Multi-Modal Fake News Detection via Bridging the Gap between Modals
Abstract
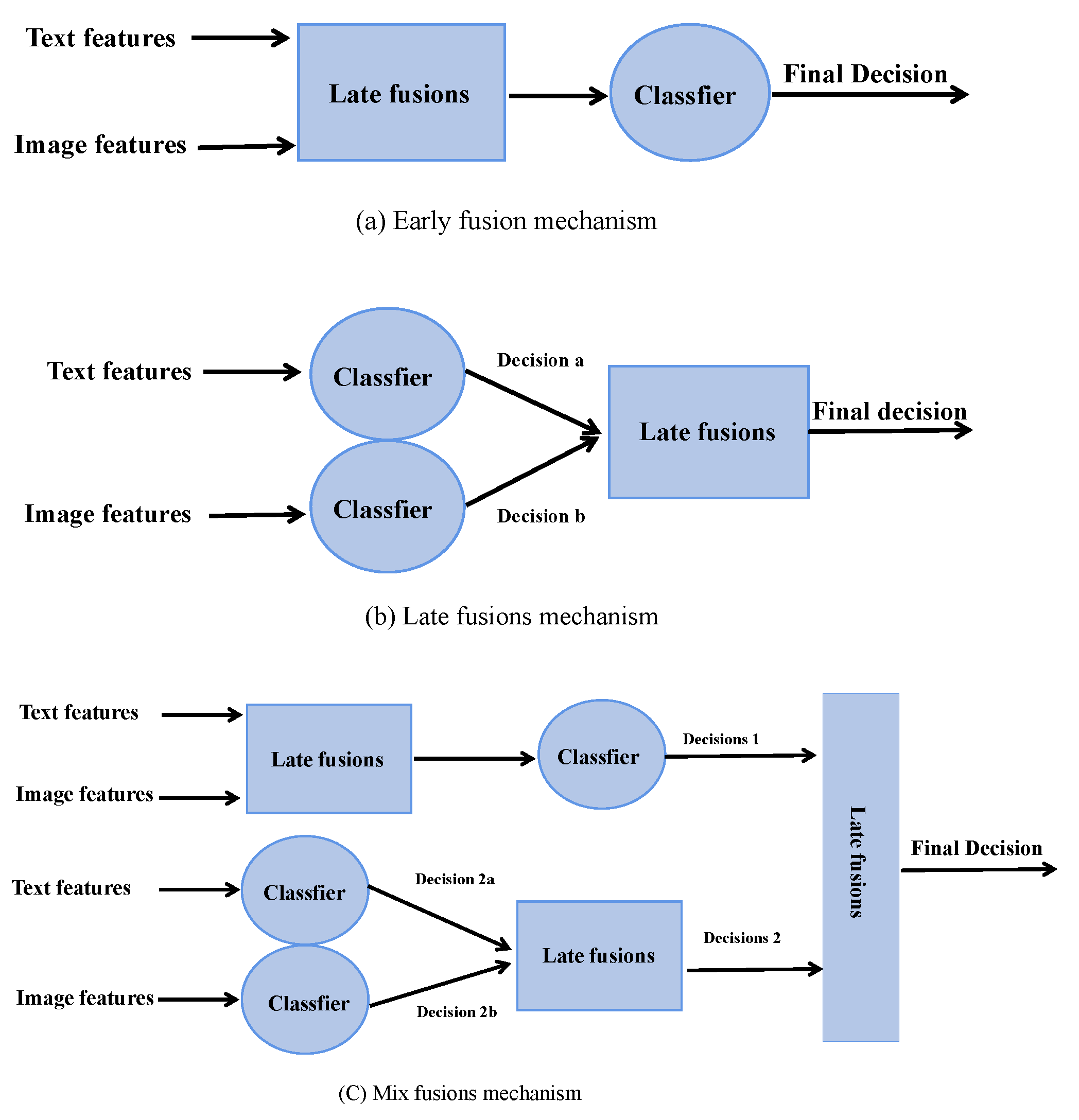
:1. Introduction
- Our proposed method leverages a transformer architecture to effectively fuse the multi-modal data, thereby modeling the semantic relationships between images and texts.
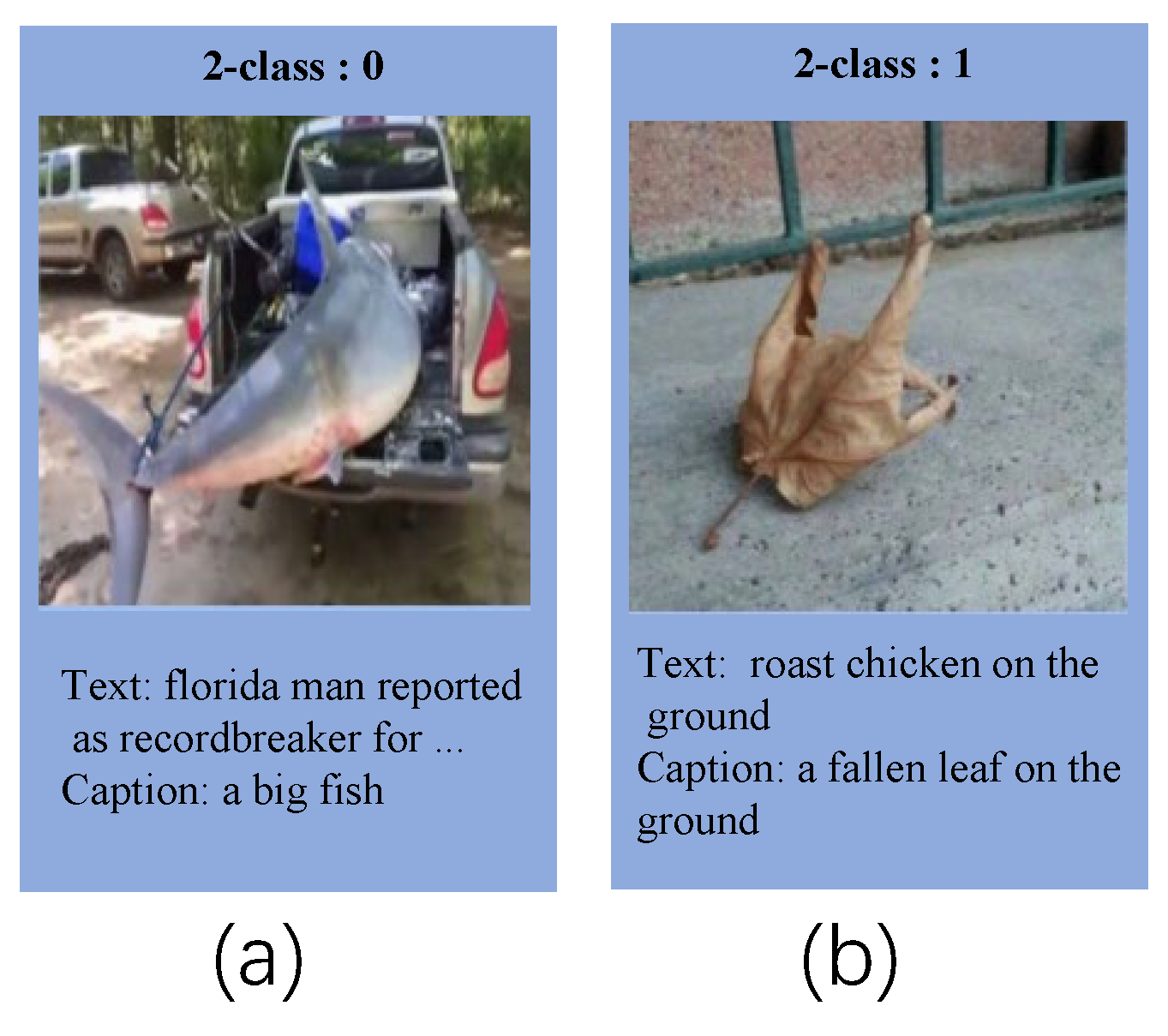
- To capture the complex relationship between the image and text in multi-modal news, we analyze and propose utilizing image description information as a solution to enhance semantic interaction between the text and image.
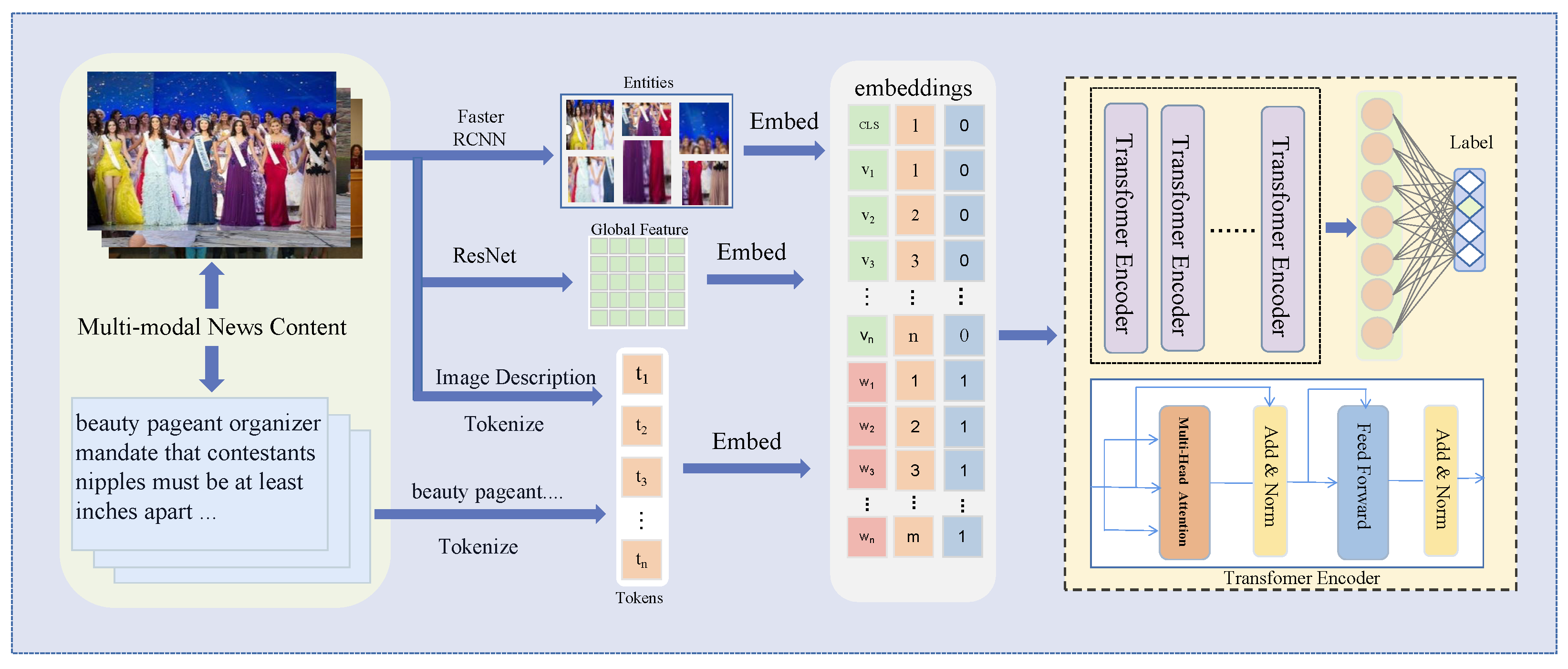
- To further improve the exploration of the relationship between text and image and optimize image utilization, we combine entity features with global features to create comprehensive features.
2. Related Works
2.1. Fake News Detection
2.2. Image Caption
2.3. Multi-Modal Transformers
3. Method
3.1. Problem Definition
3.2. Model Overview
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
- Fakeddit [57] The Fakeddit dataset is a comprehensive dataset for fake news detection that has been collected from Reddit, a popular social media platform. The dataset comprises over one million samples and provides multi-grained labels covering text, images, metadata, and comments. It includes labeling information for 2, 3, and 6 categories, which offers increasing granularity of classification. For 2 categories, it determines whether a piece of news is real or fake. The others label information provides even greater specificity, enabling a more detailed classification of the news samples. All the samples are labeled through distant supervision and are further reviewed through multiple stages to ensure accuracy.
- Weibo [33] The Weibo dataset originates from China’s popular social media platform Weibo. The dataset contains both real and fake news samples. Each news item in the dataset includes the corresponding text, image, and label information.
4.2. Baseline Methods
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy:
- Precision:
- Recall:
- F1:
4.4. Implementation Details
4.5. Comparison Experiments
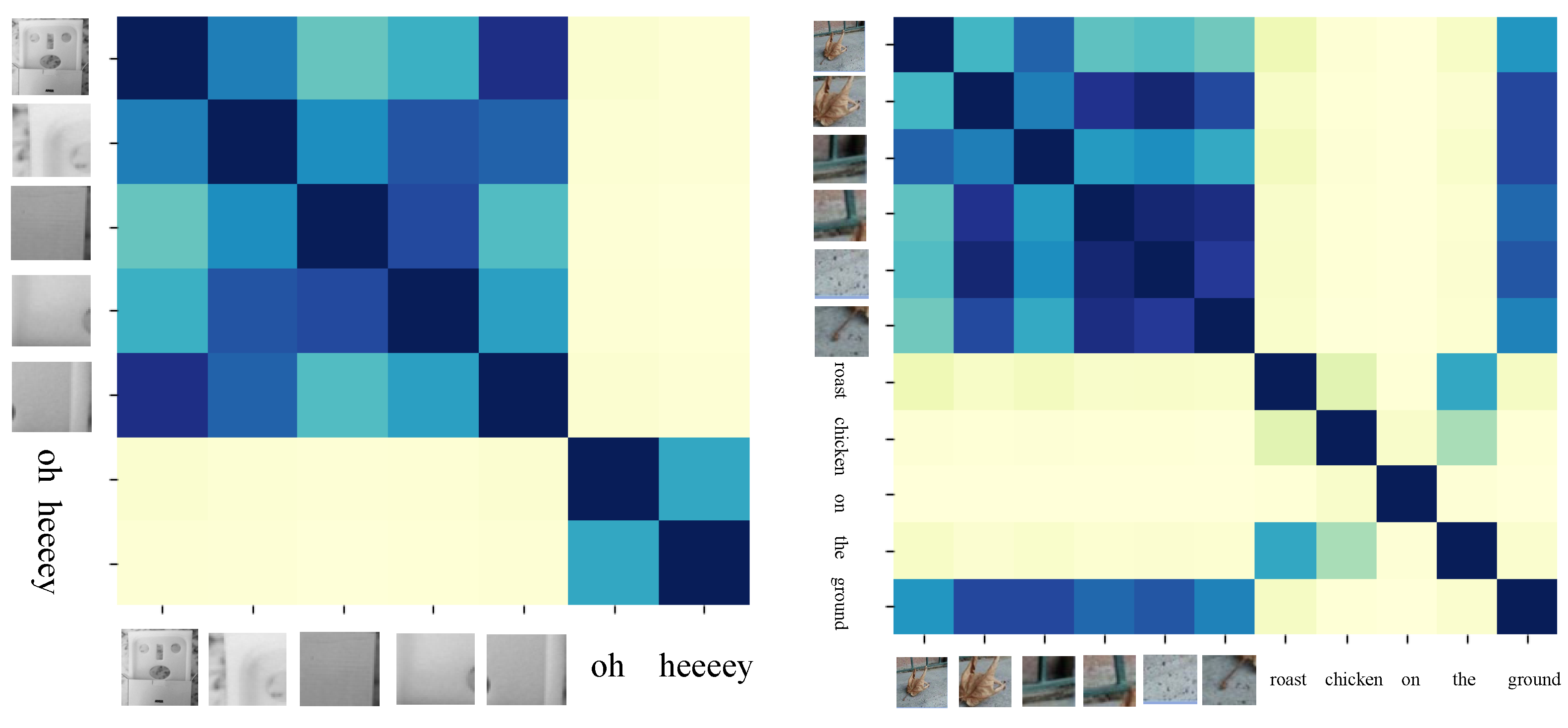
4.6. Relationship of Cross-Modal
4.7. The Impact of Image Caption
4.8. The Impact of Local Regions
4.9. Image Caption on Single-Modal
4.10. Ablation Experiments
5. Conclusions
6. Implications for Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Fake news detection on social media: A data mining perspective. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2017, 19, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheufele, D.A.; Krause, N.M. Science audiences, misinformation, and fake news. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7662–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allcott, H.; Gentzkow, M. Social media and fake news in the 2016 election. J. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 31, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, Y.M.; de Moura, G.A.; Desidério, G.A.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Lourenço, F.D.; de Figueiredo Nicolete, L.D. The impact of fake news on social media and its influence on health during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. J. Public Health 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosoughi, S.; Roy, D.; Aral, S. The spread of true and false news online. Science 2018, 359, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyar, R.K.; Goswami, A.; Narang, P. EchoFakeD: Improving fake news detection in social media with an efficient deep neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 8597–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, E. ZoKa: A fake news detection method using edge-weighted graph attention network with transfer models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 11669–11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.B.; Elnagar, A.; Elgendy, O.; Afadar, Y. Arabic fake news detection based on deep contextualized embedding models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 16019–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, D.K. Predicting image credibility in fake news over social media using multi-modal approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 21503–21517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.F. Early detection of fake news on social media through propagation path classification with recurrent and convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R. Network-based fake news detection: A pattern-driven approach. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2019, 21, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhania, S.; Fernandez, N.; Rao, S. 3han: A deep neural network for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 24th International Conference, ICONIP 2017, Guangzhou, China, 14–18 November 2017; Proceedings, Part II 24. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Gao, W.; Mitra, P.; Kwon, S.; Jansen, B.J.; Wong, K.F.; Cha, M. Detecting Rumors from Microblogs with Recurrent Neural Networks; AAAI Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khattar, D.; Goud, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Varma, V. Mvae: Multimodal variational autoencoder for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 2915–2921. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xiong, X.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Qiang, B.H. Multi-modal transformer using two-level visual features for fake news detection. Appl. Intell. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Zafarani, R. Similarity-Aware Multi-modal Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining: 24th Pacific-Asia Conference, PAKDD 2020, Singapore, 11–14 May 2020, Proceedings, Part II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Vienna, Austria, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Segura-Bedmar, I.; Alonso-Bartolome, S. Multimodal fake news detection. Information 2022, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdali, S. Multi-modal Misinformation Detection: Approaches, Challenges and Opportunities. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.13883. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Cresci, S.; Chakraborty, T.; Silvestri, F.; Dimitrov, D.; Martino, G.D.S.; Shaar, S.; Firooz, H.; Nakov, P. A survey on multimodal disinformation detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.12541. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loos, E.; Nijenhuis, J. Consuming Fake News: A Matter of Age? The perception of political fake news stories in Facebook ads. In Proceedings of the Human Aspects of IT for the Aged Population. Technology and Society: 6th International Conference, ITAP 2020, Held as Part of the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; Proceedings, Part III 22; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Zhou, J. Human Aspects of IT for the Aged Population. Technologies, Design and User Experience: 6th International Conference, ITAP 2020, Held as Part of the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020, Proceedings, Part I; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Salvendy, G. Human Aspects of IT for the Aged Population. Design for Aging: Second International Conference, ITAP 2016, Held as Part of HCI International 2016, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016, Proceedings, Part I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9754.
- Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Z.; Guo, W.; Miao, C.; Cui, L. BDANN: BERT-based domain adaptation neural network for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jha, K.; Su, L.; Gao, J. Eann: Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Cao, J.; Yang, T.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Exploiting multi-domain visual information for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; pp. 518–527. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, S.; Shah, R.R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P.; Satoh, S. Spotfake: A multi-modal framework for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), Singapore, 11–13 September 2019; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Zafarani, R. Safe: Similarity-aware multi-modal fake news detection (2020). In Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. PAKDD 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Hu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, J. Multi-level word features based on CNN for fake news detection in cultural communication. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2020, 24, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. Multimodal fusion with recurrent neural networks for rumor detection on microblogs. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 795–816. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Q.; Qian, S.; Xu, C. Multi-modal knowledge-aware event memory network for social media rumor detection. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1942–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Toshev, A.; Bengio, S.; Erhan, D. Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; He, X.; Buehler, C.; Teney, D.; Johnson, M.; Gould, S.; Zhang, L. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6077–6086. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, A.; Mathews, A.; Xie, L. Transform and tell: Entity-aware news image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13035–13045. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Chen, X.; Hua, G.; Hu, H.; He, X. Stacked cross attention for image-text matching. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.Y. Attention on attention for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 4634–4643. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, P.N.; Sain, A.; Bhunia, A.K.; Xiang, T.; Gryaditskaya, Y.; Song, Y.Z. FS-COCO: Towards understanding of freehand sketches of common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part VIII; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fan, H.; Yan, C.; Xu, M.; Yang, Y. Cascaded revision network for novel object captioning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z.; Luo, G.; Lin, L. Fine-grained image captioning with global-local discriminative objective. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 2413–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornia, M.; Stefanini, M.; Baraldi, L.; Cucchiara, R. Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10578–10587. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, R.; Shen, Y.; Yang, M. Interactive dual generative adversarial networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11588–11595. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Ding, N.; Tan, M.; Wu, Q. Length-controllable image captioning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XIII 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 712–729. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F. Exploring region relationships implicitly: Image captioning with visual relationship attention. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 109, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, R.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, J. Show, deconfound and tell: Image captioning with causal inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18041–18050. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zha, Z.J.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, F. Densely Supervised Hierarchical Policy-Value Network for Image Paragraph Generation. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 975–981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, X.; Luo, J. Cross-domain image captioning via cross-modal retrieval and model adaptation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Goswami, V.; Rohrbach, M.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. 12-in-1: Multi-task vision and language representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10437–10446. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.H.; Yatskar, M.; Yin, D.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W. Visualbert: A simple and performant baseline for vision and language. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.03557. [Google Scholar]
- Mokady, R.; Hertz, A.; Bermano, A.H. Clipcap: Clip prefix for image captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09734. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Levy, S.; Wang, W.Y. Fakeddit: A New Multimodal Benchmark Dataset for Fine-grained Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 6149–6157. [Google Scholar]
- Kiela, D.; Bhooshan, S.; Firooz, H.; Perez, E.; Testuggine, D. Supervised multimodal bitransformers for classifying images and text. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.02950. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]





| Dataset | Train (No.) | Validate (No.) | Test (No.) | Label | R:F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fakeddit | 563,523 | 59,283 | 59,257 | 2/3/6 | 2:3 |
| 7183 | - | 1840 | 2 | 1:1 |
| Method | 2-Class | 3-Class | 6-Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | P | R | F1 | Acc | Acc | ||
| Single-modal | Naive Bayes | 0.7933 | 0.8139 | 0.8522 | 0.8326 | 0.7750 | 0.6469 |
| BERT | 0.8788 | 0.9147 | 0.8814 | 0.8977 | 0.8731 | 0.8070 | |
| ResNet | 0.7534 | 0.8032 | 0.7832 | 0.7911 | 0.7442 | 0.6936 | |
| Multi-modal | EANN | 0.8750 | 0.9043 | 0.8811 | 0.8926 | 0.8702 | 0.8319 |
| MVAE | 0.8875 | 0.9011 | 0.9139 | 0.9074 | 0.8838 | 0.8413 | |
| BERT and ResNet | 0.8942 | 0.9124 | 0.9122 | 0.9123 | 0.8926 | 0.8502 | |
| MMBT | 0.9111 | 0.9274 | 0.9251 | 0.9263 | 0.9058 | 0.8830 | |
| MTTV | 0.9188 | 0.9348 | 0.9303 | 0.9325 | 0.9162 | 0.8982 | |
| Our | 0.9251 | 0.9383 | 0.9374 | 0.9379 | 0.9221 | 0.9057 | |
| Method | Acc | P | R | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-modal | Naive Bayes | 0.7130 | 0.6685 | 0.8213 | 0.7371 |
| BERT | 0.8538 | 0.8427 | 0.8624 | 0.8524 | |
| ResNet | 0.6451 | 0.6483 | 0.6016 | 0.6241 | |
| Multi-modal | EANN | 0.7950 | 0.8060 | 0.7950 | 0.8000 |
| MVAE | 0.8240 | 0.8540 | 0.7690 | 0.8090 | |
| BERT and ResNet | 0.8603 | 0.9055 | 0.7980 | 0.8484 | |
| MMBT | 0.8658 | 0.8733 | 0.8491 | 0.8610 | |
| MTTV | 0.8766 | 0.8616 | 0.8912 | 0.8762 | |
| Our | 0.8886 | 0.8692 | 0.9201 | 0.8939 | |
| Modal | 2-Class | 3-Class | 6-Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | P | R | F1 | Acc | Acc | |
| Text | 0.8788 | 0.9147 | 0.8814 | 0.8977 | 0.8731 | 0.8070 |
| Text w/ IC | 0.8940 | 0.9141 | 0.9099 | 0.9120 | 0.8881 | 0.8134 |
| Image | 0.7534 | 0.8032 | 0.7832 | 0.7911 | 0.7442 | 0.6936 |
| Image w/ IC | 0.8103 | 0.8626 | 0.8154 | 0.8384 | 0.8016 | 0.7600 |
| Modal | Acc | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Text | 0.8538 | 0.8427 | 0.8624 | 0.8524 |
| Text w/ IC | 0.8571 | 0.8603 | 0.8594 | 0.8598 |
| Image | 0.6451 | 0.6483 | 0.6016 | 0.6241 |
| Image w/ IC | 0.6565 | 0.6574 | 0.6826 | 0.6698 |
| Configuration | Acc | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remove GF | 0.8815 | 0.8523 | 0.9286 | 0.8896 |
| Remove EF | 0.8820 | 0.8525 | 0.9297 | 0.8894 |
| Remove IC | 0.8766 | 0.8429 | 0.9318 | 0.8889 |
| Our | 0.8886 | 0.8692 | 0.9201 | 0.8939 |
| Configuration | 2-Class | 3-Class | 6-Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | P | R | F1 | Acc | Acc | |
| Remove GF | 0.9205 | 0.9221 | 0.9482 | 0.9350 | 0.9202 | 0.9018 |
| Remove EF | 0.9211 | 0.9305 | 0.9394 | 0.9349 | 0.9206 | 0.9031 |
| Remove IC | 0.9139 | 0.9212 | 0.9374 | 0.9293 | 0.9169 | 0.8913 |
| Our | 0.9251 | 0.9383 | 0.9374 | 0.9379 | 0.9221 | 0.9057 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Qian, W.; Xu, D.; Ren, B.; Cao, J. Multi-Modal Fake News Detection via Bridging the Gap between Modals. Entropy 2023, 25, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040614
Liu P, Qian W, Xu D, Ren B, Cao J. Multi-Modal Fake News Detection via Bridging the Gap between Modals. Entropy. 2023; 25(4):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040614
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Wenhua Qian, Dan Xu, Bingling Ren, and Jinde Cao. 2023. "Multi-Modal Fake News Detection via Bridging the Gap between Modals" Entropy 25, no. 4: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040614
APA StyleLiu, P., Qian, W., Xu, D., Ren, B., & Cao, J. (2023). Multi-Modal Fake News Detection via Bridging the Gap between Modals. Entropy, 25(4), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25040614









