Demonstration of Three True Random Number Generator Circuits Using Memristor Created Entropy and Commercial Off-the-Shelf Components
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrical Components and Measurements
2.2. Circuits Tested
2.3. Jiang’s TRNG
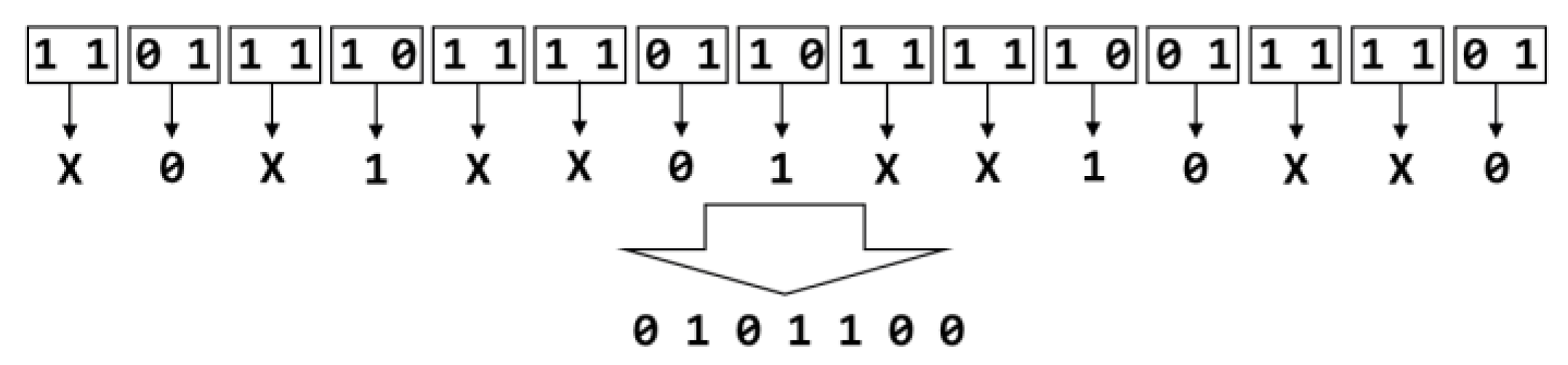
2.3.1. Jiang’s Circuit Operation
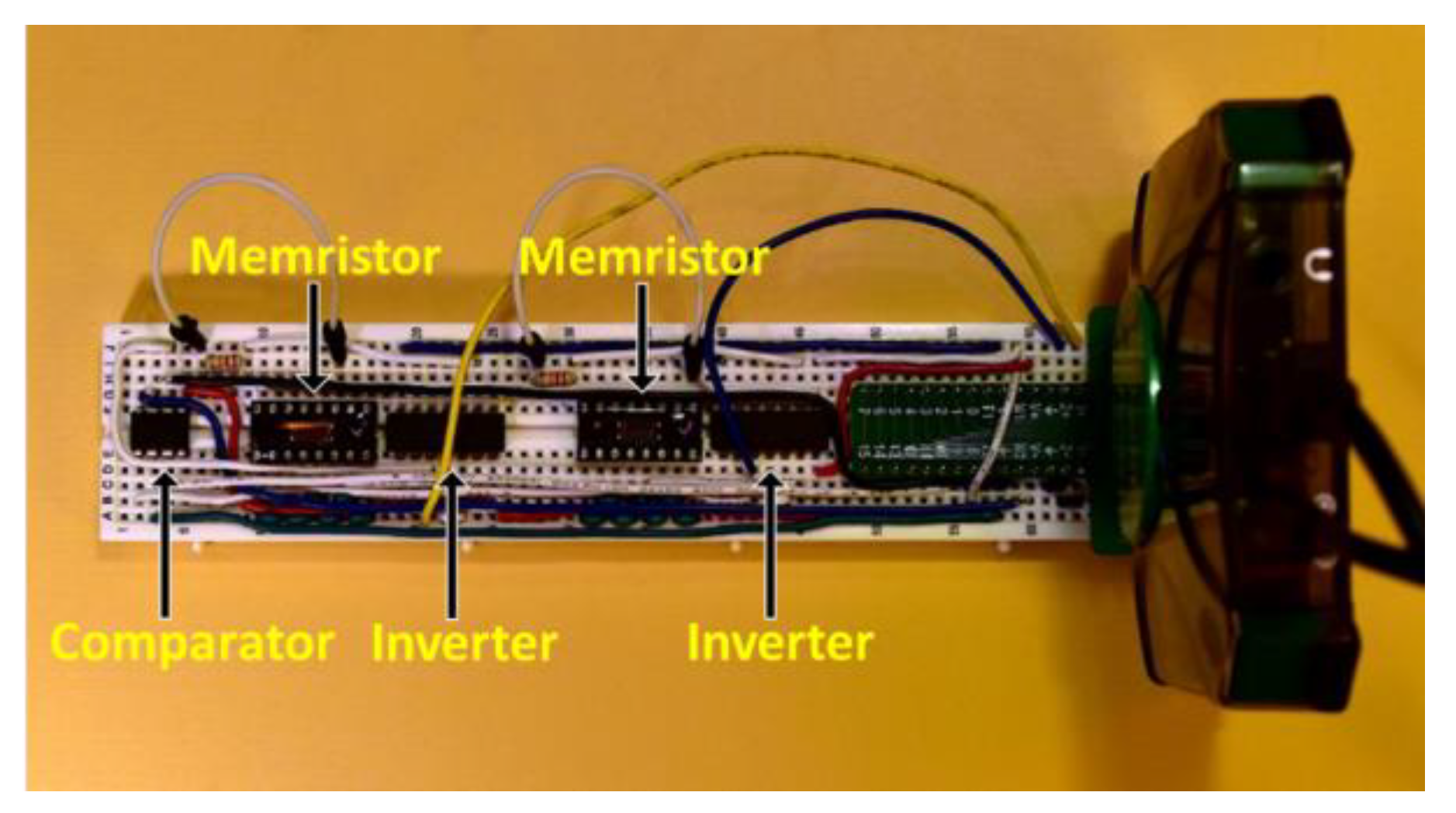
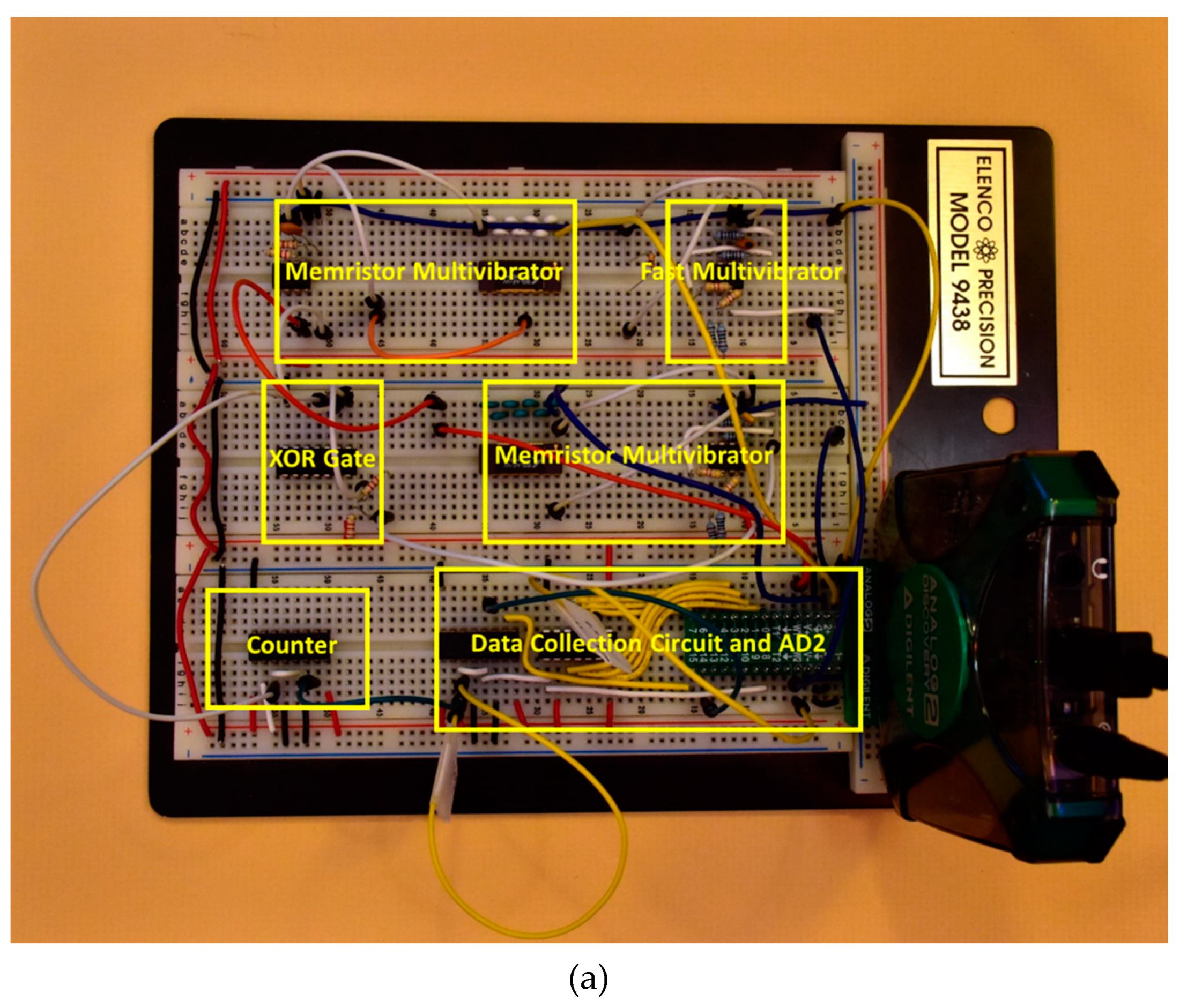
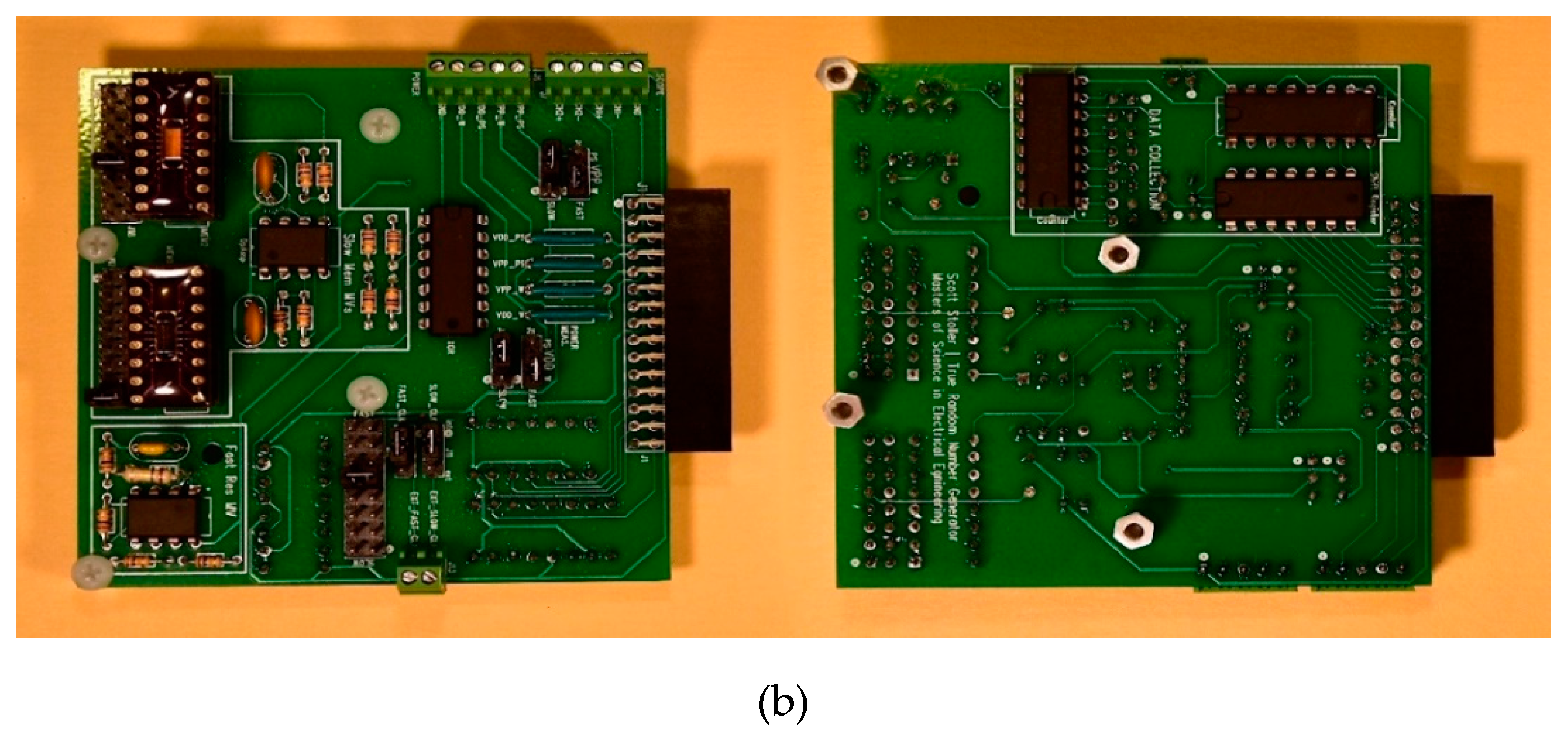
2.3.2. Breadboard Implementation and Measurements of Jiang’s Circuit
2.4. Rai’s TRNG
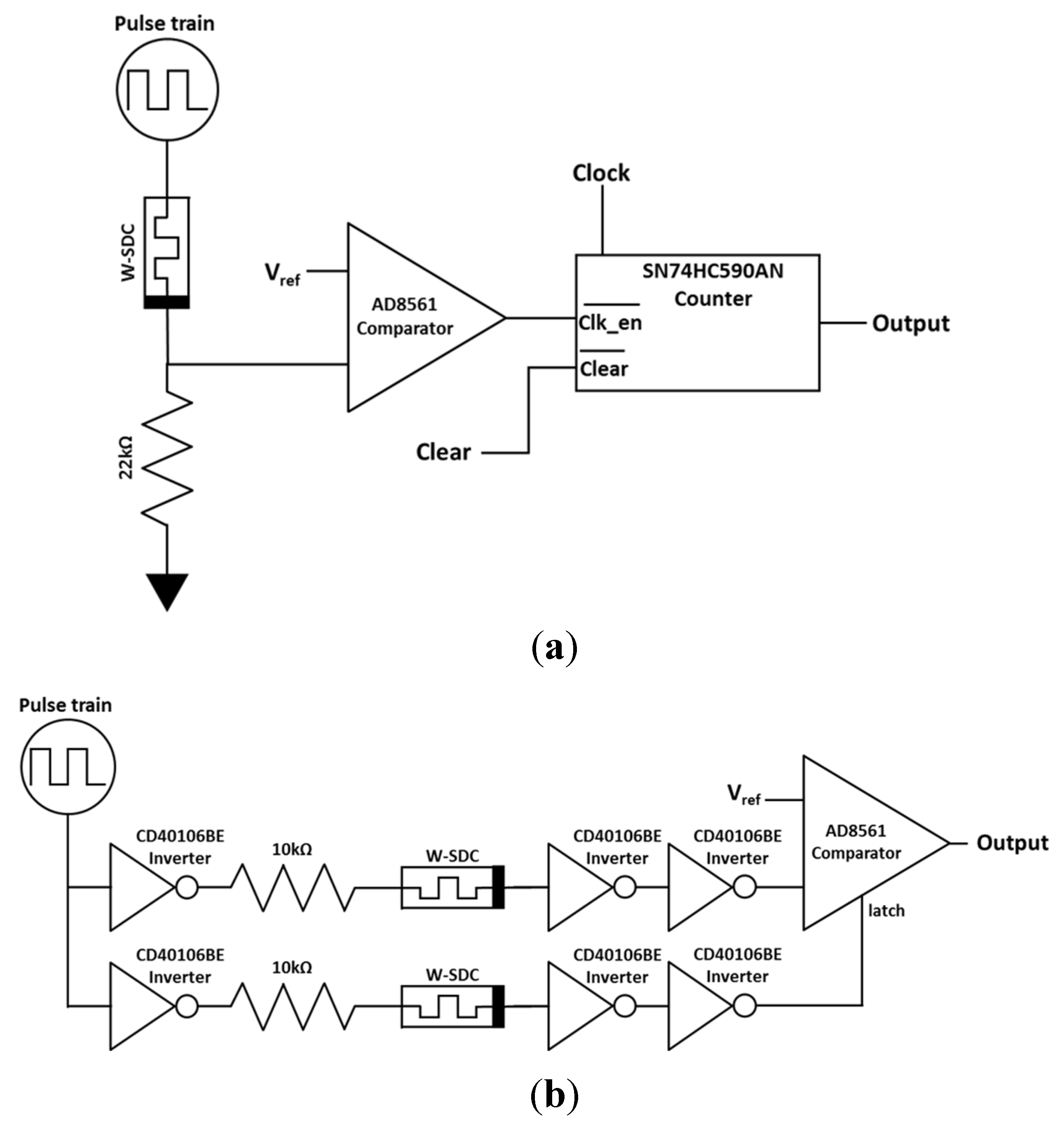
2.4.1. Rai’s Circuit Operation
2.4.2. Breadboard Implementation and Measurements of Rai’s Circuit
2.5. S-TRNG
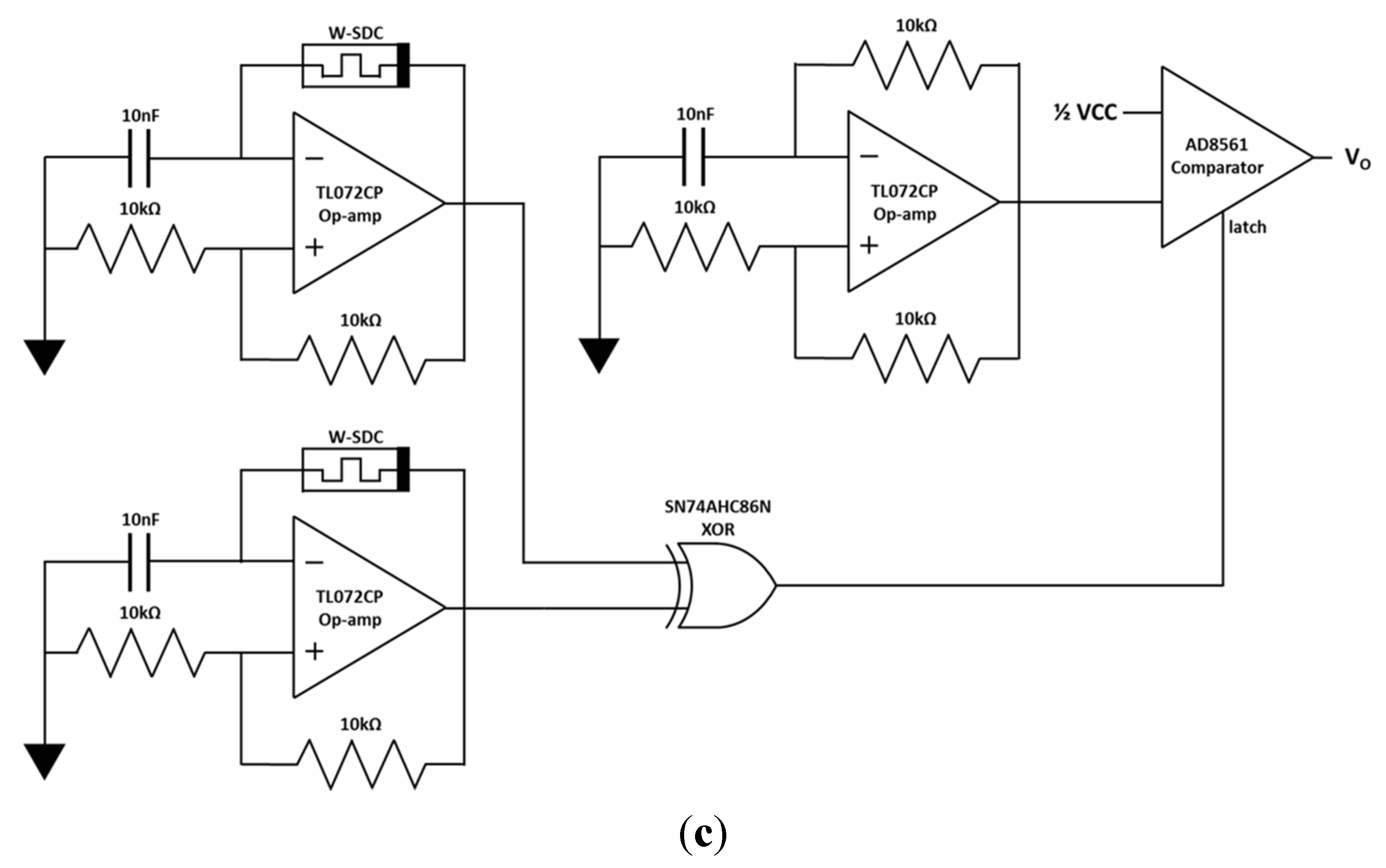
2.5.1. S-TRNG Circuit Operation
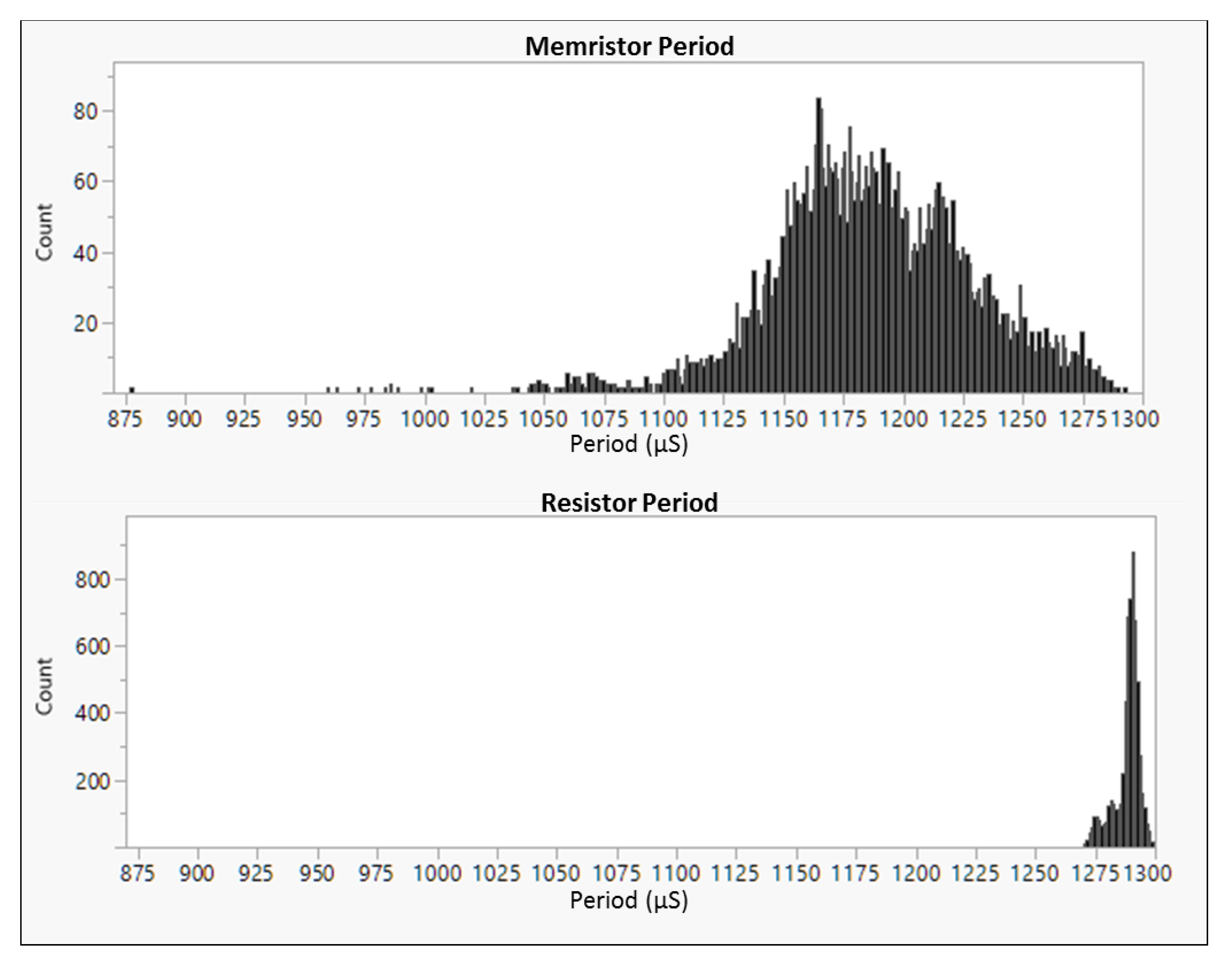
2.5.2. Breadboard Implementation and Measurements of S-TRNG Circuit
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Frequency (Monobits) Test
Appendix A.2. Frequency Test Within a Block
Appendix A.3. Runs Test
Appendix A.4. Longest Runs Test
Appendix A.5. Binary Matrix Rank Test
Appendix A.6. Discrete Fourier Transform (Spectral) Test
Appendix A.7. Non-Overlapping Template Matching Test
Appendix A.8. Overlapping Template Matching Test
Appendix A.9. Maurer’s “Universal Statistical” Test
Appendix A.10. Linear Complexity Test
Appendix A.11. Serial Test
Appendix A.12. Approximate Entropy Test
Appendix A.13. Cumulative Sums Test
Appendix A.14. Random Excursions Test
Appendix A.15. Random Excursions Variant Test
References
- Jiang, H.; Belkin, D.; Savel’ev, S.E.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Joshi, S.; Midya, R.; Li, C.; Rao, M.; et al. A novel true random number generator based on a stochastic diffusive memristor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Tripath, S.; Mathew, J. Memristor based random number generator: Architectures and evaluation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 125, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.; Germani, L.; Luzzi, R.; Trifiletti, A.; Varanonuovo, M. High-Speed Oscillator-Based Truly Random Number Source for Cryptographic Applications on a Smart Card IC. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2003, 52, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. Hardware Designs for Security in Ultra-Low-Power IoT Systems: An Overview and Survey. IEEE Micron. 2017, 37, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.A.N.; Loong, J.T.H.; Ghazali, A.; Hamid, F.A. Memristor based ring oscillators true random number generator with different window functions for applications in cryptography. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 14, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskiran, Z.G.C.; Taskiran, M.; Killioglu, M.; Kahraman, N.; Sedef, H. A novel memristive true random number generator design. Compel Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 39, 1931–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunar, B.; Martin, W.J.; Stinson, D.R. A Provably Secure True random number generator with built-in tolerance to active attacks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2007, 56, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattis, R.S.; Kavasseri, R.G.; Sai, V. Pseudorandom bit generation using coupled congruential generators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2010, 57, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Various techniques used in connection with random digits. In Monte Carlo Method; Householder, A.S., Forsythe, G.E., Germond, H.H., Eds.; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1951; Volume 12, pp. 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Generating Random Binary Data from Geiger Counters. Available online: http://www.ciphergoth.org/crypto/unbiasing/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Linux Random: Random(3)—Linux Man Page. Available online: https://linux.die.net/man/3/randon (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Linux Urandom: Urandom(4)—Linux Man Page. Available online: https://linux.die.net/man/4/urandom (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Rakitin, V.V.; Rusakov, S.G. Memristor Based Pulse Train Generator. Russ. Microelectron. 2019, 48, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, S. A Ring Oscillator Based Truly Random Number Generator. Master’s Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.P.; Koley, J.; Akgul, A.; Gurevin, B.; Roy, B.K. A new chaotic oscillator containing generalized memristor, single op-amp and RLC with chaos suppression and an application for the random number generation. Eur. Phys. J. 2019, 228, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A. Design and Analysis of Digital True Random Number Generator. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Intel® Digital Random Number Generator (DRNG) Software Implementation Guide. Available online: https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/articles/intel-digital-random-number-generator-drng-software-implementation-guide.html (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Campbell, K.A. Self-Directed channel memristor for high temperature operation. Microelectron. J. 2017, 59, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. The Fourth Element. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Tappertzhofen, S.; Choi, S.; Waser, R.; Valov, I.; Lu, W.D. Electrochemical Dynamics of Nanoscale Metallic Inclusions in Dielectrics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, J.; Karri, R.; Wendt, J.B.; Potkonjak, M.; McDonald, N.; Rose, G.S.; Wysocki, B. Nano meets security: Exploring nanoelectronic devices for security applications. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Garg, A.; Suri, M. True random number generation from commodity NVM chips. IEEE Trans. Elect. Dev. 2020, 67, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuka, C.S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Alkahtani, M. An innovative near-field communication security based on the chaos generated by memristive circuits adopted as symmetrical key. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 167975–167984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowm: W+SDC Memristor 8 Discrrete 16 DIP. Available online: https://knowm.com/collections/frontpage/products/m-sdc-memristor-8-discrete-16-dip (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Digikey Electronics. Available online: https://www.digikey.com/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Bassham, L.E.; Rukhin, A.L.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.R.; Smid, M.E.; Barker, E.B.; Leigh, S.D.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.L.; et al. A statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Special Publication 800-22, Revision 1a; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, ML, USA, 2010.
- Digilent AD2: USB Oscilloscope and Logic Analyzer. Available online: https://store.digilentinc.com/analog-discovery-2-100msps-usb-oscilloscope-logic-analyzer-and-variable-power-supply/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- NIST SP 800-22: Documentation and Software. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/Projects/Random-Bit-Generation/Documentation-and-Software (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Steward, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The Missing Memristor Found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| NIST STS Test | Jiang TRNG (from [1]) | Jiang TRNG | Rai TRNG (from [2]) | Rai TRNG | S-TRNG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 97% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 98% |
| Block Frequency | 99% | 99% | - | 100% | 98% |
| Cumulative Sums | 97% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 97% |
| Runs | 99% | 98% | 100% | 100% | 82% |
| Longest Run | 100% | 99% | - | 100% | 100% |
| Rank | 100% | 96% | - | 100% | 98% |
| FFT | 99% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 97% |
| Non Overlapping Template | 98% | 99% | - | 99% | 99% |
| Overlapping Template | 99% | 98% | - | 100% | 98% |
| Universal | 100% | 99% | - | 100% | 100% |
| Approximate Entropy | 99% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 94% |
| Random Excursions | 98% | 98% | - | 96% | 98% |
| Random Excursions Variant | 99% | 99% | - | 98% | 99% |
| Serial | 100% | 99% | - | 96% | 98% |
| Linear Complexity | 100% | 99% | - | 100% | 100% |
| Sequence Length | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 5000 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Sequences Tested | 76 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Debiasing applied | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Circuit Implementation | Hardware | Hardware | SPICE | Hardware | Hardware |
| Memristor Device | Ag:SiO2 | W-SDC | Model for TiO2 [28] | W-SDC | W-SDC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stoller, S.; Campbell, K.A. Demonstration of Three True Random Number Generator Circuits Using Memristor Created Entropy and Commercial Off-the-Shelf Components. Entropy 2021, 23, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030371
Stoller S, Campbell KA. Demonstration of Three True Random Number Generator Circuits Using Memristor Created Entropy and Commercial Off-the-Shelf Components. Entropy. 2021; 23(3):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030371
Chicago/Turabian StyleStoller, Scott, and Kristy A. Campbell. 2021. "Demonstration of Three True Random Number Generator Circuits Using Memristor Created Entropy and Commercial Off-the-Shelf Components" Entropy 23, no. 3: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030371
APA StyleStoller, S., & Campbell, K. A. (2021). Demonstration of Three True Random Number Generator Circuits Using Memristor Created Entropy and Commercial Off-the-Shelf Components. Entropy, 23(3), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030371







