A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient and Permutation Entropy for Ship-Radiated Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2. Permutation Entropy
2.3. Reverse Weighted Permutation Entropy
2.4. Maximal Information Coefficient and Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient
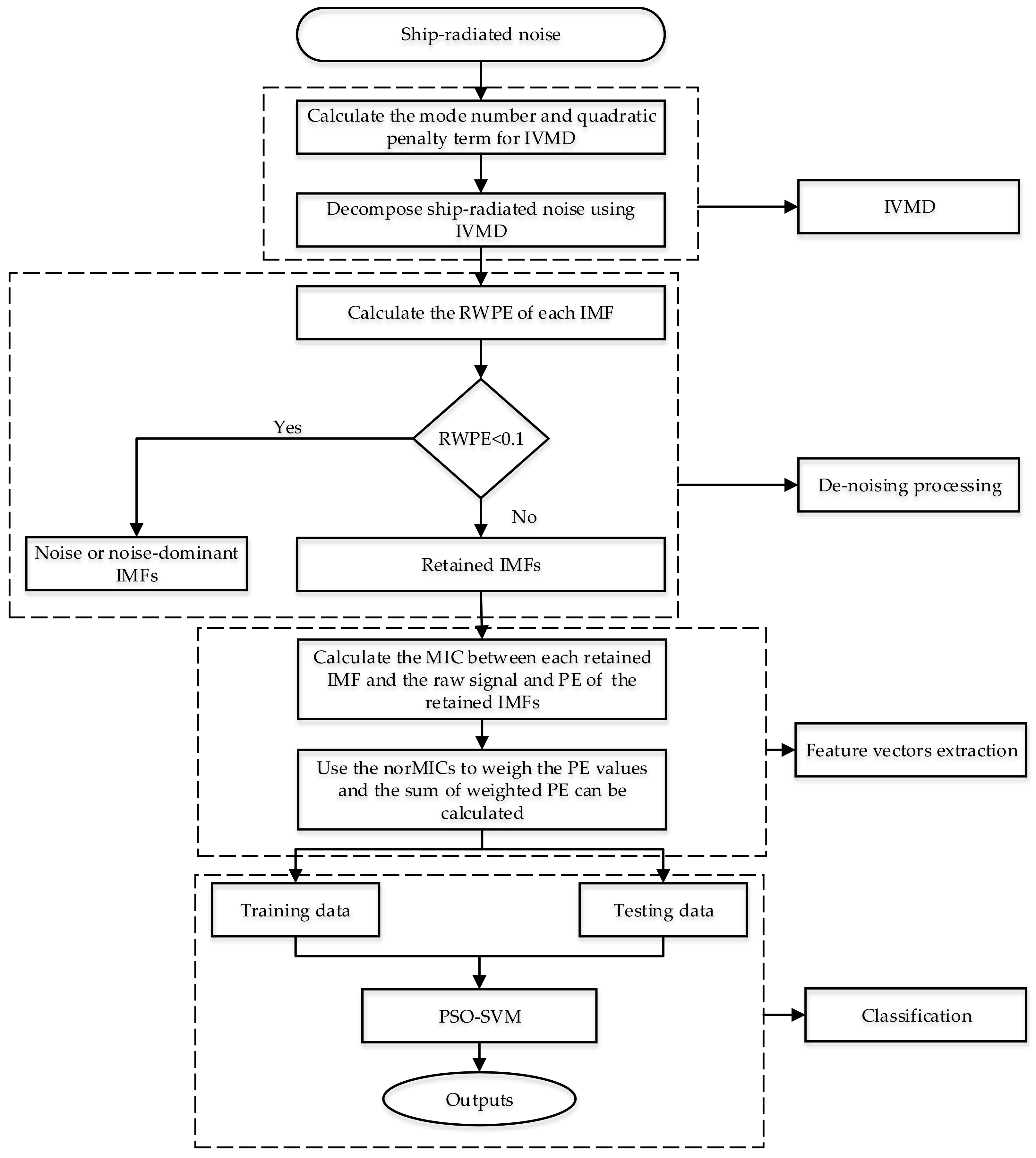
3. The Proposed Feature Extraction Method for Ship-Radiated Noise
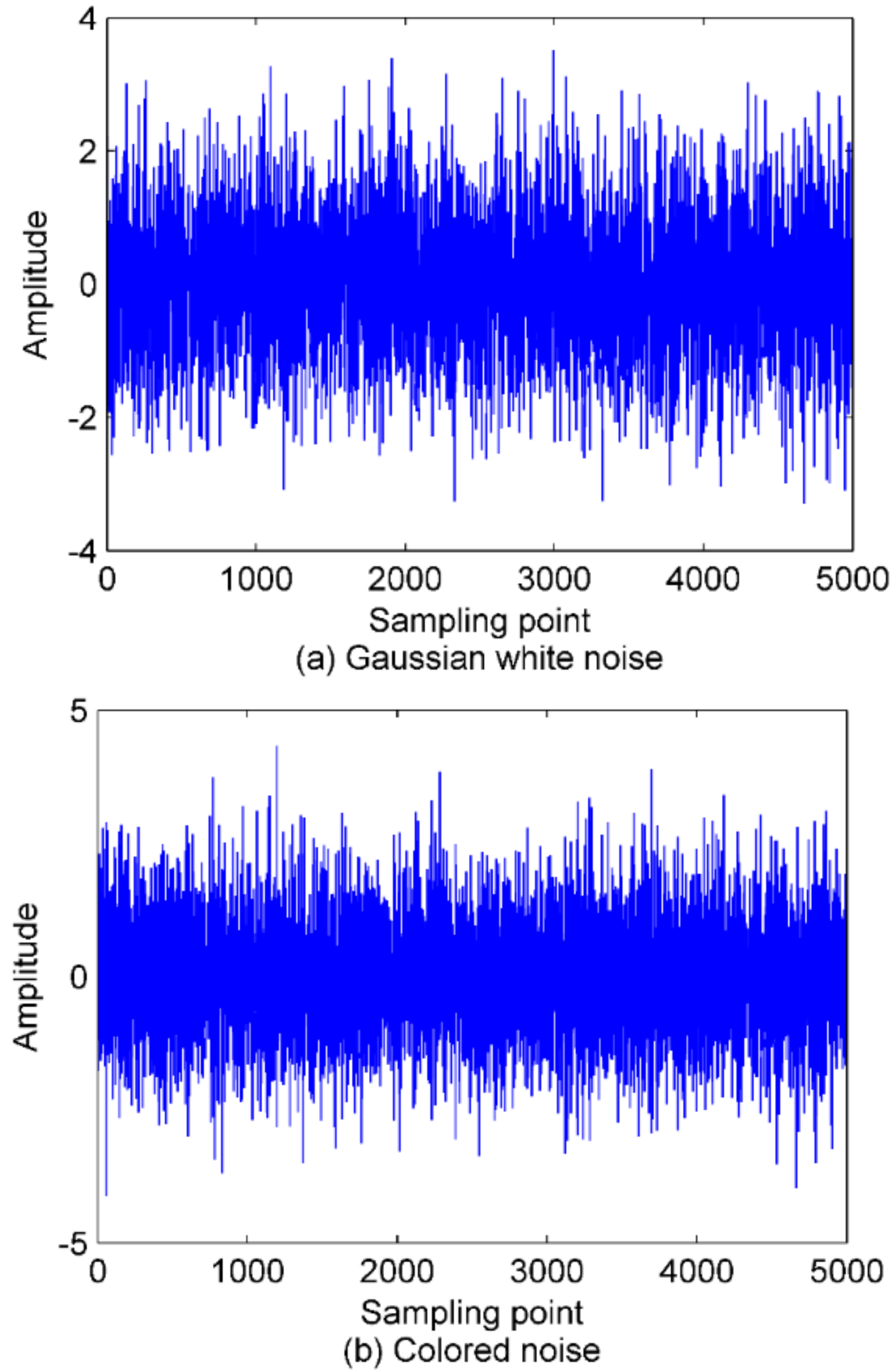
4. Simulation Signals Analysis
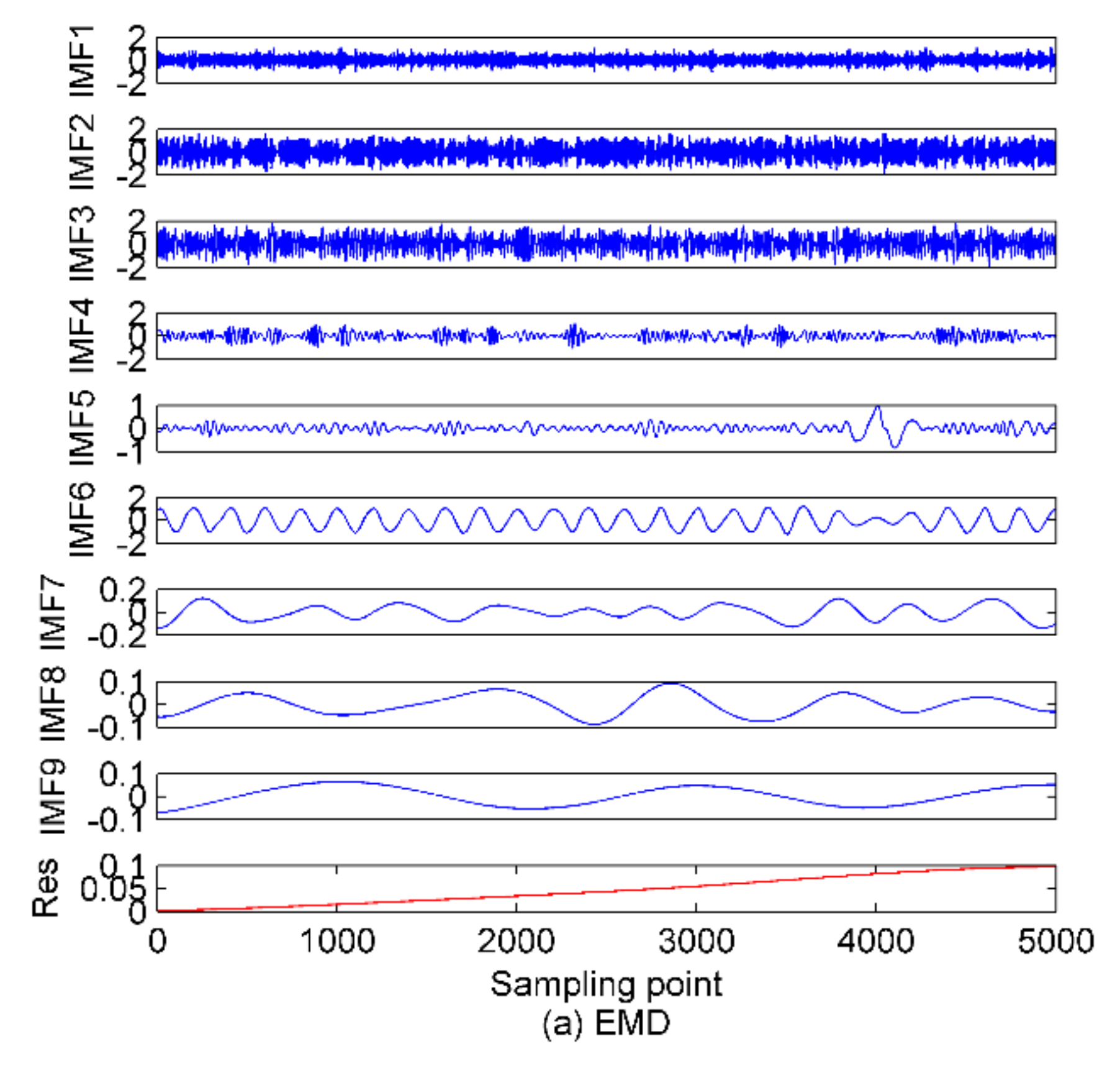
4.1. IVMD of Simulation Signals
4.2. Denoising of Simulation Signals
4.3. Analysis of PE Properties
5. Feature Extraction of SRN Signals Based on IVMD-norMIC-PE
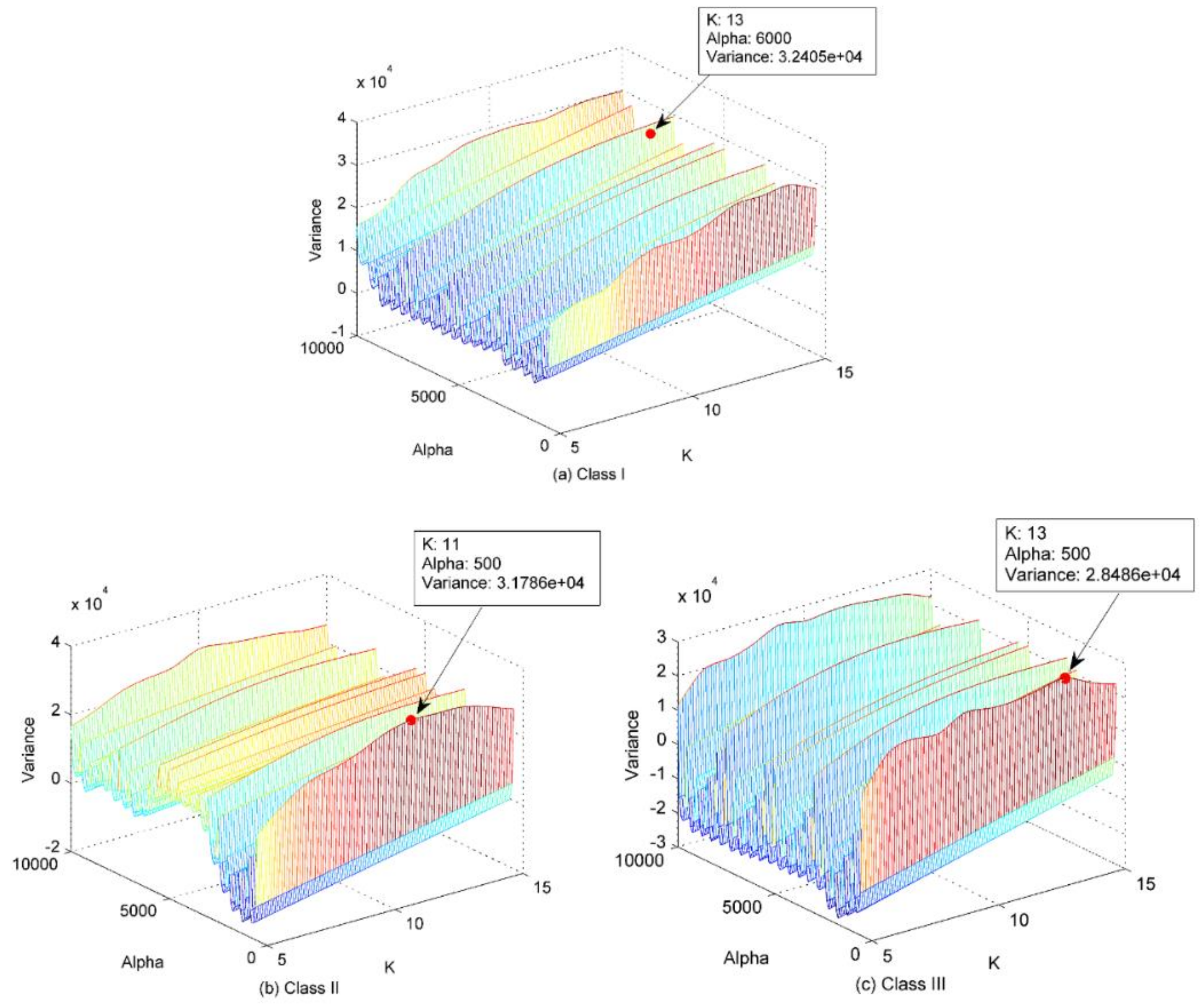
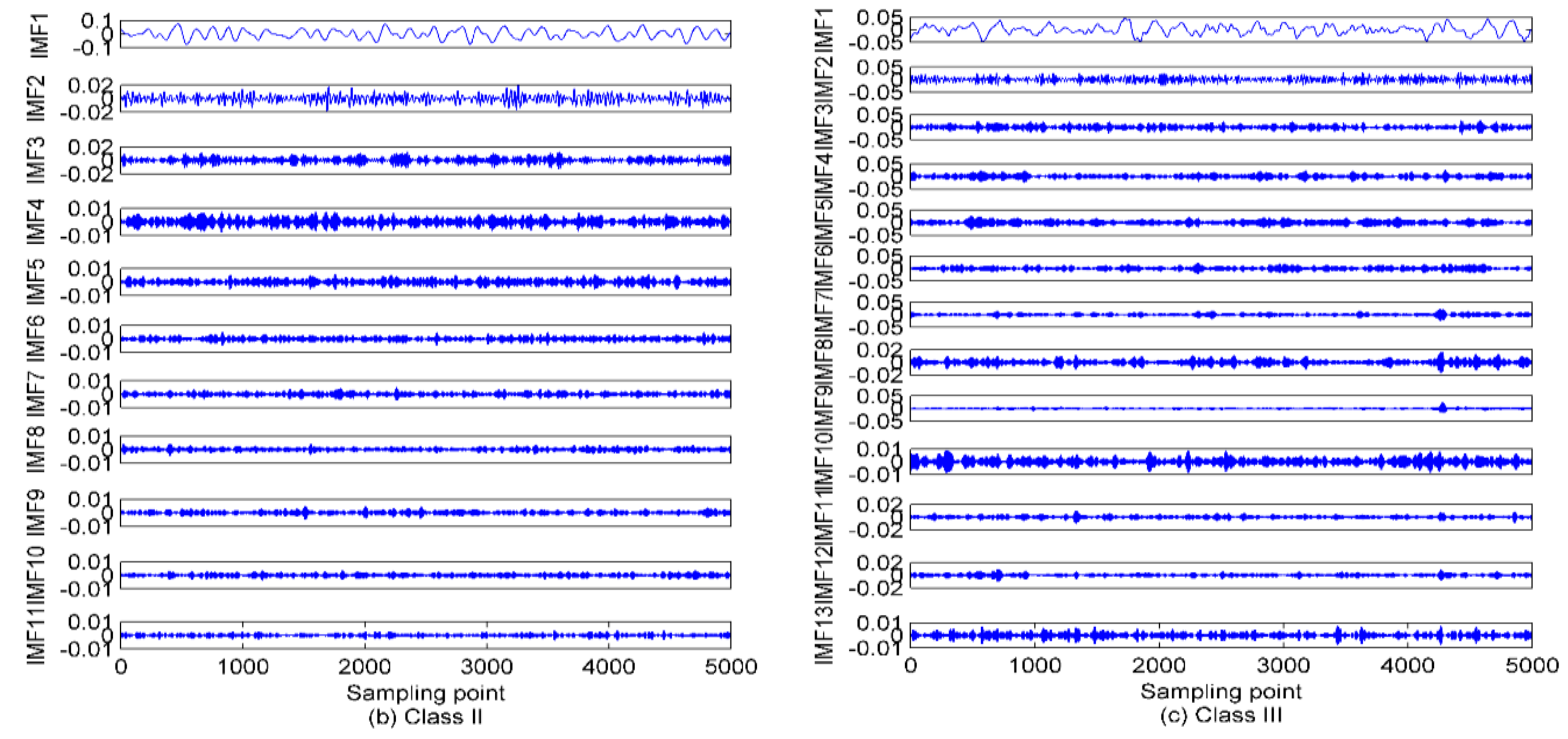
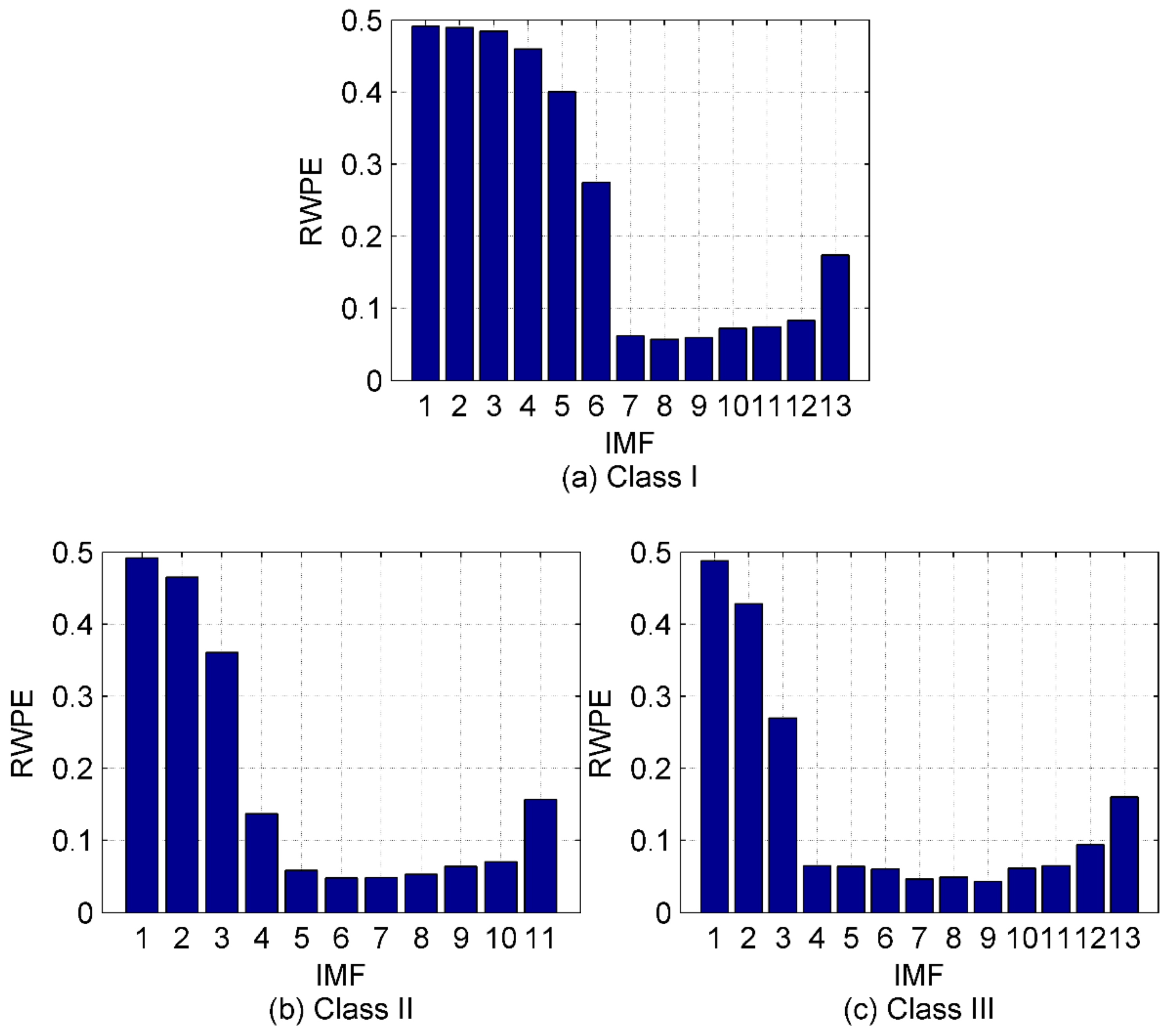
5.1. IVMD of SRN Signals
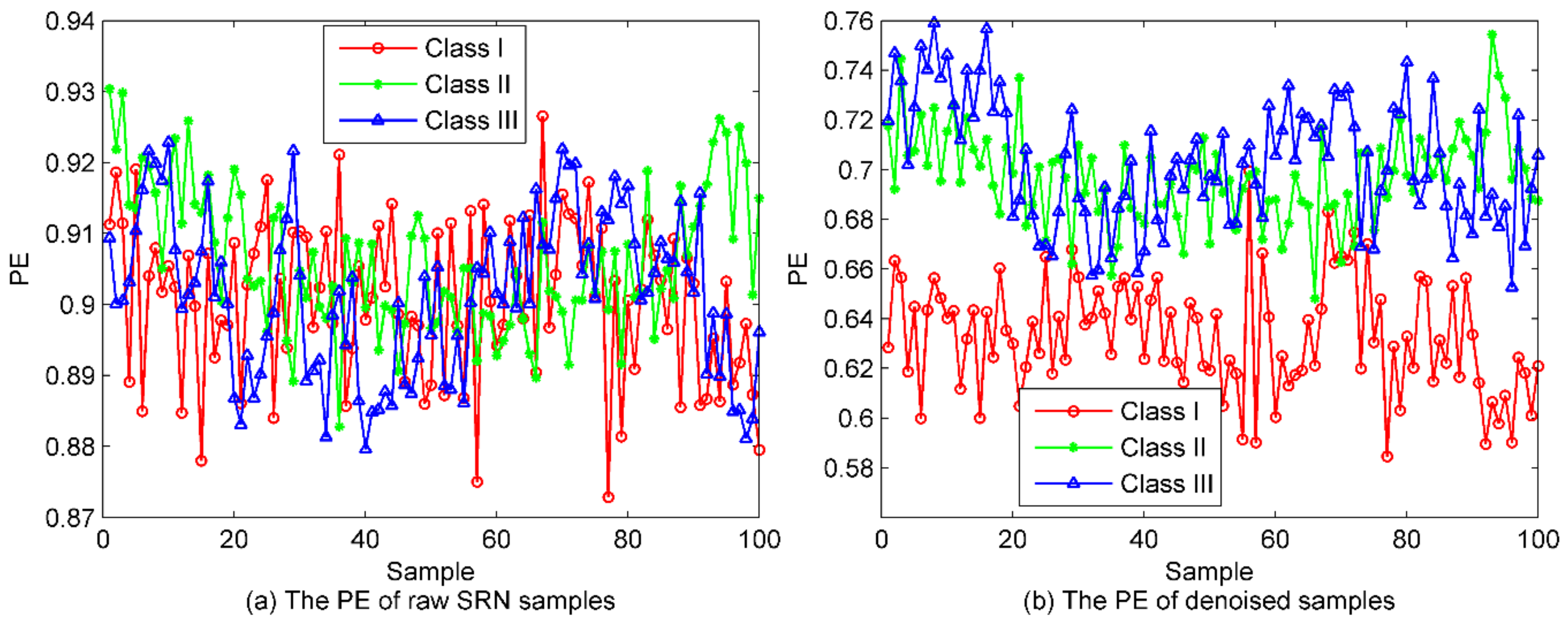
5.2. Denoising of SRN Signals
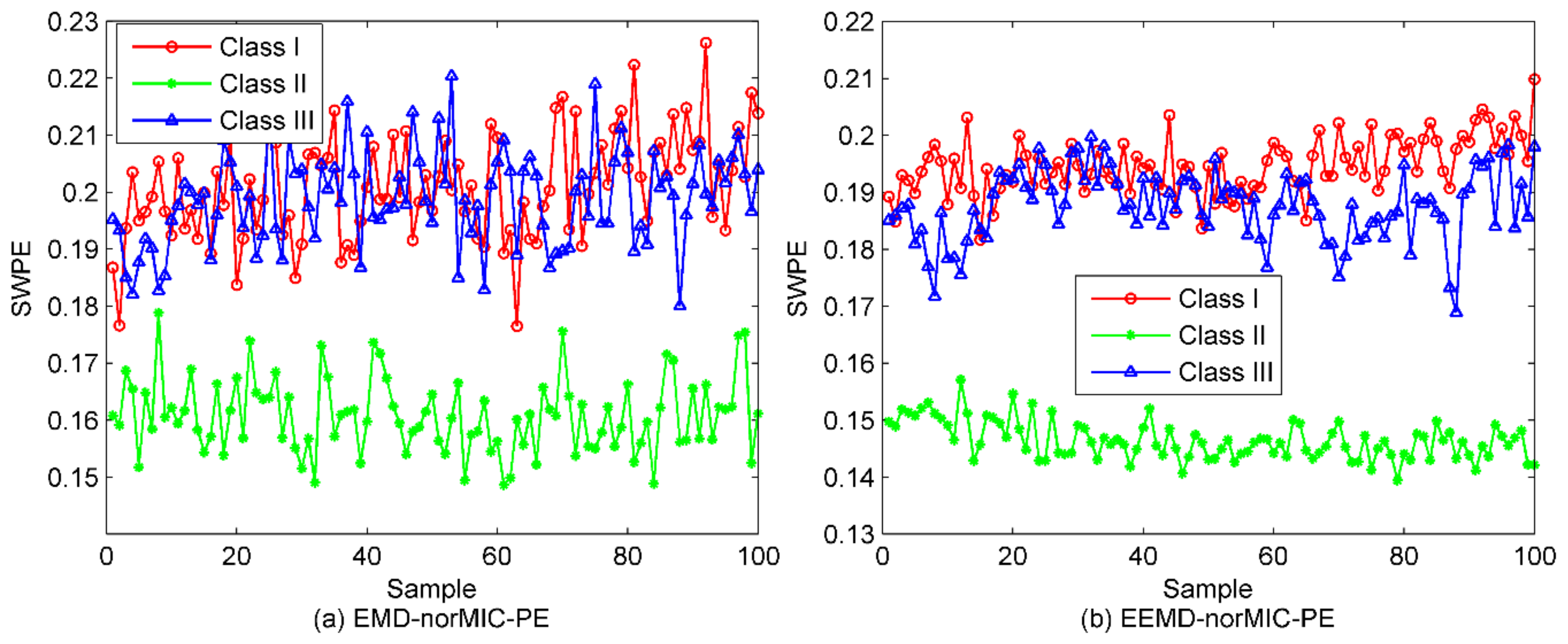
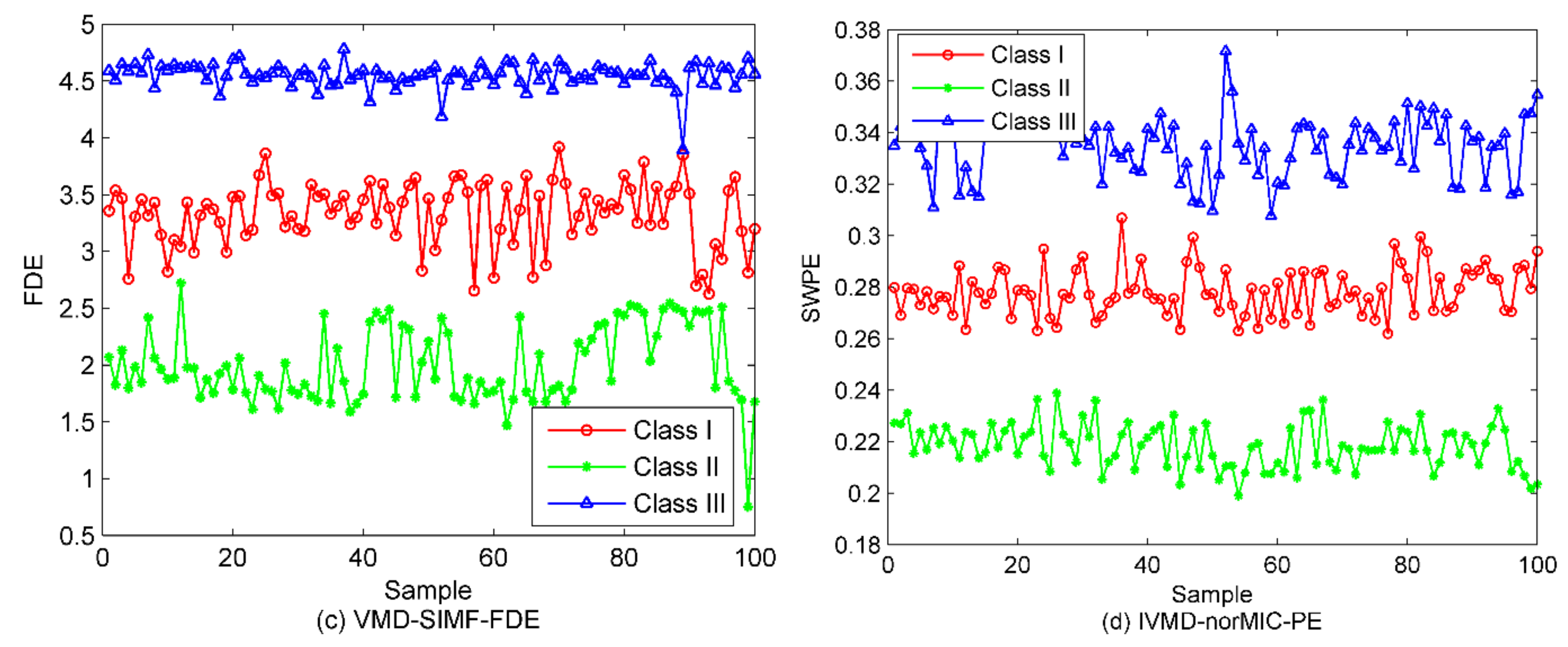
5.3. Classification of SRN Samples
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merchant, N.D.; Pirotta, E.; Barton, T.R.; Thompson, P.M. Monitoring ship noise to assess the impact of coastal developments on marine mammals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 78, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredianelli, L.; Nastasi, M.; Bernardini, M.; Fidecaro, F.; Licitra, G. Pass-by Characterization of Noise Emitted by Different Categories of Seagoing Ships in Ports. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Intrinsic Time-Scale Decomposition and a Statistical Complexity Measure. Entropy 2019, 21, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. A novel feature extraction method for ship-radiated noise based on variational mode decomposition and multi-scale permutation entropy. Entropy 2017, 19, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Roul, S.; Kumar, C.; Das, A. Ambient noise estimation in territorial waters using AIS data. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 148, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. Feature extraction of ship-radiated noise based on regenerated phase-shifted sinusoid-assisted EMD, mutual information, and differential symbolic entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracewell, R.N. The Fourier Transform and Its Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Durak, L.; Arikan, O. Short-time Fourier transform: Two fundamental properties and an optimal implementation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Wavelet Transforms. In Encyclopedia of Imaging Science and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. An improved wavelet transform using singular spectrum analysis for wind speed forecasting based on elman neural network. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Du, S. Ship classification using nonlinear features of radiated sound: An approach based on empirical mode decomposition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Ship recognition via its radiated sound: The fractal based approaches. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.S.; Lake, D.E.; Moorman, R.J. Sample entropy. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 384, pp. 172–184. [Google Scholar]
- Christoph, B.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Physical Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar]
- Redelico, F.O.; Traversaro, F.; García, M.D.; Silva, W.; Rosso, O.A.; Risk, M. Classification of normal and pre-ictal eeg signals using permutation entropies and a generalized linear model as a classifier. Entropy 2017, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.M. Credit market Jitters in the course of the financial crisis: A permutation entropy approach in measuring informational efficiency in financial assets. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 499, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Self-adaptive bearing fault diagnosis based on permutation entropy and manifold-based dynamic time warping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 114, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Esmaiel, H.; Sun, H.; Qi, J.; Qasem, Z.A. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2020, 22, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, B.; Chen, B.; Keil, A.; Príncipe, J. Weighted-permutation entropy: A complexity measure for time series incorporating amplitude information. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 022911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Shang, P. Weighted permutation entropy based on different symbolic approaches for financial time series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 443, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Qian, S.; Chang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, Y. A novel bearing multi-fault diagnosis approach based on weighted permutation entropy and an improved SVM ensemble classifier. Sensors 2018, 18, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Cai, L.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Multivariate multi-scale weighted permutation entropy analysis of EEG complexity for Alzheimer’s disease. Cognit. Neurodyn. 2017, 11, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, B. A new kind of permutation entropy used to classify sleep stages from invisible EEG microstructure. Entropy 2017, 19, 197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Reverse Weighted-Permutation Entropy: A Novel Complexity Metric Incorporating Distance and Amplitude Information. Multidiscip. Dig. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2019, 46, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.R.; Shieh, J.S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Zosso, Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Woo, W.L.; Dlay, S.S. Single-Channel Source Separation Using EMD-Subband Variable Regularized Sparse Features. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, G. A new ship-radiated noise feature extraction technique based on variational mode decomposition and fluctuation-based dispersion entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, R.; Ali, W.; Yu, J.; Liang, H. A New Feature Extraction Method for Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Improved CEEMDAN, Normalized Mutual Information and Multiscale Improved Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. A Denoising Method of Ship Radiated Noise Signal Based on Modified CEEMDAN, Dispersion Entropy, and Interval Thresholding. Electronics 2019, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. Denoising and feature extraction algorithms using NPE combined with VMD and their applications in ship-radiated noise. Symmetry 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Domínguez, D.; Torres-Guijarro, S.; Cardenal-López, A.; Pena-Gimenez, A. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIBSVM -- A Library for Support Vector Machines. Available online: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/ (accessed on 1 May 2020).








| Methods | Center Frequency/Hz | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVMD | 5.09 | 50.02 | 100.02 | 184.55 | 246.22 | 307.54 | 364.42 | 417.07 | 471.72 |
| EMD | EEMD | IVMD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | IMF6: 0.9156 | IMF7: 0.9769 | IMF1: 0.9899 |
| f2 | IMF3: 0.8263 | IMF4: 0.9383 | IMF2: 0.9895 |
| f3 | IMF2: 0.8280 | IMF3: 0.9078 | IMF3: 0.9866 |
| Before Denoising | EMD-RWPE | EEMD-RWPE | IVMD-RWPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR/db | 7.6921 | 10.8008 | 12.0176 | 15.8777 |
| RMSE | 0.5052 | 0.3532 | 0.3070 | 0.2387 |
| Method | Number of Misclassified Samples | Recognition Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Class II | Class III | ||
| PE before denoising | 24 | 20 | 32 | 36.6667 |
| PE after denoising | 2 | 11 | 30 | 65.8333 |
| EMD-norMIC-PE | 26 | 0 | 7 | 72.5 |
| EEMD-norMIC-PE | 7 | 0 | 17 | 80 |
| VMD-SIMF-FDE (31) | 2 | 0 | 1 | 97.5 |
| IVMD-norMIC-PE | 1 | 0 | 0 | 99.1667 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, D.; Sun, H.; Qi, J. A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient and Permutation Entropy for Ship-Radiated Noise. Entropy 2020, 22, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060620
Xie D, Sun H, Qi J. A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient and Permutation Entropy for Ship-Radiated Noise. Entropy. 2020; 22(6):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060620
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Dongri, Haixin Sun, and Jie Qi. 2020. "A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient and Permutation Entropy for Ship-Radiated Noise" Entropy 22, no. 6: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060620
APA StyleXie, D., Sun, H., & Qi, J. (2020). A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Improved Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Maximal Information Coefficient and Permutation Entropy for Ship-Radiated Noise. Entropy, 22(6), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060620






