Non-Equilibrium Enhancement of Classical Information Transmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Non-Equilibrium Information Dynamics for Memoryless Channel
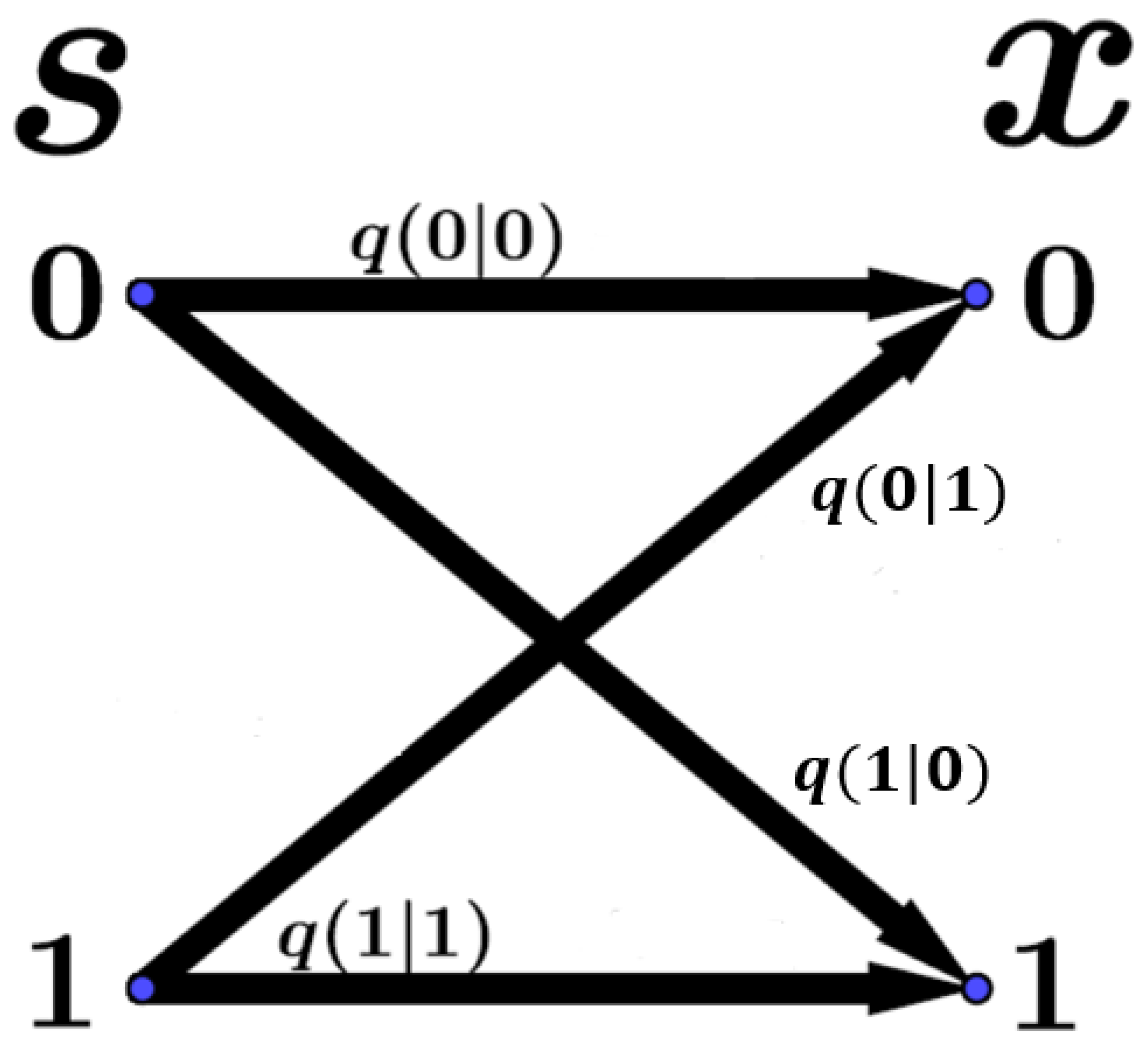
2.1. Information Dynamics for Memoryless Channel
2.2. Non-Equilibrium Strength
2.3. Non-Equilibrium Decomposition of Transmission Probabilities
3. Information Transmission Enhanced by Non-Equilibrium Strength
3.1. Mutual Information and Non-Equilibrium Strength
3.2. Channel Capacity and Non-Equilibrium Strength
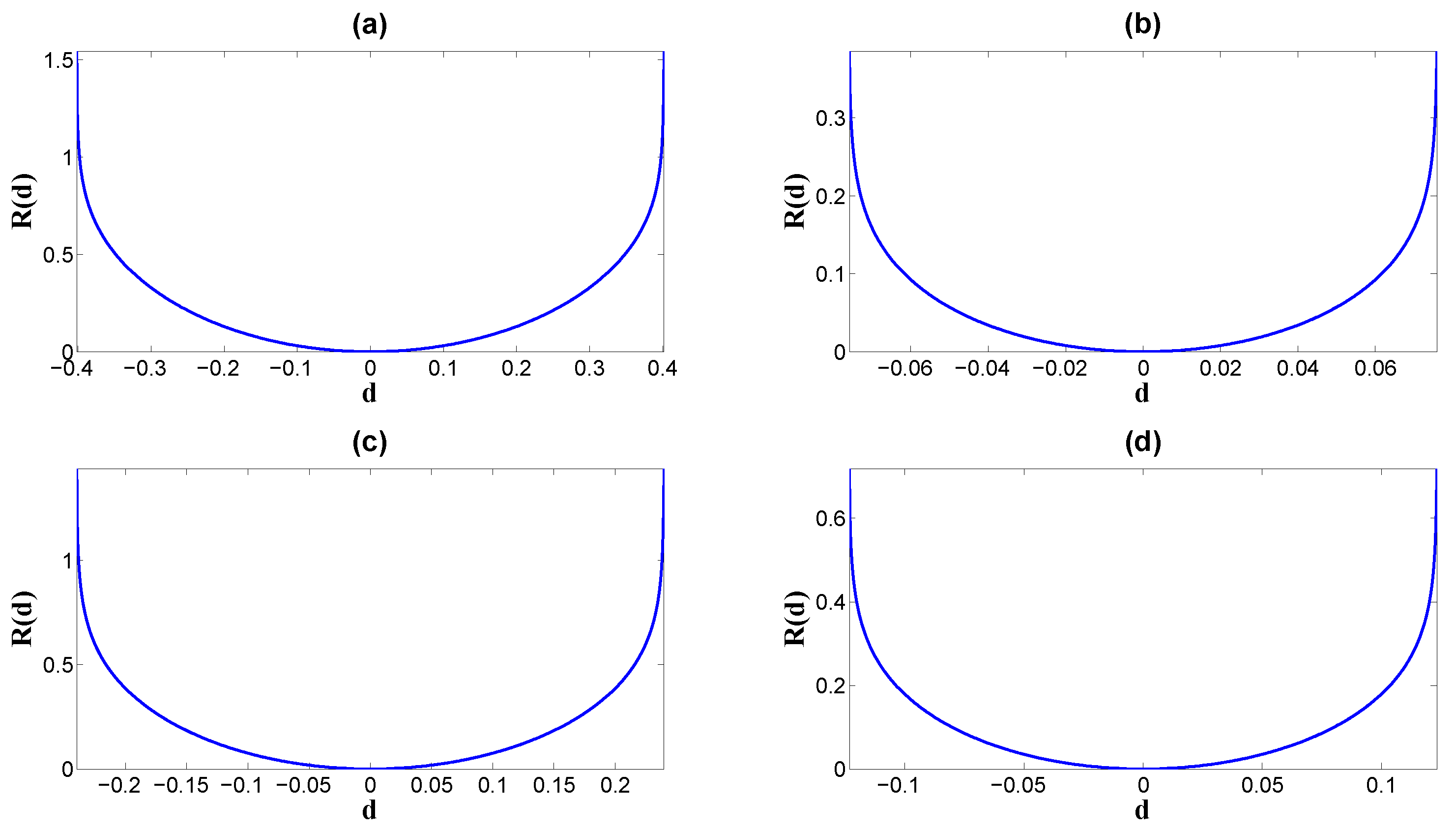
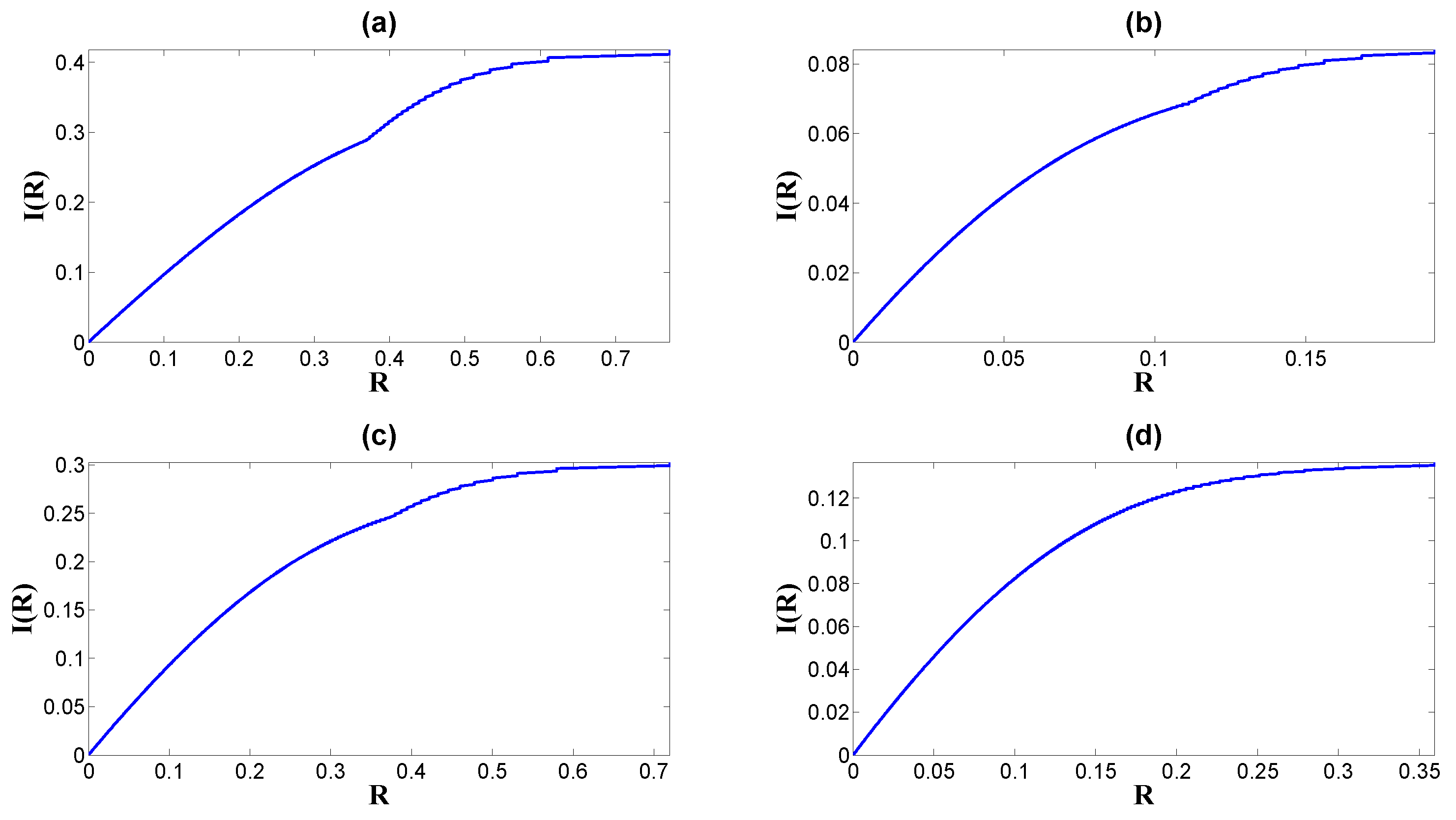
4. Better Information Transfer Efficiency under Larger Dissipation
4.1. Information Dissipation Enlarges Mutual Information
4.2. Better Information Capacity under Larger Dissipation
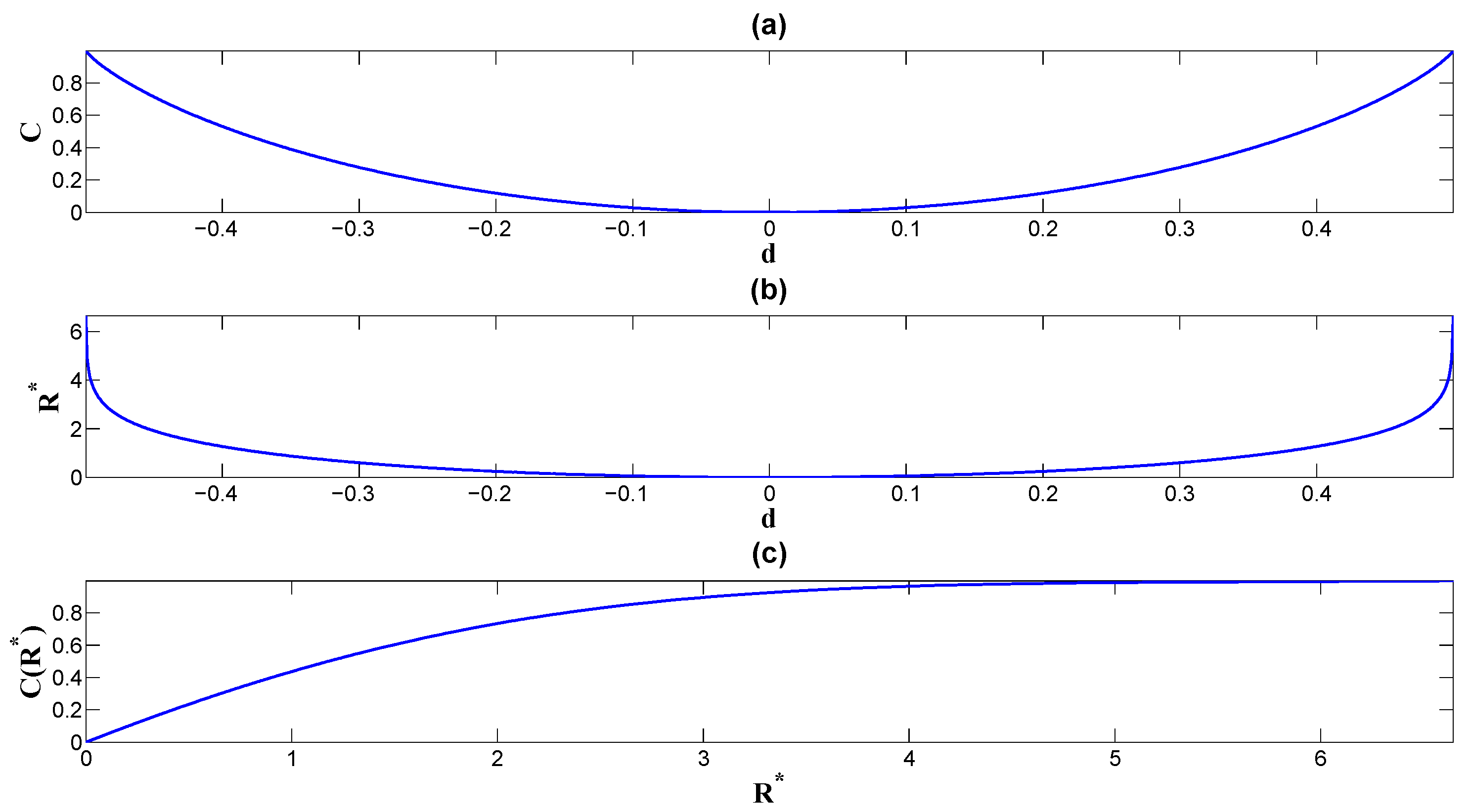
5. A Case with a Binary Memoryless Channel
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
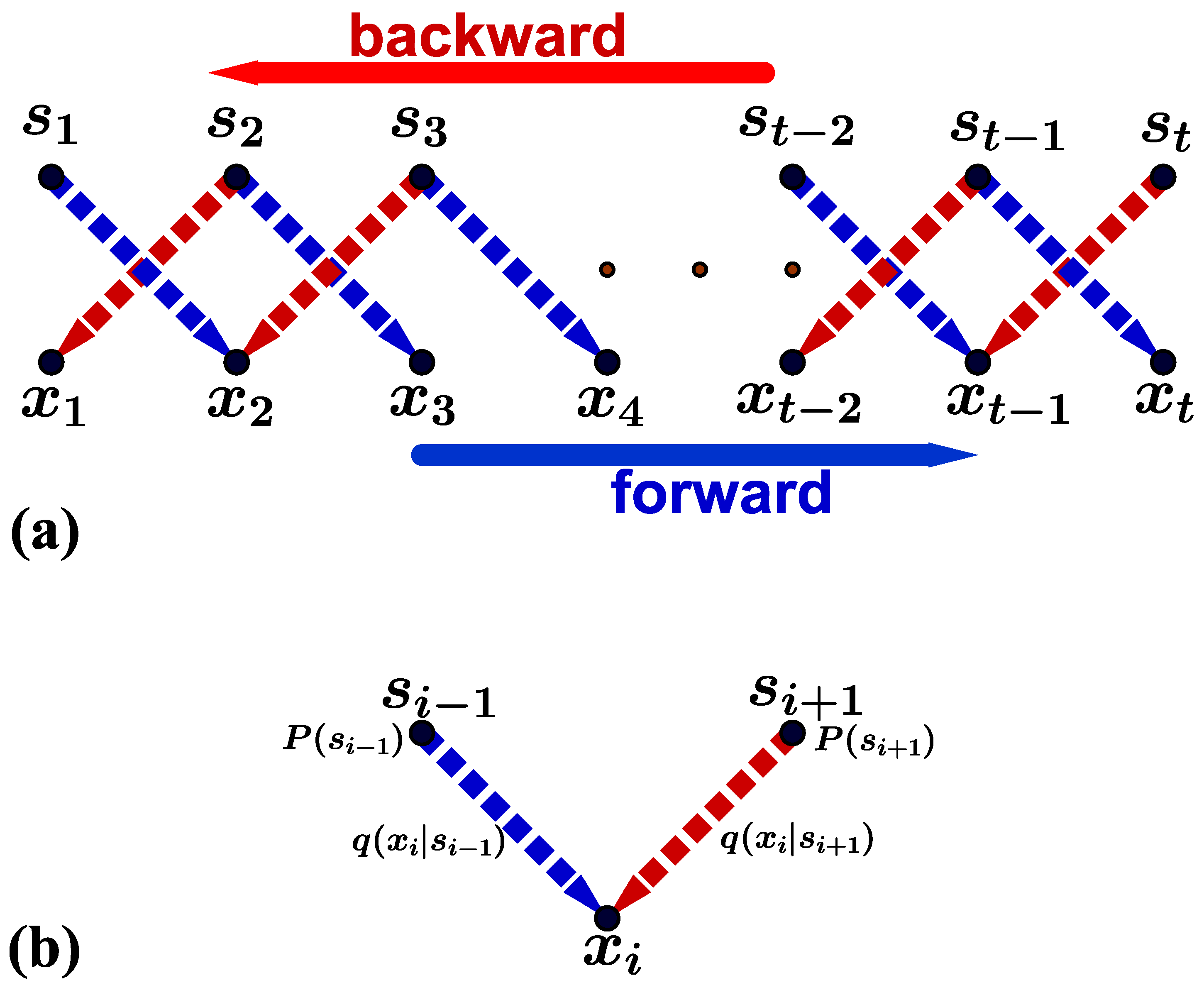
Appendix A. Probability Flux, Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium Forces, and Time-Irreversibility
Appendix B. Convexity of the Set of d
Appendix C. Convexity of Mutual Information and Channel Capacity
References
- Andersen, J.B. Antenna arrays in mobile communications: Gain, diversity, and channel capacity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollt, E.; Lai, Y.C.; Grebogi, C. Coding, Channel Capacity, and Noise Resistance in Communicating with Chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 3787–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.Y. Estimate of Channel Capacity in Rayleigh Fading Environment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 39, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouff, E.; Rivain, M. Theoretical and practical aspects of mutual information-based side channel analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Mor, T.; Smolin, J.A. Parity bit in quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 1996, 54, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Wultschleger, J. Zero-error information and applications in cryptography. In Proceedings of the Information Theory Workshop, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24–29 October 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy, S.; Spitzer, M.H.; Mingueneau, M.; Bendall, S.C.; Litvin, O.; Stone, E.; Pe’er, D.; Nolan, G.P. Conditional density-based analysis of T cell signaling in single-cell data. Science 2014, 346, 1250689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voliotis, M.; Perrett, R.M.; McWilliams, C.; McArdle, C.A.; Bowsher, C.G. Information transfer by leaky, heterogeneous, protein kinase signaling systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E326–E333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, B.W.; Iglesias, P.A. An information-theoretic characterization of the optimal gradient sensing response of cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregowska, J. Szczepanski, and E. Wajnryb, Mutual information against correlations in binary communication channels. BMC Neurosci. 2015, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Boes, J.L.; Frey, K.A.; Meyer, C.R. Mutual Information for Automated Unwarping of Rat Brain Autoradiographs. Neuroimage 1997, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Hsieh, J.C.; Wu, Y.Z.; Lee, P.L.; Chen, S.S.; Niddam, D.M.; Yeh, T.C.; Wu, Y.T. Mutual-Information-Based Approach for Neural Connectivity during Self-Paced Finger Lifting Task. Human. Brain Mapp. 2008, 29, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haueisen, J.; Leistritz, L.; Süsse, T.; Curio, G.; Witte, H. Identifying mutual information transfer in the brain with differential-algebraic modeling: Evidence for fast oscillatory coupling between cortical somatosensory areas 3b and 1. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Spangler, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Leveraging sentiment analysis for topic detection. Web Intell. Agent. Syst. 2008, 1, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- De Choudhury, M.; Sundaram, H.; John, A.; Seligmann, D.D. What makes conversations interesting? Themes, participants and consequences of conversations in online social media. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW 2009, Madrid, Spain, 20–24 April 2009; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hänggi, P. Stochastic Resonance in Biology: How Noise Can Enhance Detection of Weak Signals and Help Improve Biological Information Processing. ChemPhysChem 2002, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, J. Information Landscape and Flux, Mutual Information Rate Decomposition and Connections to Entropy Production. Entropy 2017, 19, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, J. Non-Markovian nonequilibrium information dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 032123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzynski, C. Nonequilibrium Equality for Free Energy Differences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, E.G. Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, 2721–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, U. Entropy Production along a Stochastic Trajectory and an Integral Fluctuation Theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 040602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, T.; Ueda, M. Generalized Jarzynski Equality under Nonequilibrium Feedback Control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 090602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrondo, J.M.R.; Horowitz, J.M.; Sagawa, T. Thermodynamics of information. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, T.; Ueda, M. Fluctuation theorem with information exchange: Role of correlations in stochastic thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 180602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J.M.; Esposito, M. Thermodynamics with Continuous Information Flow. Phys. Rev. X 2014, 4, 031015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallager, R.G. Information Theory and Reliable Communication; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Holliday, T.; Goldsmith, A.; Glynn, P. Capacity of Finite State Channels Based on Lyapunov Exponents of Random Matrices. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barato, C.; Hartich, D.; Seifert, U. Rate of Mutual Information between Coarse-Grained Non-Markovian Variables. J. Stat. Phys. 2013, 153, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdu, S.; Han, T.S. A general formula for channel capacity. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1994, 40, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberg, H.; Nitzan, A. Energy Conversion and Entropy Production in Biased Random Walk Processes—From Discrete Modeling to the Continuous Limit. Entropy 2023, 25, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
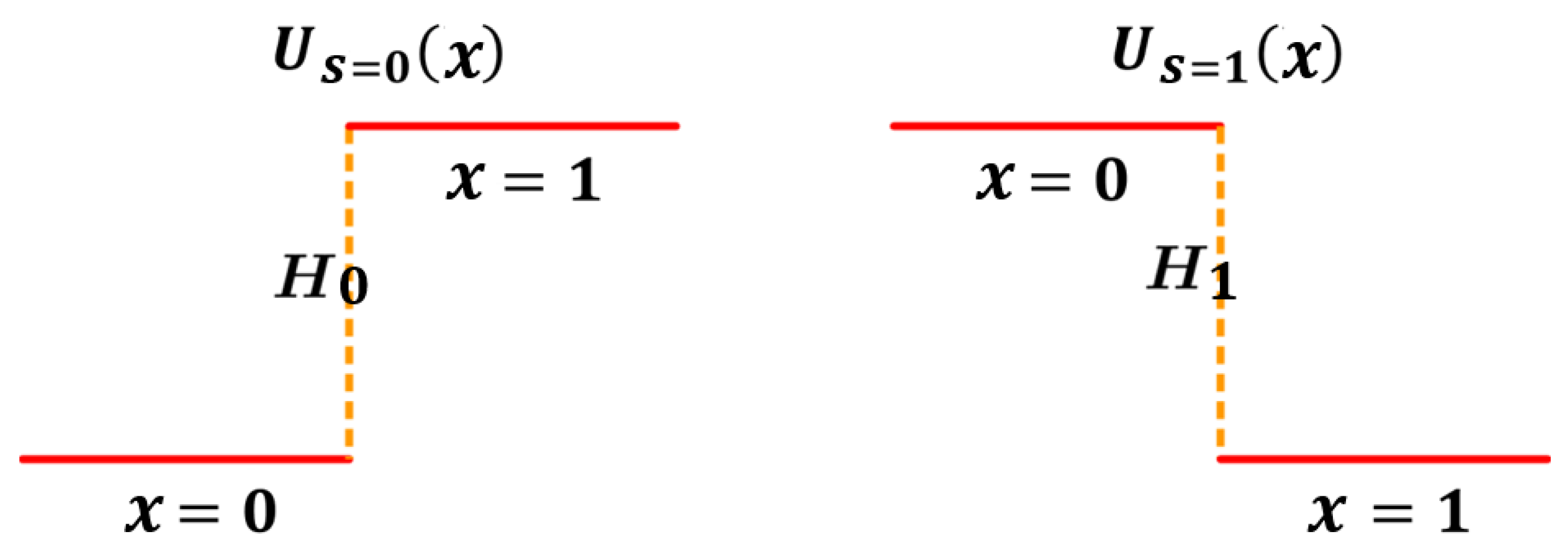


| Set 1 | Set 2 | Set 3 | Set 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | ||||
| p |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Q.; Wang, J. Non-Equilibrium Enhancement of Classical Information Transmission. Entropy 2024, 26, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26070581
Zeng Q, Wang J. Non-Equilibrium Enhancement of Classical Information Transmission. Entropy. 2024; 26(7):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26070581
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Qian, and Jin Wang. 2024. "Non-Equilibrium Enhancement of Classical Information Transmission" Entropy 26, no. 7: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26070581
APA StyleZeng, Q., & Wang, J. (2024). Non-Equilibrium Enhancement of Classical Information Transmission. Entropy, 26(7), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26070581






