Revisiting Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using the Majorization-Minimization Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an alternative derivation method for PFCM, which begins by formulating an equivalent and simplified optimization problem, followed by solving it using the MM method. Finally, we demonstrate the equivalence of the new derivation method with PFCM.
- Due to the presence of a proportional term in the derived simplified optimization problem, we further transform it into an easily solvable equivalent form by introducing a new intermediate variable s. Then, the MM method is employed to design an iterative sub-problem. We refer to this method as MMPFCM.
- The complexity analysis indicates that MMPFCM and PFCM share the same computational complexity. However, MMPFCM utilizes the intermediate variable s of size instead of the variable V of size to update U and T, resulting in smaller space complexity.
- It is theoretically proven that when the inner loop of MMPFCM is executed only once, MMPFCM degenerates to the original PFCM method.
- Experimental studies show that MMPFCM obtains better local minima compared to PFCM. In addition, compared with other state-of-the-art clustering methods, MMPFCM also shows its superiority.
2. Related Works
2.1. Notations
2.2. Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
2.3. Majorization-Minimization Method
3. Alternative Derivation Method for Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
3.1. Formulation
3.2. Optimization Procedure
| Algorithm 1 Alternative derivation method for PFCM |
4. Majorization-Minimization Method for Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering
4.1. Formulation
4.2. Optimization Procedure
| Algorithm 2 Majorization-minimization method for possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering (MMPFCM) |
4.3. An Interesting Observation
5. Theoretical Analysis
5.1. Convergence Analysis
5.2. Complexity Analysis
6. Experiments
6.1. Evaluation Metrics
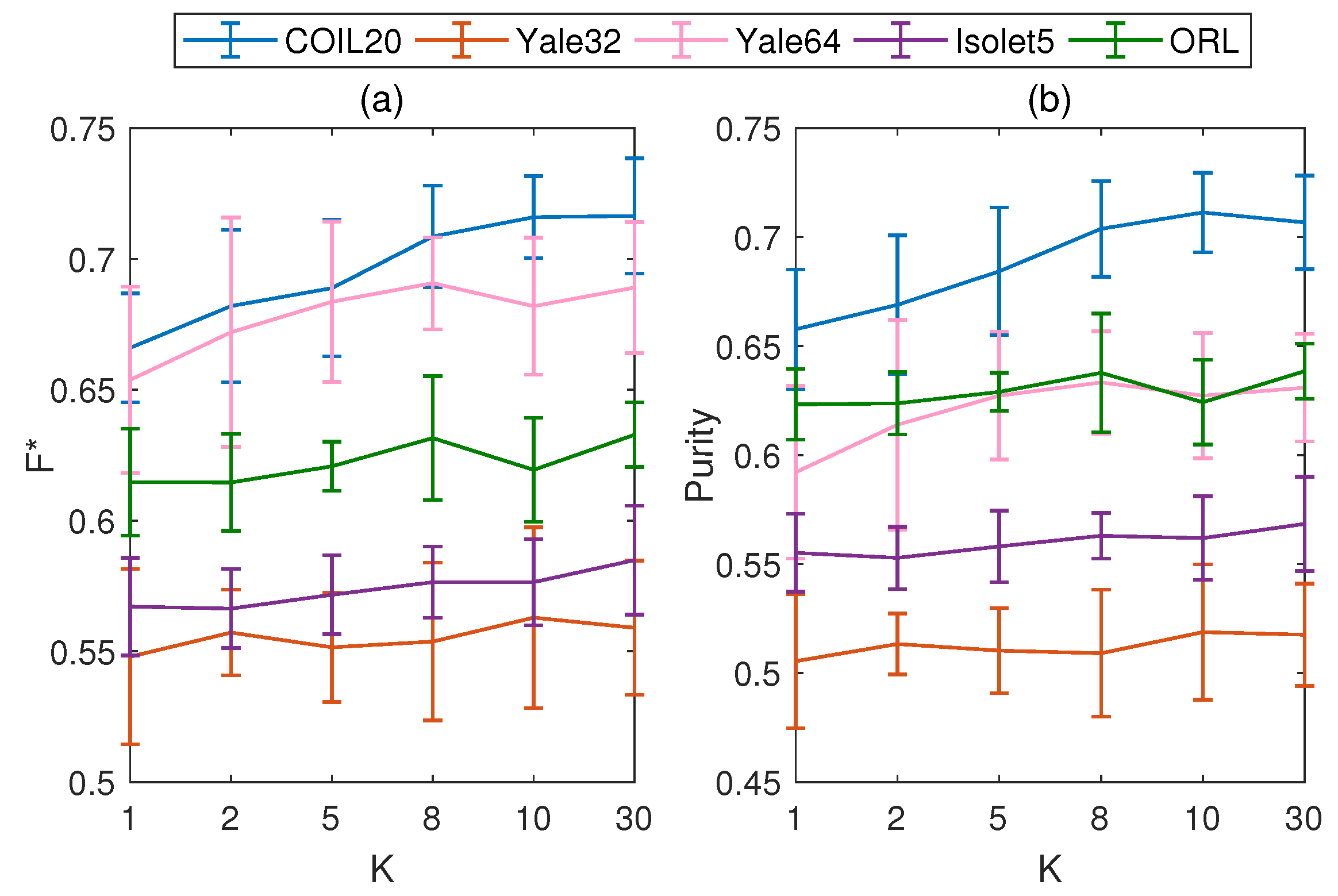
6.2. Setting of the Iterations in the Inner Loop
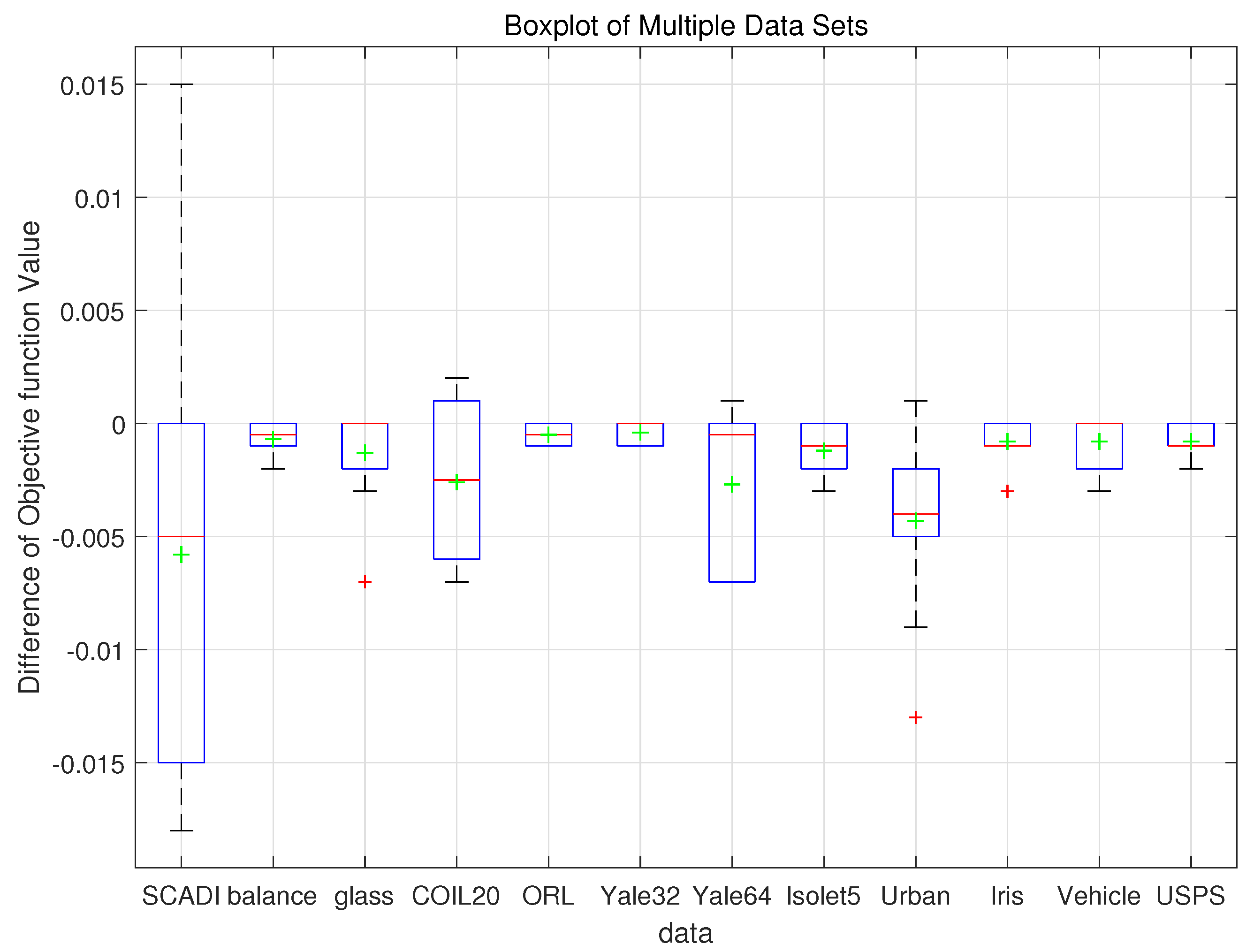
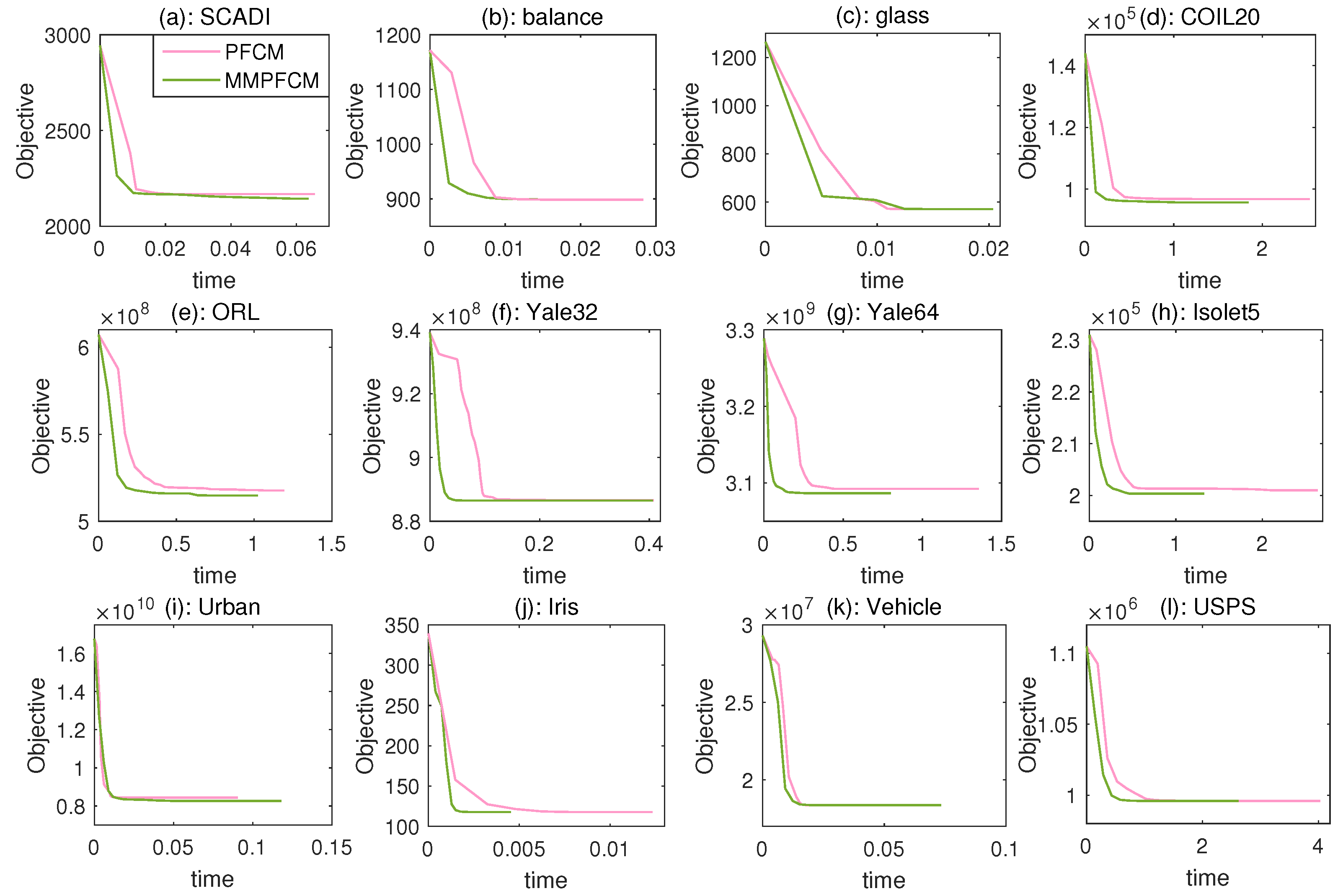
6.3. Comparison between PFCM and MMPFCM
6.4. Comparison between MMPFCM and Other Methods
- Fuzzy c-means (FCM) [11];
- Iteratively re-weighted algorithm for fuzzy c-means (IRWFCM) [14];
- An effective optimization method For fuzzy c-means with entropy regularization (IRWERFCM) [16];
- A possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm (PFCM) [20];
- Generalized entropy-based possibilistic fuzzy c-means for clustering noisy data and its convergence proof (EPFCMR) [23];
- A feature-weighted suppressed possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm and its application to color image segmentation (FW-S-PFCM) [24].
- Comparing the fourth and last columns of each dataset, MMPFCM consistently outperforms PFCM across all four clustering evaluation metrics on ten datasets. In addition, MMPFCM outperforms PFCM in terms of the ARI and FM on the ORL and USPS datasets, and MMPFCM outperforms PFCM in terms of purity on the ORL dataset. These results indicate the superiority of the proposed method under the same initialization conditions.
- PFCM-type clustering algorithms have better clustering results than FCM-type clustering algorithms on the SCADI, balance, Yale32, Yale64, Iris, and USPS datasets. This is because PFCM-type clustering algorithms are better equipped to handle data with noise and outliers.
- The total running time of FW-S-PFCM is the lowest on these twelve datasets, but this is achieved under the condition of tuning more hyperparameters. The time taken by MMPFCM and PFCM is at the same linear level, which confirms that their time complexities have the same linear relationship.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Lemma
Appendix B. Supplementary Experiments
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM | mean | 5.7170 × 103 | 2.2766 × 103 | 3.1379 × 103 | 5.4845 × 105 | 5.5244 × 109 | 2.9639 × 109 | 9.4645 × 109 |
| std | (98.484) | (0.400) | (499.729) | (1.5326 × 104) | (2.9492 × 107) | (2.4593 × 107) | (1.1713 × 108) | |
| MMPCM | mean | 5.7159 × 103 | 2.2761 × 103 | 3.1379 × 103 | 5.4832 × 105 | 5.5243 × 109 | 2.9632 × 109 | 9.4636 × 109 |
| std | (95.202) | (0.290) | (499.729) | (1.5683 × 104) | (2.9515 × 107) | (2.5872 × 107) | (1.1731 × 108) |
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM | 1.135 (0.168) | 14.651 (1.271) | 14.038 (11.615) | 2.978 (0.423) | 17.458 (44.440) | 410.359 (676.450) | 41.938 (39.779) |
| MMPCM | 1.126 (0.140) | 13.184 (0.852) | 12.543 (12.909) | 2.945 (0.372) | 16.418 (44.697) | 353.354 (681.000) | 41.748 (39.996) |
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 | Urban | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM | mean | 919.448 | 516.059 | 300.328 | 2.9395 × 104 | 1.5808 × 108 | 1.9207 × 108 | 6.1863 × 108 | 2.3351 × 109 |
| std | (26.876) | (0.001) | (4.875) | (304.055) | (6.3947 × 105) | (3.4124 × 105) | (1.5950 × 106) | (6.9282 × 107) | |
| MMFCM | mean | 910.441 | 516.059 | 295.703 | 2.9098 × 104 | 1.5856 × 108 | 1.9206 × 108 | 6.1835 × 108 | 2.2868 × 109 |
| std | (25.466) | (0.001) | (7.960) | (261.530) | (4.4893 × 105) | (2.5943 × 105) | (1.7965 × 106) | (4.1709 × 107) |
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 | Urban |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBI | ||||||||
| FCM | 1.168 (0.123) | 5.657 (0.015) | 0.629 (0.041) | 1.925 (0.072) | 2.206 (0.149) | 3.499 (0.293) | 2.367 (0.353) | 0.924 (0.049) |
| MMFCM | 1.113 (0.084) | 5.656 (0.009) | 0.591 (0.066) | 1.896 (0.079) | 2.181 (0.173) | 3.470 (0.210) | 2.123 (0.299) | 0.904 (0.060) |
| XB | ||||||||
| FCM | 0.806 (0.162) | 1.513 (0.002) | 0.489 (0.015) | 1.154 (0.064) | 2.338 (0.459) | 3.125 (0.377) | 3.302 (1.042) | 1.082 (0.052) |
| MMFCM | 0.694 (0.063) | 1.512 (0.002) | 0.475 (0.024) | 1.130 (0.068) | 2.231 (0.565) | 3.111 (0.406) | 2.611 (0.958) | 1.075 (0.163) |
References
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, C.; Lesot, M.J.; Kruse, R. Data analysis with fuzzy clustering methods. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2006, 51, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.R.; Van der Zwet, P.M.; Lelieveldt, B.; Van der Geest, R.J.; Reiber, J.H. A multiresolution image segmentation technique based on pyramidal segmentation and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D.; Gottlieb, A. Algorithm for data clustering in pattern recognition problems based on quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 88, 018702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhou, S.; Pedrycz, W. Accelerated fuzzy c-means clustering based on new affinity filtering and membership scaling. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 12337–12349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Fu, C. Improved fuzzy c-means clustering by varying the fuzziness parameter. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 157, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Prasad, M.; Gupta, A.; Bharill, N.; Patel, O.P.; Tiwari, A.; Er, M.J.; Ding, W.; Lin, C.T. A review of clustering techniques and developments. Neurocomputing 2017, 267, 664–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lange, K. Power k-means clustering. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6921–6931. [Google Scholar]
- Ruspini, E.H. Numerical methods for fuzzy clustering. Inf. Sci. 1970, 2, 319–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond k-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Nie, F.; Wang, R.; Li, X. Iteratively reweighted algorithm for fuzzy c-means. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 4310–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Mukaidono, M. Fuzzy c-means as a regularization and maximum entropy approach. In Proceedings of the IFSA’97 Prague: Proceedings of the Seventh International Fuzzy Systems Association World Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 25–30 June 1997; Volume 2, pp. 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Nie, F. An effective optimization method for fuzzy k-means with entropy regularization. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 2846–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Pi, D.; Kantardzic, M.; Yin, Q.; Liu, X. A weight possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Sci. Program. 2021, 2021, 9965813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnapuram, R.; Keller, J.M. A possibilistic approach to clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1993, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.B.M.; Yang, M.S. Weighted multiview possibilistic c-means clustering with L2 regularization. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 30, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.R.; Pal, K.; Keller, J.M.; Bezdek, J.C. A possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2005, 13, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jiang, L.; Fan, J.; Lan, R. Double-suppressed possibilistic fuzzy Gustafson-Kessel clustering algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 276, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.S.; Ngo, L.T.; Trinh, L.H.; Hagras, H. A hybrid interval type-2 semi-supervised possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering and particle swarm optimization for satellite image analysis. Inf. Sci. 2021, 548, 398–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, S.; Montazerin, N.; Zarandi, M.F.; Hakimi, E. Generalized entropy based possibilistic fuzzy c-means for clustering noisy data and its convergence proof. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jiang, L.; Fan, J.; Xie, S.; Lan, R. A feature-weighted suppressed possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm and its application on color image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 241, 122270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, X. A self-learning iterative weighted possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering via adaptive fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.; Hsu, C.; Nguyen, T.P.Q.; Tsai, C. Hybrid multi-objective metaheuristic and possibilistic intuitionistic fuzzy c-means algorithms for cluster analysis. Soft Comput. 2024, 28, 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Xia, Y.; Sun, Q.; Cao, G. Interval-valued possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2014, 253, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, X.; Pedrycz, W.; Song, X. Possibilistic fuzzy clustering with high-density viewpoint. Neurocomputing 2019, 329, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, V.; Guerrero, J.A.; Romero, G. Possibilistic fuzzy c-means with partial supervision. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2022, 449, 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Lei, B. Semi-supervised possibilistic c-means clustering algorithm based on feature weights for imbalanced data. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 286, 111388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.M.; Rheinboldt, W.C. Iterative Solution of Nonlinear Equations in Several Variables; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Babu, P.; Palomar, D.P. Majorization-Minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 794–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Stoica, P. Sinusoidal parameter estimation from signed measurements via majorization–minimization based RELAX. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, L.; Arabie, P. Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 1985, 2, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Miao, C. Large scale document categorization with fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 25, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.L.; Bouldin, D.W. A cluster separation measure. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, 2, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.L.; Beni, G. A validity measure for fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Xue, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Li, X. Coordinate descent method for k-means. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 2371–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
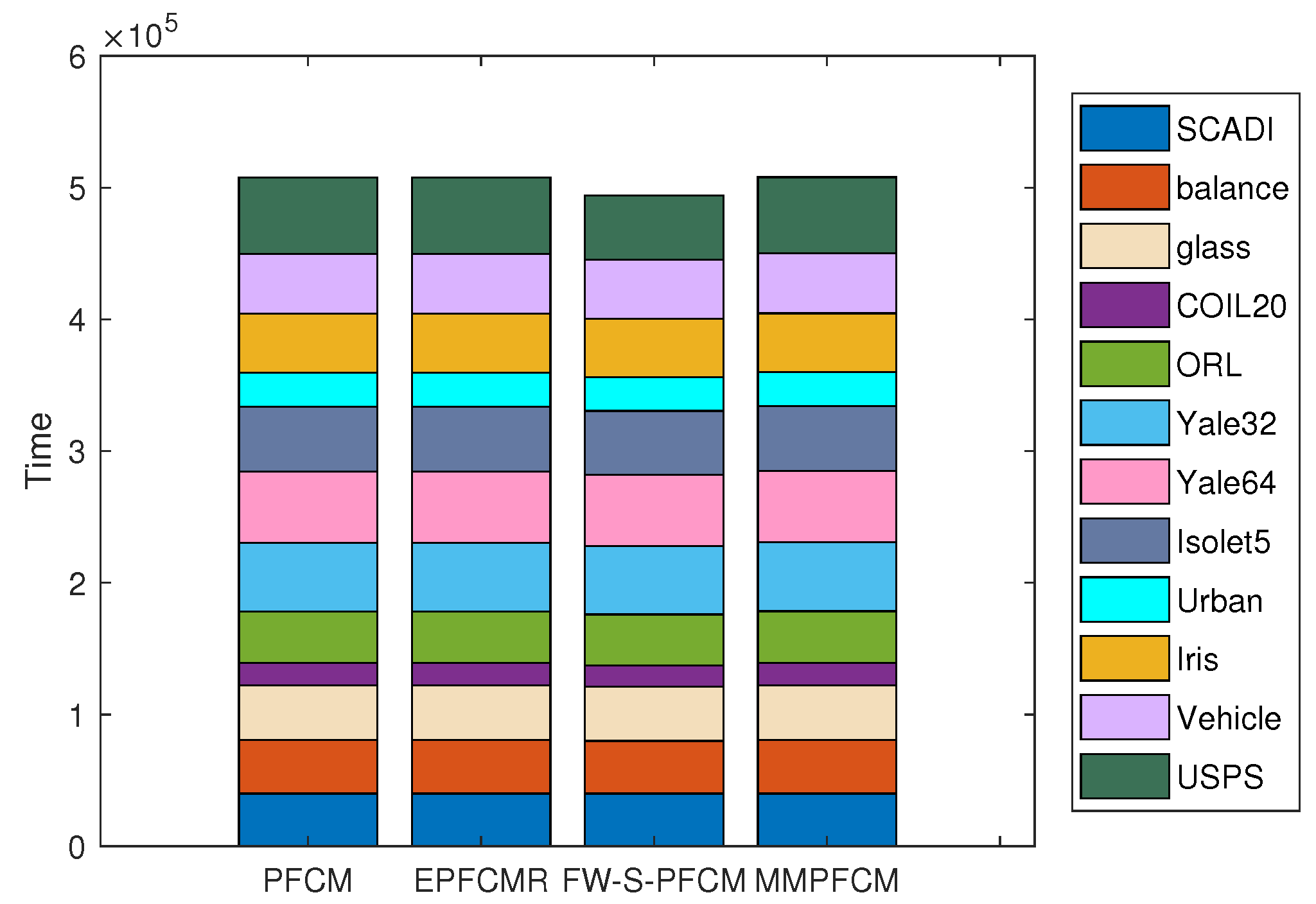
| Datasets | Instance | Feature | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCADI | 70 | 205 | 7 |
| balance | 625 | 4 | 3 |
| glass | 214 | 9 | 7 |
| COIL20 | 1440 | 1024 | 20 |
| ORL | 400 | 1024 | 40 |
| Yale32 | 165 | 1024 | 15 |
| Yale64 | 165 | 4096 | 15 |
| Isolet5 | 1559 | 617 | 26 |
| Urban | 168 | 147 | 9 |
| Iris | 150 | 4 | 3 |
| Vehicle | 846 | 18 | 4 |
| USPS | 9298 | 256 | 10 |
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 | Isolet5 | Urban | Iris | Vehicle | USPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBI | |||||||||||||
| PFCM | mean | 1.430 | 1.611 | 4.427 | 2.284 | 2.045 | 2.598 | 1.860 | 4.471 | 1.558 | 0.639 | 0.682 | 3.367 |
| std | (0.137) | (0.000) | (1.856) | (0.170) | (0.058) | (0.096) | (0.127) | (0.324) | (0.129) | (0.017) | (0.007) | (0.001) | |
| MMPFCM | mean | 1.275 | 1.610 | 4.305 | 2.258 | 2.037 | 2.561 | 1.806 | 4.448 | 1.507 | 0.634 | 0.682 | 3.366 |
| std | (0.097) | (0.000) | (1.707) | (0.119) | (0.075) | (0.100) | (0.137) | (0.329) | (0.078) | (0.017) | (0.007) | (0.001) | |
| XB | |||||||||||||
| PFCM | mean | 1.046 | 0.833 | 10.193 | 1.483 | 1.902 | 2.319 | 1.881 | 3.905 | 2.926 | 0.276 | 0.868 | 2.055 |
| std | (0.256) | (0.000) | (2.509) | (0.265) | (0.216) | (0.257) | (0.409) | (1.347) | (1.066) | (0.008) | (0.013) | (0.002) | |
| MMPFCM | mean | 0.808 | 0.833 | 10.092 | 1.350 | 1.811 | 2.317 | 1.706 | 3.871 | 2.071 | 0.274 | 0.867 | 2.054 |
| std | (0.168) | (0.000) | (2.202) | (0.125) | (0.205) | (0.281) | (0.429) | (1.281) | (0.110) | (0.008) | (0.013) | (0.002) | |
| Datasets | SCADI | Balance | Glass | COIL20 | ORL | Yale32 | Yale64 | Isolet5 | Urban | Iris | Vehicle | USPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBI | |||||||||||||
| PFCM | mean | 1.433 | 1.617 | 3.415 | 2.286 | 2.048 | 2.596 | 1.858 | 4.469 | 1.609 | 0.639 | 0.682 | 3.366 |
| std | (0.138) | (0.008) | (1.127) | (0.172) | (0.057) | (0.096) | (0.135) | (0.322) | (0.130) | (0.015) | (0.011) | (0.002) | |
| MMPFCM | mean | 1.275 | 1.615 | 3.279 | 2.258 | 2.041 | 2.564 | 1.805 | 4.447 | 1.562 | 0.635 | 0.681 | 3.365 |
| std | (0.097) | (0.008) | (0.888) | (0.118) | (0.077) | (0.099) | (0.135) | (0.329) | (0.088) | (0.016) | (0.011) | (0.003) | |
| XB | |||||||||||||
| PFCM | mean | 0.155 | 0.059 | 3.764 | 1.053 | 0.497 | 0.457 | 0.417 | 1.321 | 1.668 | 0.178 | 0.797 | 0.905 |
| std | (0.033) | (0.000) | (0.327) | (0.172) | (0.052) | (0.050) | (0.091) | (0.451) | (0.371) | (0.005) | (0.010) | (0.001) | |
| MMPFCM | mean | 0.125 | 0.059 | 3.747 | 0.973 | 0.470 | 0.454 | 0.374 | 1.309 | 1.344 | 0.177 | 0.796 | 0.905 |
| std | (0.022) | (0.000) | (0.254) | (0.083) | (0.058) | (0.057) | (0.089) | (0.426) | (0.079) | (0.005) | (0.010) | (0.001) | |
| Datasets | Metrics | FCM | IRWFCM | IRWERFCM | PFCM | EPFCMR | FW-S-PFCM | MMPFCM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCADI | ARI | 0.267 (0.064) | 0.300 (0.001) | 0.327 (0.057) | 0.429 (0.064) | 0.434 (0.072) | 0.261 (0.042) | 0.436 (0.080) |
| F* | 0.535 (0.052) | 0.560 (0.003) | 0.581 (0.050) | 0.630 (0.026) | 0.632 (0.028) | 0.528 (0.031) | 0.637 (0.032) | |
| NMI | 0.492 (0.034) | 0.505 (0.000) | 0.518 (0.028) | 0.524 (0.019) | 0.523 (0.019) | 0.488 (0.029) | 0.531 (0.026) | |
| Purity | 0.734 (0.024) | 0.759 (0.005) | 0.753 (0.022) | 0.631 (0.009) | 0.636 (0.018) | 0.736 (0.024) | 0.637 (0.018) | |
| balance | ARI | 0.116 (0.131) | 0.114 (0.095) | 0.108 (0.077) | 0.128 (0.119) | 0.130 (0.123) | 0.130 (0.011) | 0.131 (0.125) |
| F* | 0.529 (0.119) | 0.543 (0.078) | 0.539 (0.056) | 0.552 (0.089) | 0.551 (0.093) | 0.577 (0.009) | 0.555 (0.088) | |
| NMI | 0.106 (0.119) | 0.098 (0.086) | 0.102 (0.068) | 0.112 (0.100) | 0.113 (0.104) | 0.112 (0.009) | 0.114 (0.105) | |
| Purity | 0.605 (0.102) | 0.629 (0.067) | 0.635 (0.060) | 0.640 (0.075) | 0.639 (0.079) | 0.656 (0.016) | 0.642 (0.077) | |
| glass | ARI | 0.235 (0.058) | 0.243 (0.056) | 0.241 (0.000) | 0.221 (0.042) | 0.175 (0.005) | 0.234 (0.054) | 0.246 (0.064) |
| F* | 0.549 (0.017) | 0.552 (0.005) | 0.536 (0.000) | 0.527 (0.022) | 0.457 (0.015) | 0.556 (0.014) | 0.558 (0.025) | |
| NMI | 0.425 (0.032) | 0.426 (0.003) | 0.349 (0.000) | 0.409 (0.019) | 0.322 (0.005) | 0.431 (0.023) | 0.435 (0.036) | |
| Purity | 0.591 (0.009) | 0.592 (0.002) | 0.565 (0.000) | 0.587 (0.008) | 0.538 (0.017) | 0.593 (0.008) | 0.594 (0.008) | |
| COIL20 | ARI | 0.593 (0.026) | 0.601 (0.018) | 0.590 (0.026) | 0.573 (0.012) | 0.575 (0.007) | 0.554 (0.023) | 0.593 (0.030) |
| F* | 0.682 (0.025) | 0.695 (0.019) | 0.686 (0.018) | 0.659 (0.011) | 0.664 (0.006) | 0.650 (0.022) | 0.695 (0.029) | |
| NMI | 0.773 (0.012) | 0.782 (0.008) | 0.782 (0.015) | 0.772 (0.005) | 0.778 (0.005) | 0.766 (0.010) | 0.783 (0.013) | |
| Purity | 0.683 (0.030) | 0.691 (0.020) | 0.679 (0.022) | 0.640 (0.013) | 0.640 (0.005) | 0.642 (0.018) | 0.689 (0.029) | |
| ORL | ARI | 0.445 (0.021) | 0.459 (0.024) | 0.438 (0.028) | 0.456 (0.023) | 0.450 (0.017) | 0.427 (0.015) | 0.466 (0.013) |
| F* | 0.620 (0.016) | 0.630 (0.022) | 0.609 (0.019) | 0.622 (0.022) | 0.621 (0.020) | 0.603 (0.013) | 0.637 (0.010) | |
| NMI | 0.784 (0.006) | 0.788 (0.009) | 0.776 (0.012) | 0.786 (0.010) | 0.785 (0.008) | 0.777 (0.006) | 0.784 (0.006) | |
| Purity | 0.626 (0.020) | 0.647 (0.019) | 0.610 (0.019) | 0.629 (0.020) | 0.616 (0.017) | 0.607 (0.011) | 0.650 (0.012) | |
| Yale32 | ARI | 0.278 (0.011) | 0.276 (0.009) | 0.253 (0.029) | 0.295 (0.027) | 0.289 (0.023) | 0.250 (0.024) | 0.304 (0.019) |
| F* | 0.528 (0.014) | 0.524 (0.010) | 0.500 (0.032) | 0.537 (0.032) | 0.535 (0.024) | 0.496 (0.026) | 0.559 (0.025) | |
| NMI | 0.536 (0.006) | 0.538 (0.007) | 0.524 (0.020) | 0.553 (0.020) | 0.551 (0.019) | 0.521 (0.018) | 0.553 (0.013) | |
| Purity | 0.479 (0.023) | 0.468 (0.017) | 0.453 (0.023) | 0.495 (0.032) | 0.485 (0.022) | 0.453 (0.024) | 0.518 (0.023) | |
| Yale64 | ARI | 0.367 (0.023) | 0.375 (0.021) | 0.347 (0.043) | 0.396 (0.020) | 0.402 (0.025) | 0.350 (0.016) | 0.410 (0.017) |
| F* | 0.619 (0.028) | 0.635 (0.015) | 0.606 (0.040) | 0.654 (0.021) | 0.670 (0.023) | 0.602 (0.018) | 0.674 (0.019) | |
| NMI | 0.603 (0.019) | 0.615 (0.017) | 0.594 (0.032) | 0.623 (0.014) | 0.632 (0.018) | 0.599 (0.011) | 0.634 (0.011) | |
| Purity | 0.575 (0.021) | 0.592 (0.008) | 0.550 (0.033) | 0.605 (0.021) | 0.619 (0.025) | 0.556 (0.017) | 0.619 (0.021) | |
| Isolet5 | ARI | 0.434 (0.019) | 0.457 (0.023) | 0.440 (0.020) | 0.449 (0.019) | 0.451 (0.019) | 0.454 (0.014) | 0.460 (0.015) |
| F* | 0.559 (0.015) | 0.578 (0.025) | 0.552 (0.016) | 0.563 (0.016) | 0.570 (0.020) | 0.573 (0.015) | 0.579 (0.012) | |
| NMI | 0.704 (0.006) | 0.711 (0.010) | 0.708 (0.013) | 0.706 (0.008) | 0.708 (0.008) | 0.710 (0.013) | 0.712 (0.006) | |
| Purity | 0.547 (0.011) | 0.565 (0.025) | 0.536 (0.023) | 0.536 (0.016) | 0.549 (0.022) | 0.567 (0.019) | 0.561 (0.013) | |
| Urban | ARI | 0.115 (0.014) | 0.121 (0.005) | 0.117 (0.002) | 0.109 (0.003) | 0.120 (0.012) | 0.107 (0.030) | 0.129 (0.000) |
| F* | 0.353 (0.011) | 0.358 (0.002) | 0.364 (0.005) | 0.365 (0.006) | 0.367 (0.014) | 0.346 (0.033) | 0.368 (0.000) | |
| NMI | 0.278 (0.017) | 0.286 (0.010) | 0.271 (0.009) | 0.273 (0.003) | 0.280 (0.013) | 0.266 (0.037) | 0.303 (0.000) | |
| Purity | 0.371 (0.013) | 0.375 (0.000) | 0.373 (0.000) | 0.354 (0.003) | 0.380 (0.013) | 0.362 (0.036) | 0.369 (0.000) | |
| Iris | ARI | 0.743 (0.000) | 0.743 (0.000) | 0.667 (0.129) | 0.780 (0.007) | 0.781 (0.006) | 0.716 (0.000) | 0.783 (0.005) |
| F* | 0.899 (0.000) | 0.899 (0.000) | 0.850 (0.090) | 0.917 (0.003) | 0.918 (0.003) | 0.885 (0.000) | 0.919 (0.002) | |
| NMI | 0.758 (0.000) | 0.758 (0.000) | 0.709 (0.062) | 0.763 (0.006) | 0.765 (0.004) | 0.742 (0.000) | 0.767 (0.008) | |
| Purity | 0.900 (0.000) | 0.900 (0.000) | 0.848 (0.096) | 0.918 (0.003) | 0.919 (0.003) | 0.887 (0.000) | 0.919 (0.002) | |
| Vehicle | ARI | 0.123 (0.000) | 0.123 (0.000) | 0.117 (0.022) | 0.117 (0.003) | 0.129 (0.004) | 0.123 (0.000) | 0.141 (0.002) |
| F* | 0.451 (0.000) | 0.451 (0.000) | 0.462 (0.033) | 0.461 (0.003) | 0.471 (0.003) | 0.455 (0.000) | 0.479 (0.002) | |
| NMI | 0.172 (0.000) | 0.172 (0.000) | 0.159 (0.017) | 0.152 (0.003) | 0.166 (0.005) | 0.187 (0.000) | 0.184 (0.003) | |
| Purity | 0.453 (0.000) | 0.453 (0.000) | 0.439 (0.022) | 0.437 (0.004) | 0.450 (0.003) | 0.453 (0.000) | 0.458 (0.002) | |
| USPS | ARI | 0.521 (0.014) | 0.527 (0.010) | 0.536 (0.000) | 0.562 (0.005) | 0.555 (0.001) | 0.526 (0.000) | 0.571 (0.000) |
| F* | 0.682 (0.016) | 0.688 (0.012) | 0.697 (0.000) | 0.720 (0.004) | 0.714 (0.002) | 0.689 (0.000) | 0.725 (0.000) | |
| NMI | 0.605 (0.006) | 0.607 (0.004) | 0.613 (0.000) | 0.611 (0.001) | 0.612 (0.001) | 0.605 (0.000) | 0.610 (0.000) | |
| Purity | 0.718 (0.017) | 0.725 (0.012) | 0.734 (0.000) | 0.724 (0.017) | 0.732 (0.020) | 0.725 (0.000) | 0.718 (0.000) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhou, S. Revisiting Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using the Majorization-Minimization Method. Entropy 2024, 26, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26080670
Chen Y, Zhou S. Revisiting Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using the Majorization-Minimization Method. Entropy. 2024; 26(8):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26080670
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuxue, and Shuisheng Zhou. 2024. "Revisiting Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using the Majorization-Minimization Method" Entropy 26, no. 8: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26080670
APA StyleChen, Y., & Zhou, S. (2024). Revisiting Possibilistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Using the Majorization-Minimization Method. Entropy, 26(8), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26080670






