The Quantum Zeno Capacity and Dynamic Evolution Mode of a Quantum System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Geometric Framework of Generalized Quantum Zeno Effect
2.2. Quantum Zeno Factor
2.3. Controlling the Quantum Zeno Effect
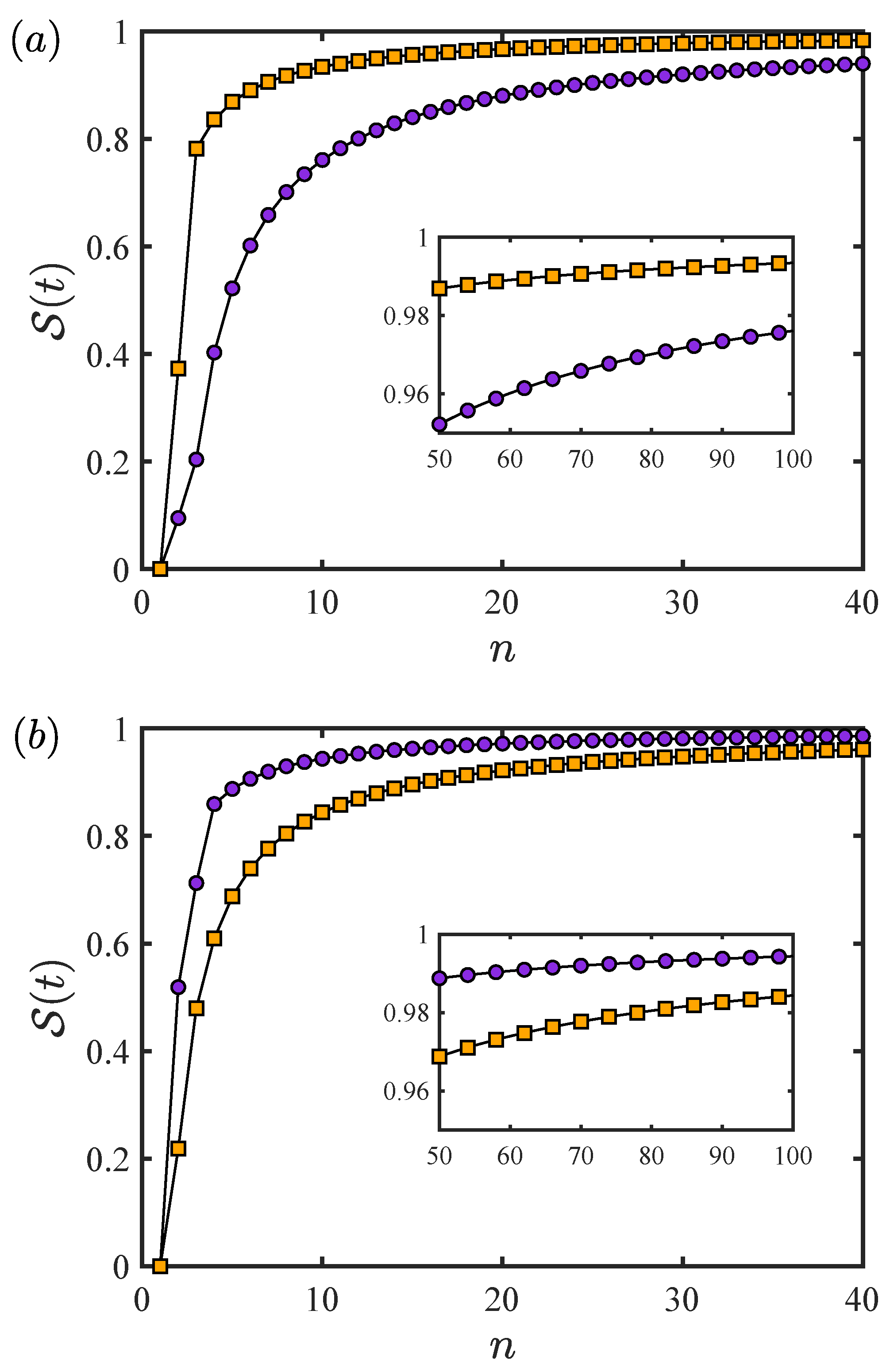
3. Numerical Results
3.1. Three-Level System
3.2. Coupled Qubit System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QZE | Quantum Zeno Effect |
| QAZE | Quantum Anti-Zeno Effect |
| QZD | Quantum Zeno Dynamics |
| QSL | Quantum Speed Limit |
Appendix A. Details of the Examples
Appendix A.1. The Three-Level Quantum System
Appendix A.2. Coupled-Qubit System
References
- von Neumann, J. Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Degasperis, A.; Fonda, L.; Ghirardi, G.C. Does the lifetime of an unstable system depend on the measuring apparatus? Il Nuovo Cimento A 1974, 21, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.; Sudarshan, E.C.G. The Zeno’s paradox in quantum theory. J. Math. Phys. 1977, 18, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.B.; Sudarshan, E.C.G.; Misra, B. Time evolution of unstable quantum states and a resolution of Zeno’s paradox. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 16, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braginsky, V.B.; Khalili, F.Y. Quantum Measurement; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Facchi, P.; Nakazato, H.; Pascazio, S. From the Quantum Zeno to the Inverse Quantum Zeno Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.Z. A general framework for the Quantum Zeno and anti-Zeno effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brion, E.; Harel, G.; Kebaili, N.; Akulin, V.M.; Dumer, I. Coherence protection by the Zeno effect. Europhys. Lett. 2004, 66, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.J. What are Quantum Jumps? Phys. Scr. 1988, T21, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, W.M.; Heinzen, D.J.; Bollinger, J.J.; Wineland, D.J. Quantum Zeno effect. Phys. Rev. A 1990, 41, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Medina, B.; Raizen, M.G. Observation of the Quantum Zeno and Anti-Zeno Effects in an Unstable System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 040402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, S. Nonexponential Decay Via Tunneling in Tight-Binding Lattices and the Optical Zeno Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Fisher, M.P.A. Quantum Zeno effect and the many-body entanglement transition. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 205136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Kuwahara, T.; Saito, K. Fate of Measurement-Induced Phase Transition in Long-Range Interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 010603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.; Bao, Y.; Choi, S.; Altman, E.; Yao, N.Y. Measurement-Induced Transition in Long-Range Interacting Quantum Circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 010604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, N.; Gordon, G.; Nest, M.; Kurizki, G. Thermodynamic control by frequent quantum measurements. Nature 2008, 452, 724–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.A.; Rao, D.D.B.; Frydman, L.; Kurizki, G. Zeno and Anti-Zeno Polarization Control of Spin Ensembles by Induced Dephasing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 160401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šafránek, D.; Deffner, S. Quantum Zeno effect in correlated qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 032308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, B.; Chaudhry, A.Z. The quantum Zeno and anti-Zeno effects: From weak to strong system-environment coupling. Eur. Phys. J. D 2019, 73, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, S.; Avella, A.; Piacentini, F.; Gramegna, M.; Opatrný, T.; Kofman, A.G.; Kurizki, G.; Gherardini, S.; Caruso, F.; Degiovanni, I.P.; et al. Quantum Zeno and Anti-Zeno Probes of Noise Correlations in Photon Polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; He, W.T.; Zhang, N.N.; Tang, K.; Lin, Z.; Liu, H.; Nie, X.; Feng, G.; Li, J.; Xin, T.; et al. Entanglement-Enhanced Quantum Metrology in Colored Noise by Quantum Zeno Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 070502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, S.; Patra, S. A Testable Theory for the Emergence of the Classical World. Entropy 2022, 24, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Sánchez, J.; Castillo-Alvarado, F.d.L.; Hernández-Pozos, J.L. Manipulation of Population Levels through Zeno-Type Measurements. Photonics 2023, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchi, P.; Pascazio, S. Quantum Zeno Subspaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 080401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchi, P.; Pascazio, S. Quantum Zeno dynamics: Mathematical and physical aspects. J. Phys. A 2008, 41, 493001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, N.; Cramer, J.; Twitchen, D.J.; Markham, M.; Hanson, R.; Taminiau, T.H. Experimental creation of quantum Zeno subspaces by repeated multi-spin projections in diamond. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, C.M. Zeno subspace in quantum-walk dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 052108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; You, J.Q.; Nori, F. Quantum entanglement via two-qubit quantum Zeno dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 77, 062339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Yi, X.X.; Long, G.L. Dissipative preparation of steady Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states for Rydberg atoms with quantum Zeno dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 062315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Jia, S.; Hu, Y. Fractional Quantum Zeno Effect Emerging from Non-Hermitian Physics. Phys. Rev. X 2023, 13, 031009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgarth, D.; Facchi, P.; Nakazato, H.; Pascazio, S.; Yuasa, K. Quantum Zeno Dynamics from General Quantum Operations. Quantum 2020, 4, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, F.; Herrera, I.; Cherukattil, S.; Lovecchio, C.; Cataliotti, F.S.; Caruso, F.; Smerzi, A. Experimental realization of quantum zeno dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barontini, G.; Hohmann, L.; Haas, F.; Estève, J.; Reichel, J. Deterministic generation of multiparticle entanglement by quantum Zeno dynamics. Science 2015, 349, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Silva, G.A.; Rezakhani, A.T.; Dominy, J.M.; Lidar, D.A. Zeno Effect for Quantum Computation and Control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 080501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franson, J.D.; Jacobs, B.C.; Pittman, T.B. Quantum computing using single photons and the Zeno effect. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 062302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakci, V.; Ozaydin, F. Quantum Zeno repeaters. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, A.; Falci, G.; Paladino, E. Quantum Zeno and anti-Zeno effect on a two-qubit gate by dynamical decoupling. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 227, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, S.; Francica, F.; Zaffino, R.L.; Lo Gullo, N.; Plastina, F. Protecting Entanglement via the Quantum Zeno Effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 090503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfaoui, K.; Kerkouche, E.H.; Boudjedaa, T.; Chaoui, A. Entanglement swapping via quantum zeno dynamics in noisy environment. Quantum Inf. Process. 2024, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaydin, F.; Bayrakci, V.; Altintas, A.A.; Bayindir, C. Superactivating Bound Entanglement in Quantum Networks via Quantum Zeno Dynamics and a Novel Algorithm for Optimized Zeno Evolution. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaydin, F.; Bayindir, C.; Altintas, A.A.; Yesilyurt, C. Nonlocal activation of bound entanglement via local quantum Zeno dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 022439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, E.; Mor, C.; Diringer, A.A.; Martin, L.S.; Lewalle, P.; Burgarth, D.; Whaley, K.B.; Hacohen-Gourgy, S. Demonstration of universal control between non-interacting qubits using the Quantum Zeno effect. Npj Quantum Inf. 2022, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardini, S.; Gupta, S.; Cataliotti, F.S.; Smerzi, A.; Caruso, F.; Ruffo, S. Stochastic quantum Zeno by large deviation theory. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 013048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedenzu, W.; Mukherjee, V.; Ghosh, A.; Kofman, A.G.; Kurizki, G. Quantum engine efficiency bound beyond the second law of thermodynamics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, F.; Barkai, E.; Kessler, D.A. First Detected Arrival of a Quantum Walker on an Infinite Line. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yin, R.; Ziegler, K.; Barkai, E. Quantum walks: The mean first detected transition time. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zheng, Y. First Detection and Tunneling Time of a Quantum Walk. Entropy 2023, 25, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchi, P.; Klein, A.; Pascazio, S.; Schulman, L. Berry phase from a quantum Zeno effect. Phys. Lett. A 1999, 257, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.V.; Gessner, M.; Cataliotti, F.S.; Smerzi, A. Measuring geometric phases with a dynamical quantum Zeno effect in a Bose-Einstein condensate. Phys. Rev. Res. 2019, 1, 033028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukunda, N.; Simon, R. Quantum Kinematic Approach to the Geometric Phase. I. General Formalism. Ann. Phys. 1993, 228, 205–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, I.; Życzkowski, K. Geometry of Quantum States: An Introduction to Quantum Entanglement, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Burgarth, D.K.; Facchi, P.; Giovannetti, V.; Nakazato, H.; Pascazio, S.; Yuasa, K. Exponential rise of dynamical complexity in quantum computing through projections. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, J.; Aharonov, Y. Geometry of quantum evolution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 65, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunstein, S.L.; Caves, C.M. Statistical distance and the geometry of quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 3439–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, A.K. Geometric phase, geometric distance and length of the curve in quantum evolution. J. Phys. A 1992, 25, L1001–L1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.K. Geometric aspects of noncyclic quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. A 1995, 52, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zheng, Y. Distinct Bound of the Quantum Speed Limit via the Gauge Invariant Distance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 180403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Peng, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, Y. Quantum Speed Limit Quantified by the Changing Rate of Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffner, S.; Campbell, S. Quantum speed limits: From Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle to optimal quantum control. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2017, 50, 453001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelstam, L.; Tamm, I. The Uncertainty Relation Between Energy and Time in Non-relativistic Quantum Mechanics. In Selected Papers; Bolotovskii, B.M., Frenkel, V.Y., Peierls, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Margolus, N.; Levitin, L.B. The maximum speed of dynamical evolution. Phys. D 1998, 120, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.K. Limit on the frequency of measurements in the quantum Zeno effect. Phys. Lett. A 1996, 215, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerzi, A. Zeno Dynamics, Indistinguishability of State, and Entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 150410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, A.; Egusquiza, I.L.; Plenio, M.B.; Huelga, S.F. Quantum Speed Limits in Open System Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 050403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.M.; Escher, B.M.; Davidovich, L.; de Matos Filho, R.L. Quantum Speed Limit for Physical Processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 050402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deffner, S.; Lutz, E. Quantum Speed Limit for Non-Markovian Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 010402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; An, J.H. Quantum speed limit from a quantum-state-diffusion method. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 108, 012204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, V.; Lloyd, S.; Maccone, L. Quantum limits to dynamical evolution. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 67, 052109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrás, A.; Casas, M.; Plastino, A.R.; Plastino, A. Entanglement and the lower bounds on the speed of quantum evolution. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 022326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zheng, Y. Quantum dynamical speedup in a nonequilibrium environment. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 052104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, L.B.; Toffoli, T. Fundamental Limit on the Rate of Quantum Dynamics: The Unified Bound Is Tight. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 160502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, A.M.; Farhi, E.; Preskill, J. Robustness of adiabatic quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 65, 012322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Dowling, M.R.; Gu, M.; Doherty, A.C. Quantum Computation as Geometry. Science 2006, 311, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ni, Z.; Zheng, Y. Energetic cost as a consequence of parallel transporting speed limit. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 095125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlin, Y.; Scöhn, G.; Shnirman, A. Josephson-junction qubits with controlled couplings. Nature 1999, 398, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milburn, G.J.; Laflamme, R.; Sanders, B.C.; Knill, E. Quantum dynamics of two coupled qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 65, 032316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, J.; Bacon, D.; Lidar, D.A.; Whaley, K.B. Theory of decoherence-free fault-tolerant universal quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 042307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidar, D.A.; Chuang, I.L.; Whaley, K.B. Decoherence-Free Subspaces for Quantum Computation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storcz, M.J.; Wilhelm, F.K. Decoherence and gate performance of coupled solid-state qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 67, 042319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Bofill, J.M.; Moreira, I.d.P.R.; Albareda, G. Highly Adiabatic Time-Optimal Quantum Driving at Low Energy Cost. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 129, 180402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, Y. The Quantum Zeno Capacity and Dynamic Evolution Mode of a Quantum System. Entropy 2024, 26, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121080
Ni Z, Peng Y, Zheng Y. The Quantum Zeno Capacity and Dynamic Evolution Mode of a Quantum System. Entropy. 2024; 26(12):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121080
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Zhenbo, Yonggang Peng, and Yujun Zheng. 2024. "The Quantum Zeno Capacity and Dynamic Evolution Mode of a Quantum System" Entropy 26, no. 12: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121080
APA StyleNi, Z., Peng, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2024). The Quantum Zeno Capacity and Dynamic Evolution Mode of a Quantum System. Entropy, 26(12), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26121080





