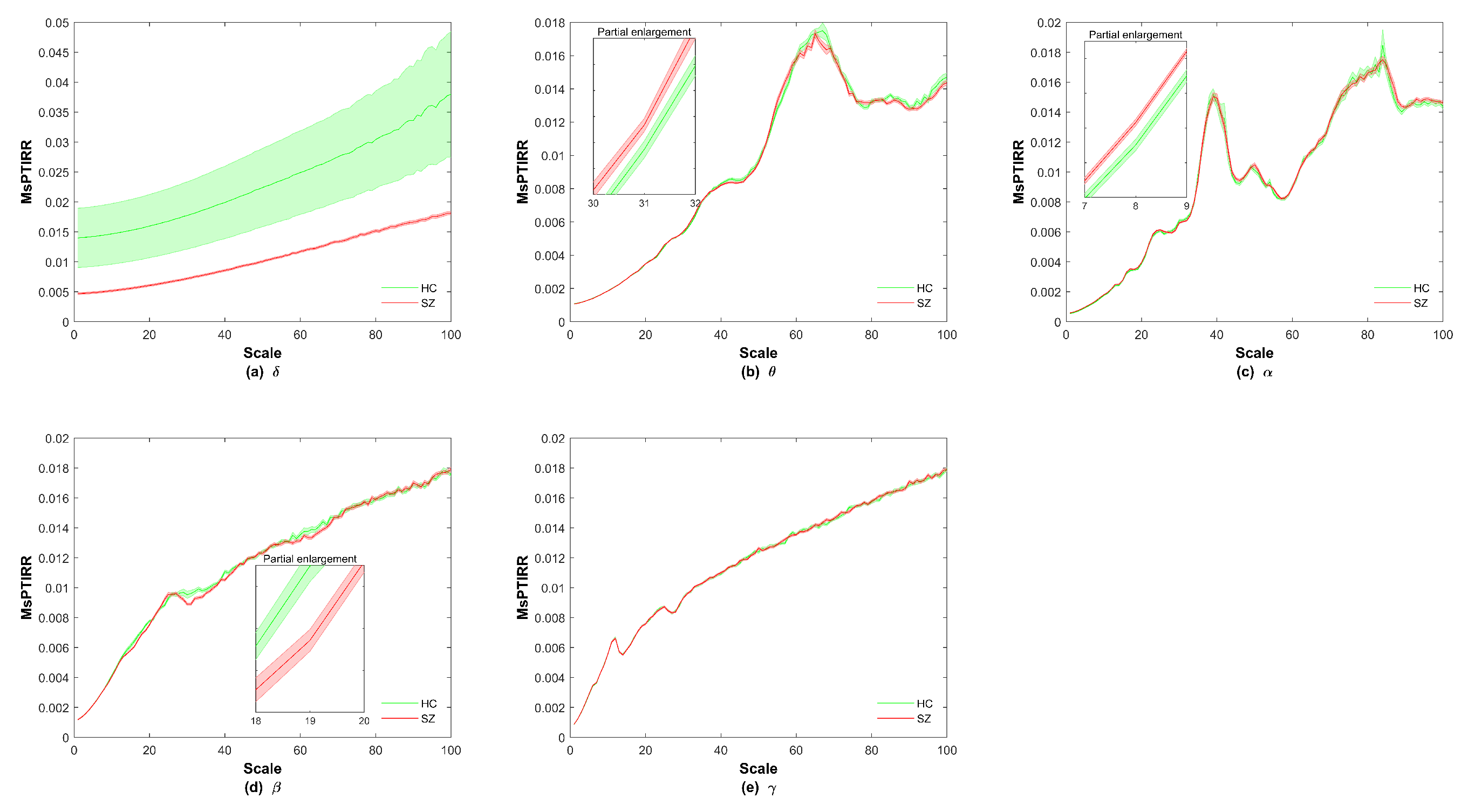
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jauhar, S.; Johnstone, M.; McKenna, P.J. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2022, 399, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, A.T.; Drew, W.; Stubbs, J.L.; Taylor, J.J.; Liloia, D.; Grafman, J.; Silbersweig, D.; Fox, M.D.; Siddiqi, S.H. Heterogeneous patterns of brain atrophy in schizophrenia localize to a common brain network. Nature Mental Health 2025, 3, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Ju, H.; Ding, W.; Zhang, D. AGBN-Transformer: Anatomy-guided brain network transformer for schizophrenia diagnosis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 102, 107226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Marques, T.R.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia—An overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Wen, P.; Song, B.; Li, Y. 3D convolutional neural network for schizophrenia detection using as EEG-based functional brain network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 89, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, S.; Sarma, M.; Samanta, D. Graph signal processing and graph learning approaches to Schizophrenia pattern identification in brain Electroencephalogram. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xue, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Homotopic functional connectivity disruptions in schizophrenia and their associated gene expression. Neuroimage 2024, 289, 120551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosala, B.; Kapgate, P.D.; Jain, P.; Chaurasia, R.N.; Gupta, M. Wavelet transforms for feature engineering in EEG data processing: An application on Schizophrenia. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 85, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Ran, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, W.; et al. Schizophrenia classification and abnormalities reveal of brain region functional connection by deep-learning multiple sparsely connected network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 96, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Keefe, R.S.; McGuire, P.K. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: Aetiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1902–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, D.C. Cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia: From pathophysiology to treatment. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlati, S.; Nibbio, G.; Vita, A. Evidence-based psychosocial interventions in schizophrenia: A critical review. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2024, 37, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, R.; Nasrallah, H.; Akbarian, S.; Carpenter, W.T., Jr.; DeLisi, L.E.; Gaebel, W.; Green, M.F.; Gur, R.E.; Heckers, S.; Kane, J.M.; et al. The schizophrenia syndrome, circa 2024: What we know and how that informs its nature. Schizophr. Res. 2024, 264, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, U.; Hanif, M.; Rashid, A.; Qaisar, S.M.; Subasi, A. EEG-based schizophrenia classification using penalized sequential dictionary learning in the context of mobile healthcare. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 90, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K. Artificial intelligence system for verification of schizophrenia via theta-EEG rhythm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 81, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, N.; O’Gorman, C.; Horgan, I.; Weeratunga, M.; Halstead, S.; Moussiopoulou, J.; Campana, M.; Yakimov, V.; Wagner, E.; Siskind, D. Inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid markers in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 69 studies with 5710 participants. Schizophr. Res. 2024, 266, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, C.; Wang, L.; Jiao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Cai, H. Long non-coding RNAs in schizophrenia: Genetic variations, treatment markers and potential targeted signaling pathways. Schizophr. Res. 2023, 260, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathi, N.; Sankaran, K.S. Advances and clinical Implications of neuroanatomical biomarkers in schizophrenia by optimizing brain tissue segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 102, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fred, A.L.; Kumar, S.N.; Kumar Haridhas, A.; Ghosh, S.; Purushothaman Bhuvana, H.; Sim, W.K.J.; Vimalan, V.; Givo, F.A.S.; Jousmäki, V.; Padmanabhan, P.; et al. A brief introduction to magnetoencephalography (MEG) and its clinical applications. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, M.J.; Leggett, J.; Rea, M.; Hill, R.M.; Holmes, N.; Boto, E.; Bowtell, R. Magnetoencephalography with optically pumped magnetometers (OPM-MEG): The next generation of functional neuroimaging. Trends Neurosci. 2022, 45, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Z.J.; Pham, T.; Chen, S.A.; Makowski, D. Brain entropy, fractal dimensions and predictability: A review of complexity measures for EEG in healthy and neuropsychiatric populations. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 5047–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, S.I.; Rabbani, M.; Povinelli, R.J. A comprehensive survey on detection of non-linear analysis techniques for EEG signal. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Digital Health (ICDH), Chicago, IL, USA, 2–8 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shang, P.; Shang, B. Time irreversibility analysis and abnormality detection based on Riemannian geometry for complex time series. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 117, 106985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, J.; Kafri, Y.; Tailleur, J.; van Wijland, F. Time irreversibility in active matter, from micro to macro. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022, 4, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, J.; Perc, M.; Yao, W.; Dai, J.; Guo, D.; Yao, D. Time irreversibility and amplitude irreversibility measures for nonequilibrium processes. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 96, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petelczyc, M.; Czechowski, Z. Effect of nonlinearity and persistence on multiscale irreversibility, non-stationarity, and complexity of time series—Case of data generated by the modified Langevin model. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 33, 053107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, M.; Zebrowski, J.J.; Rams, K.; Ozimek, M.; Baranowski, R. Assessment of time irreversibility in a time series using visibility graphs. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2022, 2, 877474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Modified symbolic relative entropy based electroencephalogram time irreversibility analysis. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 038701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Güntekin, B.; Aktürk, T.; Hanoğlu, L.; Papo, D. Time irreversibility of resting-state activity in the healthy brain and pathology. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yao, W.; Wang, J.; Dai, J. Quantifying time irreversibility using probabilistic differences between symmetric permutations. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 383, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhoumi, K.; Lina, J.; Gotman, J. Discriminating Preictal and Interictal States Using Time Irreversibility of the Intracerebral Eeg in Patients with Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. In Epilepsia; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 54, pp. 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W. Permutation time irreversibility in sleep electroencephalograms: Dependence on sleep stage and the effect of equal values. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 109, 054104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, D.; Shannahoff-Khalsa, D.; Sale, J.; Wright, J.A.; Fadiga, L.; Papo, D. The time scales of irreversibility in spontaneous brain activity are altered in obsessive compulsive disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1158404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Song, J.; Li, D. Multiscale Irreversibility Analysis of Time Series Based on Permutation Jensen-Shannon Distance. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2025, 24, 2550013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 71, 021906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennel, M.B.; Brown, R.; Abarbanel, H.D. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Eykholt, R.; Salas, J. Nonlinear dynamics, delay times, and embedding windows. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1999, 127, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, U. Stochastic thermodynamics, fluctuation theorems and molecular machines. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 126001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, É.; Parrondo, J.M. Entropy production and Kullback-Leibler divergence between stationary trajectories of discrete systems. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2012, 85, 031129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Xue, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Deng, H.; Tan, S. Dynamics and synchronization control in schizophrenia for EEG signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dvorak, D.; Fenton, A.A. Targeting neural synchrony deficits is sufficient to improve cognition in a schizophrenia-related neurodevelopmental model. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braus, D. Temporal perception and organisation, neuronal synchronisation and schizophrenia. Fortschritte Neurol. Psychiatr. 2002, 70, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Howes, O.D. Dopamine and glutamate in schizophrenia: Biology, symptoms and treatment. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.C.; McCollum, L.A.; Schoonover, K.E.; Mabry, S.J.; Roche, J.K.; Lahti, A.C. Ultrastructural evidence for glutamatergic dysregulation in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2022, 249, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Li, N.; Cai, H. Candidate metabolic biomarkers for schizophrenia in CNS and periphery: Do any possible associations exist? Schizophr. Res. 2020, 226, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Fan, F.; Chen, S.; Tian, B.; Cui, Y.; Tian, L.; Tan, S.; et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody and white matter deficits in schizophrenia treatment-resistance. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, O.D.; Shatalina, E. Integrating the neurodevelopmental and dopamine hypotheses of schizophrenia and the role of cortical excitation-inhibition balance. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 92, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.; Beck, K.; Jauhar, S.; Howes, O.D. Defining the locus of dopaminergic dysfunction in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis and test of the mesolimbic hypothesis. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Wang, W.; Williams, J.; Ma, K.; Cao, Q.; Yan, Z. Stress exposure in dopamine D4 receptor knockout mice induces schizophrenia-like behaviors via disruption of GABAergic transmission. Schizophr. Bull. 2019, 45, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, S.P.; Angelescu, I.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Mizrahi, R.; Shahrezaei, V.; Howes, O.D. Heterogeneity of striatal dopamine function in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of variance. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, M.; Brandl, F.; Knolle, F.; Cabello, J.; Leucht, C.; Scherr, M.; Mustafa, M.; Koutsouleris, N.; Leucht, S.; Ziegler, S.; et al. Aberrant striatal dopamine links topographically with cortico-thalamic dysconnectivity in schizophrenia. Brain 2020, 143, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedehouder, J.; Kushner, S. Myelination of parvalbumin interneurons: A parsimonious locus of pathophysiological convergence in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Kubicki, M.; Koerte, I.; Otsuka, T.; Rathi, Y.; Pasternak, O.; Bouix, S.; Eckbo, R.; Kikinis, Z.; von Hohenberg, C.C.; et al. Impaired white matter connectivity between regions containing mirror neurons, and relationship to negative symptoms and social cognition, in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ono, C.; Yu, Z.; Iizuka, K.; Takano, Y.; Kakuto, Y.; Funakoshi, S.; Ono, T.; et al. Ethnicity-dependent effects of schizophrenia risk variants of the OLIG2 gene on OLIG2 transcription and white matter integrity. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Yao, W.; Yan, W.; Wang, J. Network analysis of magnetoencephalogram signals in schizophrenia patients when viewing emotional facial stimuli. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelaria-Cook, F.T.; Stephen, J.M. Test–retest reliability of magnetoencephalography resting-state functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 551952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lottman, K.K.; Gawne, T.J.; Kraguljac, N.V.; Killen, J.F.; Reid, M.A.; Lahti, A.C. Examining resting-state functional connectivity in first-episode schizophrenia with 7T fMRI and MEG. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfratello, L.; Houck, J.M.; Calhoun, V.D. Relationship between MEG global dynamic functional network connectivity measures and symptoms in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 209, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, B.; D’Andrea, D.; Collins, M.O.; Rees, E.; Steward, T.G.; Zhu, Y.; Chapman, G.; Legge, S.E.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Harwood, A.J.; et al. Transcriptional programs regulating neuronal differentiation are disrupted in DLG2 knockout human embryonic stem cells and enriched for schizophrenia and related disorders risk variants. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, H.O. Altered growth factor signaling pathways as the basis of aberrant stem cell maturation in schizophrenia. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Yalcin, E.; Presumey, J.; Aw, E.; Ma, M.; Whelan, C.W.; Stevens, B.; McCarroll, S.A.; Carroll, M.C. Overexpression of schizophrenia susceptibility factor human complement C4A promotes excessive synaptic loss and behavioral changes in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, G.; Mirnics, K. Synaptic changes in the brain of subjects with schizophrenia. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, D.; Yao, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Multiscale weighted permutation entropy analysis of schizophrenia magnetoencephalograms. Entropy 2022, 24, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J. Network localization of state and trait of auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2024, 50, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shah, C.; Li, Q.; Sweeney, J.A.; Li, F.; Gong, Q. Cortical thickness abnormalities at different stages of the illness course in schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uscătescu, L.C.; Said-Yürekli, S.; Kronbichler, L.; Stelzig-Schöler, R.; Pearce, B.G.; Reich, L.A.; Weber, S.; Aichhorn, W.; Kronbichler, M. Reduced intrinsic neural timescales in schizophrenia along posterior parietal and occipital areas. NPJ Schizophr. 2021, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ren, Y.; Gu, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, Z. QEEG Biomarkers for ECT Treatment Response in Schizophrenia. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2022, 53, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, S.P.; Howes, O.D. Heterogeneity and homogeneity of regional brain structure in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Burgess, S.; Suckling, J.; Lalousis, P.A.; Batool, F.; Griffiths, S.L.; Palmer, E.; Karwath, A.; Barsky, A.; Gkoutos, G.V.; et al. Inflammation and brain structure in schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshiyama, D.; Miyakoshi, M.; Tanaka-Koshiyama, K.; Joshi, Y.B.; Sprock, J.; Braff, D.L.; Light, G.A. Abnormal phase discontinuity of alpha-and theta-frequency oscillations in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 231, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Knott, V.J.; Labelle, A.; Fisher, D.J. Alterations of resting EEG in hallucinating and nonhallucinating schizophrenia patients. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2021, 52, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, I.S.; Pokorny, V.J.; Lynn, P.A.; Klein, S.D.; Sponheim, S.R. Limited consistency and strength of neural oscillations during sustained visual attention in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2024, 9, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhu, G.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, B. Brain network analysis of working memory in schizophrenia based on multi graph attention network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 80, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
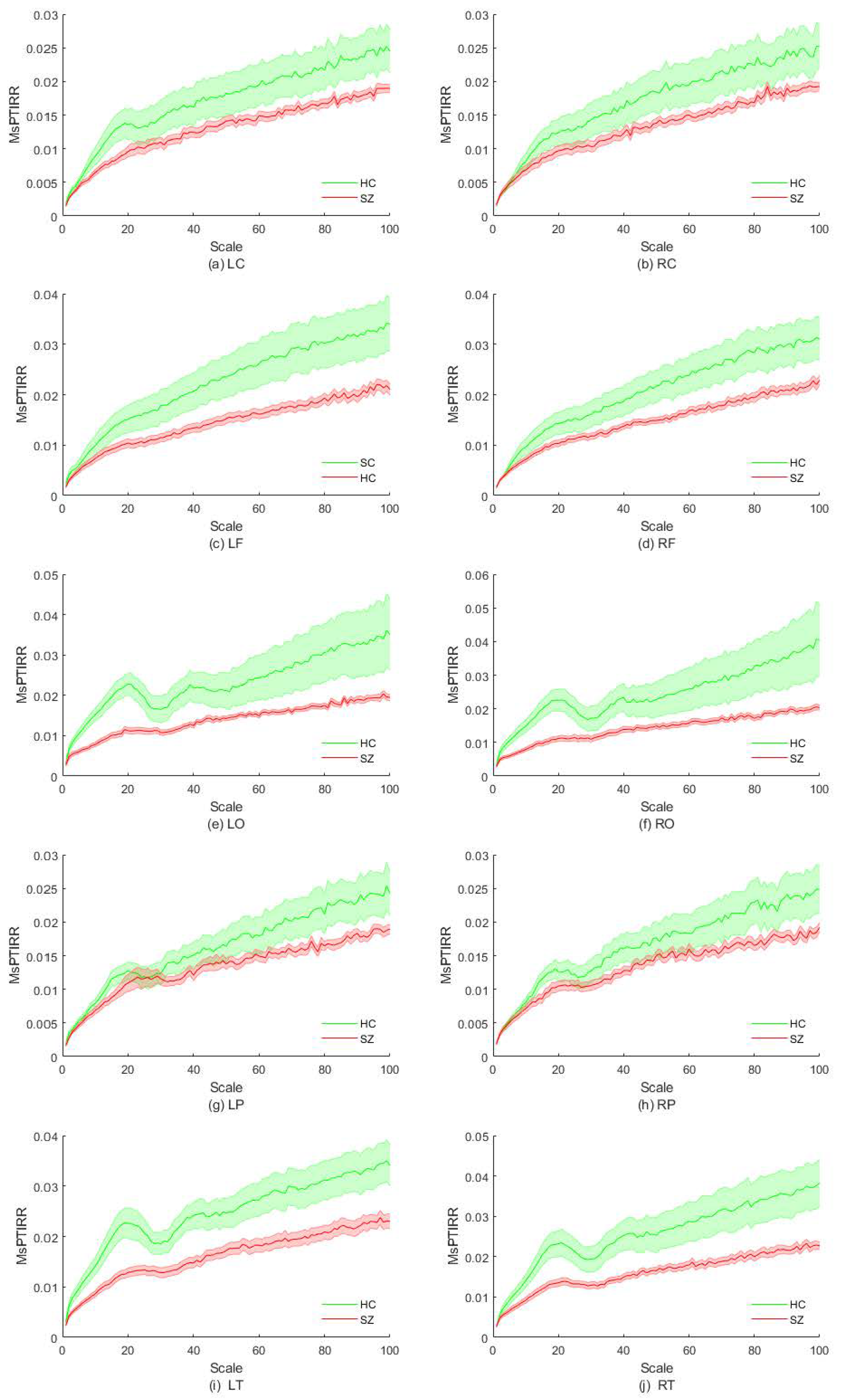
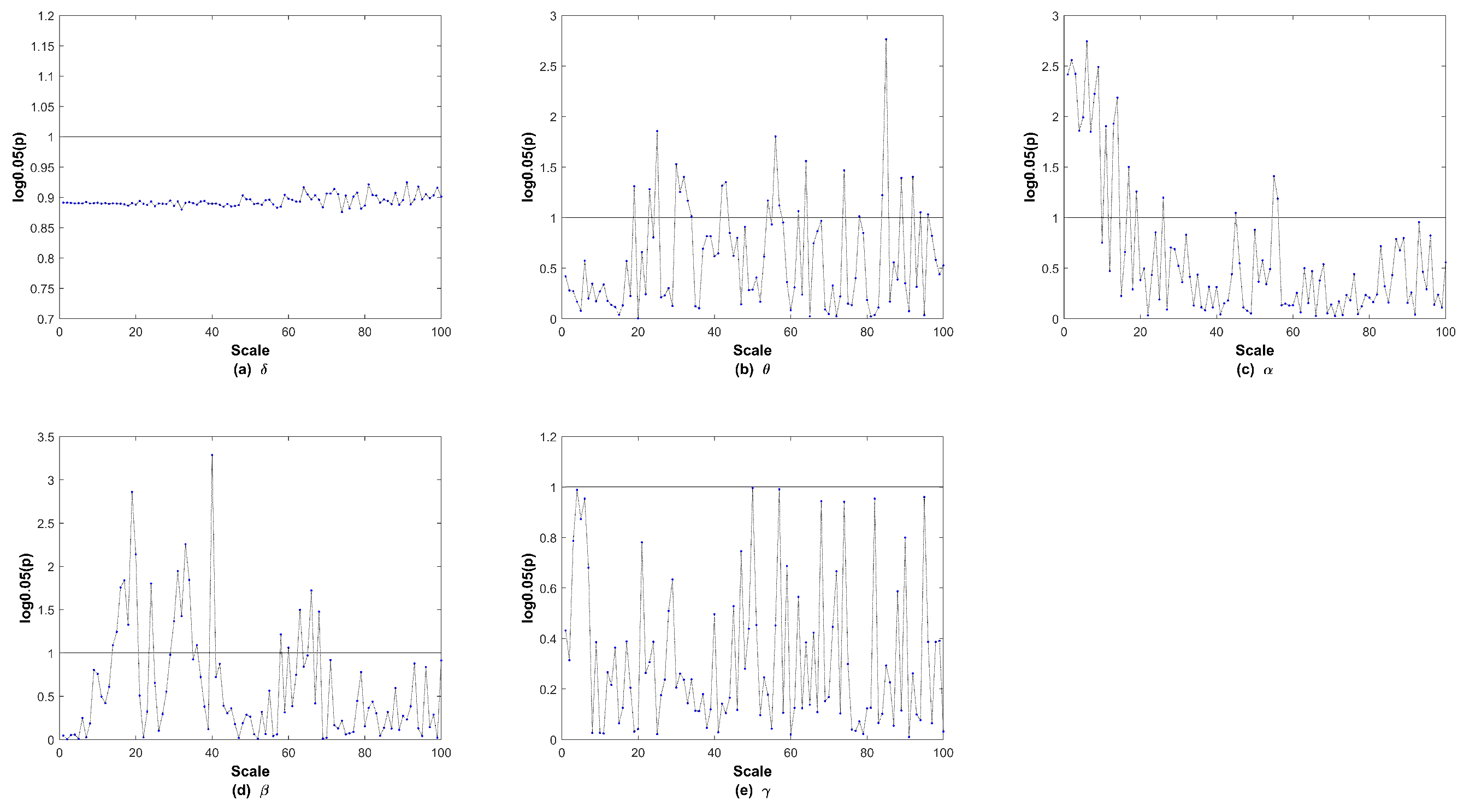
| Brain Regions | Scale Intervals with Significant Differences |
|---|---|
| LC | [15,20] |
| RC | No significant difference |
| LF | [43,100] |
| RF | [75,100] |
| LO | [2,27] and [34,45] |
| RO | [2,26] and [37,41] |
| LP | No significant difference |
| RP | No significant difference |
| LT | [2,100] |
| RT | [2,27] and [32,100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, D.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, J. Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility Analysis of MEG in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy 2025, 27, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101038
Bai D, Xue M, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chen X, Yao W, Wang J. Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility Analysis of MEG in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy. 2025; 27(10):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101038
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Dengxuan, Muxuan Xue, Yining Wang, Zhen Zhang, Xiaoli Chen, Wenpo Yao, and Jun Wang. 2025. "Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility Analysis of MEG in Patients with Schizophrenia" Entropy 27, no. 10: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101038
APA StyleBai, D., Xue, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, X., Yao, W., & Wang, J. (2025). Multiscale Permutation Time Irreversibility Analysis of MEG in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy, 27(10), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101038







