Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Entropy and Its Application in Implicit Generalized Predictive Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
2.1. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
2.2. Remove the Influence of Velocity Term
2.3. Weight Attenuation Strategy Combined with SR
2.4. Local Optimal Judgment Threshold
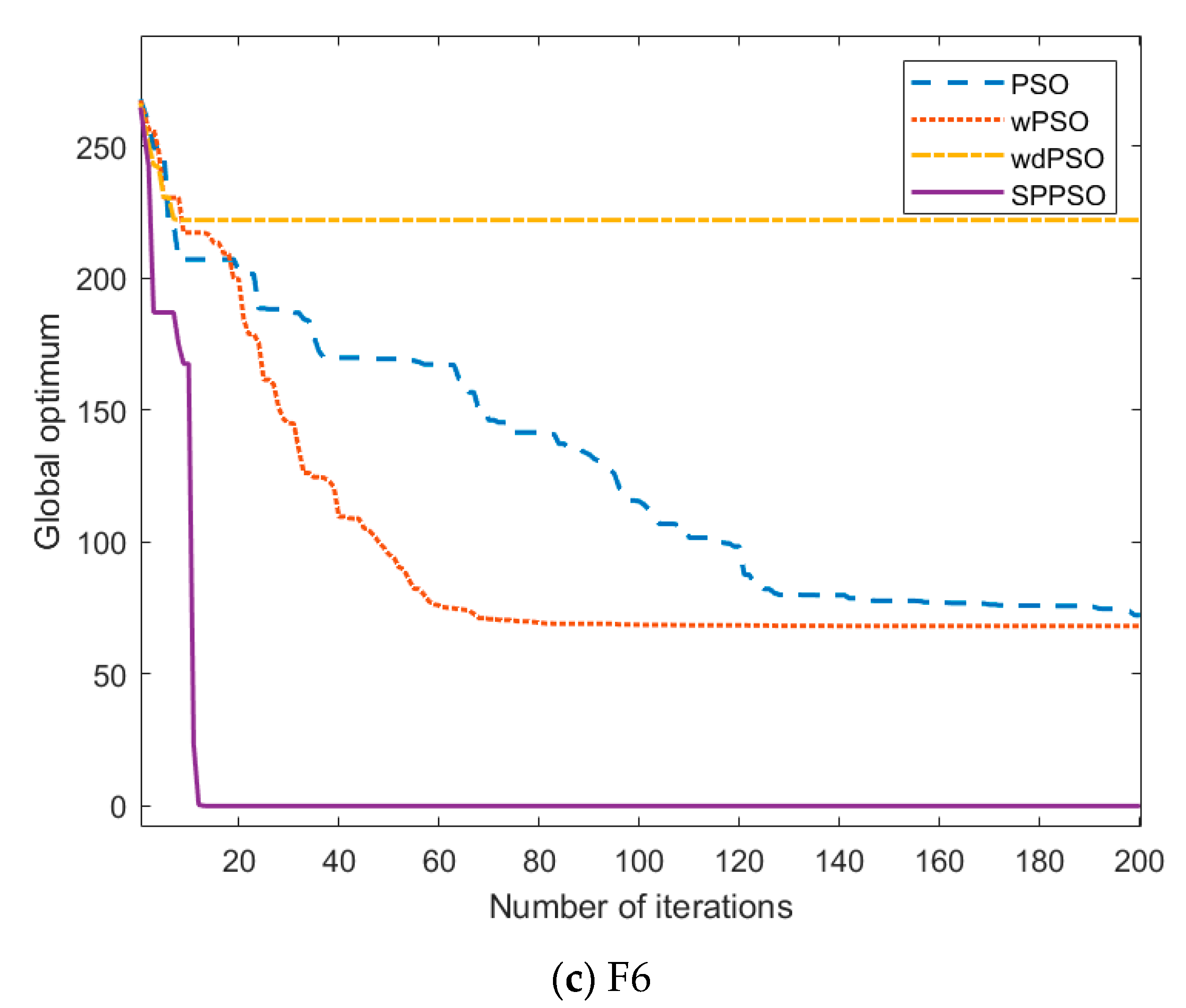
2.5. Simulation Analysis
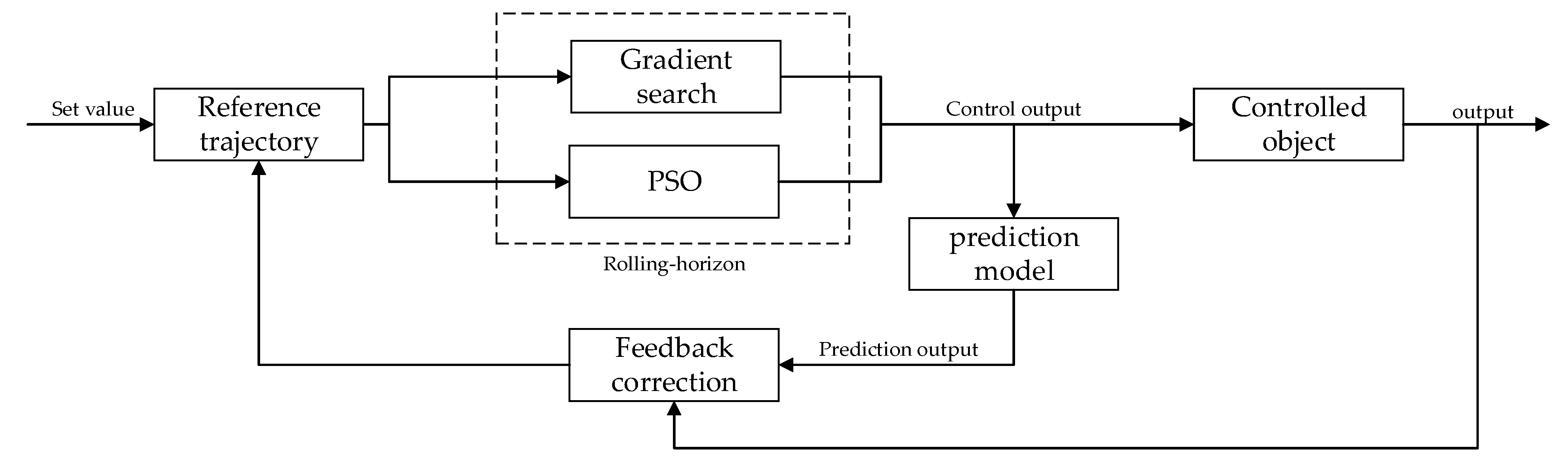
3. Implicit Generalized Predictive Control Algorithm-Based SPPSO
3.1. Generalized Predictive Control Algorithm
3.1.1. Prediction Model
3.1.2. Rolling-Horizon
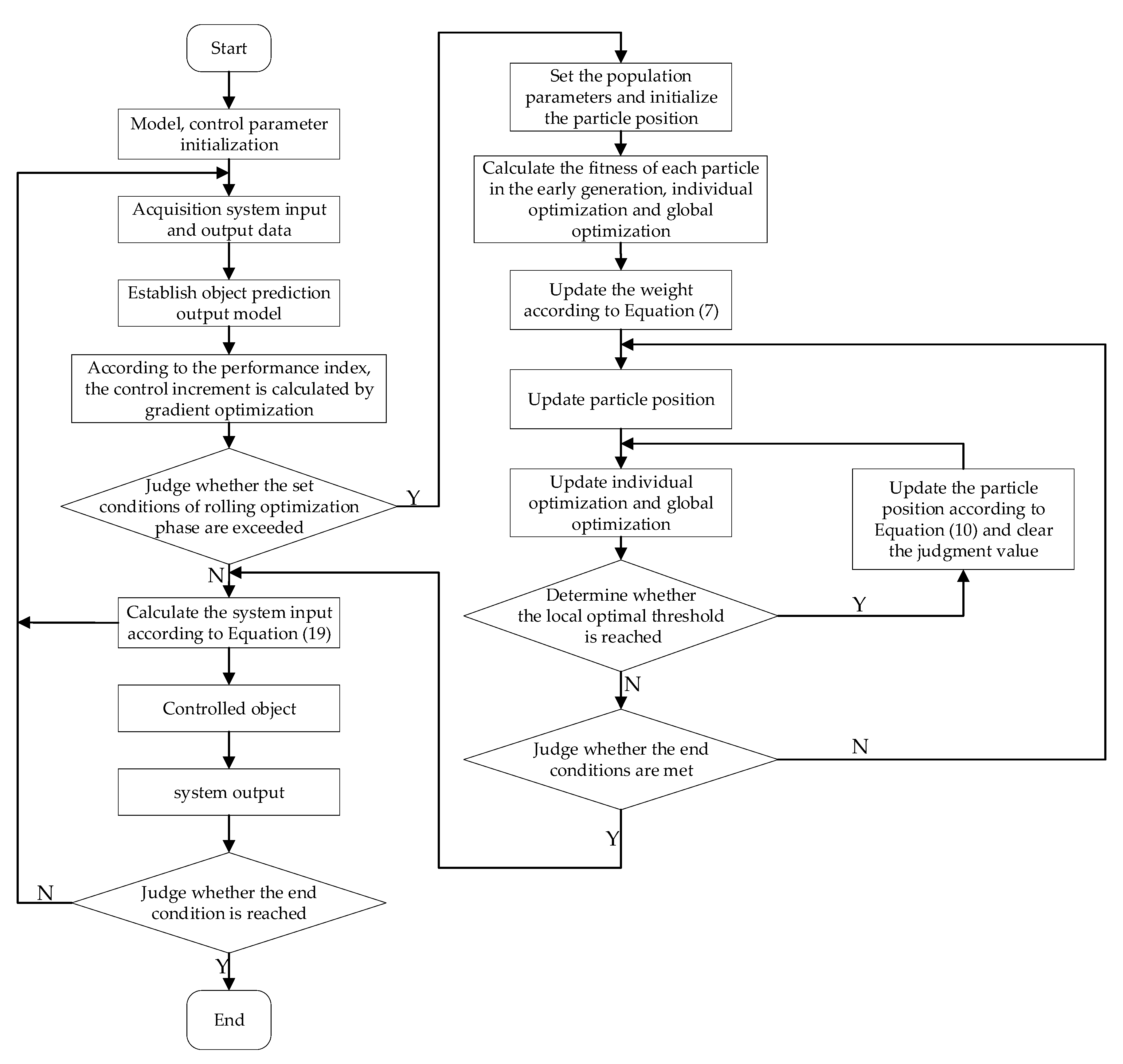
3.2. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization-Based IGPC
4. Simulation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Hu, L.; Sun, Z. A generalized model predictive control method for series elastic actuator driven exoskeleton robots. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 94, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Peng, C.; Zhang, T. Fuzzy K-Means Cluster Based Generalized Predictive Control of Ultra Supercritical Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 4575–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Fan, D.; Yang, F.; Fu, Q.; Li, Y. Active generalized predictive control of turbine tip clearance for aero-engines. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, W.; Chao, R.; Sun, Y. Adaptive levitation control for characteristic model of low speed maglev vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.W.; Mohtadi, C.; Tuffs, P.S. Generalized predictive control—Part I. The basic algorithm. Automatica 1987, 23, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, W.; Lideng, P.; Quanshan, L. Multivariable continuous-time generalized predictive control with multiple time delays. In Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control Conference, Kunming, China, 16–18 July 2008; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. Simulation of implicit generalized predictive control algorithm with input constraints. J. Syst. Simul. 2004, 16, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Wang, W.; Qiu, X. An Improved Generalized Predictive Control Algorithm Based on PID. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), Changsha, China, 20–22 October 2008; pp. 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones, O.A.; Rojas, A.J.; Sbarbaro, D. Generalized Predictive PI Controller: Analysis and Design for Time Delay Systems. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 May 2021; pp. 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Peng, C.; Zeng, D.; Gang, Y.; Mi, H. An Improved Neuro-fuzzy Generalized Predictive Control of Ultra-supercritical Power Plant. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, R.; Estrabis, T.; Batista, E.A.; Andrea, C.Q.; Gentil, G. Ramp-Tracking Generalized Predictive Control System-Based on Second-Order Difference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Zang, T.; Chen, P.; Zeng, D. Generalized Predictive Control with Two-stage Neural Network Model for Nonlinear Time-delay Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 5072–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, T.X. Improved generalized predictive control and parameter optimization based on ant colony algorithm. Instrum. Users 2021, 28, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M. On the design and realization of active disturbance rejection generalized predictive control. IMA J. Math. Control. Inf. 2018, 36, 1275–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X. An Improved GPC Hybrid Network Control. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Control and Robotics Engineering (ICCRE), Beijing, China, 15–17 April 2020; pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X. Implicit generalized predictive control based on improved particle swarm optimization. Ind. Instrum. Autom. Devices 2020, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida, T.; Nishizaki, I.; Sekizaki, S.; Takamori, Y. Improvement of Two-swarm Cooperative Particle Swarm Optimization Using Immune Algorithms and Swarm Clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Applications (IWCIA), Hiroshima, Japan, 9–10 November 2019; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Liu, K. ADS-B Ground Station Site Selection Analysis Based on Intelligent Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology (ICCASIT), Weihai, China, 14–16 October 2020; pp. 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xiang, K.; Pang, M.; Zhanxia, Z. Multi-robot path planning using an improved self-adaptive particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420936154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Liu, L.; Wei, F.; Ge, H.; Feng, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Computational offloading Strategy based on Dynamic Particle Swarm for Multi-User Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Xiamen, China, 6–9 December 2019; pp. 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowska, B. Influence of Social Coefficient on Swarm Motion. In Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Proceedings of the ICAISC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Zakopane, Poland, 16–20 June 2019; Rutkowski, L., Scherer, R., Korytkowski, M., Pedrycz, W., Tadeusiewicz, R., Zurada, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11508. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R.C. A modified particle swarm optimizer. In Proceedings of the IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–9 May 1998; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, Z.W.; Sun, H. Improvement of Inertia Weight Declining Strategy Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computing Science (ICAICS 2019), HangZhou, China, 24–25 March 2019; Advanced Science and Technology Application Research Center: Hong Kong, China, 2019; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Peng, P.; Huang, X.; Xu, B. A Hybrid Multi-phased Particle Swarm Optimization with Sub Swarms. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE), Beijing, China, 23–25 October 2020; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, T.; Nishizaki, I.; Sekizaki, S.; Takamori, Y. Improvement of Particle Swarm Optimization Focusing on Diversity of the Particle Swarm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 11–14 October 2020; pp. 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, W.; Yan, S. Load frequency control based on multivariable constrained GPC. Control. Eng. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Liu, L. Denitration optimization research and application based on multivariable generalized predictive control algorithm. China Electr. Power 2019, 52, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, M. The swarm and the queen: Towards a deterministic and adaptive particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99, Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; pp. 1951–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J. Predictive control strategy of main steam temperature of thermal power generating units based on IGPC. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2021, 6, 36–43. [Google Scholar]






| Function Name | Function |
|---|---|
| F1 | |
| F2 | |
| F3 | |
| F4 | |
| F5 | |
| F6 |
| Function Name | Dimension | Maximum Position | Minimum Position | Optimal Value | Algorithm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | X | wPSO | X | wdPSO | X | SPPSO | X | |||||
| F1 | 80 | 100 | −100 | 0 | 2.60468 | 107 | 2.18797 | 85 | 37 | 31 | ||
| F2 | 80 | 10 | −10 | 0 | 12.8512 | 163 | 10.8976 | 79 | 86 | 64 | ||
| F3 | 80 | 100 | −100 | 0 | 0.53274 | 109 | 0.33094 | 89 | 87 | 61 | ||
| F4 | 80 | 5.12 | −5.12 | 0 | 14.4857 | 191 | 9.94959 | 51 | 35.26952 | 40 | 0 | 28 |
| F5 | 80 | 32 | −32 | 0 | 3.2367 | 138 | 2.50804 | 80 | 112 | 30 | ||
| F6 | 80 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 76.6912 | 143 | 68.1844 | 69 | 222.093 | 7 | 0 | 12 |
| Step | Content |
|---|---|
| Step 1 | Set the given value , initialize the parameters and storage variables, and calculate the prediction model Formula (11). |
| Step 2 | Use IGPC to solve the control increment , and judge whether SPPSO is used for optimization according to the constraint range. If the result is Yes, go to Step 3; if the result is No, go to Step 4. |
| Step 3 | Initialize the population, set Equation (15) as the fitness function for optimization. |
| Step 4 | Work out the system input according to equation (19), and then calculate the output . |
| Step 5 | Update the status storage sequence and repeat steps two through five until control is complete. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, J. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Entropy and Its Application in Implicit Generalized Predictive Control. Entropy 2022, 24, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010048
Zhang J, Zhai Y, Han Z, Lu J. Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Entropy and Its Application in Implicit Generalized Predictive Control. Entropy. 2022; 24(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinfang, Yuzhuo Zhai, Zhongya Han, and Jiahui Lu. 2022. "Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Entropy and Its Application in Implicit Generalized Predictive Control" Entropy 24, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010048
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhai, Y., Han, Z., & Lu, J. (2022). Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Based on Entropy and Its Application in Implicit Generalized Predictive Control. Entropy, 24(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010048






