Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
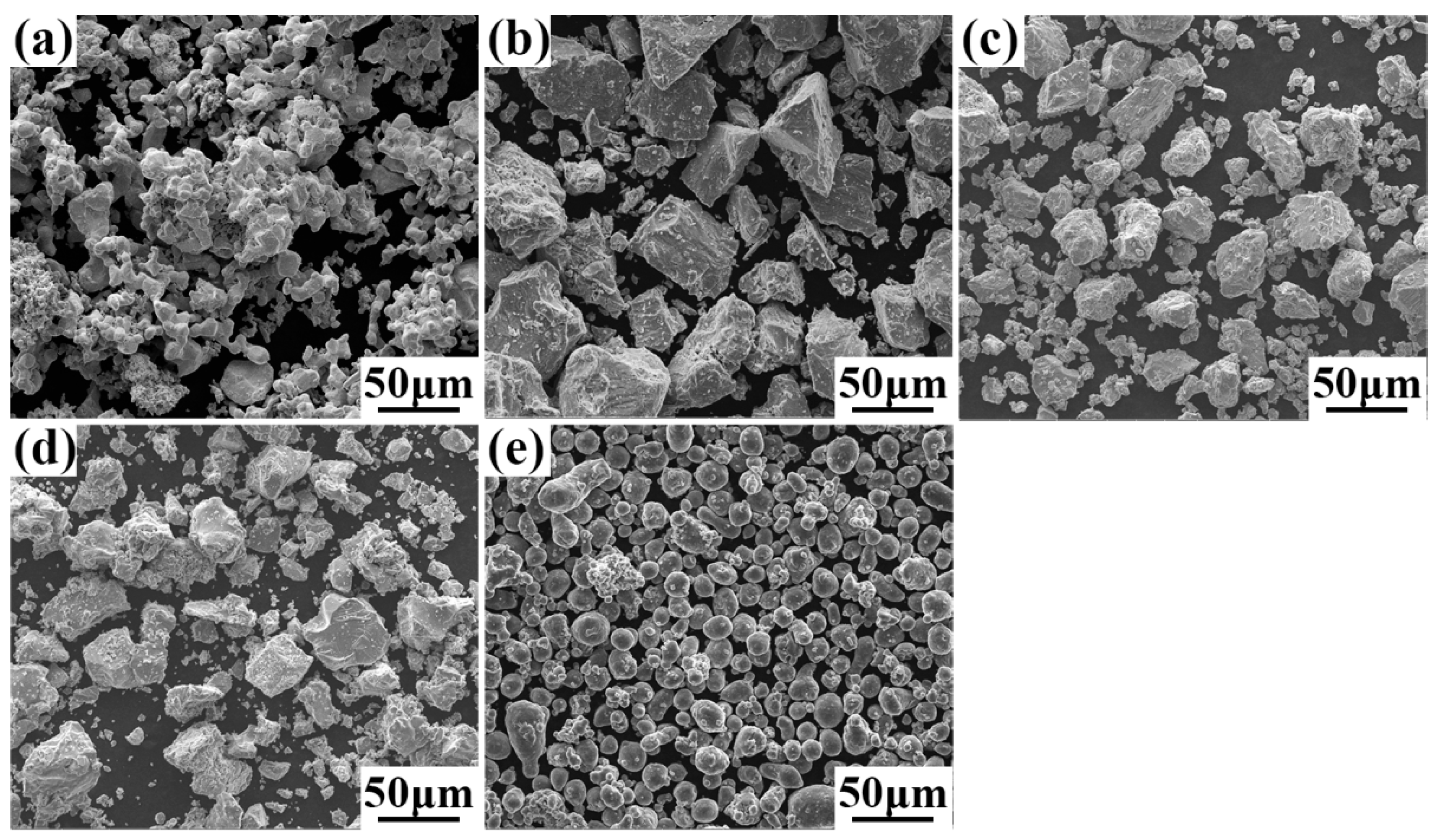
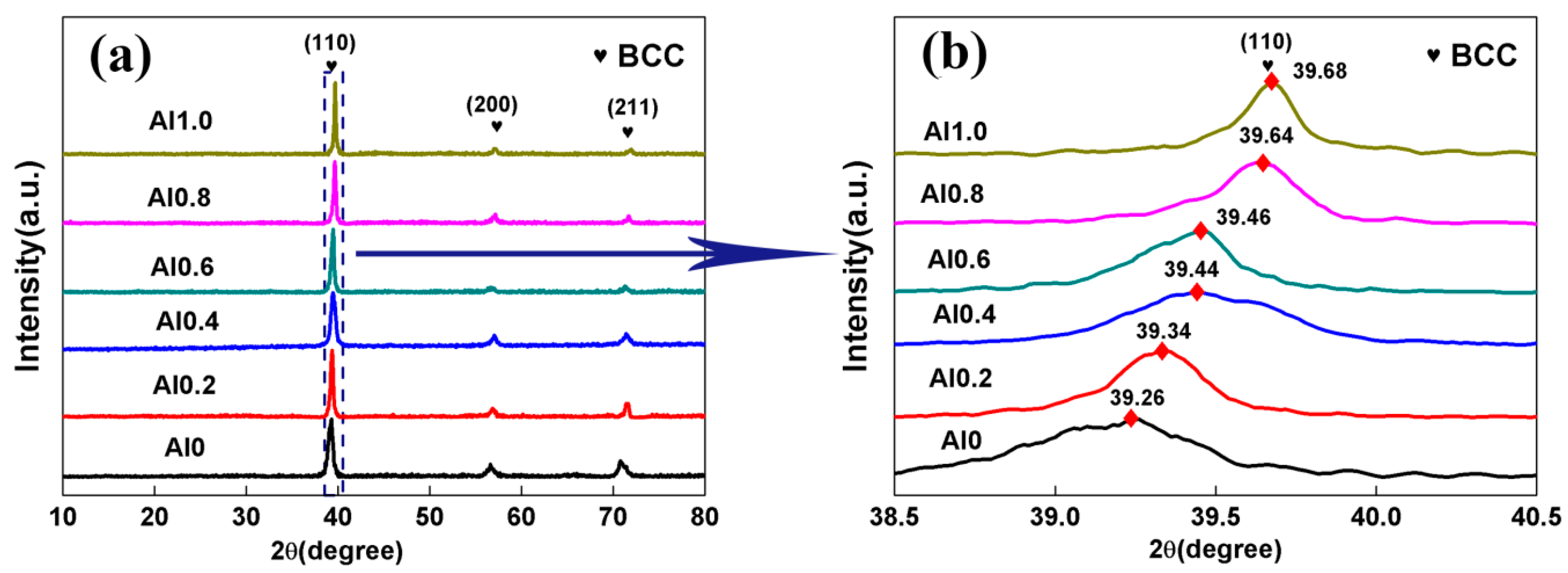
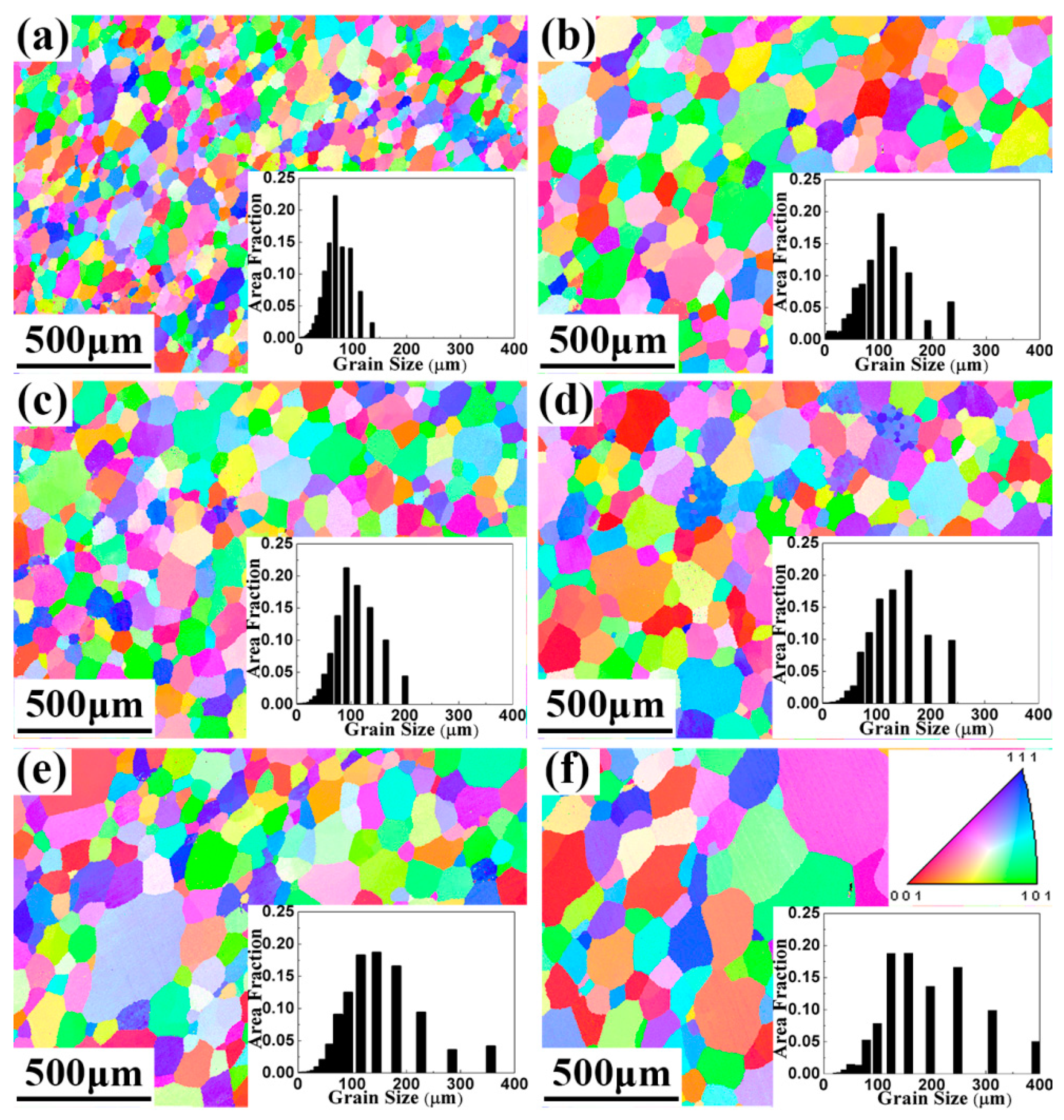
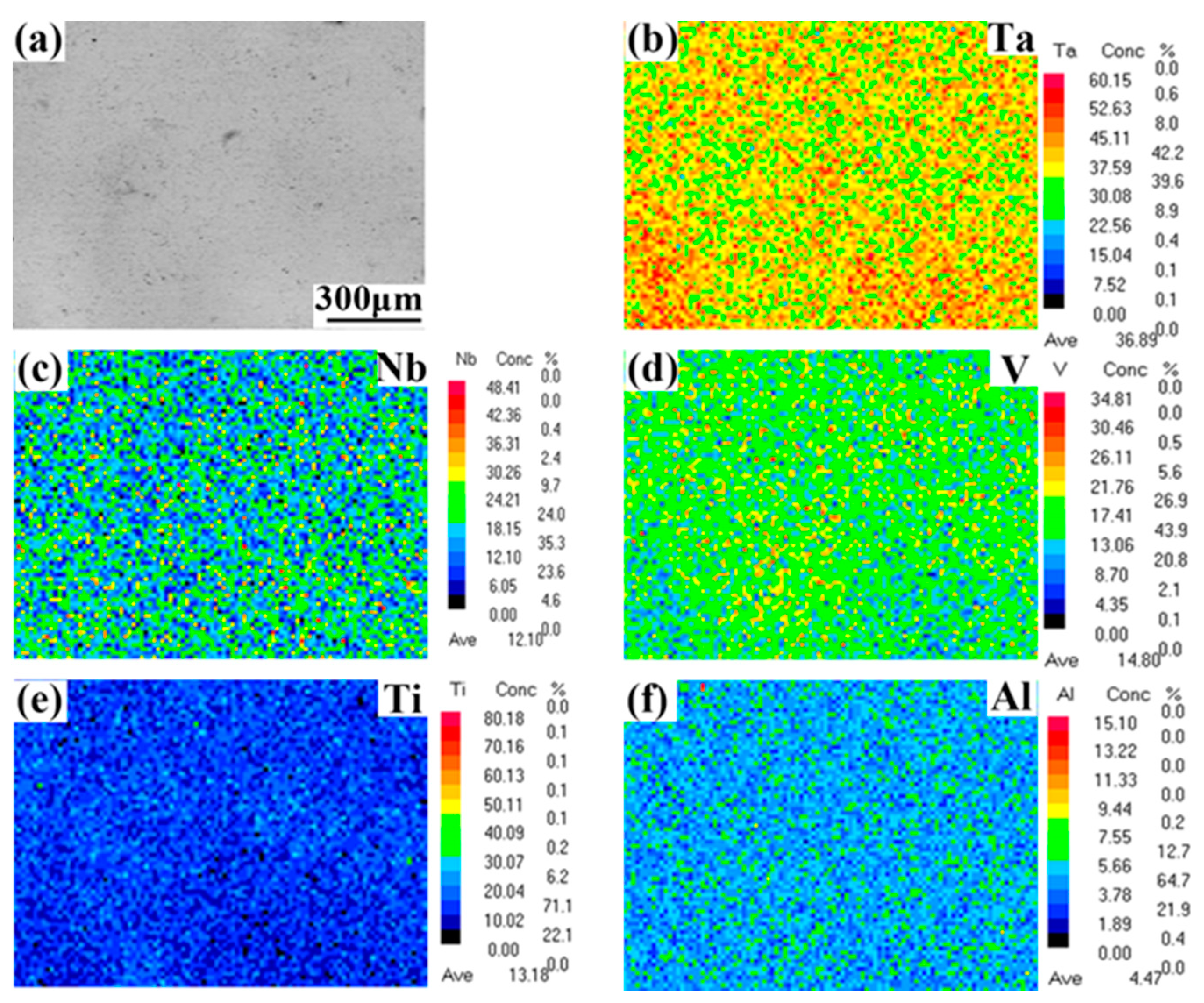
3.1. Microstructures of the TaNbVTiAlx RHEAs
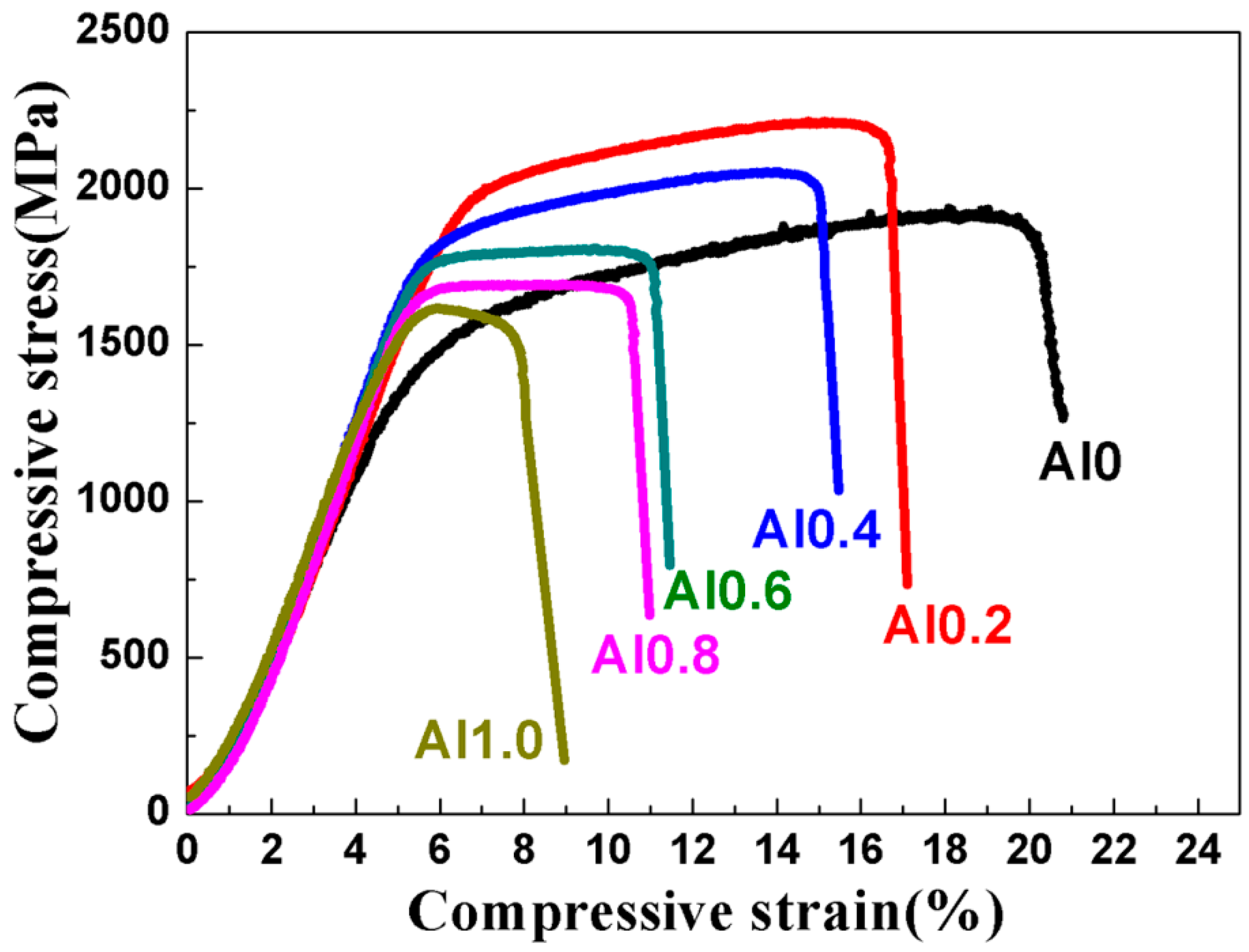
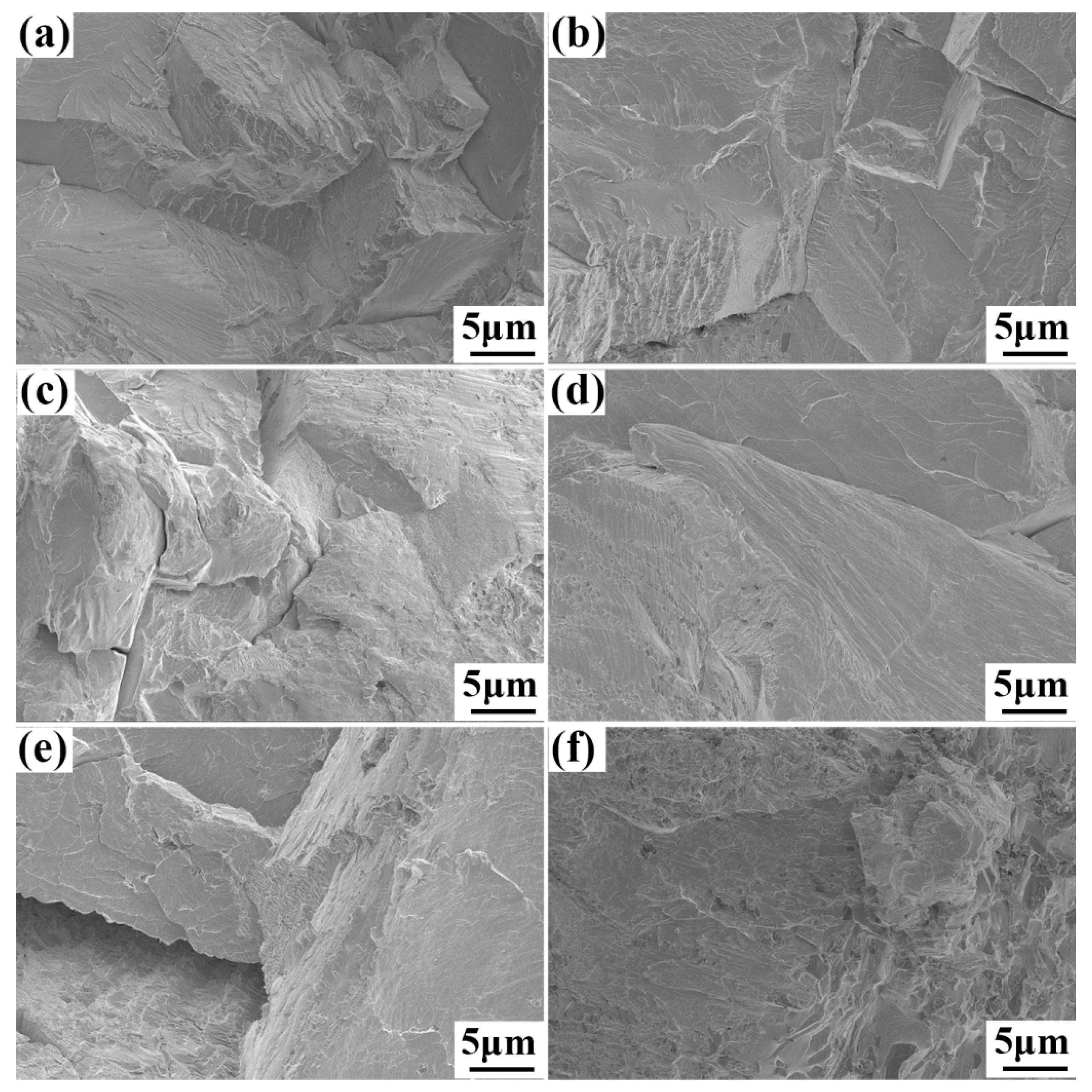
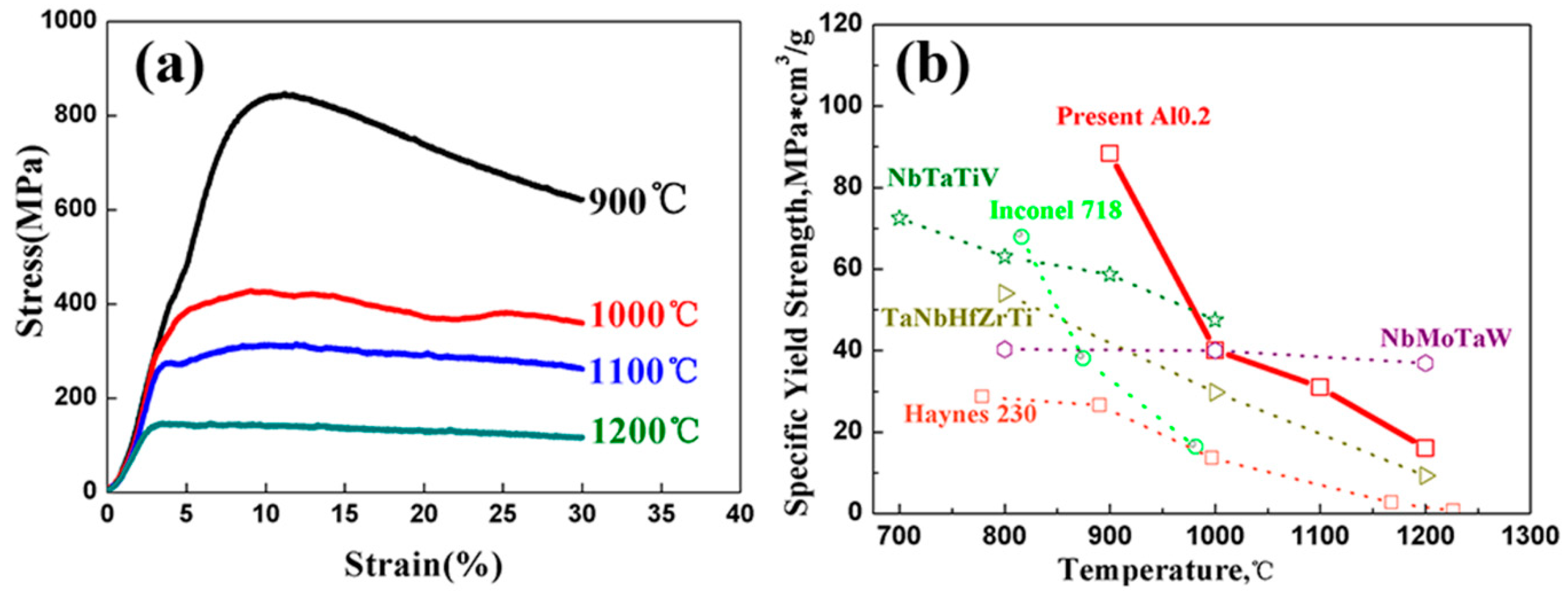
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the TaNbVTiAlx RHEAs
4. Discussion
4.1. Phase Prediction
4.2. Strengthening Mechanism
5. Conclusions
- The P/M TaNbVTiAlx RHEAs showed a simple BCC microstructure with no obvious segregation. The average grain sizes were 69, 101, 106, 135, 147, and 187 μm for the Al0, Al0.2, Al0.4, Al0.6, Al0.8, and Al1.0 RHEAs, respectively.
- The P/M TaNbVTiAlx RHEAs showed excellent room-temperature specific strength (207.11 MPa*cm3/g) and high-temperature specific strength (88.37 MPa*cm3/g at 900 °C and 16.03 MPa*cm3/g at 1200 °C) with reasonable plasticity, suggesting that the material has the possibility for use at high temperatures > 1200 °C.
- The reasons for the excellent mechanical properties of the P/M TaNbVTiAl0.2 RHEA were the uniform microstructure and solid solution strengthening effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high–temperature properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 760, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qiao, J.-W.; Gao, M.; Hawk, J.; Ma, S.-G.; Zhou, H.; Yao, H.; Qiao, J.-W.; Gao, M.C.; Hawk, J.A.; et al. MoNbTaV Medium-Entropy Alloy. Entropy 2016, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Luan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Li, X.Y.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Fang, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. A particle reinforced NbTaTiV refractory high entropy alloy based composite with attractive mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Fu, A.; Li, L.; Yan, N.; Fang, Q. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Particulate Reinforced NbMoCrTiAl High Entropy Based Composite. Entropy 2018, 20, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, K. Microstructure, phase stability and mechanical properties of Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr and Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr–Hf high entropy alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2015, 25, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qin, G.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Chiu, Y.; Ding, H.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Composition design of high entropy alloys using the valence electron concentration to balance strength and ductility. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Shafeie, S.; Hu, Q.; Ahlström, J.; Persson, C.; Veselý, J.; Zýka, J.; Klement, U.; Guo, S. Alloy design for intrinsically ductile refractory high-entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 164902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Fu, A.; Fang, Q.; Nie, Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of ductile NbTaTiV refractory high entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 776, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchenko, N.Y.; Stepanov, N.D.; Shaysultanov, D.G.; Tikhonovsky, M.A.; Salishchev, G.A. Effect of Al content on structure and mechanical properties of the AlxCrNbTiVZr (x=0; 0.25; 0.5; 1) high-entropy alloys. Mater. Charact. 2016, 121, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ma, Z.L.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.W.; Tan, Y.D.; Cheng, X.W. Design of novel low-density refractory high entropy alloys for high-temperature applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 755, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Microstructure and Compressive Properties of NbTiVTaAlx High Entropy Alloys. Procedia Eng. 2012, 36, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W. Precipitation behavior during hot deformation of powder metallurgy Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-Al high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 100, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Microstructure, mechanical property and Hall-Petch relationship of a light-weight refractory Al0.1CrNbVMo high entropy alloy fabricated by powder metallurgical process. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Dahmen, K.; Liaw, P.; Zhang, Y. Microstructures and Crackling Noise of AlxNbTiMoV High Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2014, 16, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Qian, M.; Shi, Z.; Song, T.; Huang, L.; Zou, J. A novel quaternary equiatomic Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta medium entropy alloy (MEA). Intermetallics 2018, 101, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Juan, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Yeh, J.W. Effect of Al addition on mechanical properties and microstructure of refractory AlxHfNbTaTiZr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 624, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhuang, X.; Nie, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical property and microstructure of a powder metallurgy nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 754, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Steurer, W. Structural-disorder and its effect on mechanical properties in single-phase TaNbHfZr high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 106, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and room temperature properties of a high-entropy TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Si, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hui, X. Phase stability and mechanical properties of AlHfNbTiZr high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Meisenkothen, F.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4062–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Song, G.; Gao, M.C.; Feng, R.; Chen, P.; Brechtl, J.; Chen, Y.; An, K.; Guo, W.; Poplawsky, J.D.; et al. Lattice distortion in a strong and ductile refractory high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 160, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effects of electro-negativity on the stability of topologically close-packed phase in high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 52, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-component Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liaw, P.K. Alloy Design and Properties Optimization of High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2012, 64, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ng, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, C.T. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, J.M.; Chan, H.M.; Harmer, M.P.; Smeltzer, J.A.; Marvel, C.J.; Roy, A.; Balasubramanian, G. Materials informatics for the screening of multi-principal elements and high-entropy alloys. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G. The Peierls—Nabarro Model of Dislocations: A Venerable Theory and its Current Development. Handb. Mater. Model. 2005, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Meng, L. Deformation twinning behaviors of the low stacking fault energy high-entropy alloy: An in-situ TEM study. Scr. Mater. 2017, 137, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alloys | Ta (at.%) | Nb (at.%) | V (at.%) | Ti (at.%) | Al (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al0 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0 |
| Al0.2 | 23.81 | 23.81 | 23.81 | 23.81 | 4.76 |
| Al0.4 | 22.73 | 22.73 | 22.73 | 22.73 | 9.09 |
| Al0.6 | 21.74 | 21.74 | 21.74 | 21.74 | 13.04 |
| Al0.8 | 20.83 | 20.83 | 20.83 | 20.83 | 16.67 |
| Al1.0 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Raw Powder | Average Particle Size (μm) | O (wt.%) | C (wt.%) | H (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ta | 24.5 | 0.13 | 0.0064 | 0.0008 |
| Nb | 26.1 | 0.34 | 0.0220 | 0.0015 |
| V | 22.6 | 0.29 | 0.0096 | 0.0014 |
| Ti | 29.0 | 0.28 | 0.0150 | 0.0147 |
| Al | 18.6 | 0.27 | 0.0250 | 0.0017 |
| Ta | Nb | V | Ti | Al | Al0 | Al0.2 | Al0.4 | Al0.6 | Al0.8 | Al1.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal structure | BCC | BCC | BCC | HCP | FCC | BCC | BCC | BCC | BCC | BCC | BCC |
| Calculated lattice parameter (Å) | - | - | - | - | - | 3.243 | 3.236 | 3.228 | 3.227 | 3.213 | 3.210 |
| Theoretical lattice parameter (Å) | 3.303 | 3.301 | 3.039 | 3.276 | 4.050 | 3.230 | 3.269 | 3.304 | 3.337 | 3.366 | 3.394 |
| Atomic radius (Å) | 1.47 | 1.47 | 1.35 | 1.46 | 1.43 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tm (K) | 3293 | 2750 | 2202 | 1946 | 933.5 | 2548 | 2471 | 2401 | 2337 | 2278 | 2225 |
| ρ(g/cm3) | 16.65 | 8.57 | 6.11 | 4.51 | 2.70 | 9.16 | 8.86 | 8.58 | 8.33 | 8.10 | 7.89 |
| Materials | Density (g/cm3) | Preparation Methods | Phase Structure | Yield Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strength (MPa) | Plastic Strain | Specific Yield Strength (MPa*cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NbMoTaW [3] | 13.7 | As-cast | BCC | 1058 | 1211 | 1.5% | 77.23 |
| TaNbHfZr [23] | 11.1 | As-cast | BCC | 1315 | 1885 | 21.6% | 118.47 |
| TiZrNbTa [19] | 9.94 | As-cast | BCC | 1100 | - | 48% | 110.66 |
| TaNbHfZrTi [24] | 9.9 | As-cast | BCC | 929 | - | >50% | 93.84 |
| Al0.4Hf0.6NbTaTiZr [12] | 9.05 | As-cast | BCC | 1841 | 2269 | ~5% | 203.43 |
| Al0.21HfNbTiZr [25] | 8.12 | As-cast | BCC | 831 | 915.2 | ~20% | 102.34 |
| NbTiVTa [15] | 9.16 | As-cast | BCC | 1092 | - | >50% | 119.21 |
| NbTiVTaAl0.25 [15] | 8.78 | As-cast | BCC | 1330 | - | >50% | 151.48 |
| NbTiVTa0.5 [15] | 8.45 | As-cast | BCC | 1012 | - | >50% | 119.76 |
| NbTiVTa1.0 [15] | 7.89 | As-cast | BCC | 991 | - | >50% | 125.60 |
| TaNbVTi | 9.16 | PM | BCC | 1391 | 1932 | 15% | 151.86 |
| TaNbVTiAl0.2 | 8.86 | PM | BCC | 1835 | 2217 | 10% | 207.11 |
| TaNbVTiAl0.4 | 8.58 | PM | BCC | 1719 | 2054 | 9% | 200.35 |
| TaNbVTiAl0.6 | 8.33 | PM | BCC | 1697 | 1810 | 5.5% | 203.72 |
| TaNbVTiAl0.8 | 8.10 | PM | BCC | 1606 | 1695 | 5% | 198.27 |
| TaNbVTiAl1.0 | 7.89 | PM | BCC | 1450 | 1619 | 2.5% | 183.78 |
| Alloys | ΔSmix (J/K·mol) | ΔHmix (kJ/mol) | Tm(K) | Ω | VEC | δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al0 | 11.53 | −0.25 | 2548 | 117.51 | 4.75 | 3.53 |
| Al0.2 | 12.57 | −3.99 | 2471 | 7.78 | 4.67 | 3.44 |
| Al0.4 | 13.01 | −7.07 | 2401 | 4.42 | 4.59 | 3.37 |
| Al0.6 | 13.24 | −9.60 | 2337 | 3.22 | 4.52 | 3.29 |
| Al0.8 | 13.35 | −11.70 | 2278 | 2.60 | 4.46 | 3.23 |
| Al1.0 | 13.38 | −13.44 | 2225 | 2.22 | 4.40 | 3.16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, L.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Fu, A.; Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2020, 22, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030282
Xiang L, Guo W, Liu B, Fu A, Li J, Fang Q, Liu Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy. 2020; 22(3):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030282
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Li, Wenmin Guo, Bin Liu, Ao Fu, Jianbo Li, Qihong Fang, and Yong Liu. 2020. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys" Entropy 22, no. 3: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030282
APA StyleXiang, L., Guo, W., Liu, B., Fu, A., Li, J., Fang, Q., & Liu, Y. (2020). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy, 22(3), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22030282





