Spectral Properties of Complex Distributed Intelligence Systems Coupled with an Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Theoretical Background
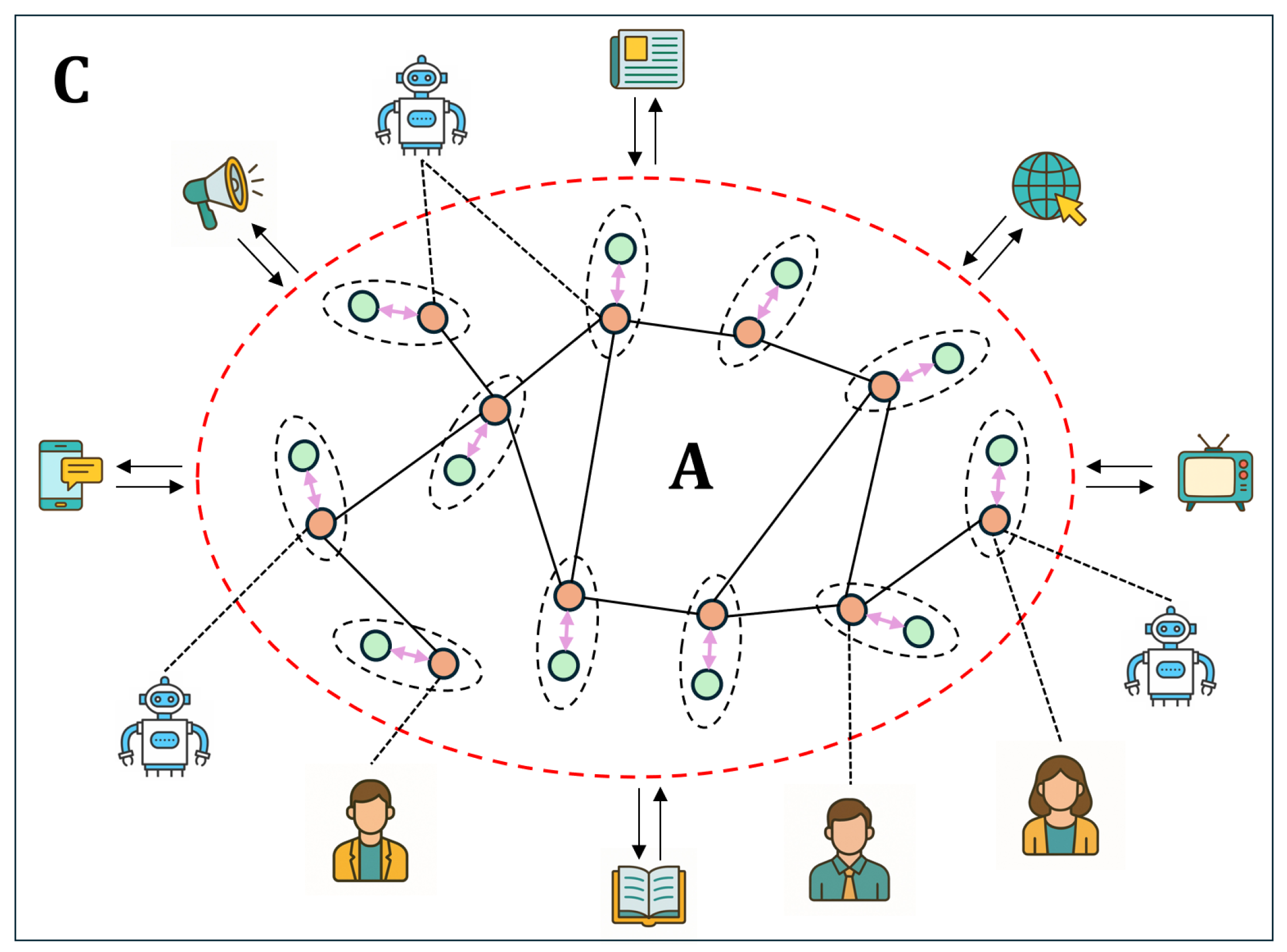
3.1. Dis Network Models
3.2. Basic Equations
4. Results
4.1. Renormalization Group for Field Eigenstates
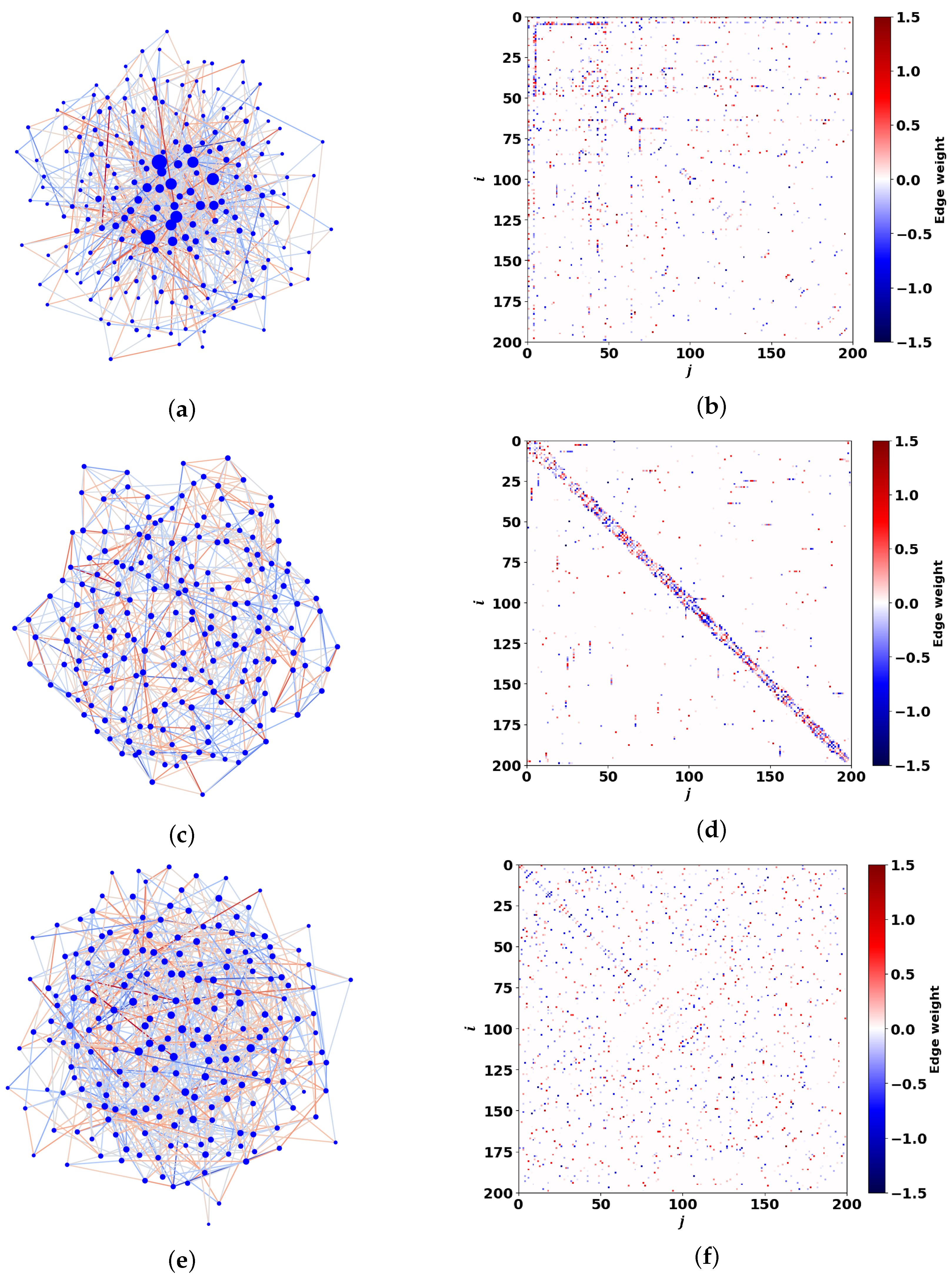
4.2. Dis Network in the Presence of Inhomogeneous Coupling with the Reservoir
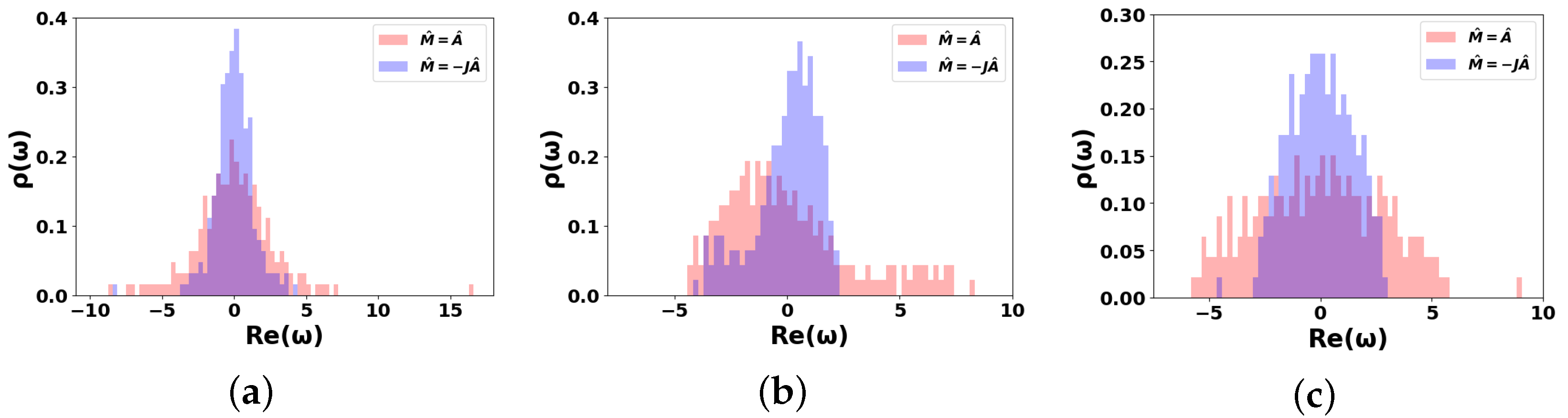
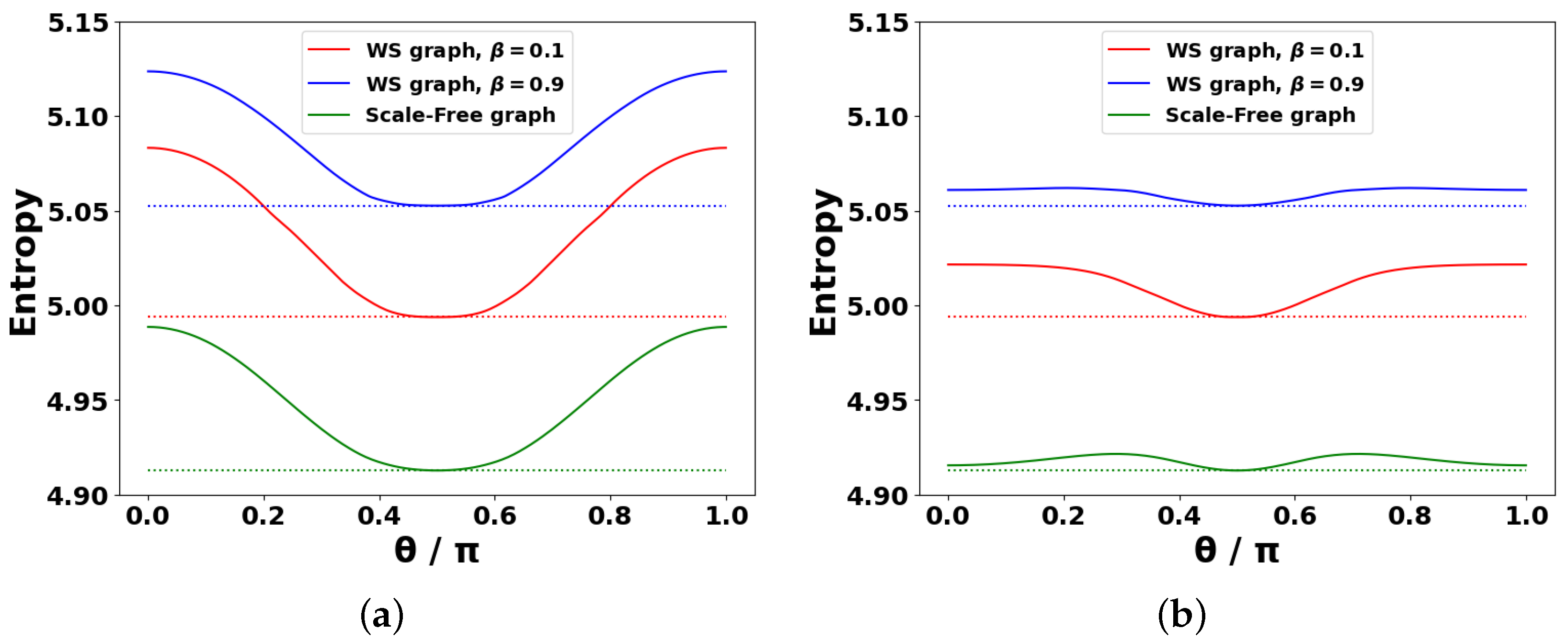
4.3. Spectral Entropy
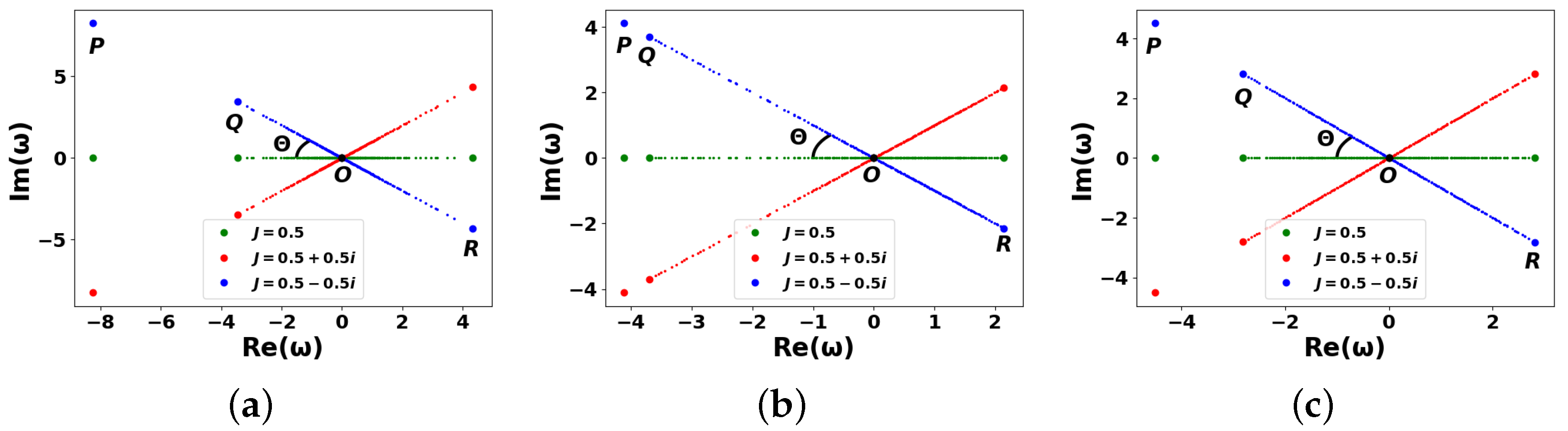
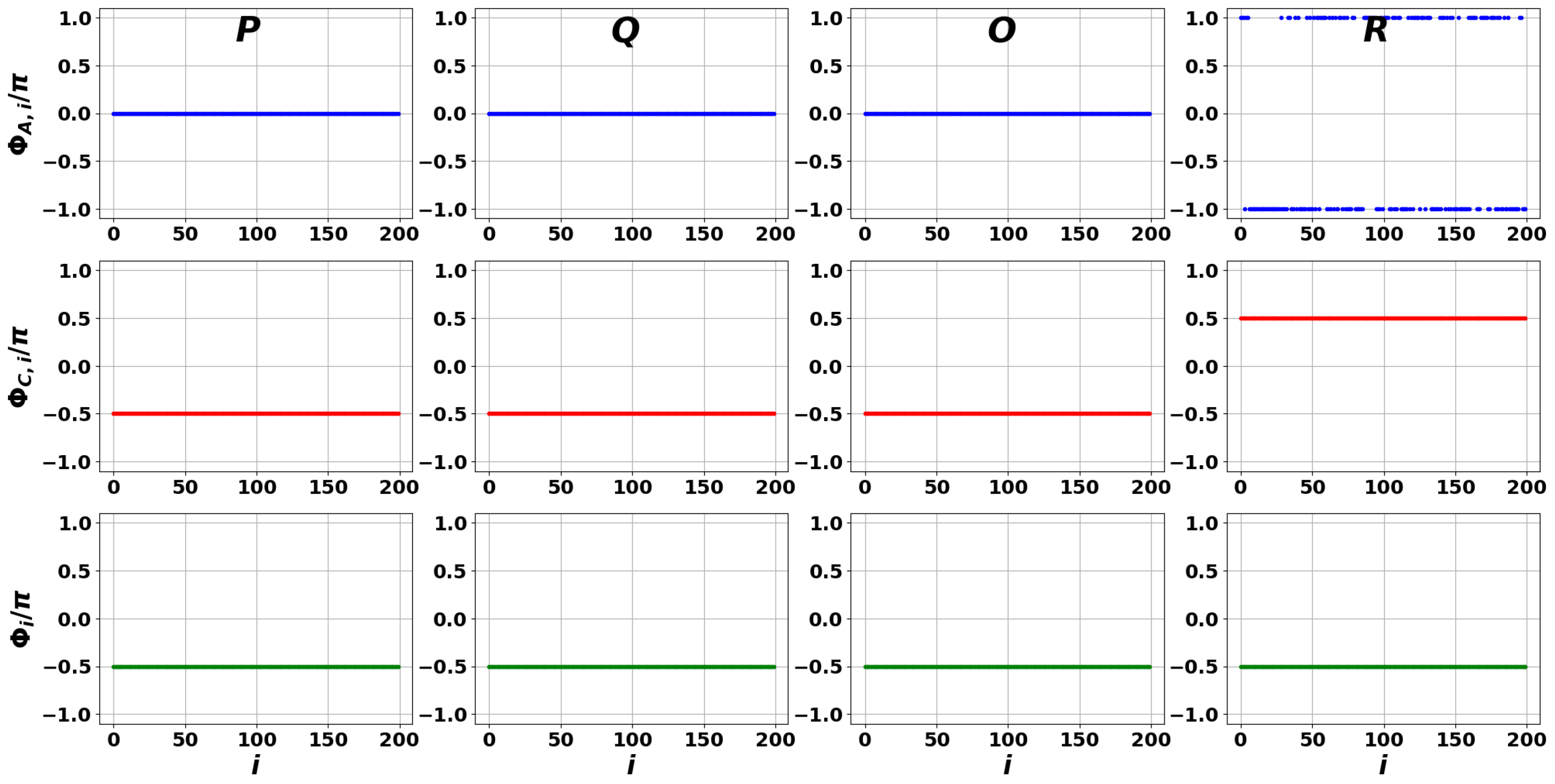
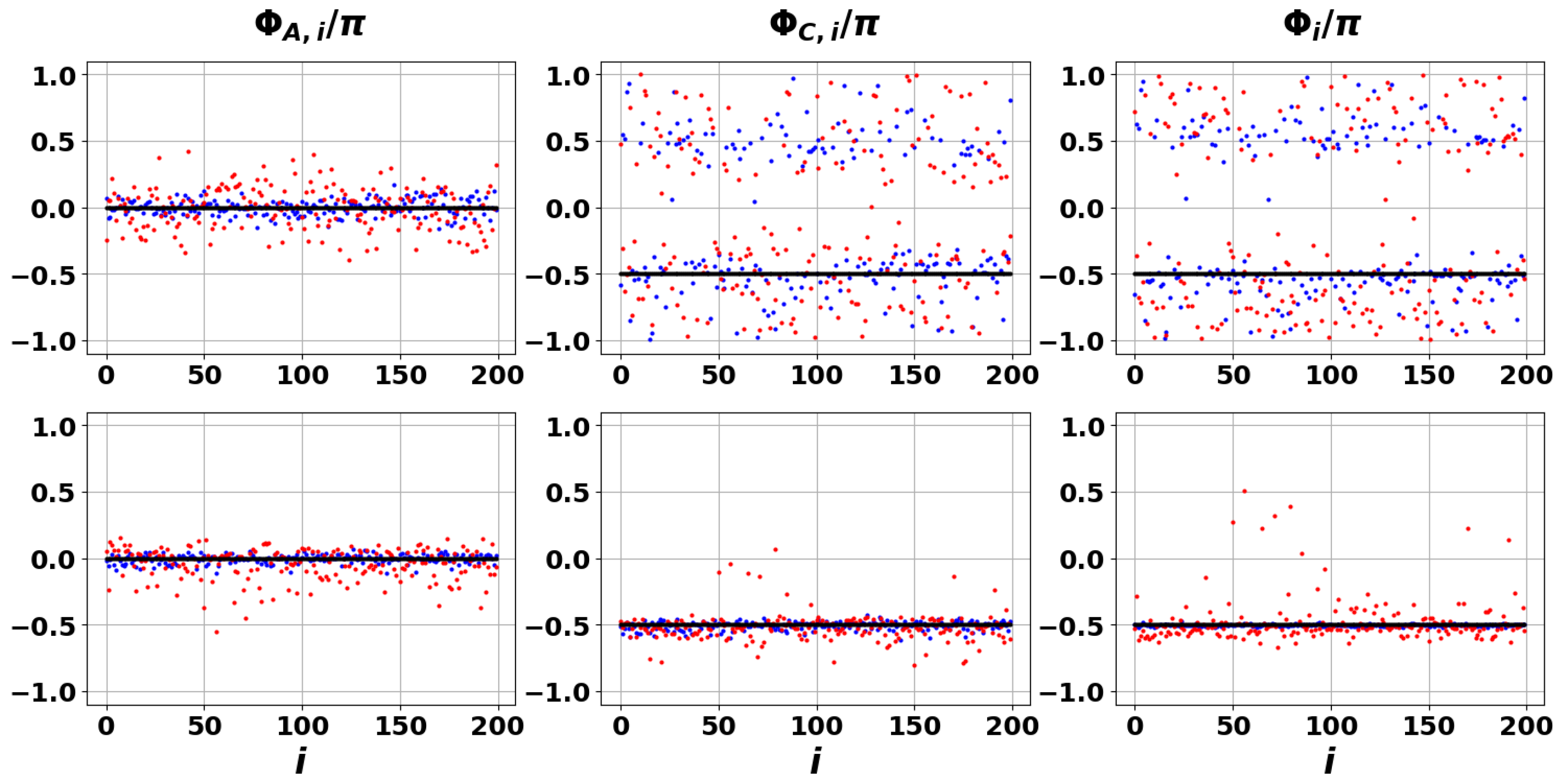
5. Phase Properties
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawless, W.; Mittu, R.; Sofge, D.; Brambilla, M. Introduction to bidirectionality in human–AI collaborative systems. In Bi-Directionality in Human-AI Collaborative Systems; Lawless, W., Mittu, R., Sofge, D., Brambilla, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Q.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, W.; Jackson, M.O. A Turing test of whether AI chatbots are behaviorally similar to humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2313925121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zeng, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. A survey on LLM-based multi-agent systems: Workflow, infrastructure, and challenges. Vicinagearth 2024, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X.; Hong, S.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yin, F.; Zhao, J.; et al. Exploring Large Language Model based Intelligent Agents: Definitions, Methods, and Prospects. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yue, Y.; Sun, X.; Wan, G.; Yu, M.; Fang, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, T.; Cheng, D. G-Designer: Architecting Multi-agent Communication Topologies via Graph Neural Networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2410.11782. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, P.; Heimerl, A.; Hossain, S.; Siegel, L.; Alexandersson, J.; Gebhard, P.; André, E.; Schneeberger, T. Recognizing Emotion Regulation Strategies from Human Behavior with Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.04420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, R.; Hooi, B.; Deng, S. Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Ku, L.W., Martins, A., Srikumar, V., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Bangkok, Thailand, 2024; pp. 14544–14607. [Google Scholar]
- Guleva, V.; Shikov, E.; Bochenina, K.; Kovalchuk, S.; Alodjants, A.; Boukhanovsky, A. Emerging complexity in distributed intelligent systems. Entropy 2020, 22, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, B.; Šuvakov, M. Can human-like Bots control collective mood: Agent-based simulations of online chats. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2013, 2023, P10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Dang, Y.; Du, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Scaling Large-Language-Model-based Multi-Agent Collaboration. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; You, Z.; Li, R.; Guan, Y.; Qian, C.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Internet of Agents: Weaving a Web of Heterogeneous Agents for Collaborative Intelligence. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.07061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyst, J.A.; Kacperski, K.; Schweitzer, F. Phase transitions in social impact models of opinion formation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2000, 285, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdyan, A.; Galstyan, A. Emergence of Leadership in Communication. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, E. Directions in Hybrid Intelligence: Complementing AI Systems with Human Intelligence. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-16), New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; IJCAI/AAAI Press: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2016; pp. 4070–4073. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Kirchner, L.; Gajos, K.Z.; Kamar, E. Towards a Science of Human-AI Decision Making: A Survey of Empirical Studies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.S.; Goyal, A.; Harlalka, N.; Suresh, S.; Hawkins, R.; Yang, S.; Shah, D.; Hu, J.; Rogers, T.T. Simulating Opinion Dynamics with Networks of LLM-based Agents. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.09618. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Lee, Y. Multi-Agents are Social Groups: Investigating Social Influence of Multiple Agents in Human-Agent Interactions. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2411.04578. [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot, M.H. Reaching a consensus. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedkin, N.E.; Johnsen, E.C. Social influence and opinions. J. Math. Sociol. 1990, 15, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafini, C. Consensus problems on networks with antagonistic interactions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodjants, A.; Bazhenov, A.; Khrennikov, A.; Boukhanovsky, A. Mean-field theory of social laser. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alodjants, A.; Tsarev, D.; Avdyushina, A.; Khrennikov, A.; Boukhanovsky, A. Quantum-inspired modeling of distributed intelligence systems with artificial intelligent agents self-organization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.; Frossard, P.; Kovacević, J.; Moura, J.M.F.; Vandergheynst, P. Graph Signal Processing: Overview, Challenges, and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 808–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Tran, Q.V.; Trinh, M.H.; Moore, K.L.; Ye, M.; Liu, J. Cooperative Opinion Dynamics on Multiple Interdependent Topics: Modeling and Analysis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.04406. [Google Scholar]
- Leus, G.; Marques, A.G.; Moura José, M.F.; Ortega, A.; Shuman, D.I. Graph Signal Processing: History, Development, Impact, and Outlook. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2023, 40, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Thanou, D.; Toni, L.; Bronstein, M.; Frossard, P. Graph Signal Processing for Machine Learning: A Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, F.; Isufi, E.; Leus, G.; Ribeiro, A. Graphs, Convolutions, and Neural Networks: From Graph Filters to Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Bolton, T.A.W.; Medaglia, J.D.; Bassett, D.S.; Ribeiro, A.; Van De Ville, D. A Graph Signal Processing Perspective on Functional Brain Imaging. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.; Magli, E.; Tanaka, Y.; Ng, M. Graph Spectral Image Processing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.04749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, A.; Vollero, L. GSP based subsampling of IoT sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Trondheim, Norway, 20–23 June 2022; ISBN 978-1-6654-0633-8. [Google Scholar]
- Brémaud, P. Random Walks on Graphs. In Markov Chains; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 31, pp. 255–287. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, A.M.; Farhi, E.; Gutmann, S. An example of the difference between quantum and classical random walks. Quantum Inf. Process. 2002, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.; Lu, L. Complex Graphs and Networks (Cbms Regional Conference Series in Mathematics); American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, K.I.; Kahng, B.; Kim, D. Spectra and eigenvectors of scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 051903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, I.J.; Derényi, I.; Barabási, A.L.; Vicsek, T. Spectra of “real-world” graphs: Beyond the semicircle law. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 026704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorogovtsev, S.N.; Goltsev, A.V.; Mendes, J.F.F. Pseudofractal scale-free web. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 066122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchenkov, D. Mathematical Frameworks for Network Dynamics: A Six-Pillar Survey for Analysis, Control, and Inference. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, R. Spectra of sparse random matrices. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2008, 41, 295002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.; Castillo, I.P.; Kühn, R.; Takeda, K. Cavity approach to the spectral density of sparse symmetric random matrices. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 031116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, F.; Gargano, F.; Saluto, L. Density matrices and entropy operator for non-Hermitian quantum mechanics. J. Math. Phys. 2025, 66, 023504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, G. Quantum-like states on complex synchronized networks. Proc. R. Soc. A 2024, 480, 20240209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P.; Misra, A.; Sur, S.; Petrosyan, D.; Kurizki, G. Sensing multiatom networks in cavities via photon-induced excitation resonance. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2025, 10, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdyan, A.E.; Balian, R.; Nieuwenhuizen, T.M. Understanding quantum measurement from the solution of dynamical models. Phys. Rep. 2013, 525, 1–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hance, J.; Hossenfelder, S. Bell’s theorem allows local theories of quantum mechanics. Nat. Phys. 2022, 18, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, D.; Nikolopoulos, G.M.; Lambropoulos, P. State transfer in static and dynamic spin chains with disorder. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 042307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Ding, Y.; Busemeyer, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y.; Tang, J. Modeling indirect influence on twitter. Int. J. Semant. Web Inf. Syst. 2012, 8, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A.; Toffano, Z.; Dubois, F. Concept of information laser: From quantum theory to behavioural dynamics. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 227, 2133–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A. Ubiquitous Quantum Structure: From Psychology to Finances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Bruza, P.D. Quantum Models of Cognition and Decision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, D.M.; Meeder, B.; Kleinberg, J. Differences in the mechanics of information diffusion across topics: Idioms, political hashtags, and complex contagion on twitter. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW ’11, Hyderabad, India, 28 March–1 April 2011; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 695–704. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, K.; Zhang, S. A Survey on Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks: Models and Methods. Information 2017, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhu, L. Turing instability analysis of a reaction–diffusion system for rumor propagation in continuous space and complex networks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, D. A short introduction to the Lindblad master equation. Aip Adv. 2020, 10, 025106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccati, F.; Palma, G.M.; Ciccarello, F.; Bagarello, F. Non-Hermitian Physics and Master Equations. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 2022, 29, 2250004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Ohya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Basieva, I.; Khrennikov, A. Quantum-like model of brain’s functioning: Decision making from decoherence. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 281, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, M.; Ohya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Khrennikov, A.; Basieva, I. On application of Gorini-Kossakowski-Sudarshan-Lindblad equation in cognitive psychology. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 2011, 18, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, R.; Fedichkin, L.; Tsarev, D.; Alodjants, A. High-dimensional graphs convolution for quantum walks photonic applications. Quantum Inf. Process 2024, 23, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguñá, M.; Bonamassa, I.; De Domenico, M.; Havlin, S.; Krioukov, D.; Serrano, M. Network geometry. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadanoff, L.; Houghton, A.; Yalabik, M. Variational approximations for renormalization group transformations. J. Stat. Phys. 1976, 14, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Kao, Y.J. Neural Monte Carlo renormalization group. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 023230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarev, D.; Zakharenko, P.; Alodjants, A. Complex networks for random lasers and photonic computing. Phys. Rev. A 2025, 112, 033508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A. Social laser: Action amplification by stimulated emission of social energy. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2016, 374, 20150094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A.; Alodjants, A.; Trofimova, A.; Tsarev, D. On interpretational questions for quantum-Like modeling of social lasing. Entropy 2018, 20, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A. Social Laser; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Holyst, J.A. Cyberemotions: Collective Emotions in Cyberspace; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, A.L. Network science. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerose, A.; Sonner, M.; Abanin, D. Influence Matrix Approach to Many-Body Floquet Dynamics. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 021040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedkin, N.E.; Johnsen, E.C. Social influence networks and opinion change. Adv. Group Process. 1999, 16, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.; Strogatz, S. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelmann, A.; Clerk, A.A. Nonreciprocal Photon Transmission and Amplification via Reservoir Engineering. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, F.; Neri, I.; Rogers, T. Spectral theory of sparse non-Hermitian random matrices. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2019, 52, 434003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.; Wang, L.; Zha, Q. Opinion dynamics in social networks under competition: The role of influencing factors in consensus-reaching. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 211732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Seneta, E. Toward Consensus: Some Convergence Theorems on Repeated Averaging. J. Appl. Probab. 1977, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandryhaila, A.; Moura, J.M.F. Discrete Signal Processing on Graphs. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilyén, A.; Su, Y.; Low, G.H.; Wiebe, N. Quantum Singular Value Transformation and Beyond: Exponential Improvements for Quantum Matrix Arithmetics. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC 2019), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 23–26 June 2019; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, D.J.; Schroeter, D.F. Introduction to Quantum Mechanics, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Ha, M.; Jeong, H.; Noh, J.D.; Park, H. Critical behavior of the Ising model in annealed scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 051127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, T.A.; Flores, J.; French, J.B.; Mello, P.A.; Pandey, A.; Wong, S.S.M. Random-matrix physics: Spectrum and strength fluctuations. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1981, 53, 385–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.L. Random Matrices, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Saad, Y.; Yang, C. Approximating Spectral Densities of Large Matrices. SIAM Rev. 2016, 58, 34–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, D.; Rafayelyan, M.; Conti, C.; Gigan, S. Scalable Spin-Glass Optical Simulator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, 034087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Moura, A.; de Araújo, C.; Raposo, E. Lévy Statistics and Spin Glass Behavior in Random Lasers; Jenny Stanford Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ohya, M.; Watanabe, N. Quantum Entropy and Its Applications to Quantum Communication and Statistical Physics. Entropy 2010, 12, 1194–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowshowitz, A.; Dehmer, M. Entropy and the Complexity of Graphs Revisited. Entropy 2012, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, H. Eigenvalue-based entropy and spectrum of bipartite digraph. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, M.D.; Biamonte, J. Spectral Entropies as Information-Theoretic Tools for Complex Network Comparison. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 041062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, G. Large Coherent States Formed from Disordered k-Regular Random Graphs. Entropy 2023, 20, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alodjants, A.P.; Tsarev, D.V.; Zakharenko, P.V.; Khrennikov, A.Y. Spectral Properties of Complex Distributed Intelligence Systems Coupled with an Environment. Entropy 2025, 27, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101016
Alodjants AP, Tsarev DV, Zakharenko PV, Khrennikov AY. Spectral Properties of Complex Distributed Intelligence Systems Coupled with an Environment. Entropy. 2025; 27(10):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlodjants, Alexander P., Dmitriy V. Tsarev, Petr V. Zakharenko, and Andrei Yu. Khrennikov. 2025. "Spectral Properties of Complex Distributed Intelligence Systems Coupled with an Environment" Entropy 27, no. 10: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101016
APA StyleAlodjants, A. P., Tsarev, D. V., Zakharenko, P. V., & Khrennikov, A. Y. (2025). Spectral Properties of Complex Distributed Intelligence Systems Coupled with an Environment. Entropy, 27(10), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27101016








