Thermodynamic Stability Theories of Irreversible Processes and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Generate perturbed trajectories by introducing sufficiently small perturbations (not necessarily along the original trajectory);
- Define suitable thermodynamic perturbation coordinates, construct the corresponding thermodynamic perturbation space, and calculate the rate of change of the perturbation coordinates;
- Identify a sign-definite thermodynamic Lyapunov function, dependent on the perturbation coordinates, that vanishes only on the unperturbed trajectory;
- Determine the sign as well as the mathematical behavior of the variation with time of the chosen thermodynamic Lyapunov function.
2. The Concept of Virtual Displacement
3. Gibbs–Duhem Theory of Stability of Irreversible Processes
- The impossibility described by the envisaged third transformation in each one of them stems from the fact that the rate of entropy production cannot change its sign as per the second law of thermodynamics.
- In view of the preceding fact, the first transformation in each one of them is also not possible, which demonstrates the nonconservative nature of the entropy function.
- Thus, it is also demonstrated that the envisaged virtual displacement in the reverse direction on a given irreversible trajectory is impossible. This impossibility remains true from any position on the irreversible trajectory.
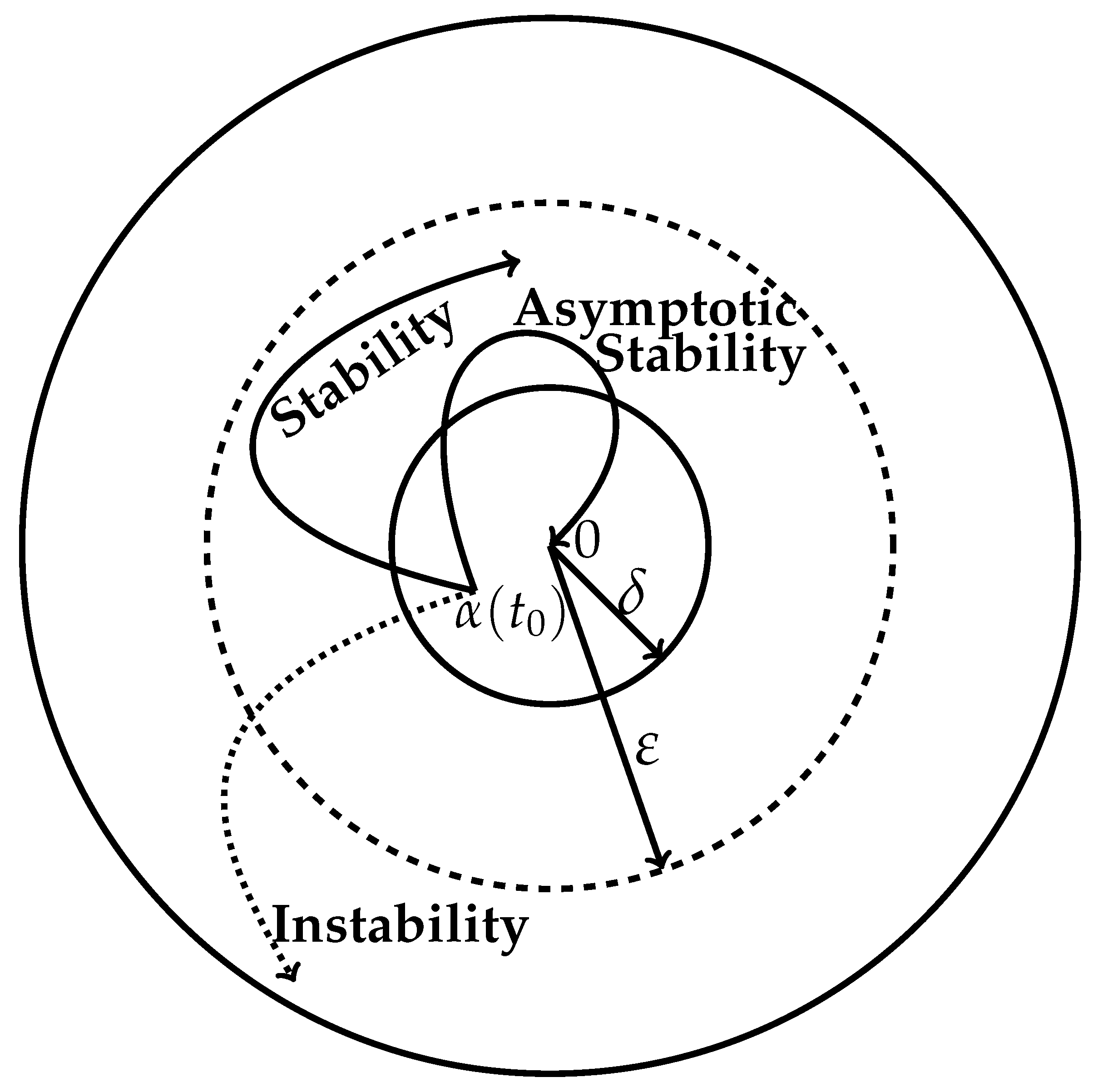
4. Stability of Motion in Terms of Lyapunov Functions
- Stable motion is described bywhere the continuous function W has strict minima at the coordinate origin, . This implies that after a small lapse of time, beyond , nonetheless, we have but . That can happen in the vicinity of the origin because initially, L is assumed to be a decreasing function of time (cf. Equation (15)).
- Asymptotically stable motion is described byThat is, asymptotic stability requires the vanishing of only at the origin, whereas in the case of stability, it can vanish very close to the origin.
- When a motion is asymptotically stable and if all are bounded in absolute value, then according to Malkin’s theorem [7,9], the motion is stable under constantly operating small disturbances. A physical example of motion under constantly acting disturbances is that of an air flight experiencing rough weather.
- Asymptotic exponential stability is described bywhere is the time of the initial perturbation. Thus, we see that for positive decay constant ,Negative would result in divergence, i.e., instability of the trajectory. How rapidly the perturbed trajectory returns to the unperturbed one depends on the value of , which needs to be determined experimentally.
5. Thermodynamic Stability Based on the Thermodynamic Lyapunov Function of LTS
6. Theorems of Thermodynamic Stability Using the Thermodynamic Lyapunov Function
- The thermodynamic stability of an unperturbed trajectory is guaranteed when we haveThat is, the unperturbed motion described by Equation (28), i.e., , is stable. However, we see that in this way, the thermodynamic trajectories are obtained as merely stable. This is the case because mere stability means the perturbed trajectory finally settles in the close vicinity of the unperturbed one. This condition implies thatis a possibility.
- The asymptotic thermodynamic stability of an unperturbed trajectory follows wheneverThat is, vanishes only when the perturbed trajectory reaches the unperturbed trajectory, making , which happens only when all perturbation coordinates vanish.
- Trajectories that are asymptotically stable as described by Equation (37) are, in view of Malkin’s theorem [7,9], also thermodynamically stable under constantly acting perturbations if, in addition, the derivativesat the local level are bounded in absolute value. Such constantly acting perturbations are, as said in the name, constantly being applied as opposed to the perturbations, leading to stability or to asymptotic stability, which are of a brief duration and then disappear, leaving the system to recover. This aspect of stability analysis using LTS is of practical use. For example, an industrial process runs continuously, and there is a possibility of repeated disturbances originating, say, due to the malfunctioning of heat exchangers to a reasonably small extent.
- When a trajectory is asymptotically stable in the Lyapunov sense and additionally the following condition is obeyed,then the unperturbed trajectory is said to be exponentially stable.Of course, in this case too, the result is , which happens only when all perturbation coordinates vanish. How fast the perturbed trajectory would approach the unperturbed one is determined by the magnitude of , the rate constant of the exponential convergence.
7. Thermodynamic Stability of Irreversible Processes Using the Thermodynamic Lyapunov Function: A Generalized Description
8. Thermodynamic Lyapunov Function-Based Generalized Thermodynamic Stability of Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Steady States
9. Using Thermodynamic Variables Based on Gibbs Relations and the Thermodynamic Lyapunov Function of LTS. A Generalized Account
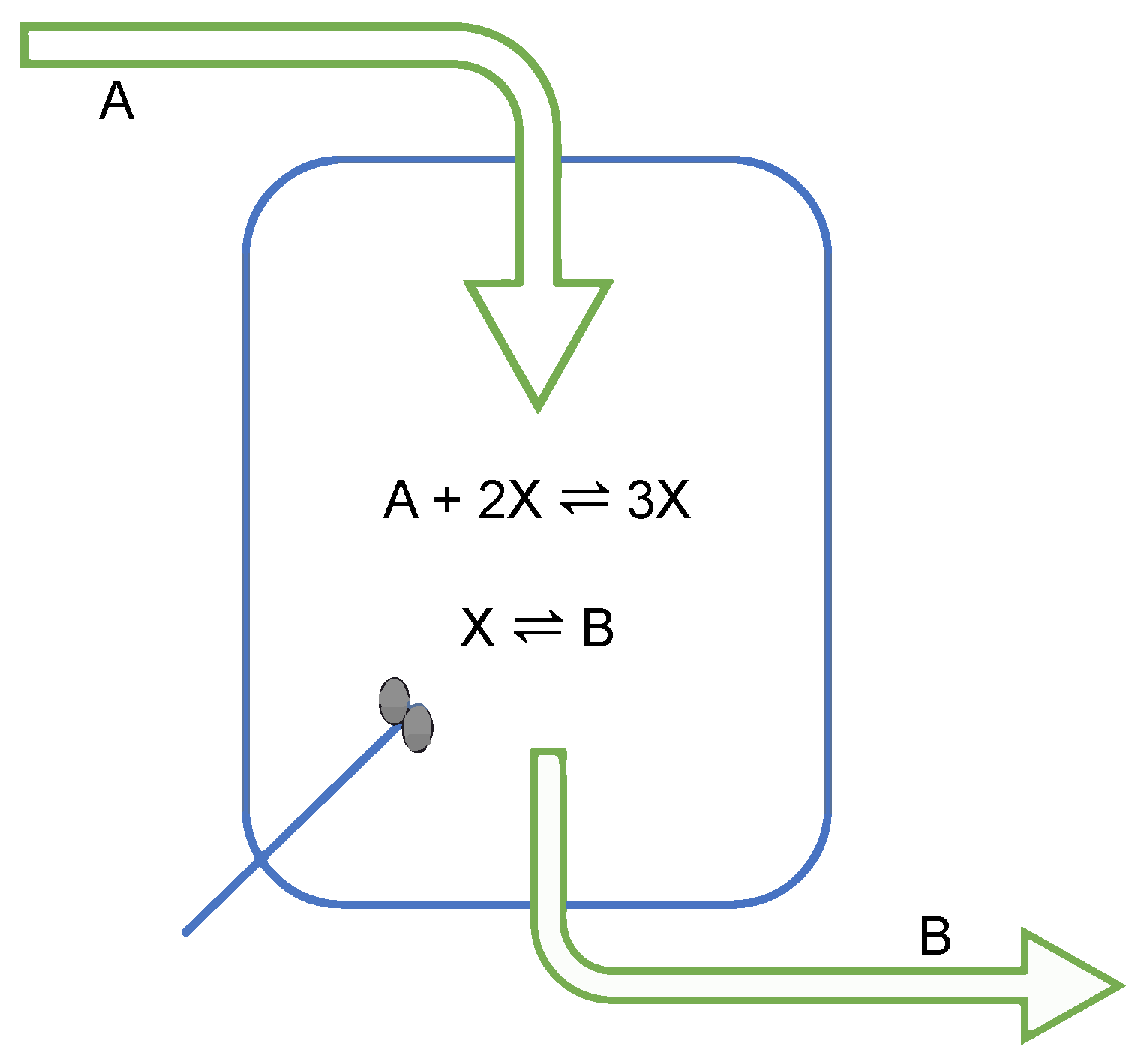
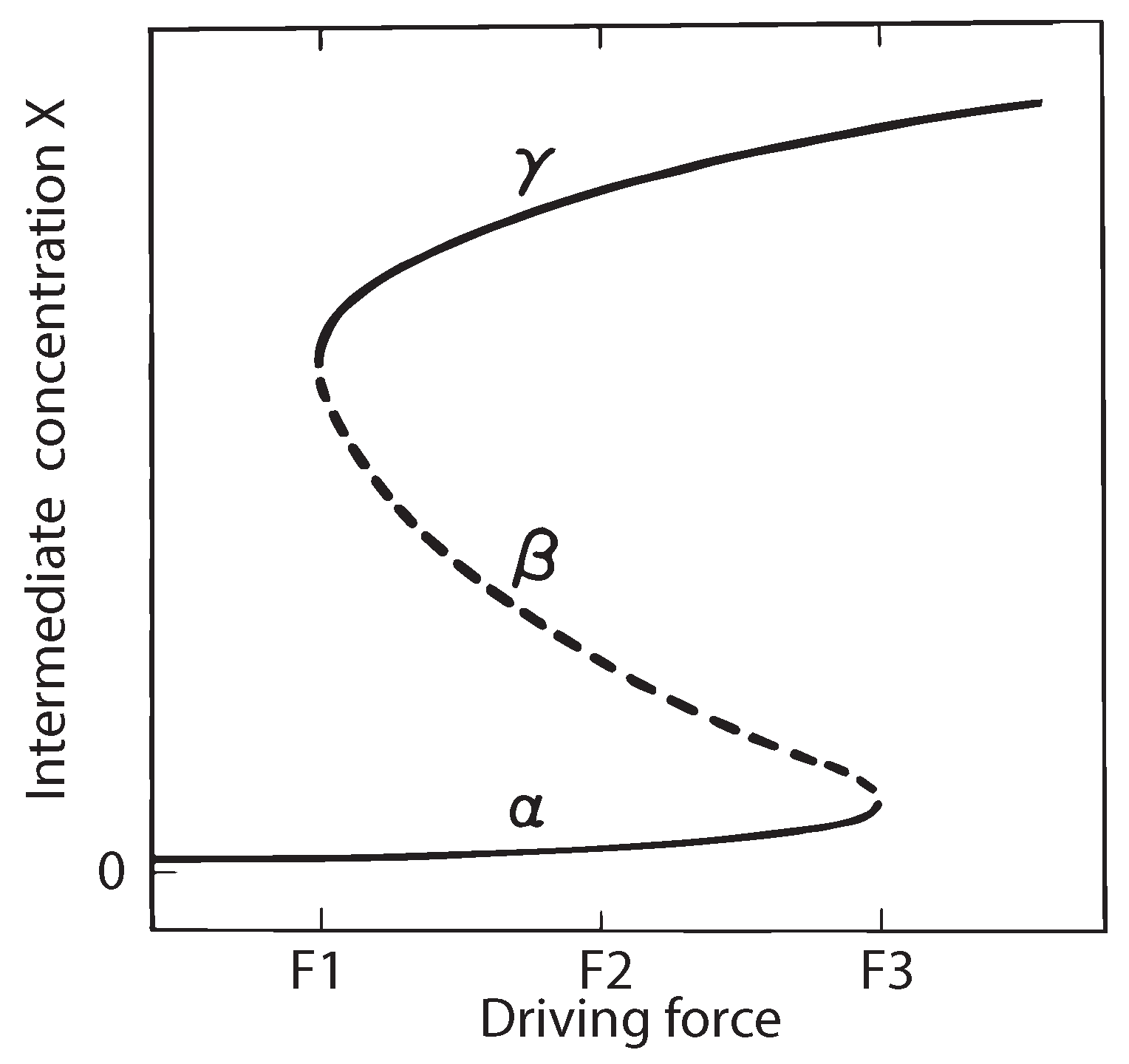
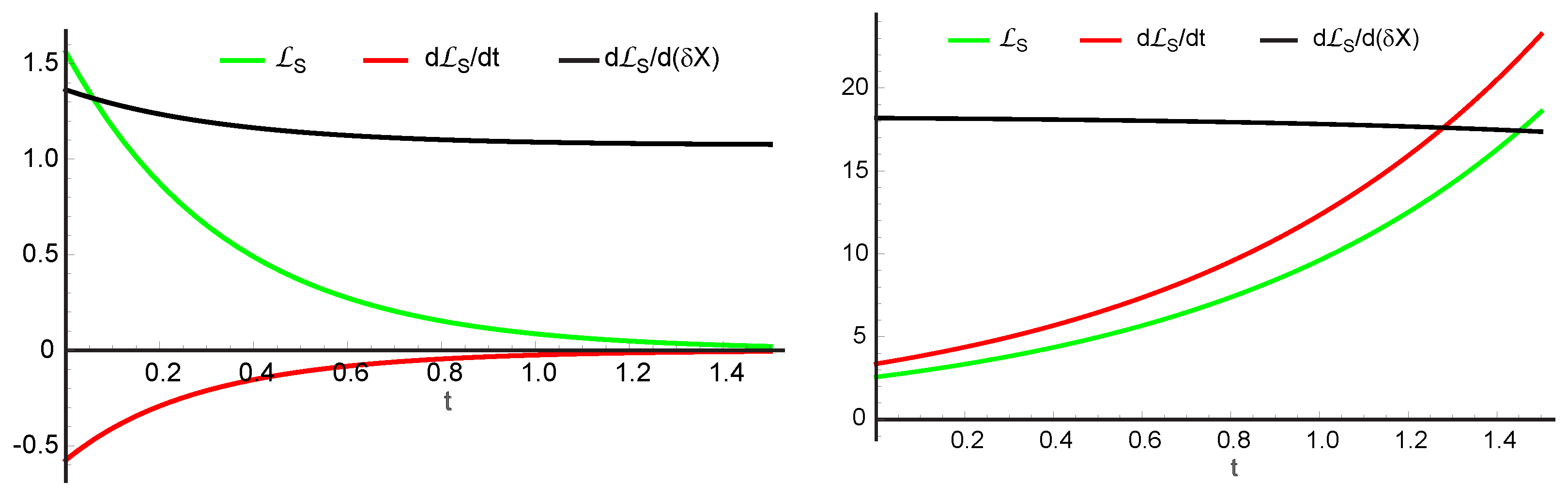
10. Thermodynamic Stability Analysis of the Schlögl Reaction
11. Formulating the “Fourth Law of Thermodynamics”
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- An ecosystem selects the pathway that maximizes the free energy storage accompanying the organization of the state [61].
- -
- A fourth law describing the nature of dark energy [62].
- -
- The impossibility to design a Carnot engine or other physical heat engine whose source has a positive (absolute) temperature and its sink has a negative (absolute) temperature [63].
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LTS | Lyapunov Thermodynamic Stability |
| NSS | Nonequilibrium Steady States |
| PIT | Phenomenological Irreversible Thermodynamics |
| eq | equilibrium state |
References
- Glansdorff, P.; Prigogine, I. Thermodynamic Theory of Structure, Stability and Fluctuations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Gromov, D.; Toikka, A. On an alternative formulation of the thermodynamic stability condition. J. Math. Chem. 2020, 58, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, D.; Toikka, A. Toward Formal Analysis of Thermodynamic Stability: Le Chatelier—Brown Principle. Entropy 2020, 22, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toikka, A.; Misikov, G.; Toikka, M. Some Remarks on the Boundary of Thermodynamic Stability. Entropy 2023, 25, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigogine, I.; Defay, R. Chemical Thermodynamics; Everett, D.H., Translator; Longmans Green: London, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Kondepudi, D.; Prigogine, I. Modern Thermodynamics: From Heat Engines to Dissipative Structures, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Malkin, I.G. Stability and Dynamic Systems; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1962; pp. 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- LaSalle, J.P.; Lefschetz, S. Stability by Liapunov’s Direct Method with Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Malkin, I.G. Theory of Stability of Motion. In ACE-tr-3352 Physics and Mathematics; US Atomic Energy Commision: Washington, DC, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Chetayev, N.G. The Stability of Motion, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Shtokalo, I.Z. Linear Differential Equations with Variable Coefficients. Criteria of Stability and Instability of Their Solutions; Hindustan: Delhi, India, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- LaSalle, J.P.; Lefschetz, S. (Eds.) Nonlinear Differential Equations and Nonlinear Mechanics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, H.T. Introduction to Nonlinear Differential and Integral Equations, 1st ed.; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, W. Theory and Applications of Lyapunov’s Direct Method; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Elsgolts, L. Differential Equations and the Calculus of Variations; Mir Publications: Moscow, Russia, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, D.A. Ordinary Differential Equations and Stability Theory. An Introduction; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Leipholz, H.H.E. Stability Theory: An Introduction to the Stability of Dynamic Systems and Rigid Bodies; B. G. Teubner/John Wiley: Stuttgart/Chichester, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, A.A. Comprehensive Thermodynamic Theory of Stability of Irreversible Processes (CTTSIP). I. The Details of a New Theory Based on Lyapunov’s Direct Method of Stability of Motion and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Far East J. Appl. Math. 2001, 5, 381–396. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, A.A. Comprehensive Thermodynamic Theory of Stability of Irreversible Processes (CTTSIP). II. A Study of Thermodynamic Stability of Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Stationary States. Far East J. Appl. Math. 2001, 5, 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, A.A.; Tangde, V.M. Thermodynamic Stability of Irreversible Processes Based on Lyapunov Function Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit and Exhibition, Cancun, Mexico, 22–26 October 2017; FLOGEN 2017, Dodds International Symposium/Energy Production. Volume 2, pp. 153–173. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, A.A.; Andresen, B. Thermodynamic Stability of Irreversible Processes. A Gibbs-Duhem type theory and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the 2017 Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit and Exhibition, Cancun, Mexico, 22–26 October 2017; FLOGEN 2017. Volume 2, pp. 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Burande, C.S.; Bhalekar, A.A. Thermodynamic Stability of Enzyme Catalytic Reactions by Lyapunov Function Analysis. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2004, 2, 495–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bhalekar, A.A.; Burande, C.S. A Study of Thermodynamic Stability of Deformation in Visco-elastic Fluids by Lyapunov Function Analysis. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2005, 30, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burande, C.S.; Bhalekar, A.A. Thermodynamic Stability of Elementary Chemical Reactions Proceeding at Finite Rates Revisited Using Lyapunov Function Analysis. Energy 2005, 30, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangde, V.M.; Bhalekar, A.A.; Venkataramani, B. Thermodynamic Stability of Sulfur Dioxide Oxidation by Lyapunov Function Analysis Against Temperature Perturbation. Phys. Scr. 2007, 75, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangde, V.M.; Bhalekar, A.A.; Venkataramani, B. Lyapunov Function Analysis of the Thermodynamic Stability of Ammonia Synthesis. Far East J. Appl. Math. 2008, 30, 297–313. [Google Scholar]
- Tangde, V.M.; Bhalekar, A.A.; Venkataramani, B. A Study of Thermodynamic Stability by Lyapunov Function Analysis of Some Elementary Chemical Reactions Against Sufficiently Small Temperature Perturbation. Bull. Cal. Math. Soc. 2008, 100, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tangde, V.M.; Rawat, S.G.; Bhalekar, A.A. A theoretical study of biological Lotka-Volterra Ecological model using CTTSIP. Int. J. Knowl. Eng. 2012, 3, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tarbell, J.M. A Note on the Relationship Between Thermodynamics and Liapunov’s Direct Method. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1982, 14, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.; Couenne, F.; Jallut, C.; Gorrec, Y.L. Thermodynamics based stability analysis and its use for nonlinear stabilization of the CSTR. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2013, 58, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Hoang, H.N. A thermodynamic Lyapunov Approach to the Stability Analysis of a Nonlinear Irreversible Process Having Multiplicity. Asean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 17, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, N.H.; Dochain, D.; Hudon, N. A Thermodynamic Approach towards Lyapunov Based Control of Reaction Rate. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulíček, M.; Málek, J.; Průša, V. Thermodynamics and Stability of Non-Equilibrium Steady States in Open Systems. Entropy 2019, 21, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favache, A.; Dochain, D. Thermodynamics and Chemical Systems Stability: The CSTR Case Study Revisited. J. Process. Control 2009, 19, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glansdorff, P.; Prigogine, I. Non-Equilibrium Stability Theory. Physica 1970, 46, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Shabd, R. Thermodynamics of Stability of Nonequilibrium Steady States. J. Chem. Educ. 1983, 60, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glansdorff, P.; Nicolis, G.; Prigogine, I. The Thermodynamic Stability Theory of Non-Equilibrium States. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keizer, J.; Fox, R.F. Qualms Regarding the Range of Validity of the Glansdorff-Prigogine Criterion for Stability of Non-Equilibrium States. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, Y. Review—Stability of Transport and Rate Processes. Int. J. Thermodyn. 2005, 8, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Romo-Hernandez, A.; Hudon, N.; Ydstie, B.E.; Dochain, D. Internal Entropy Production as a Lyapunov Function for Thermal Equilibrium in Irreversible Multiphase Systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Matsumoto, S. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics of Temporally Oscillating Chemical Reactions. J. Theor. Biol. 1975, 52, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho, P. Global and Local Thermodynamic Stability. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1999, 24, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sobrino, L. The Glansdorff-Prigogine Thermodynamic Stability Criterion in the Light of Lyapunov’s Theory. J. Theor. Biol. 1975, 54, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapovalov, V.; Kazakov, N. Generalization of Prigogine’s Theorem for the Case of Full Differential of Entropy. MethodsX 2018, 5, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.; Corlan, A.D.; Müller, S.C. Proposed Principles of Maximum Local Entropy Production. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 7858–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, D.; Weiland, S. Stability Analysis of Thermodynamic Systems: Heat Conduction in Solids. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 11533–11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, P.T. The Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. Nature 1972, 238, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfaie, S.; Shaw, J.M. On Thermodynamic Stability Theory. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1993, 18, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavenda, B.H. Concepts of Stability and Symmetry in Irreversible Thermodynamics. I. Found. Phys. 1972, 2, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieniutycz, S.; Kuran, P. A new approach to the use of Lyapunov’s functions. I. Stability and qualitative properties of paths in gas-solid systems. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 45, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Reciprocal Relations in Irreversible Processes. I. Phys. Rev. 1931, 37, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Reciprocal Relations in Irreversible Processes. II. Phys. Rev. 1931, 38, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L.; Machlup, S. Fluctuations and Irreversible Processes. Phys. Rev. 1953, 91, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, R. Emergent attractors and the law of maximum entropy production: Foundations to a theory of general evolution. Syst. Res. 1989, 6, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, R. The Fourth Law of Thermodynamics or the Law of Maximum Entropy Production (LMEP). Chemistry 2009, 18, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Kleidon, A.; Malhi, Y.; Cox, P.M. Maximum entropy production in environmental and ecological systems. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A. Non-equilibrium thermodynamics, maximum entropy production and Earth-system evolution. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyushev, L.M. Maximum Entropy Production Principle: History and Current Status. Phys. Uspekhi 2021, 64, 558–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, R.; Fleck, G. A Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. Chemistry 2006, 15, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Beretta, G.P. The Fourth Law of Thermodynamics: Steepest Entropy Ascent. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, S.E. Thermodynamics and Ecological Modelling, 1st ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shibli, M. The Foundation of the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics: Universe Dark Energy and its Nature: Can Dark Energy be Generated? RE PQJ 2007, 1, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kamal, S.A. The Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the Pakistan Institute of Physics Conference, Lahore, Pakistan, 28–30 March 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bumstead, H.A.; Name, R.G.V. (Eds.) The Scientific Papers of J. Willard Gibbs; Thermodynamics, Longmas, Green and Company: London, UK, 1906. [Google Scholar]
- Donnan, F.G.; Haas, A. (Eds.) A Commentary on the Scientific Writings of J. Willard Gibbs; New Haven, Yale University Press: London, UK, 1936; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, P. Commentary on the Principles of Thermodynamics by Pierre Duhem; Springer: Dordrecht, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, S.R.; Mazur, P. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics; North Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Tangde, V.M.; Bhalekar, A.A. How Flexible is the Concept of Local Thermodynamic Equilibrium? Entropy 2023, 25, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitts, D.D. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics. A Phenomenological Theory of Irreversible Processes in Fluid Systems; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Katchalsky, A.; Curran, P. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics in Biophysics; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Prigogine, I. Introduction to Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes; John Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, R. Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Gyarmati, I. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Lavenda, B.H. Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes; Macmillan Press: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lype, E.F. Entropy of Systems with Internal Variables. Int. J. Thermophys. 1986, 7, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J. Statistical Thermodynamics of Nonequilibrium Processes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- García-Colín, L.S. Termodinámica de Processos Irreversibles; Colección CBI-UAM Iztapalapa: Mexico City, Mexico, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Muschik, W. Six Lectures on Fundamentals and Method: Aspects of Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics, 1st ed.; Number 9 in Series in Theoretical and Applied Mechanics; World Scientific: Singapore, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Eu, B.C. Kinetic Theory and Irreversible Thermodynamics; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Grmela, M. Thermodynamics of Driven Systems. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugin, G.; Muschik, W. Thermodynamics with Internal Variables. Part I. General Concepts. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1994, 19, 217–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugin, G.; Muschik, W. Thermodynamics with Internal Variables. Part II. Applications. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 1994, 19, 250–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschik, W.; Papenfuss, C.; Ehrentraut, H. A Sketch of Continuum Thermodynamics. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 2001, 96, 255–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidas, C.; Sangaranarayanan, M.V. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics. Principles and Applications; Macmillan India: Delhi, India, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen, B. Minimizing losses—Tools of Finite-Time Thermodynamics. In Thermodynamic Optimization of Complex Energy Systems; Bejan, A., Mamut, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Rubí, J.M. The Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics Approach to the Dynamics of Mesoscopic Systems. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2005, 29, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öttinger, H.C. Beyond Equilibrium Thermodynamics, 1st ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, R.P. Introduction to Non-equilibrium Physical Chemistry. Towards Complexity and Non-linear Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nertherland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kjelstrup, S.; Bedeaux, D. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics of Heterogeneous Systems, 2nd ed.; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Parmon, V. Thermodynamics of Non-Equilibrium Processes for Chemists with a Particular Application to Catalysis, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Honing, J.M. Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes Across a Boundary: Elementary Principles. Appl. Phys. Res. 2011, 3, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, B. Current Trends in Finite-Time Thermodynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2690–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, I.; Weiss, W. Irreversible Thermodynamics—Past and Present. Eur. Phys. J. H 2012, 37, 139–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelstrup, S.; Bedeaux, D.; Johannessen, E.; Gross, G. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics for Engineers, 2nd ed.; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Wang, J. Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics in Cell Biology: Extending Equilibrium Formalism to Cover Living Systems. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2020, 49, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebon, G.; Jou, D.; Casas-Vázquez, J. Understanding Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics. Foundations, Applications, Frontiers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schlögl, F. On Thermodynamics Near a Steady State. Z. Physik 1971, 248, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, B.; Zimmermann, E.C.; Ross, J. Objections to a Proposal on the Rate of Entropy Production in Systems Far from Equilibrium. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 4676–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tangde, V.M.; Bhalekar, A.A.; Andresen, B. Thermodynamic Stability Theories of Irreversible Processes and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy 2024, 26, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060442
Tangde VM, Bhalekar AA, Andresen B. Thermodynamic Stability Theories of Irreversible Processes and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. 2024; 26(6):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060442
Chicago/Turabian StyleTangde, Vijay M., Anil A. Bhalekar, and Bjarne Andresen. 2024. "Thermodynamic Stability Theories of Irreversible Processes and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics" Entropy 26, no. 6: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060442
APA StyleTangde, V. M., Bhalekar, A. A., & Andresen, B. (2024). Thermodynamic Stability Theories of Irreversible Processes and the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy, 26(6), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060442






