Multivariate and Multiscale Complexity of Long-Range Correlated Cardiovascular and Respiratory Variability Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Measures of Complexity in Linear Multivariate Stochastic processes
2.2. Linear Multivariate Stochastic Processes with Long Range Correlations
2.3. Multiscale Complexity of VARFI Processes
3. Application to Cardiovascular Variability Processes
3.1. Experimental Protocol
3.2. Data Analysis
3.3. Statistical Analysis
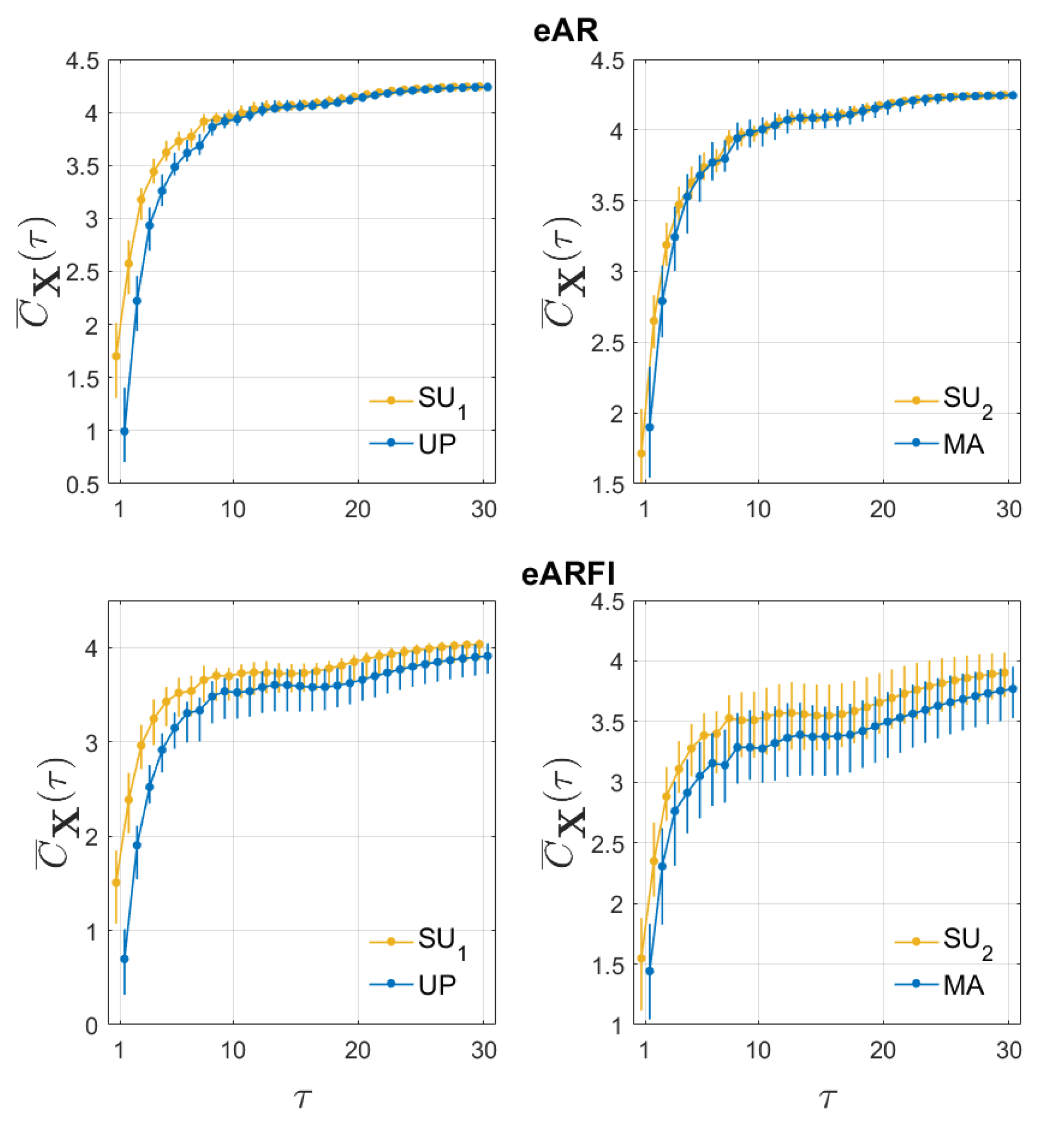
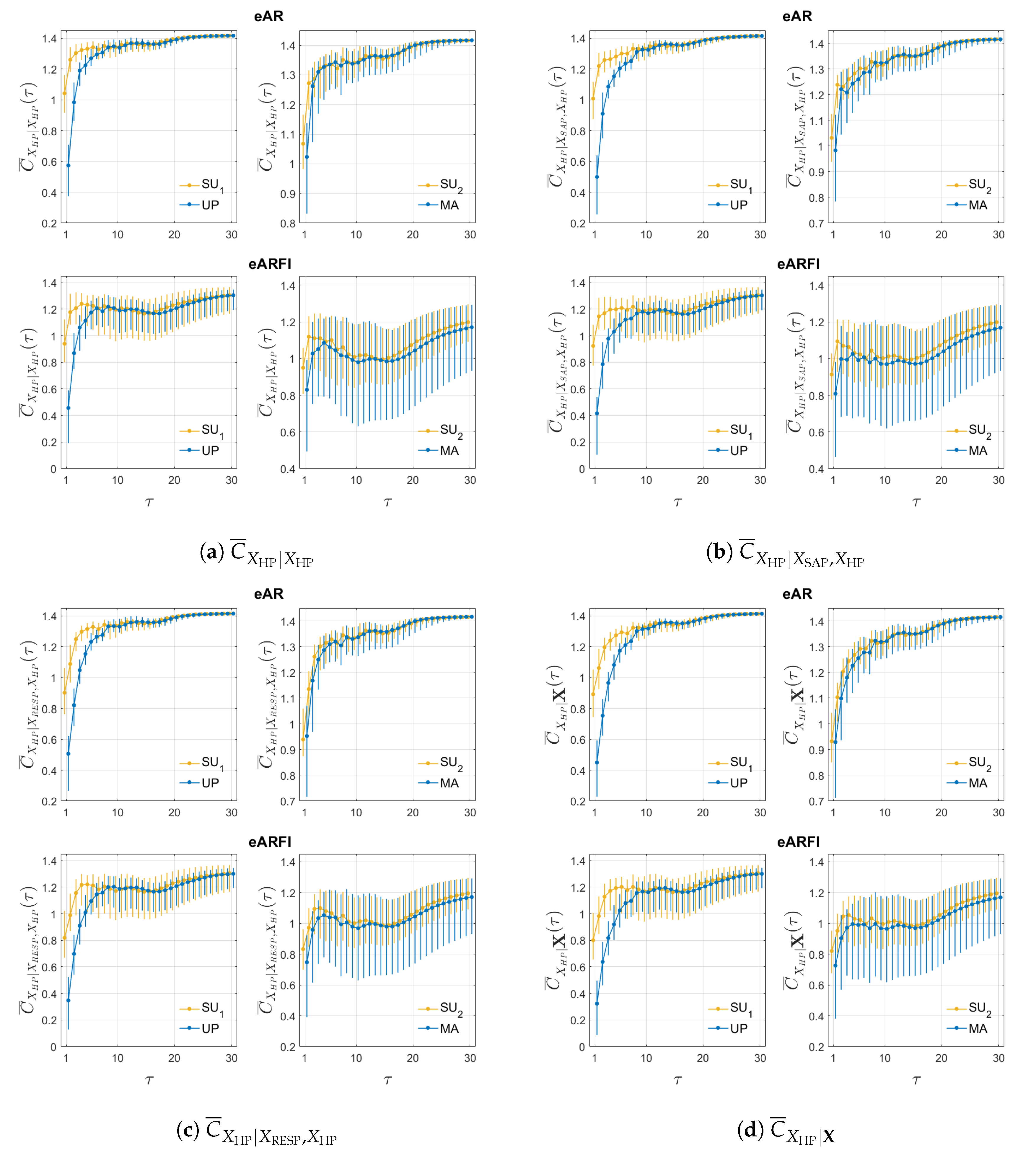
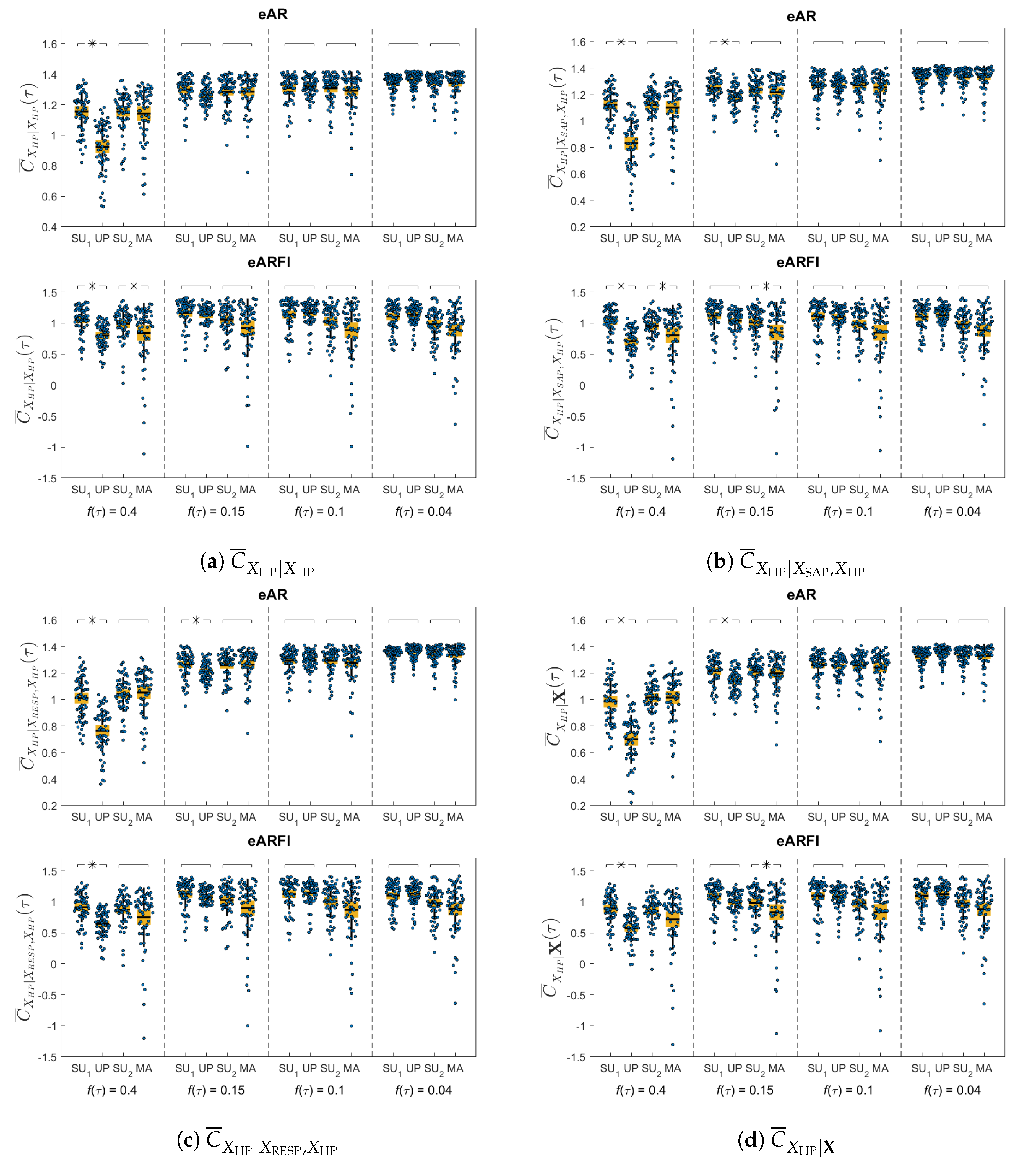
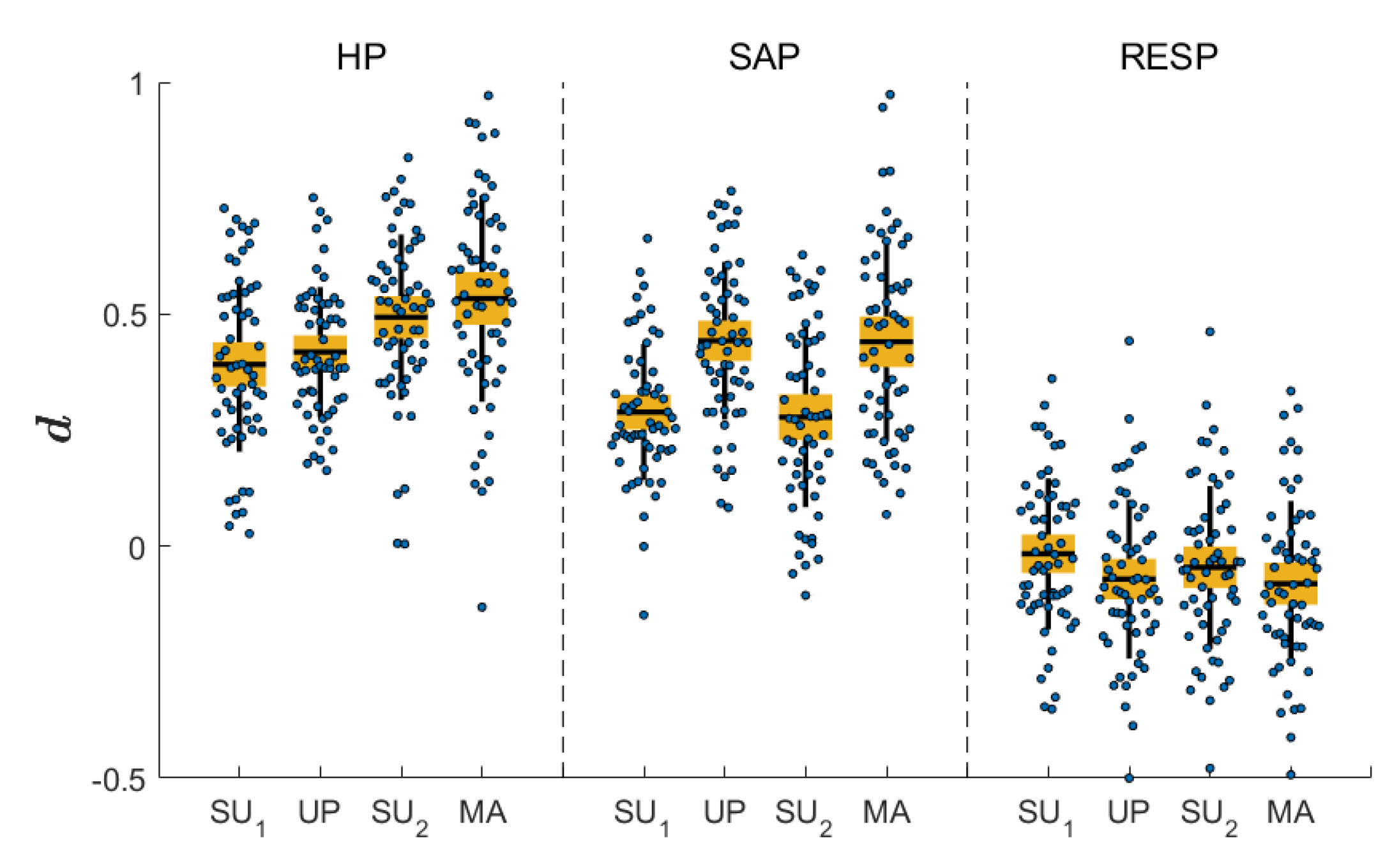
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Cohen, M.A.; Taylor, J.A. Short-term cardiovascular oscillations in man: Measuring and modelling the physiologies. J. Phys. 2002, 542, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K.; Lipsitz, L.A. What is physiologic complexity and how does it change with aging and disease? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Greater signal regularity may indicate increased system isolation. Math. Biosci. 1994, 122, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.; Porta, A.; Vallverdú, M.; Clariá, F.; Baranowski, R.; Orłowska-Baranowska, E.; Caminal, P. Refined multiscale entropy: Application to 24-h holter recordings of heart period variability in healthy and aortic stenosis subjects. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Mandic, D.P. Multivariate multiscale entropy analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2011, 19, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Porta, A.; Javorka, M.; Nollo, G. Efficient Computation of Multiscale Entropy over Short Biomedical Time Series Based on Linear State-Space Models. Complexity 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Pereira, M.A.; Silva, M.E.; Pernice, R.; Busacca, A.; Javorka, M.; Rocha, A.P. Multiscale information storage of linear long-range correlated stochastic processes. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 032115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Furlan, R.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Montano, N.; Malliani, A. Complexity and nonlinearity in short-term heart period variability: Comparison of methods based on local nonlinear prediction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Faes, L.; Ivanov, P.C. Entropy measures, entropy estimators, and their performance in quantifying complex dynamics: Effects of artifacts, nonstationarity, and long-range correlations. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 062114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.B.; Barnett, L.; Seth, A.K. Multivariate Granger causality and generalized variance. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 041907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.; Barrett, A.B.; Seth, A.K. Granger causality and transfer entropy are equivalent for Gaussian variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faes, L.; Porta, A.; Nollo, G. Information decomposition in bivariate systems: Theory and application to cardiorespiratory dynamics. Entropy 2015, 17, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Javorka, M.; Porta, A.; Bari, V.; Krohova, J.; Czippelova, B.; Turianikova, Z.; Nollo, G.; Faes, L. Univariate and multivariate conditional entropy measures for the characterization of short-term cardiovascular complexity under physiological stress. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faes, L.; Porta, A.; Nollo, G.; Javorka, M. Information decomposition in multivariate systems: Definitions, implementation and application to cardiovascular networks. Entropy 2016, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, W.J. Maximum likelihood estimation of stationary multivariate ARFIMA processes. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2010, 80, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, J.; Feng, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Kulik, R. Statistics for Long-Memory Processes: Probabilistic Properties and Statistical Methods, 2012 ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Faes, L.; Erla, S.; Nollo, G. Measuring connectivity in linear multivariate processes: Definitions, interpretation, and practical analysis. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S. Multiscale information decomposition: Exact computation for multivariate Gaussian processes. Entropy 2017, 19, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Stramaglia, S.; Marinazzo, D. Multiscale Granger causality. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 042150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Havenner, A. State space modeling of multiple time series. Econ. Rev. 1991, 10, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solo, V. State-space analysis of Granger-Geweke causality measures with application to fMRI. Neur. Comput. 2016, 28, 914–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.; Seth, A.K. Granger causality for state-space models. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 040101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krohova, J.; Faes, L.; Czippelova, B.; Turianikova, Z.; Mazgutova, N.; Pernice, R.; Busacca, A.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S.; Javorka, M. Multiscale information decomposition dissects control mechanisms of heart rate variability at rest and during physiological stress. Entropy 2019, 21, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Porta, A. Information-based detection of nonlinear Granger causality in multivariate processes via a nonuniform embedding technique. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 051112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, A.; Bassani, T.; Bari, V.; Tobaldini, E.; Takahashi, A.C.; Catai, A.M.; Montano, N. Model-based assessment of baroreflex and cardiopulmonary couplings during graded head-up tilt. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Porta, A. Information domain approach to the investigation of cardio-vascular, cardio-pulmonary, and vasculo-pulmonary causal couplings. Front. Phys. 2011, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faes, L.; Porta, A.; Cucino, R.; Cerutti, S.; Antolini, R.; Nollo, G. Causal transfer function analysis to describe closed loop interactions between cardiovascular and cardiorespiratory variability signals. Biol. Cybern. 2004, 90, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, A.; Malik, M.; Bigger, J.; Breithardt, G.; Cerutti, S.; Cohen, R.; Coumel, P.; Fallen, E.; Kennedy, H.; Kleiger, R.; et al. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J. An overview of heart rate variability metrics and norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernice, R.; Javorka, M.; Krohova, J.; Czippelova, B.; Turianikova, Z.; Busacca, A.; Faes, L. Comparison of short-term heart rate variability indexes evaluated through electrocardiographic and continuous blood pressure monitoring. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javorka, M.; Czippelova, B.; Turianikova, Z.; Lazarova, Z.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Faes, L. Causal analysis of short-term cardiovascular variability: State-dependent contribution of feedback and feedforward mechanisms. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardet, J.M.; Lang, G.; Oppenheim, G.; Philippe, A.; Taqqu, M.S. Generators of long-range dependent processes: A survey. Theory Appl. Long-Range Depend. 2003, 579–623. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, P.; Selen, Y. Model-order selection: A review of information criterion rules. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2004, 21, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D. Mixed-Effects Models in S and S-PLUS, 2000 ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, S.R.; Speed, F.M.; Milliken, G.A. Population Marginal Means in the Linear Model: An Alternative to Least Squares Means. Am. Stat. 1980, 34, 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means, R package version 1.3.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Tobaldini, E.; Guzzetti, S.; Furlan, R.; Montano, N. Progressive decrease of heart period variability entropy-based complexity during graded head-up tilt. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Furlan, R.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Entropy, entropy rate, and pattern classification as tools to typify complexity in short heart period variability series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Hayano, J. Heart rate and blood pressure variabilities during graded head-up tilt. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 78, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamad, F.; Javorka, M.; Czippelova, B.; Krohova, J.; Turianikova, Z.; Porta, A.; Baumert, M. Repolarization variability independent of heart rate during sympathetic activation elicited by head-up tilt. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Gómez-Extremera, M.; Pernice, R.; Carpena, P.; Nollo, G.; Porta, A.; Bernaola-Galván, P. Comparison of methods for the assessment of nonlinearity in short-term heart rate variability under different physiopathological states. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2019, 29, 123114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; De Cecco, M.; Pernice, R.; Maule, L.; Pertile, M.; Fornaser, A. Information dynamics of the brain, cardiovascular and respiratory network during different levels of mental stress. Entropy 2019, 21, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Montesinos, L.; Melillo, P.; James, C.; Pecchia, L. Ultra-short term HRV features as surrogates of short term HRV: A case study on mental stress detection in real life. BMC Med. Inf. Dec. Mak. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, Y.S.; Arnrich, B.; Ersoy, C. Stress detection in daily life scenarios using smart phones and wearable sensors: A survey. J. Biomed. Inf. 2019, 103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernice, R.; Nollo, G.; Zanetti, M.; De Cecco, M.; Busacca, A.; Faes, L. Minimally Invasive Assessment of Mental Stress based on Wearable Wireless Physiological Sensors and Multivariate Biosignal Processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2019-18th International Conference on Smart Technologies, Novi Sad, Serbia, 1–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, H.E. Comparisons of tests for multivariate cointegration. Stat. Pap. 1992, 33, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shang, P.; Xiong, H. Multivariate generalized information entropy of financial time series. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 525, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Mandic, D.P. Multivariate multiscale entropy: A tool for complexity analysis of multichannel data. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 061918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtiol, J.; Perdikis, D.; Petkoski, S.; Müller, V.; Huys, R.; Sleimen-Malkoun, R.; Jirsa, V.K. The multiscale entropy: Guidelines for use and interpretation in brain signal analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 273, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measure | Approach | SU → UP | SU → MA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.04 | ||
| eVAR | ↘ | ↗ | ↗ | ↗ | |||||
| eVARFI | ↘ | ↘ | ↘ | ||||||
| eVAR | ↘ | ||||||||
| eVARFI | ↘ | ↘ | |||||||
| eVAR | ↘ | ↘ | |||||||
| eVARFI | ↘ | ↘ | ↘ | ||||||
| eVAR | ↘ | ↘ | |||||||
| eVARFI | ↘ | ||||||||
| eVAR | ↘ | ↘ | |||||||
| eVARFI | ↘ | ↘ | |||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, A.; Pernice, R.; Amado, C.; Rocha, A.P.; Silva, M.E.; Javorka, M.; Faes, L. Multivariate and Multiscale Complexity of Long-Range Correlated Cardiovascular and Respiratory Variability Series. Entropy 2020, 22, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030315
Martins A, Pernice R, Amado C, Rocha AP, Silva ME, Javorka M, Faes L. Multivariate and Multiscale Complexity of Long-Range Correlated Cardiovascular and Respiratory Variability Series. Entropy. 2020; 22(3):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030315
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Aurora, Riccardo Pernice, Celestino Amado, Ana Paula Rocha, Maria Eduarda Silva, Michal Javorka, and Luca Faes. 2020. "Multivariate and Multiscale Complexity of Long-Range Correlated Cardiovascular and Respiratory Variability Series" Entropy 22, no. 3: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030315
APA StyleMartins, A., Pernice, R., Amado, C., Rocha, A. P., Silva, M. E., Javorka, M., & Faes, L. (2020). Multivariate and Multiscale Complexity of Long-Range Correlated Cardiovascular and Respiratory Variability Series. Entropy, 22(3), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030315







