Reservoir Computing with Delayed Input for Fast and Easy Optimisation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
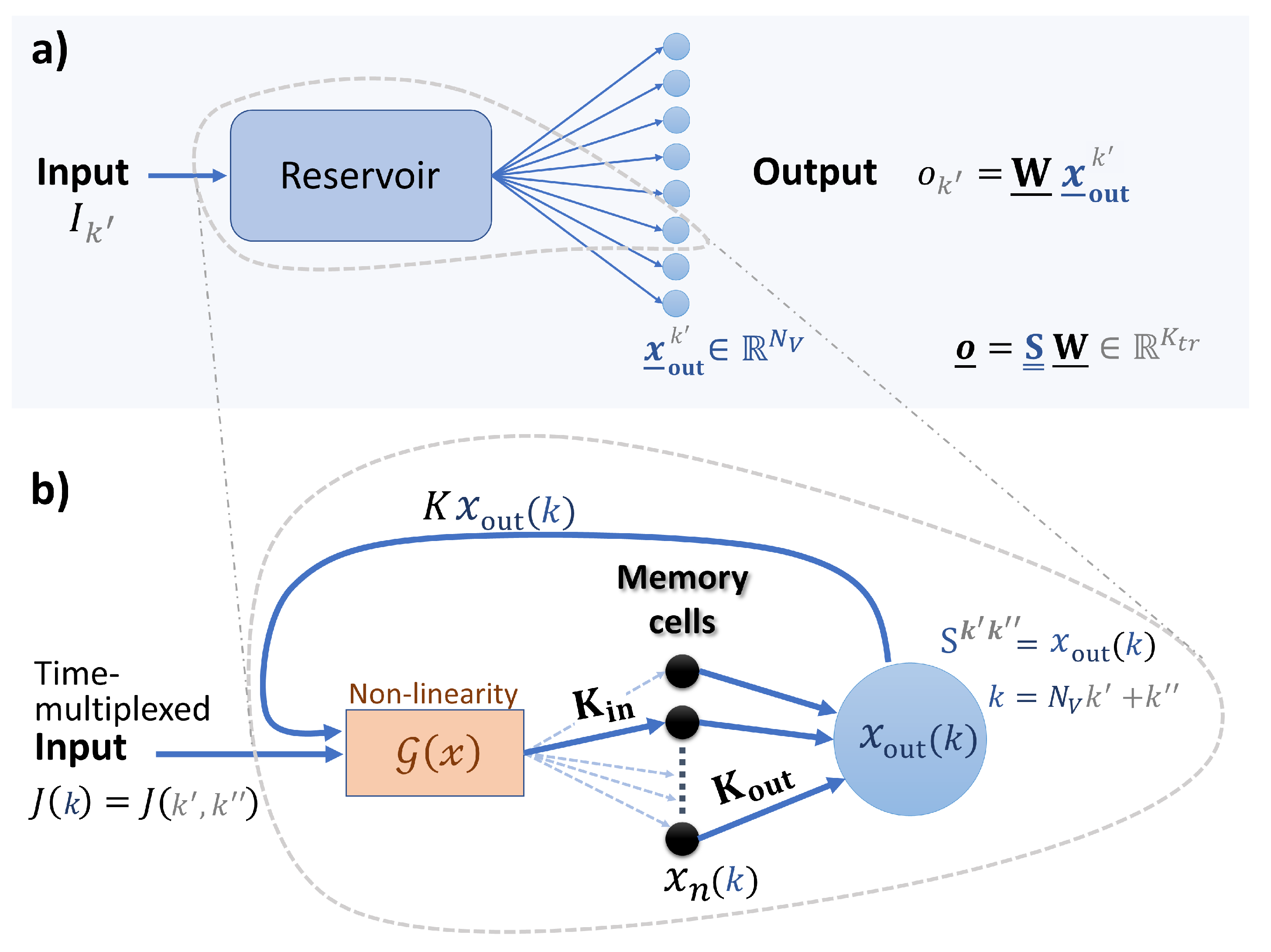
2.1. Reservoir Computing
Error Measure
2.2. Reservoir Model
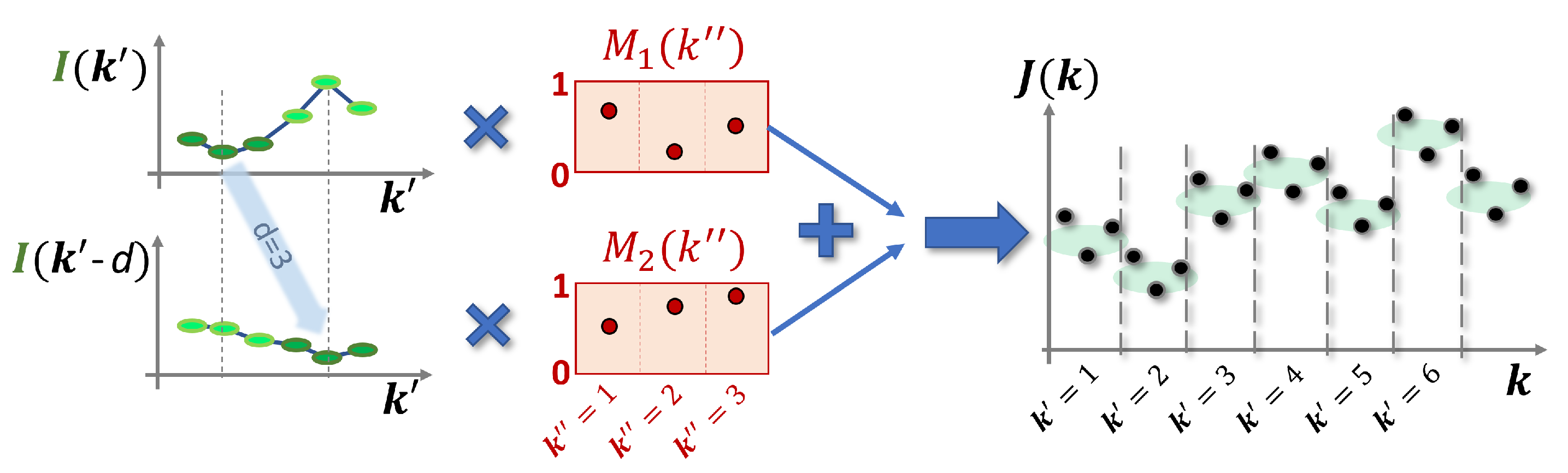
2.3. Input and Mask
2.4. Time Series Prediction Tasks
2.4.1. Mackey–Glass
2.4.2. NARMA10
2.4.3. Lorenz
2.5. Simulation Conditions
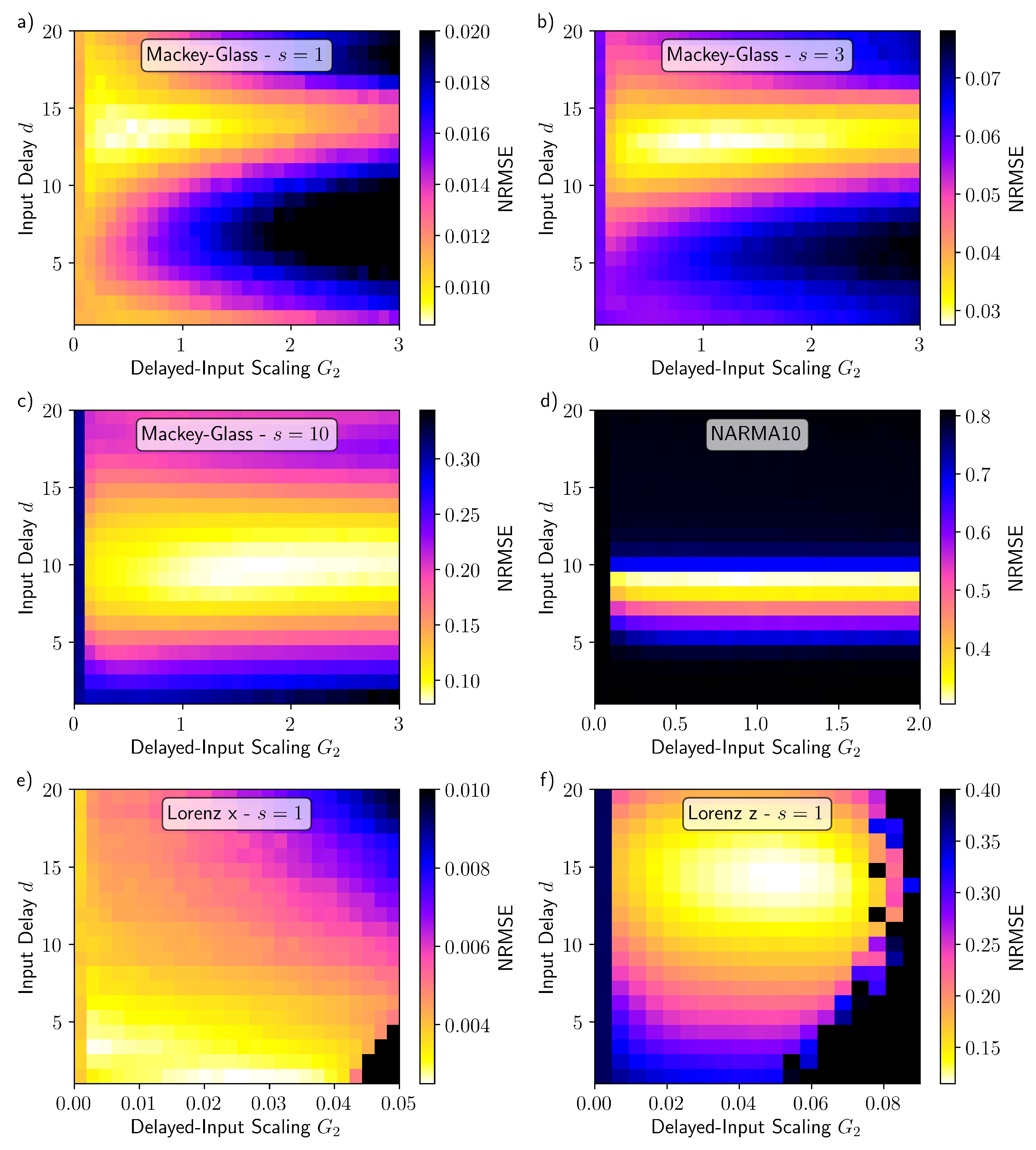
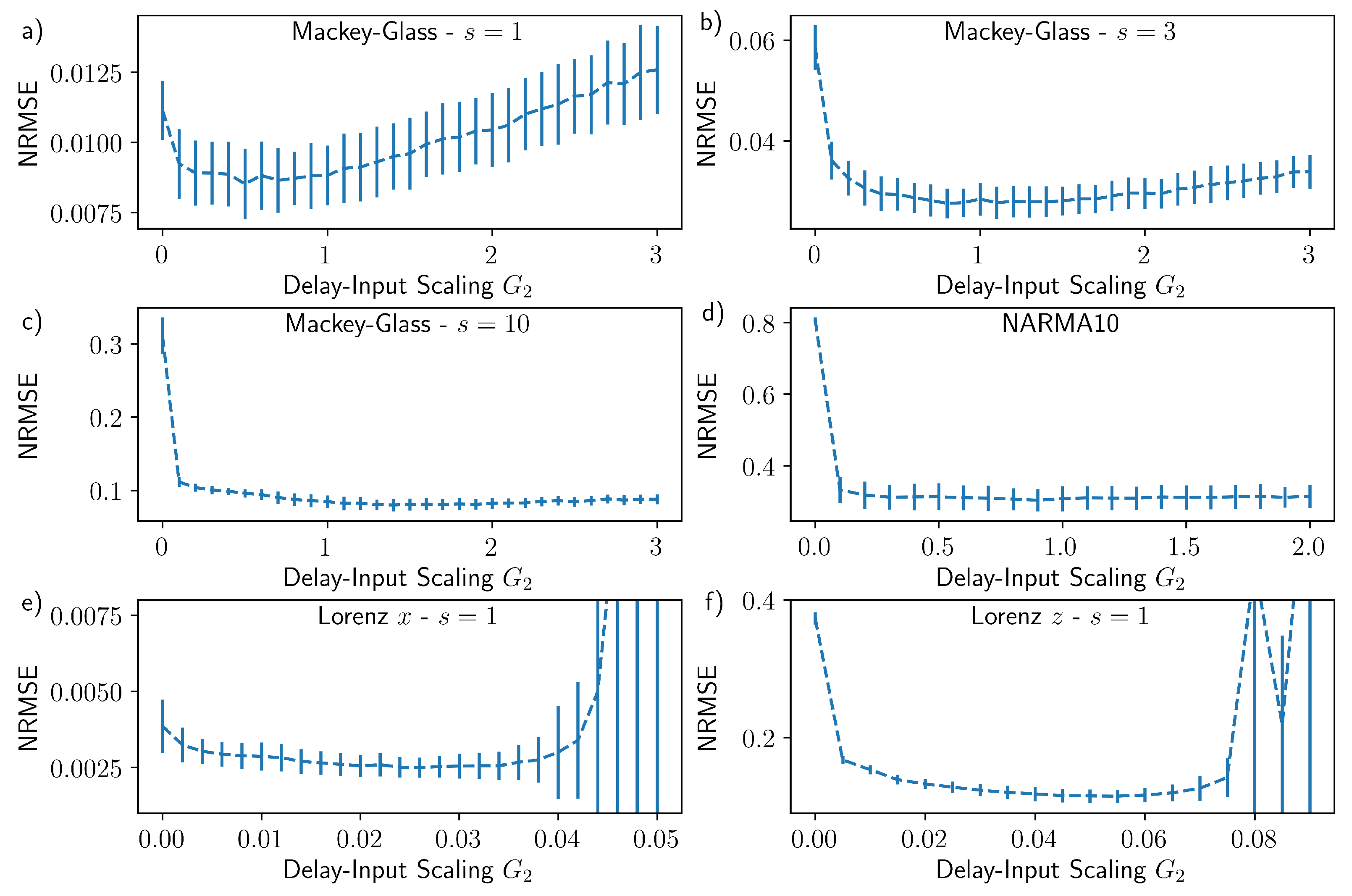
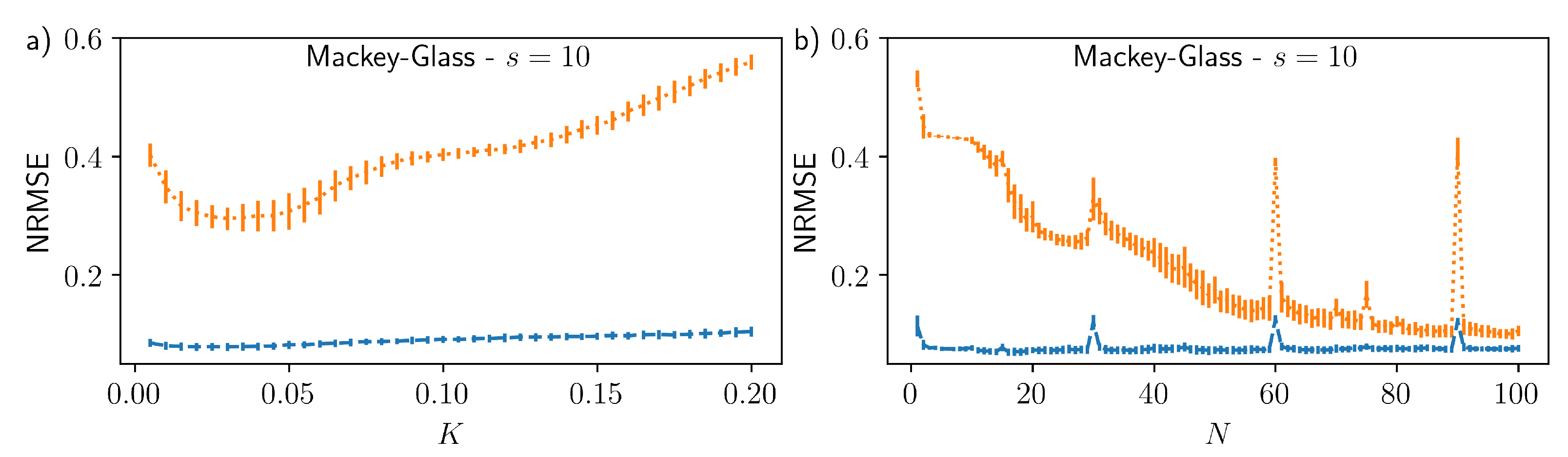
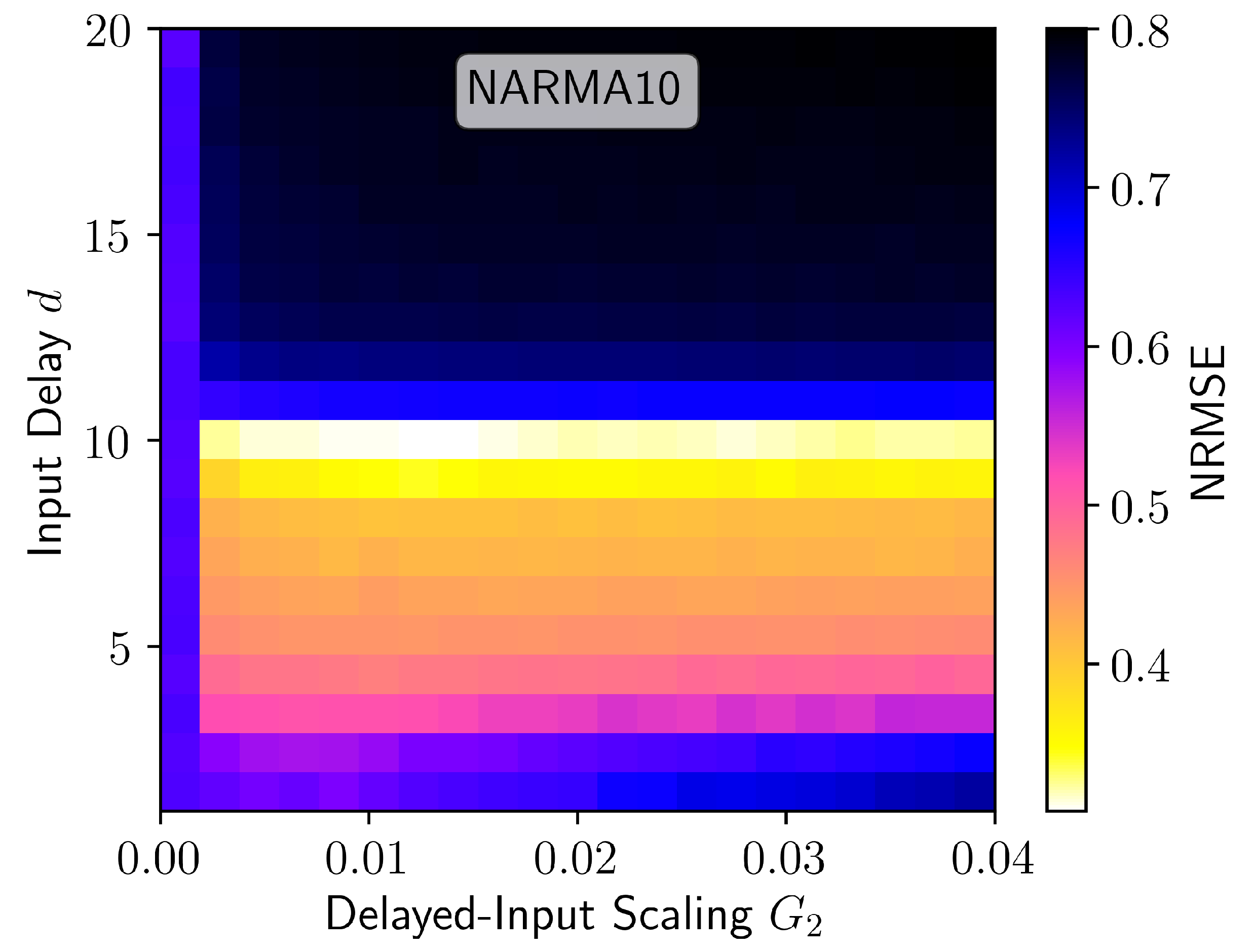
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RC | Reservoir computing |
| NVAR | Nonlinear vector autoregression |
| NRMSE | Normalised root mean squared error |
Appendix A. Optimised Input Parameters
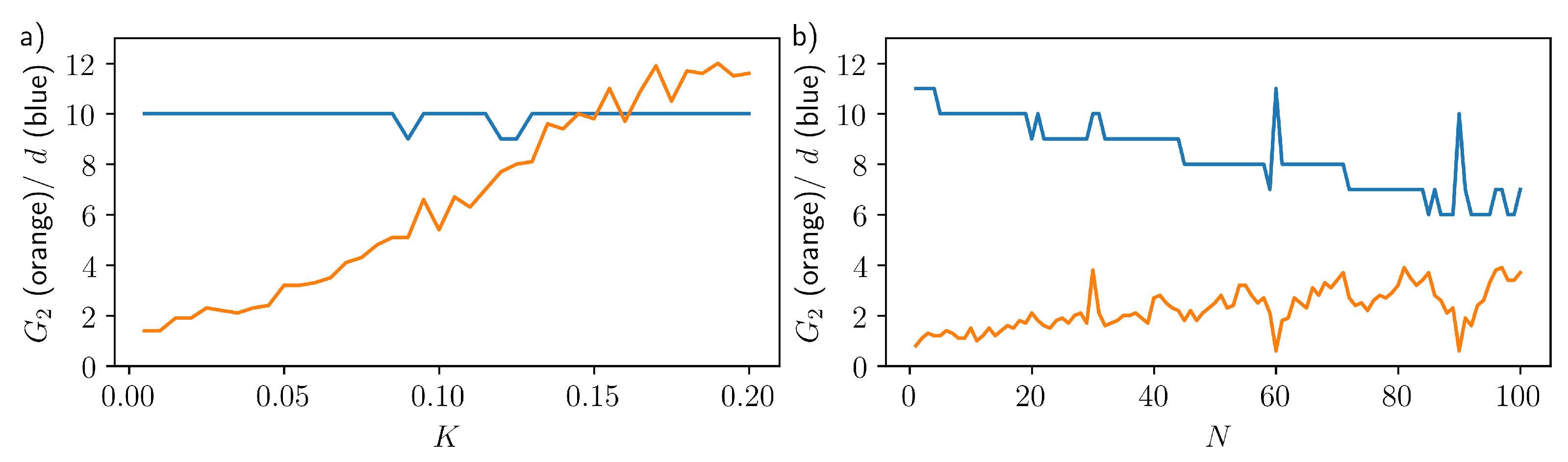
Appendix B. Stuart-Landau Delay-Based Reservoir Computer
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| −0.02 | 0 | ||
| −0.1 | K | 0.1 | |
| 105 | 0 | ||
| 30 | 1 × 10 | ||
| 0.01 | 0 | ||
| T | 80 |
References
- Nakajima, K.; Fischer, I. Reservoir Computing: Theory, Physical Implementations, and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, H. The ’Echo State’ Approach to Analysing and Training Recurrent Neural Networks; GMD Report 148; GMD—German National Research Institute for Computer Science: Darmstadt, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dutoit, X.; Schrauwen, B.; Van Campenhout, J.; Stroobandt, D.; Van Brussel, H.; Nuttin, M. Pruning and regularization in reservoir computing. Neurocomputing 2009, 72, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, A.; Tiňo, P. Minimum Complexity Echo State Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryeva, L.; Henriques, J.; Larger, L.; Ortega, J.P. Stochastic nonlinear time series forecasting using time-delay reservoir computers: Performance and universality. Neural Netw. 2014, 55, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguimdo, R.M.; Verschaffelt, G.; Danckaert, J.; Van der Sande, G. Simultaneous Computation of Two Independent Tasks Using Reservoir Computing Based on a Single Photonic Nonlinear Node With Optical Feedback. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, A.; Pomerance, A.; Gauthier, D.J. Forecasting chaotic systems with very low connectivity reservoir computers. Chaos 2019, 29, 123108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, T.L. Path length statistics in reservoir computers. Chaos 2020, 30, 083130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.Y.; Yang, W.H.; Sun, J.; Xiong, X.Y.; Li, Z.T.; Zou, X.D. Parameters optimization method for the time-delayed reservoir computing with a nonlinear duffing mechanical oscillator. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortín, S.; Pesquera, L. Reservoir Computing with an Ensemble of Time-Delay Reservoirs. Cogn. Comput. 2017, 9, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhm, A.; Lüdge, K. Multiplexed networks: Reservoir computing with virtual and real nodes. J. Phys. Commun. 2018, 2, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D. Photonic Reservoir Computing, Optical Recurrent Neural Networks; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, D.J.; Bollt, E.M.; Griffith, A.; Barbosa, W.A.S. Next generation reservoir computing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandoorne, K.; Dambre, J.; Verstraeten, D.; Schrauwen, B.; Bienstman, P. Parallel reservoir computing using optical amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duport, F.; Schneider, B.; Smerieri, A.; Haelterman, M.; Massar, S. All-optical reservoir computing. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 22783–22795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, G.; Yamane, T.; Héroux, J.B.; Nakane, R.; Kanazawa, N.; Takeda, S.; Numata, H.; Nakano, D.; Hirose, A. Recent advances in physical reservoir computing: A review. Neural Netw. 2019, 115, 100–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canaday, D.; Griffith, A.; Gauthier, D.J. Rapid time series prediction with a hardware-based reservoir computer. Chaos 2018, 28, 123119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkhoe, K.; Verschaffelt, G.; Katumba, A.; Bienstman, P.; Van der Sande, G. Demonstrating delay-based reservoir computing using a compact photonic integrated chip. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberger, M.; Sackesyn, S.; Ma, C.; Katumba, A.; Bienstman, P.; Dambre, J. Improving Time Series Recognition and Prediction With Networks and Ensembles of Passive Photonic Reservoirs. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2020, 26, 7700611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waibel, A.; Hanazawa, T.; Hinton, G.E.; Shikano, K.; Lang, K.J. Phoneme recognition using time-delay neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1989, 37, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Razavi, S.; Araghinejad, S. Long-lead seasonal rainfall forecasting using time-delay recurrent neural networks: A case study. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Han, M. An Adaptive Algorithm of Universal Learning Network for Time Delay System. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Neural Networks and Brain, Beijing, China, 13–15 October 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzini, S.M.; Da Ros, F.; Bülow, H.; Zibar, D. Tunable Optoelectronic Chromatic Dispersion Compensation Based on Machine Learning for Short-Reach Transmission. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardella, P.; Drzewietzki, L.; Krakowski, M.; Krestnikov, I.; Breuer, S. Mode locking in a tapered two-section quantum dot laser: Design and experiment. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2827–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, K.; Sugano, C.; Inubushi, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Sunada, S.; Kanno, K.; Uchida, A. Compact reservoir computing with a photonic integrated circuit. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 29424–29439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appeltant, L.; Soriano, M.C.; Van der Sande, G.; Danckaert, J.; Massar, S.; Dambre, J.; Schrauwen, B.; Mirasso, C.R.; Fischer, I. Information processing using a single dynamical node as complex system. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paquot, Y.; Duport, F.; Smerieri, A.; Dambre, J.; Schrauwen, B.; Haelterman, M.; Massar, S. Optoelectronic Reservoir Computing. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, D.; Penkovsky, B.; Marquez, B.A.; Jacquot, M.; Fischer, I.; Larger, L. Tutorial: Photonic neural networks in delay systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 152004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, D.; Soriano, M.C.; Mirasso, C.R.; Fischer, I. Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolters, J.; Buser, G.; Horsley, A.; Béguin, L.; Jöckel, A.; Jahn, J.P.; Warburton, R.J.; Treutlein, P. Simple Atomic Quantum Memory Suitable for Semiconductor Quantum Dot Single Photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 060502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Pu, Y.F.; Chang, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Duan, L.M. Experimental realization of 105-qubit random access quantum memory. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, O.; Firstenberg, O. Light storage for one second in room-temperature alkali vapor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arecchi, F.T.; Giacomelli, G.; Lapucci, A.; Meucci, R. Two-dimensional representation of a delayed dynamical system. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, R4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajnulina, M.; Lingnau, B.; Lüdge, K. Four-wave Mixing in Quantum Dot Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers: A Detailed Analysis of the Nonlinear Effects. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 3000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingnau, B.; Lüdge, K. Quantum-Dot Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers. In Handbook of Optoelectronic Device Modeling and Simulation; Series in Optics and Optoelectronics; Piprek, J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 1, Chapter 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, M.C.; Glass, L. Oscillation and chaos in physiological control systems. Science 1977, 197, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiya, A.F.; Parlos, A.G. New results on recurrent network training: Unifying the algorithms and accelerating convergence. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldmann, M.; Mirasso, C.R.; Fischer, I.; Soriano, M.C. Exploiting transient dynamics of a time-multiplexed reservoir to boost the system performance. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortín, S.; Soriano, M.C.; Pesquera, L.; Brunner, D.; San-Martín, D.; Fischer, I.; Mirasso, C.R.; Gutierrez, J.M. A Unified Framework for Reservoir Computing and Extreme Learning Machines based on a Single Time-delayed Neuron. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Köster, F.; Yanchuk, S.; Lüdge, K. Insight into delay based reservoir computing via eigenvalue analysis. J. Phys. Photonics 2021, 3, 024011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, F.; Ehlert, D.; Lüdge, K. Limitations of the recall capabilities in delay based reservoir computing systems. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhm, A.; Jaurigue, L.C.; Lüdge, K. Reservoir Computing Using Laser Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 26, 7700108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manneschi, L.; Ellis, M.O.A.; Gigante, G.; Lin, A.C.; Del Giudice, P.; Vasilaki, E. Exploiting Multiple Timescales in Hierarchical Echo State Networks. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, F.; Röhm, A.; Lüdge, K.; Yanchuk, S. Performance boost of time-delay reservoir computing by non-resonant clock cycle. Neural Netw. 2020, 124, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooteboom, P.D.; Feng, Q.Y.; López, C.; Hernández-García, E.; Dijkstra, H.A. Using network theory and machine learning to predict El Niño. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2018, 9, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 1 | ||
| K | 0.02 | N | 31 |
| 30 | 5 × 10 | ||
| (Mackey–Glass) | 1 | (Mackey–Glass) | 0 |
| (Lorenz) | 0.03 | (Lorenz) | 0.85 |
| (NARMA10) | 1.8 | (NARMA10) | 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaurigue, L.; Robertson, E.; Wolters, J.; Lüdge, K. Reservoir Computing with Delayed Input for Fast and Easy Optimisation. Entropy 2021, 23, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121560
Jaurigue L, Robertson E, Wolters J, Lüdge K. Reservoir Computing with Delayed Input for Fast and Easy Optimisation. Entropy. 2021; 23(12):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121560
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaurigue, Lina, Elizabeth Robertson, Janik Wolters, and Kathy Lüdge. 2021. "Reservoir Computing with Delayed Input for Fast and Easy Optimisation" Entropy 23, no. 12: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121560
APA StyleJaurigue, L., Robertson, E., Wolters, J., & Lüdge, K. (2021). Reservoir Computing with Delayed Input for Fast and Easy Optimisation. Entropy, 23(12), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121560






