Statistical Physics Approach to Liquid Crystals: Dynamics of Mobile Potts Model Leading to Smectic Phase, Phase Transition by Wang–Landau Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Model
2.2. Formation of the Smectic Phase
3. Nature of the Layer Melting/Evaporation
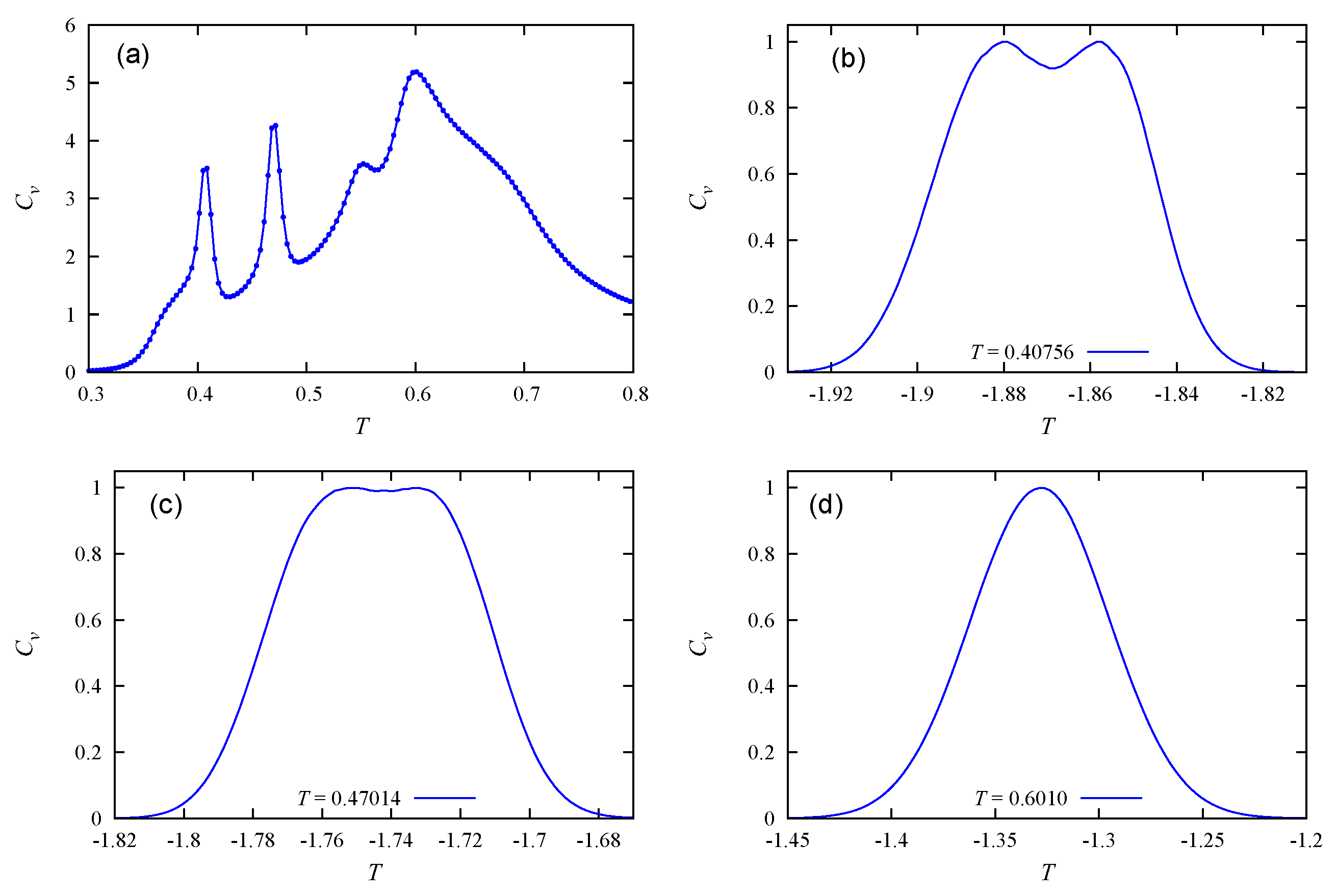
3.1. Implementation of the Wang–Landau Method
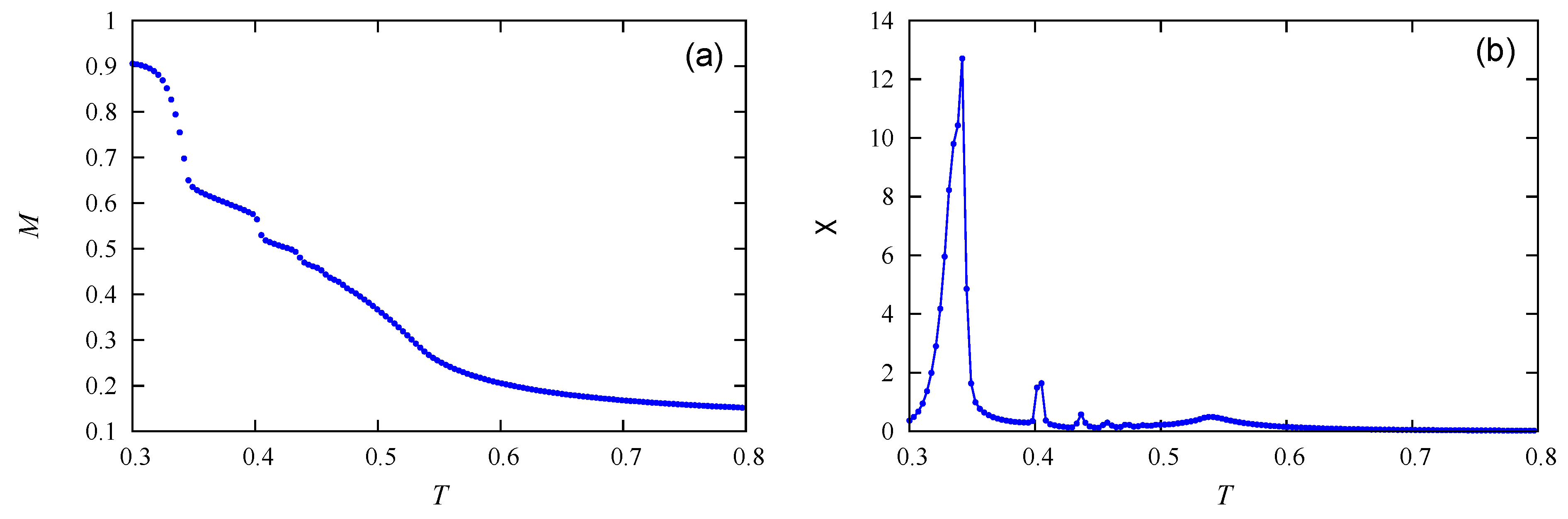
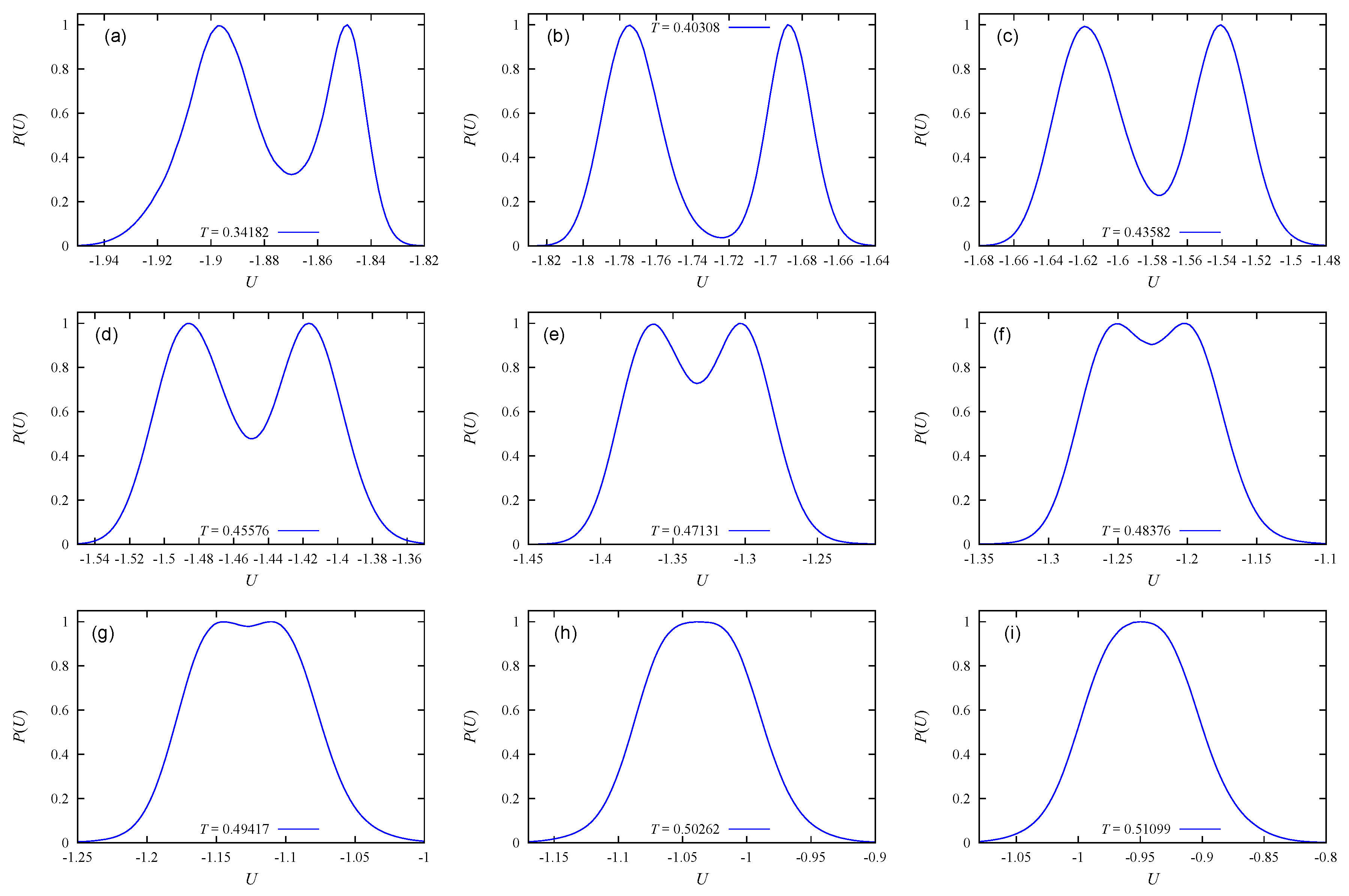
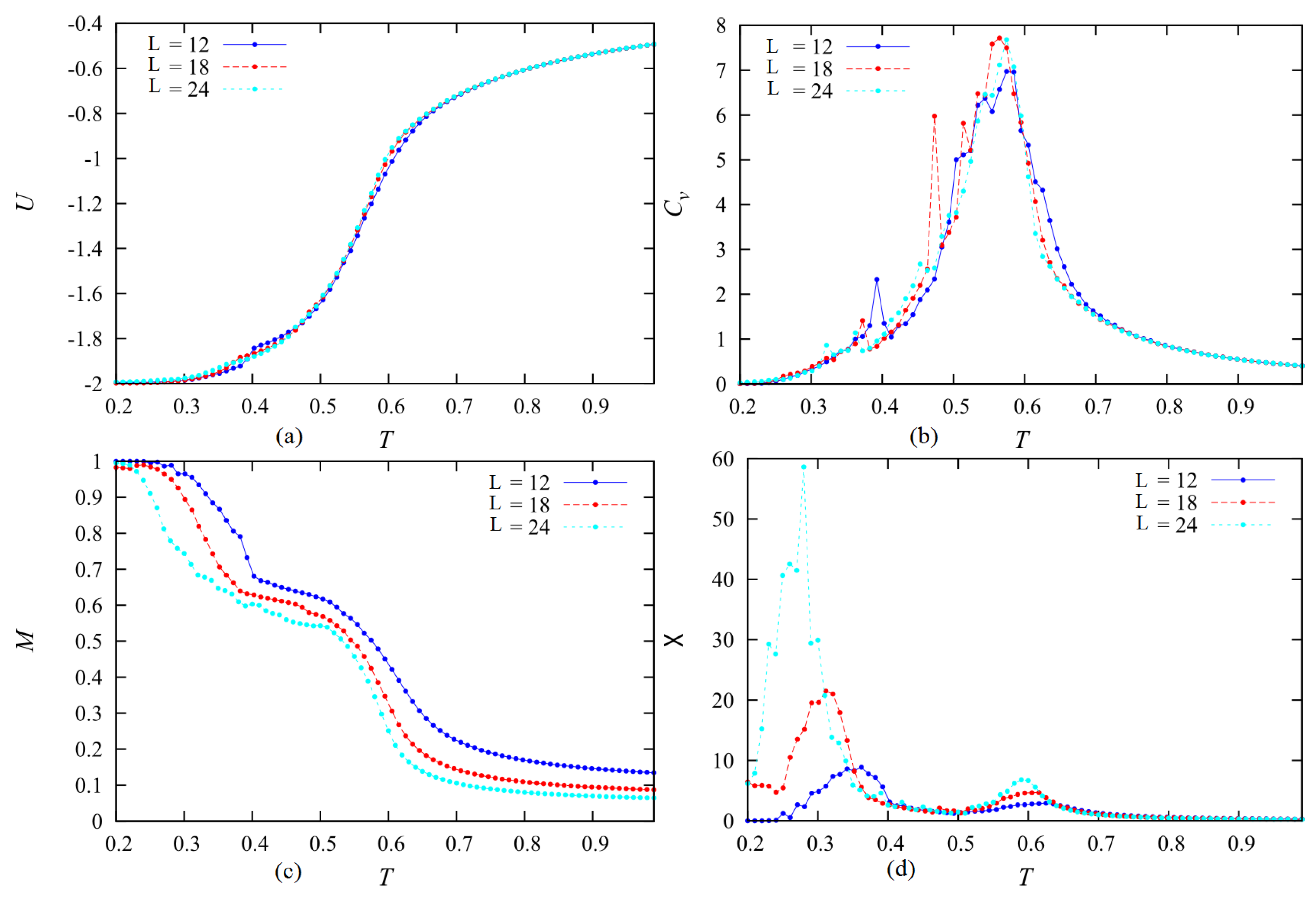
3.2. Results
3.3. Discussion
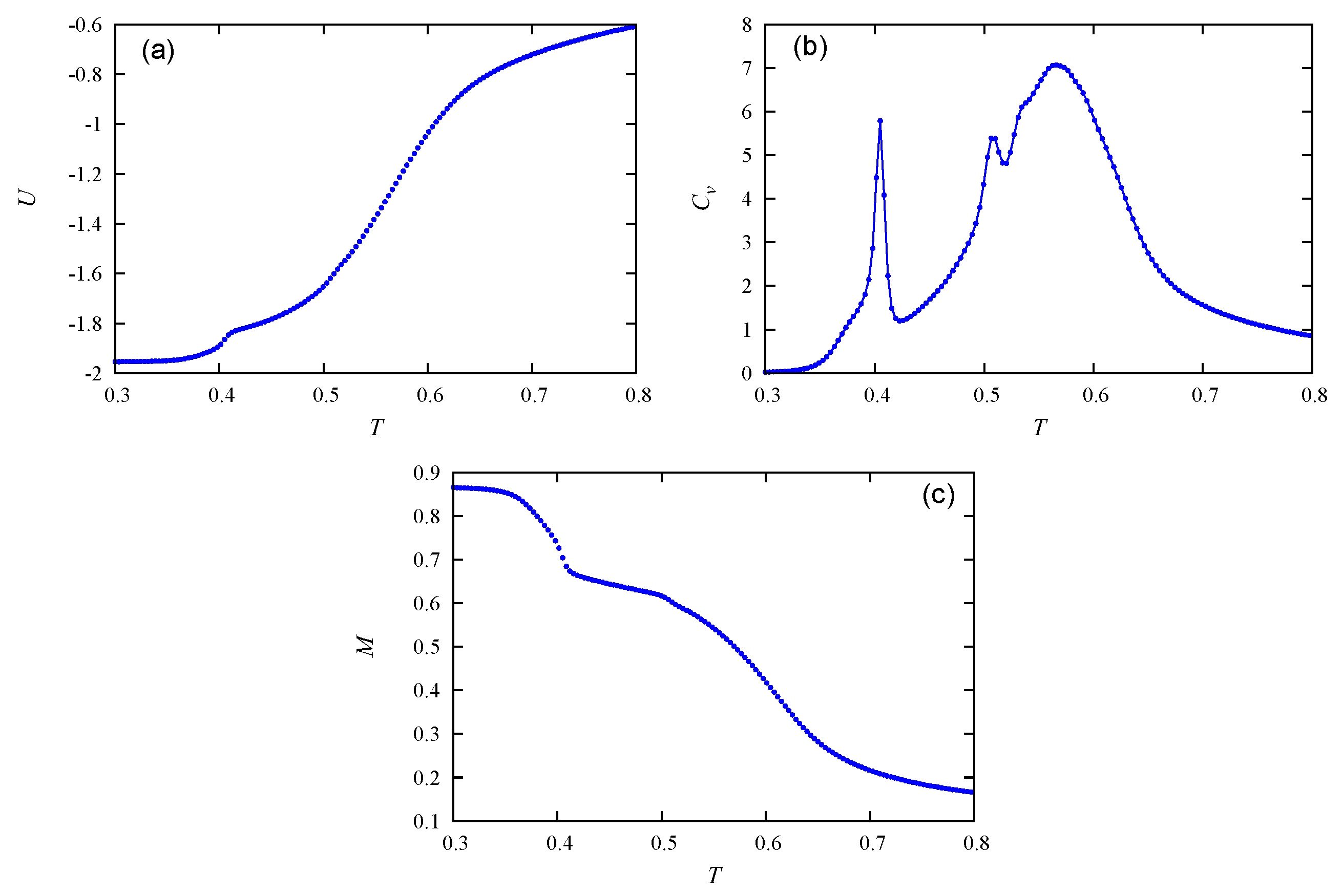
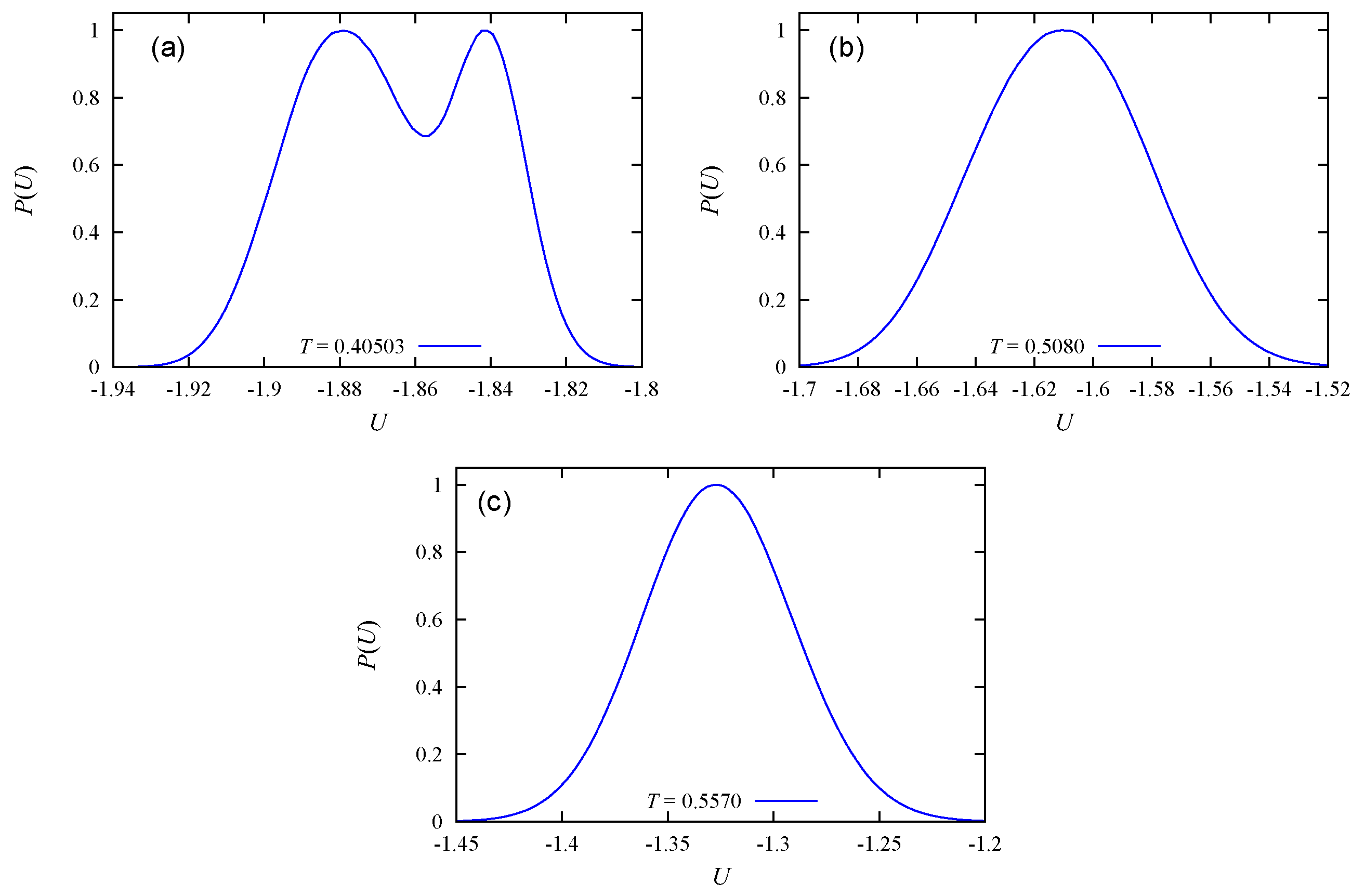
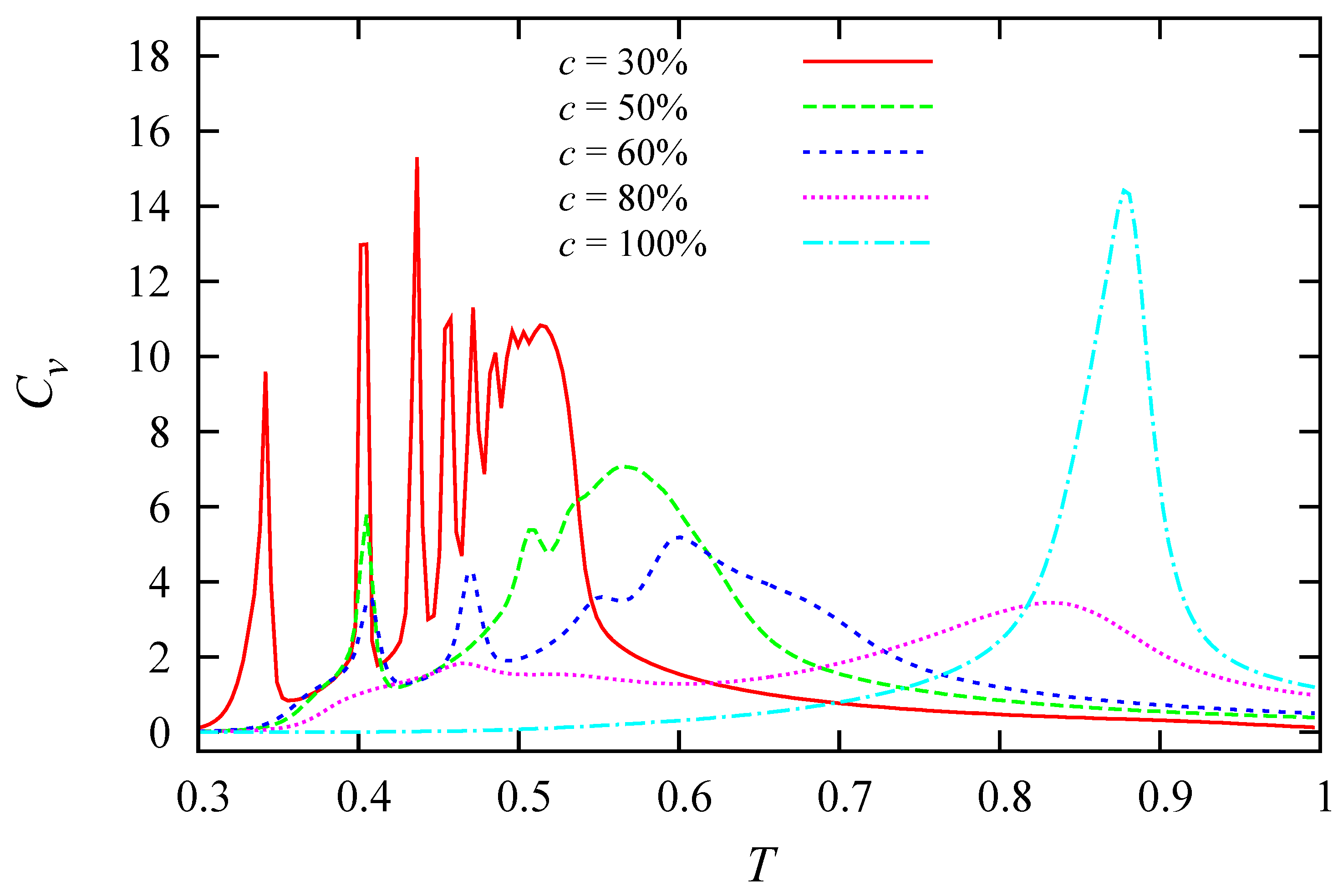
4. Size Effects—The Case of Ferromagnetic Inter-Layer Interaction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, G.P.; Zumer, S. (Eds.) Liquid Crystals in Complex Geometries; Taylor&Francis: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Diep, H.T. Statistical Physics—Fundamentals and Application to Condensed Matter; World Scientific: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gârlea, I.C.; Mulder, B.M. The Landau-de Gennes approach revisited: A minimal self-consistent microscopic theory for spatially inhomogeneous nematic liquid crystals. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 244505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lubensky, T.C. Landau-Ginzburg mean-field theory for the nematic to smectic-c and nematic to smectic-a phase transitions. Phys. Rev. A 1976, 14, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.C.; McMillan, W.L. Unified Landau theory for the nematic, smectic a, and smectic c phases of liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. A 1977, 15, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, M.; Enrique, V.; Yuri, M. Hard-body models of bulk liquid crystals. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 463101. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, Y. Scaled field particle theory of the structure and the thermodynamics of isotropic hard particle fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 1988, 89, 4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, Y. Free-energy model for the inhomogeneous hard-sphere fluid mixture and density-functional theory of freezing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoebe, T.; Mach, P.; Huang, C.C. Unusual Layer-Thinning Transition Observed near the Smectic-A-Isotropic Transition in Free-Standing Liquid-Crystal Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.-Y.; Chou, C.-F.; John, T.; Ho, S.W.; Hui, A.J.; Huang, C.C. Nature of Layer-by-Layer Freezing in Free-Standing 4O.8 Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.; Lo, C.R.; Wu, P.J.; Pan, T.C.; Veum, M.; Huang, C.C.; Surendranath, V.; Ho, J.T. Unusual Thickness-Dependent Heat-Capacity Anomalies in Free-Standing Hexatic Liquid-Crystal Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 085507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Mach, P.; Wedell, E.D.; Lintgen, F.; Neubert, M.; Huang, C.C. Layer thinning transition above the bulk smectic-A-isotropic transitionin free-standing liquid-crystal films. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 55, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ratón, Y.; Somoza, A.M.; Mederos, L.; Sullivan, D.E. Surface-enhanced ordering and layer-thinning transitions in freely suspended smectic—A films. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 55, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, Y.; Somoza, A.M.; Mederos, L.; Sullivan, D.E. Metastability of freely suspended liquid-crystal films. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 53, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.V.; Sullivan, D.E. Transition entropy, Helmholtz free energy, and heat capacity of free-standing smectic films above the bulk smectic-A-isotropic transition temperature: A mean-field treatment. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 041704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebwohl, P.A.; Lasher, G. Nematic-Liquid-Crystal Order-A Monte Carlo Calculation. Phys. Rev. A 1972, 6, 426, Erratum Phys. Rev. A 1973, 7, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, U.; Zannoni, C. A Monte Carlo investigation of the Lebwohl-Lasher lattice model in the vicinity of its orientational phase transition. Mol. Phys. 1986, 58, 763–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Robin, L.B.; Selinger, J.V.; Shashidhar, R. Monte Carlo simulation of liquid-crystal alignment and chiral symmetry-breaking. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, B.; Jürgen, H.; Richard, V.; Andres, D.V. Confinement effects on phase behavior of soft matter systems. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Julio, C.; Armas, P.; Alejandro, L.-H.; Orlando, G.; Juan, P.H.-O.; Juan, J. Theoretically Informed Monte Carlo Simulation of Liquid Crystals by Sampling of Alignment-Tensor Fields. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 044107. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, R.; Zannoni, C. Do thermotropic biaxial nematics exist? A Monte Carlo study of biaxial Gay-Berne particles. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 5971–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Fava, C.; Zannoni, C. A generalized Gay-Berne intermolecular potential for biaxial particles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 236, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio Biscarini, C.; Chiccoli, P.; Pasini, F.; Semeria, C. Phase diagram and orientational order in a biaxial lattice model: A Monte Carlo study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, T.; Buscaglia, M.; Chiccoli, C.; Mantegazza, F.; Pasini, P.; Zannoni, C. Nematics with quenched disorder: What is left when long range order is disrupted? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R. Progress in computer simulations of liquid crystals. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005, 24, 421–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolo, P.; Claudio, Z.; Žumer, S. (Eds.) Computer Simulations of Liquid Crystals and Polymers: Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Computational Methods for Polymers and Liquid Crystalline Polymers; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 177. [Google Scholar]
- Paolo, P.; Claudio, Z. (Eds.) Advances in the Computer Simulatons of Liquid Crystals; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 545. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, M.A. Atomistic Simulation and Modeling of Smectic Liquid Crystals. In Advances in the Computer Simulatons of Liquid Crystals; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 545, p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Repnik, R.; Ranjkesh, A.; Simonka, V.; Ambrozic, M.; Bradac, Z.; Kralj, S. Symmetry breaking in nematic liquid crystals: Analogy with cosmology and magnetism. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 2013, 25, 404201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhwandl, R.W.; Terentjev, E.M. Monte Carlo simulation of topological defects in the nematic liquid crystal matrix around a spherical colloid particle. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruhn, T.; Hess, S. Monte Carlo Simulation of the Director Field of a Nematic Liquid Crystal with Three Elastic Coefficients. Z. für Nat. A 1996, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurélien, B.-R. Mobile Spins on Lattice as Model for Liquid Crystals and Topological Excitations and Skyrmions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cergy-Pontoise, Paris, France, 15 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Landau, D.P. Efficient, Multiple-Range Random Walk Algorithm to Calculate the Density of States. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Landau, D.P. Determining the density of states for classical statistical models: A random walk algorithm to produce a flat histogram. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 056101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvonimir, D. Surface Freezing and a Two-Step Pathway of the Isotropic-Smectic Phase Transition in Colloidal Rods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 165701. [Google Scholar]
- Dogic, Z.; Fraden, S. Development of model colloidal liquid crystals and the kinetics of the isotropic-smectic transition. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2001, 359, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogic, Z.; Fraden, S. Smectic Phase in a Colloidal Suspension of Semiflexible Virus Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, H.J.; Strazielle, C. Pretransitional Behaviour of the Direct Isotropic to Smectic a Phase Transition of Dodecylcyanobiphenyl (12CB). Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1979, 49, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, B.M.; Braslau, A.; Pershan, P.S.; Als-Nielsen, J.; Deutsch, M. Quantized layer growth at liquid-crystal surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 94, Erratum in Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olbrich, M.; Brand, H.R.; Finkelmann, H.; Kawasaki, K. Fluctuations above the Smectic-A-Isotropic Transition in Liquid Crystalline Elastomers under External Stress. Europhys. Lett. 1995, 31, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakan, J.; Elisabet, W.; Anders, H.; Ulf, W.G. Kinetics of isotropic-smectic phase transition in liquid-crystalline polyethers. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roie, B.; Leys, J.; Denolf, K.; Glorieux, C.; Pitsi, G.; Thoen, J. Weakly first-order character of the nematic-isotropic phase transition in liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 041702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Pleiner, H.; Brand, H.R. Simple Landau model of the smectic A-isotropic phase transition. Eur. Phys. J. E 2001, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmut, R.; Prabir, K.; Harald, P. Macroscopic dynamics near the isotropic-smectic—A phase transition. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 63, 061708. [Google Scholar]
- Helmut, R.; Prabir, K.; Harald, P. Landau model of the smectic C-isotropic phase transition. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 7788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurélien Bailly-Reyre, H.; Diep, T.; Kaufman, M. Phase Transition and Surface Sublimation of a Mobile Potts Model. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 25, 042160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.P.; Binder, K. A Guide to Monte Carlo Simulations in Statistical Physics; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.; Gelman, A.; Jones, G.L.; Meng, X.-L. Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Click on the Link to See the Smectic Dynamics. On the Left of the Video: Dynamics of the Molecules, Each Color Represents a Molecular Orientation. On the Right: The Energy Per Molecule Versus T in a Cooling. Available online: https://www.dropbox.com/s/062kg8ppjvryhqx/n12c50.avi?dl=0 (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- Thanh, N.V.; Diep, H.T. Phase transition in Heisenberg stacked triangular antiferromagnets: End of a controversy. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 031119. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, N.V.; Diep, H.T. Stacked triangular XY antiferromagnets: End of a controversial issue on the phase transition. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07C712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham Phu, X.T.; Thanh Ngo, V.; Diep, H.T. Cross-Over from First to Second Order Transition in Frustrated Ising Antiferromagnetic Films. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 061106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Ngo, V.; Tien, H.D.; Diep, H.T. First-order transition in the XY model on a fully frustrated simple cubic lattice. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 041123. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh Ngo, V.; Tien, H.D.; Diep, H.T. Flat energy-histogram simulation of the phase transition in an Ising fully frustrated lattice. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 2011, 23, 226002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thanh Ngo, V.; Tien, H.D.; Diep, H.T. Phase Transition in the Heisenberg Fully Frustrated Lattice. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 25, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.; Schulhess, T.C. Wang-Landau estimation of magnetic properties for the Heisenberg model. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10E303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, B.J.; Binder, K.; Müller, M.; Landau, D.P. Avoiding boundary effects in Wang-Landau sampling. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 067102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakis, A.; Martinos, S.S.; Hadjiagapiou, I.A.; Fytas, N.G.; Kalozoumis, P. Entropic sampling via Wang-Landau random walks in dominant energy subspaces. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 066120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, W.; Mermin, A. Solid State Physics; Saunders College: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Halperin, B.I.; Nelson, D.R. Theory of Two-Dimensional Melting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 41, 121, Erratum in Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 41, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermin, N.D.; Wagner, H. Absence of Ferromagnetism or Antiferromagnetism in One- or Two-Dimensional Isotropic Heisenberg Models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 17, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.J. Exactly Solved Models in Statistical Mechanics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Surungan, T.; Komura, Y.; Okabe, Y. Probing phase transition order of q-state Potts models using Wang-Landau algorithm. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 79, 1617. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaki, Y.; Yutaka, O. Three-dimensional antiferromagnetic q-state Potts models: Application of the Wang-Landau algorithm. J. Phys. A 2001, 34, 8781. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ngo, V.T.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Diep, H.T. Statistical Physics Approach to Liquid Crystals: Dynamics of Mobile Potts Model Leading to Smectic Phase, Phase Transition by Wang–Landau Method. Entropy 2020, 22, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22111232
Ngo VT, Nguyen P-T, Diep HT. Statistical Physics Approach to Liquid Crystals: Dynamics of Mobile Potts Model Leading to Smectic Phase, Phase Transition by Wang–Landau Method. Entropy. 2020; 22(11):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22111232
Chicago/Turabian StyleNgo, V. Thanh, Phuong-Thuy Nguyen, and Hung T. Diep. 2020. "Statistical Physics Approach to Liquid Crystals: Dynamics of Mobile Potts Model Leading to Smectic Phase, Phase Transition by Wang–Landau Method" Entropy 22, no. 11: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22111232
APA StyleNgo, V. T., Nguyen, P.-T., & Diep, H. T. (2020). Statistical Physics Approach to Liquid Crystals: Dynamics of Mobile Potts Model Leading to Smectic Phase, Phase Transition by Wang–Landau Method. Entropy, 22(11), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22111232





